Small Ruminants 13+14: Alpacas
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Small Ruminants 13+14: Alpacas
Lecture 13+14: Alpacas
Describe Alpacas in terms of:
1. BCS
2. Temperature
3. RR
4. HR
5. Rumen Sounds
6. Diagnostic Considerations
1. Palpate lumbar vertebrae + Rbs behind elbow, how much eye muscle Is filled in. 1-5 score (2.5-3 ideal)
2. 37.5-39.4℃
3. 10-30 breath/m
4. 50-80 bpm
5. 3-4 rumen contraction/min
6. RBC small, flat, and elipticle. May need to manually count unless machines are calibrated
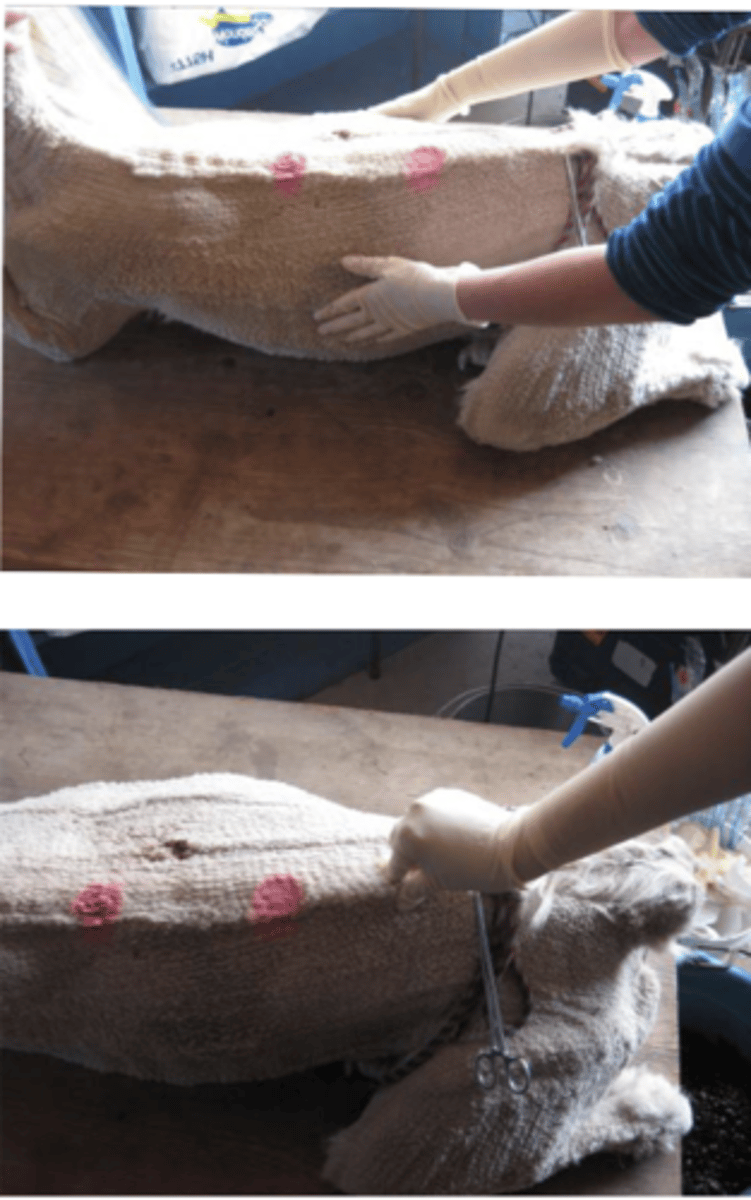

Describe Alpaca Injection Sites in terms of:
1. Intramuscular Injection Sites
2. Subcutaneous Injection Sites
3. Blood Draw Sites
1. triceps, quadriceps, lumbar epaxial muscles
2. Base of neck cranial to the shoulder
3. Right jugular vein , avoid hitting carotid, lower neck preferred
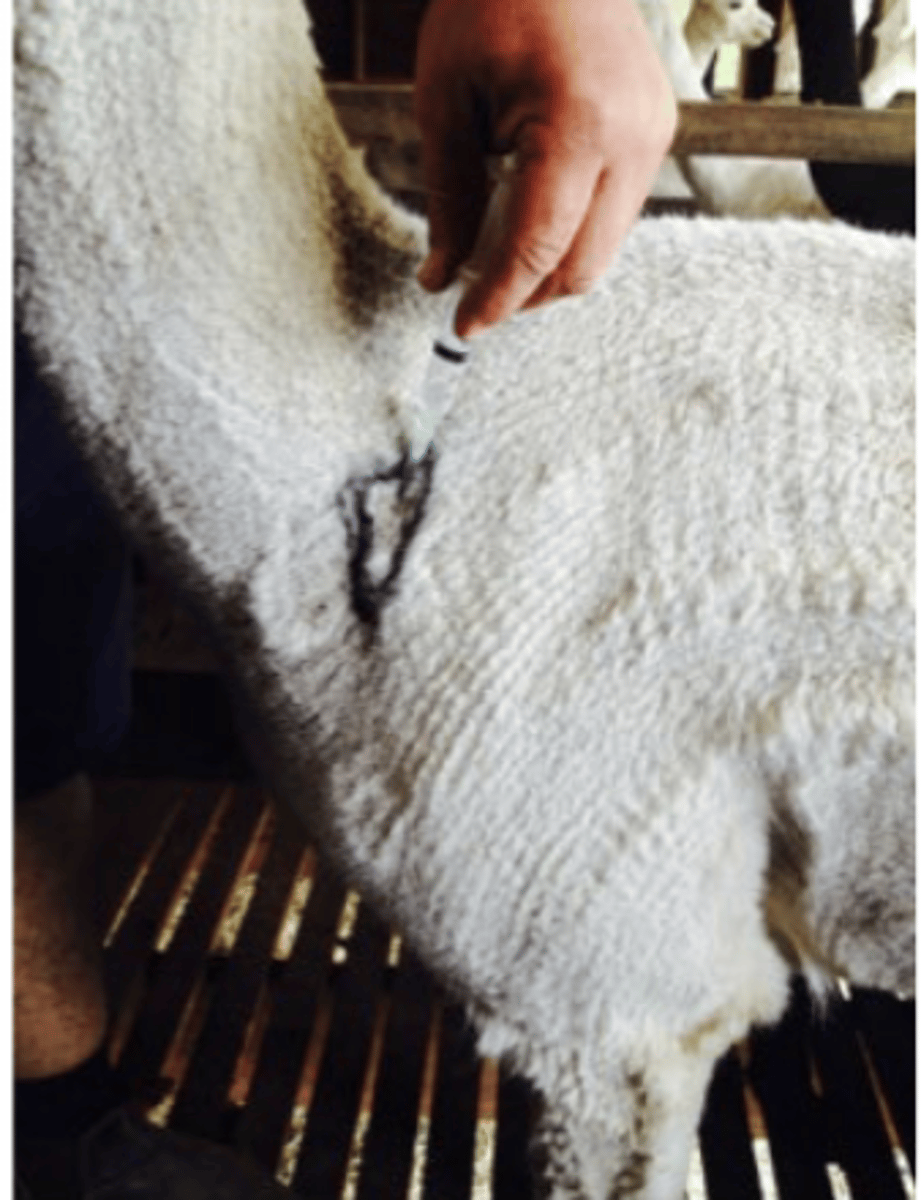
Describe Alpaca Vaccination
Use sheep 5-in-1/6-in-1
- 2 doses 4-6 weeks apart then 6 month booster

Describe Breeding in Alpacas in terms of:
1. Seasonality
2. Males
3. Females
4. 3 Naturally occuring Reproductive Statuses of Females
