DTU BIO 1 - Basis of life
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is diffusion? And what is the formula for rate of diffusion?
The process by which molecules spread from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.

What is osmotic pressure? And what is the formula to calculate it?
The pressure required to prevent the flow of a solvent into a solution through a semipermeable membrane.

What is capillarity? And what is the formula to calculate it?
The ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces without external forces, due to surface tension.
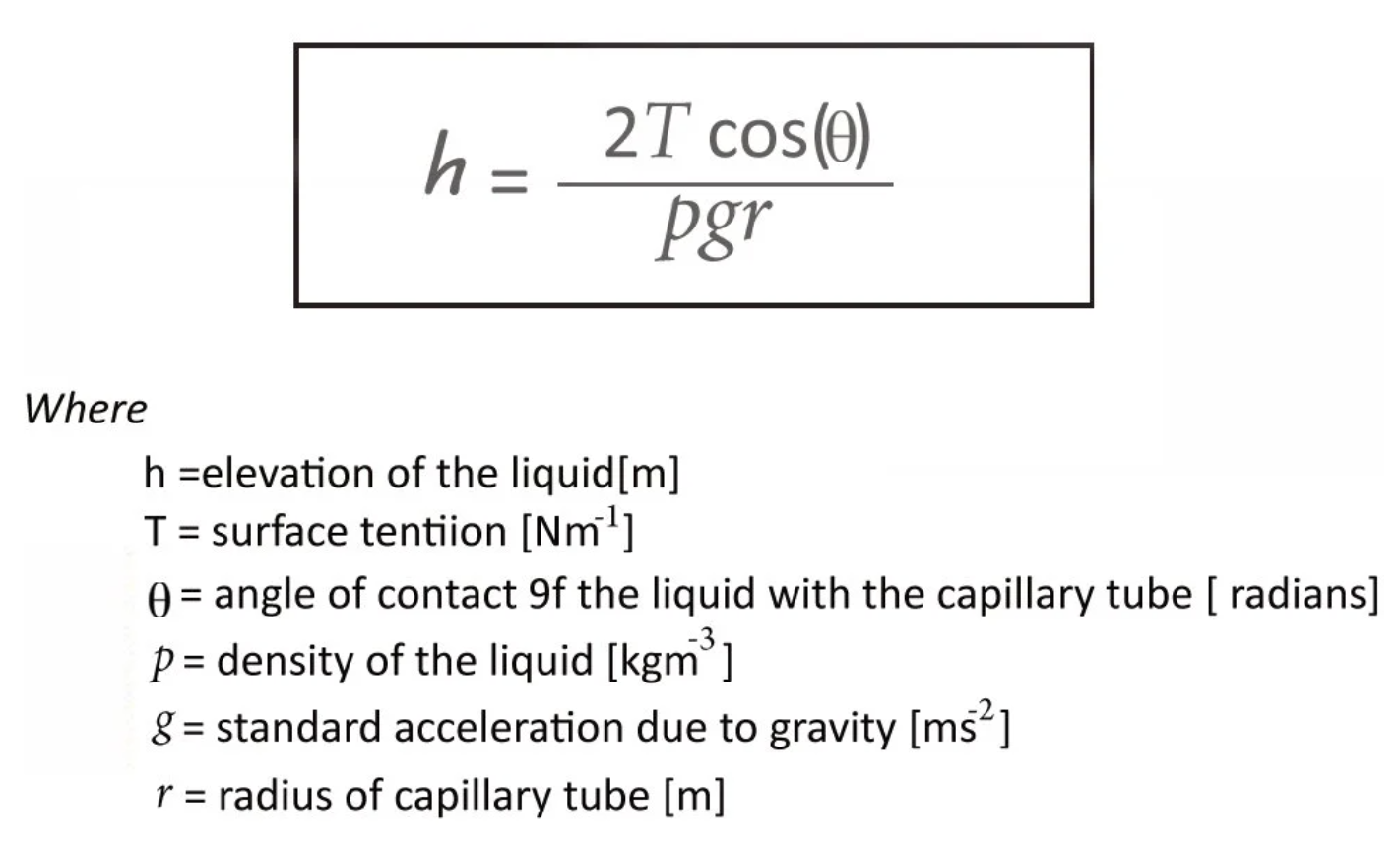
What are the requirements for life?
Water
photon energy (sun)
chemical energy (food)
and moderate temperature (Goldilocks zone).
What is the basic characteristics of living systems and why is viruses often not considered living systems?
Living systems are out of equilibrium, exhibiting constant metabolism and evolving from simple to complex structures.
Viruses lack cellular structure and do not carry out metabolic processes independently, often requiring a host to replicate.
How can we remotely find signs of life on exoplanets?
Look for signs of energysources, water, or life sediments such as atmospheric biosignatures like oxygen or methane.
What are examples of how living organisms can generate large scale geological structures?
Inorganic deposits (coral reef, chalk cliffs)
What is the role of ATP in cells?
Adenoside triphosphate (ATP)
Food is converted to ATP and at is used by the body.
What forms of energy does life use and how is energy stored in live cells?
Consumption
Light
Inorganic compounds (chemothography)
Organic compaunds (chemoorganography)
Temperature
Storagere
Gradients of ions
Long-lived Molecules
Short-lived Molecules
What is the RNA world hypothesis?
What biological properties are constrained by physical laws?
Size limitations of organisms due to gravity and heat dissipation, influencing the maximum size of living beings.
Give examples for biological properties governed by universal scaling laws.
Gravitational force. Life cant get too big. (F scales I^3)
Diffusion of substance or heat (t scales x^2)
Available chemical fuel
Fluid transport through cappilary action or pressure driven flow.
Cells have a max size because of diffusion / osmosis
Size of blood vessels
Why are dissipative structures relevant for understanding life?
Life is at state of local order the is able to dissipate energy better than non-life.
How can diffusion lead to pattern formation?
How does biological magnetoreception and temperature sensing work?
Birds detect magnetic fields for navigation, often involving metals in their beaks.
Temperature is felt as Temperature variation. Specialized nerves through the skin.
What is chemotaxis?
Chemotaxis is the movement of organisms in response to the chemical changes in the envoirement. In this example it is the bacteria swimming towards and area with higher glucose concentration.