drugs in pregnancy and lactation
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PEBC
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
teratogen
any agent that can cause Malformation or impairs the proper development of an embryo or fetus
pharmacokinetics in pregnancy
increased water content in body = need larger doses of water soluble drugs (aminoglycosides)
increased cardiovascular output = increases renal and hepatic clearance of drugs
increased GFR and renal blood flow = increase renal clearance = need more frequent dosing
decreased serum protein binding = increased toxicity for protein bound drugs (phenytoin)
decreased intestinal motility (due to progesterone mediated smooth muscle relaxation) = delayed absorption
decreased gastric acidity = increased gastric pH = impacts solubility of pH dependent drugs (iron, ketoconazole)
placental drug transfer
placenta acts as as intravenous portal for entry of drugs into fetus
drug properties increase the chance of placental transfer:
high fat solubility
low degree of ionization
low degree of protein binding
low molecular mass (<500 kDa rapid transit, 500-1000 kDa slower transit)
heparin and insulin = high weight and safe
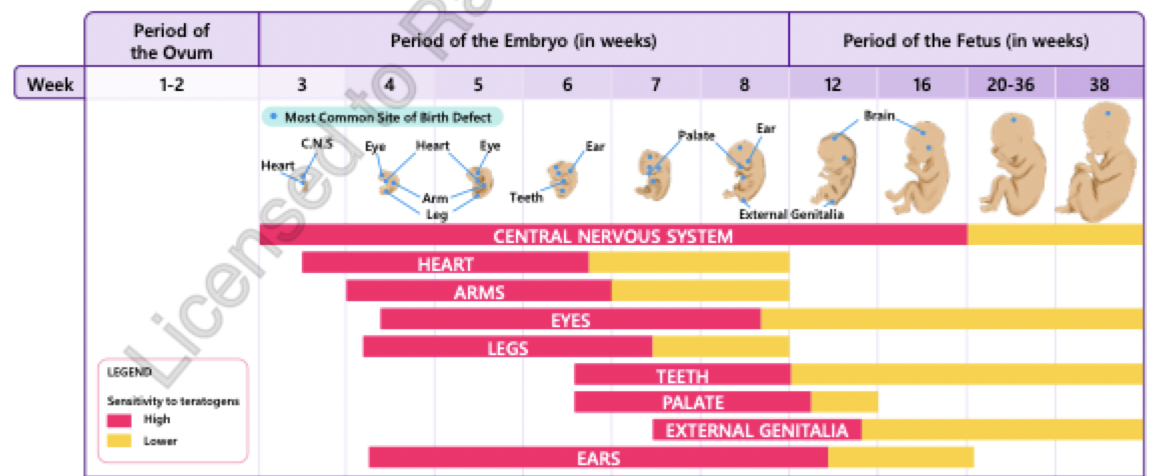
critical periods in pre-natal development
greatest period of sensitvity to teratogens is during organogenesis which lasts 6 weeks
really critical phase is when organs develop = between 6-8 weeks = 1st trimester!
teratogens during fetal period = more likely to cause problems with organ function or stunt growth rather than causing structural damage
3 trimesters:
1st = very critical about the medications
0-12 weeks
2nd = golden phase = pts have less sx and more safe bc critical period has passed
13-27 weeks
3rd =
27/28 weeks - term (38/39 weeks)
proven teratogens
ACEI/ARBs:
intrauterine renal insufficiency, neonatal hypotension, oliguria with renal failure, hyperkalemia, intrauterine growth restriction, prematurity, fetal death
Antineoplastic agents:
exposure in 1st trimester → malformations and miscarriages
Carbamazepine and Valproic acid:
exposure in 1st trimester = neural tube defects and cardiovascular malformations
supplement with folic acid 5mg 3 months before conception
Cocaine:
prematurity, death, limb defects, urinary tract malformations
Corticosteroids (systemic):
in 1st trimester = oral cleft risk (risk <1%)
Mycophenolate Mofetil:
1st trimester: CNS, facial (ear, eye, oral cleft), cardiac, GI, skeletal and urogenital malformations
warfarin:
1st trimester: fetal warfarin syndrome, restriction in intrauterine growth, delay in CNS development, hearing and vision impairment, miscarriage etc
ethanol
fetal alcohol spectrum, neuro developmental disorders
folic acid antagonists: MTX
abnormalities in CNS development and cranial ossification, intrauterine growth restriction
maternal dose of >10 mg/ week will induce defects with MTX
phenytoin
cardiovascular, craniofacial and CNS malformations
lithium
small risk of cardiac malformations if >900 mg/d
misoprostol
1st trimester: CNS abnormalities
induces uterine contractions = fetal malformations
Retinoids: high doses of vitamin A
craniofacial, cardiac and CNS malformations, miscarriage
Tetracyclines:
discolouration of teeth (after 17 weeks gestation), crowns of permanent teeth stained (close to term)
doxy has lower risk
Thalidomide:
limbs, ears, cardiac and GI malformations
Topiramate:
1st trimester: oral clefts
Valproic acid:
1st trimester: neural tube defects
possible teratogens
weigh the risk vs benefit
Diazepam
small risk between cleft lip/palate and maternal diazepam (only small studies)
Fingolimod (used in MS)
small studies: possible risk of increased congenital malformations
Fluconazole (high dose)
case reports: cardiac, skeletal and facial abnormalities
Methimazole
case reports: scalp defects
Penicillamine (high dose)
connective tissues anomalies
SMX/TMP
possible risk: oral clefts, neural tube defects, cardiac anomalies
supplementing with folic acid can reduce risk
Statins
retrospective reports = increase in limb and CNS anomalies
factors to consider (breastfeeding)
drug characteristics
route of administration:
oral = undergoes first pass metabolism before entering blood stream
IV = bypasses barriers of GI tract to enter bloodstream and milk
IM = bypasses barriers of GI tract to enter bloodstream through blood vessels surrounding the muscles
topical = low systemic absorption
CYP2D6 substrates:
codeine = can lead to increased active metabolite levels in infants causing toxicity
Baby’s age, maturity, weight and health status
GI transit time and flora, rate of metabolism and excretion
Frequency and volume of milk feedings
Premature/low birth weight infants or G6PD deficiency
infants with G6PD deficiency may develop hemolytic anemia if exposed through breastmilk
drugs that can enter breastmilk
low plasma protein binding
non-ionized
low molecular weight
lipophilic
weakly alkaline
clinical pearls (breastfeeding)

drugs incompatible with breastfeeding