5. MAting Characteristics
1. Non-seasonal
2. Have Fibroelastic penis, Non pendulous scrotum. Small, elliptical, testes
3. Induced ovulators, ovulate 30h post mating, Have follicular waves (no oestrous cycles)
4. Non-ovulatory, Ovulatory but not pregnant, Pregnant
5. Occurs in sternal recumbency, Multiple ejaculations over prolonged period, semen deposited deep into uttering horns, 20–25-minute duration
Describe Pregnancy Diagnosis in Alpacas in terms of:
1. Indirect Methods
2. Direct Methods
1. Blood/milk progesterone, sexual behaviour. “Spitting-off-test”
2. Ultrasound, manual rectal palpation, ballottement

Describe the Spitting Off Test of Pregnancy Diagnosis in terms of:
1. Definition
2. 7 Day Spitting Off Test
3. 14 Day Spitting Off Test
4. Time of CL regression if Non-Pregnant
1. Place male and female in small yard. If female is receptive, she is non-pregnant, if not receptive she’s most likely ovulating (Already been mated)
2. If receptive, no ovulation has occured, mate again. If Female spits - ovulated
3. If Receptive, ovulated but failed to conceive. If Female Spits - most likely pregnant
4. Day 11
Describe Gestation in Alpacas
- 300-350 days
- Twins rare
- 98% of pregnancies occur in the left horn

Describe the Nutritional Management of Camilids in terms of:
1. Camelid Stomach
2. Type of Feeders
3. Efficiency of Stomachs
4. Protein Requirements
1. 3 Compartments (C1,2,3)
2. Grazers (Alpaca), Grazer + browser (Llama)
3. More efficient than sheep and cattle at extracting nutrients from poor quality feed (slower passage through C1, fluid passes more rapidly through C1, 3-4 contractions per minute, Kidneys can recycle urea. Reduced feed intake compared to other ruminants
4. Lower protein and energy requirements to sheep + cattle
Describe Obesity in Camelids:
- Common in Australia, more prone to heat stress, poor milk production, infertility, dystocia
- Camillids do not need supplements
- Reduce energy intake (Feed less)
Describe Hepatic Lipidosis in Camelids in terms of:
1. Fatty Liver Disease
2. CS
3. Diagnosis
4. Prevention
1. Excessive accumulation of lipids in liver, occurs in pregnant and lactating animals (Animals with decreased feed intake but increasing energy needs). As well as any animal that stops eating
