Ib HL Biology: Photosynthesis -C1.3
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
The two types of chlorophyll
Chlorophyll alpha and beta
Paper chromatography
technique used to separate mixtures of substances
Used the mobile phase and stationary phase for the separation process
Paper: stationary phase
Solvent used to develop chronograph: mobile phase
Solvent is often made out of alcohol
photolysis
the breaking down of water into hydrogen ions, oxygen and electrons using light energy
occurs in grana
so that the hydrogen ions can be used for atp synthesis and so that the electrons can be used in photosystem 2
Main types of pigments in plants
Chlorophyll’s, beta caroten, xanthophyll
Retention factor/ Rf
Spdistance travelled by sample / distance travelled by solvent
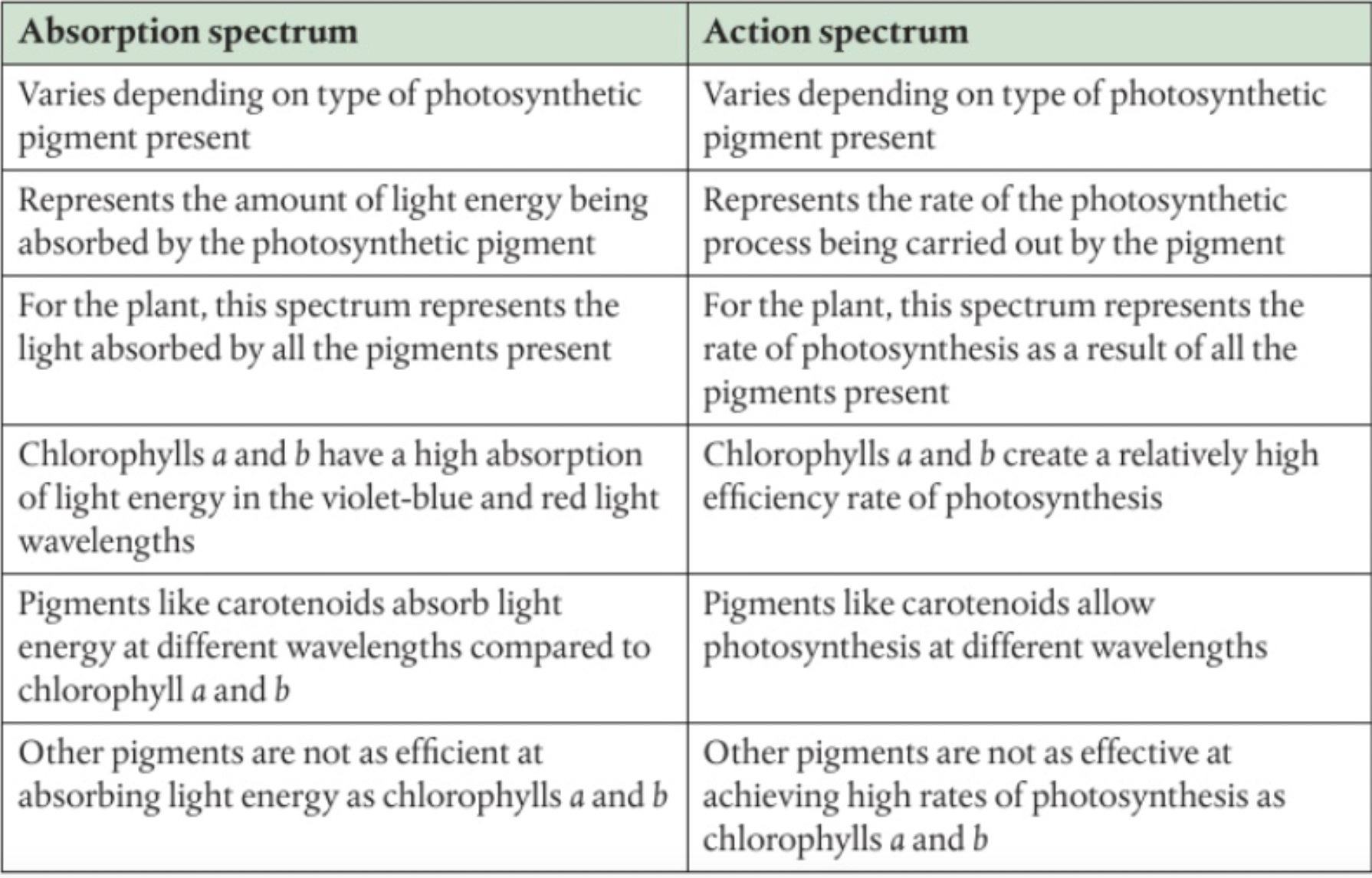
Graph which represents wavelengths of light absorbed
Absorption spectrum
Graph which shows rate of photosynthesis against wavelength
Action spectrum
Rage of wavelength which make up visible light
400-750nm
Limiting factors in rate of photosynthesis
light intensity
Température
CO2 concentration
FACE
Free air carbon dioxide enrichment experiments; CO2 is released in a circular area and sensors are used to detect concentration and keep it high
Photosystems
arrays of pigment molecules which can generate excited electrons. found in thylakoid membranes of grana
chemiosmosis
osmosis but with chemicals. in photosynthesis ATP is produced by this process using ATP synthase, by allowing hydrogen ions to leave the thylakoids by facilitated diffusion
photosphorylation
The process of generating ATP using light energy. It occurs during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, in photosystem 1, where light energy is used to phosphorylate ADP to ATP.
electron transport chain ( ETC )
A series of protein complexes in the inner membrane of the mitochondria that transfer electrons and pump protons to create a proton gradient.
basically the photosystems + electron storers
cytochrome complex
the hydrogen pump
excited electron pases, it’s energy is used to bring the hydrogen ions from a low to a high concentration
the electron goes back to the ground state
difference between absorption spectrum
action spectrum: rate of photosynthesis for each wavelength
absorption spectrum: what wavelengths are getting absorbed
How much energy required to synthesise one mole of glucose
2017Kj
Chemoautotrophs
Source of energy from chemicals
what is in photosystem 2
a water splitting enzyme that catalyses the breakdown of water
oxygen is a waste product of the reaction
electrons are used for the electron chain, hydrogen ions are used for the ATP synthase
fixation of CO2
using rubisco, a CO2 molecule is put in a RuBp molecules and they become two GP molecule ( glycerate-3-phospate)
where is NADPH used in the Calvin cycle
when glycerate- 3- phosphate ( GP ) is present with NADPH and ATP, it becomes triose phosphate ( TP )
non-cyclic phosphorylation
normal one
occurs when water is present to photolyse and produce electrons
use NADP+
cyclic phosphorylation
occurs when not enough water is present
no NADP+
electrons go back in ground state in photosystem 1
RuBp full name
ribulose bisphophate, a 5 carbon molecule which reacts with CO2 in Atmosphere
G-3-P full name
glycerol - 3 - phosphate, product of breakdown of unstable intermediate after carbon fixation
TP
triose phosphate, produced from GP, after using NADH and 2 ATP
calvin experiments
radioactive labelling ( label CO2 with carbon 14 )
double way paper chromatography
autoradiography
autoradiography