2. Loss of appetite, weight loss, weakness, recumbency
3. History, CS, blood test (increased liver enzymes + NEFA).
4. match energy and protein requirements to demands
Describe Selenium Deficiency in Camelids in terms of:
1. Selenium's role in The Body
2. Marginal Deficiency CS
3. Severe Deficiency CS
4. Diagnosis
5. Treatment
6. Prevention
1. Important antioxidant. Deficiency common on acid soils
2. decreased fertility (EED, retained placentas), reduced growth rate, immunosuppression
3. Muscle damage (white muscle disease), skeletal damage, dyspnoea due to intercostal muscle damage, cardiac muscle damage = sudden death
4. History, blood samples
5. IM/SC selenium injection
6. Annual SC depot of barium selenate/topdress pasture
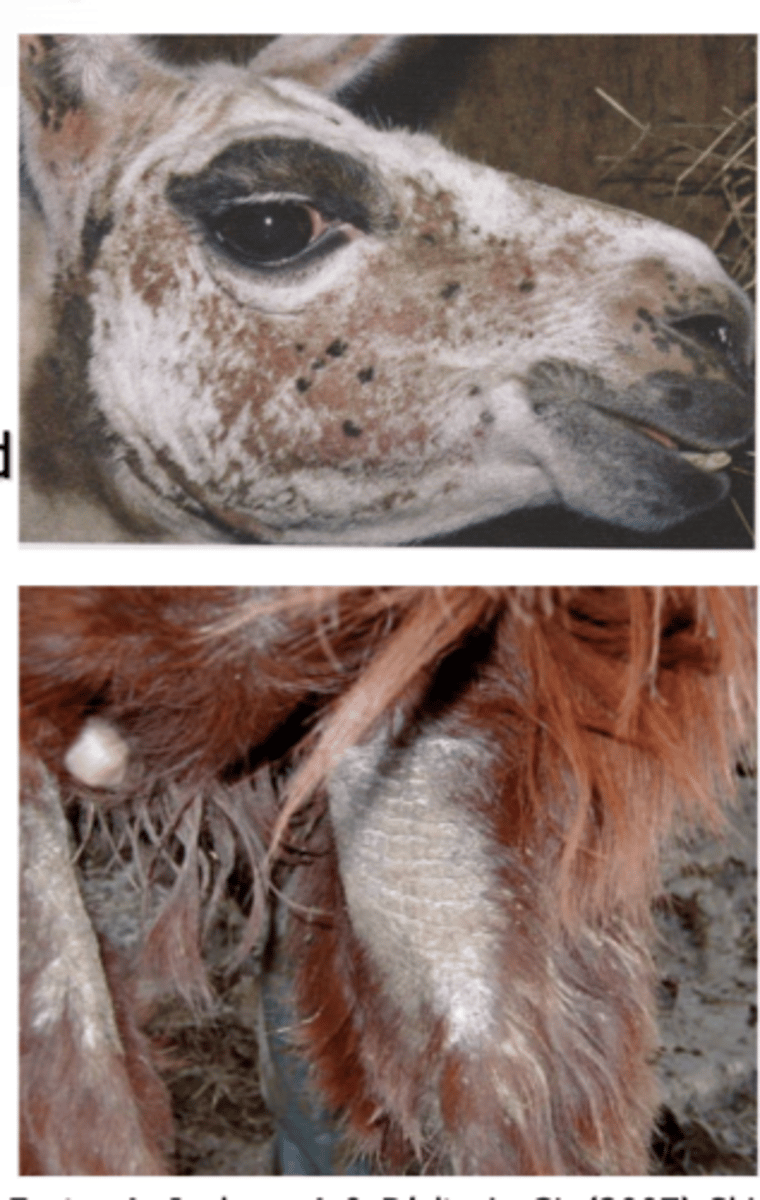
Describe Zinc Deficiency in Camelids in terms of:
1. Clinical Signs
2. Ddx
1. Zinc responsive dermatosis: Alopecia, thickening of skin, scaling, hyperpigmentation. Occurs on areas without wool
2. Mange

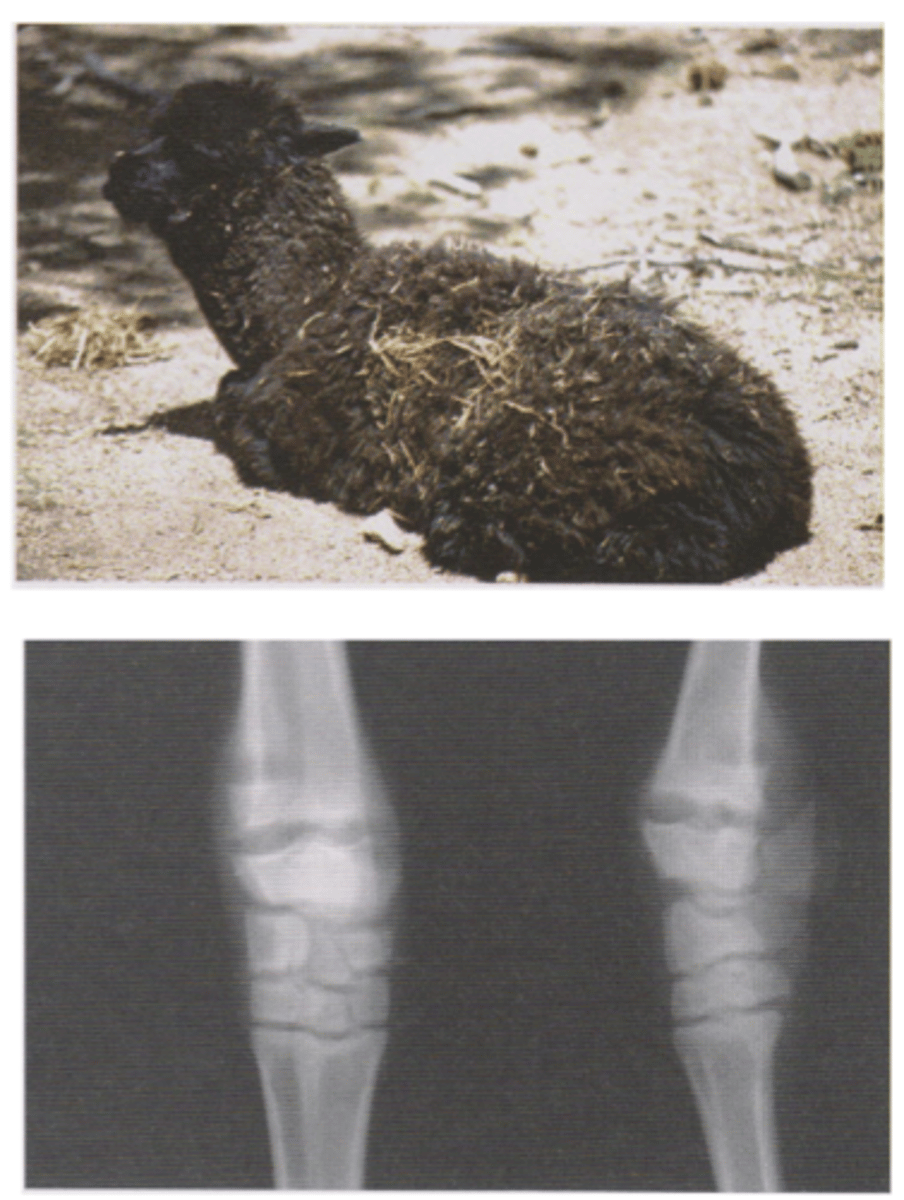
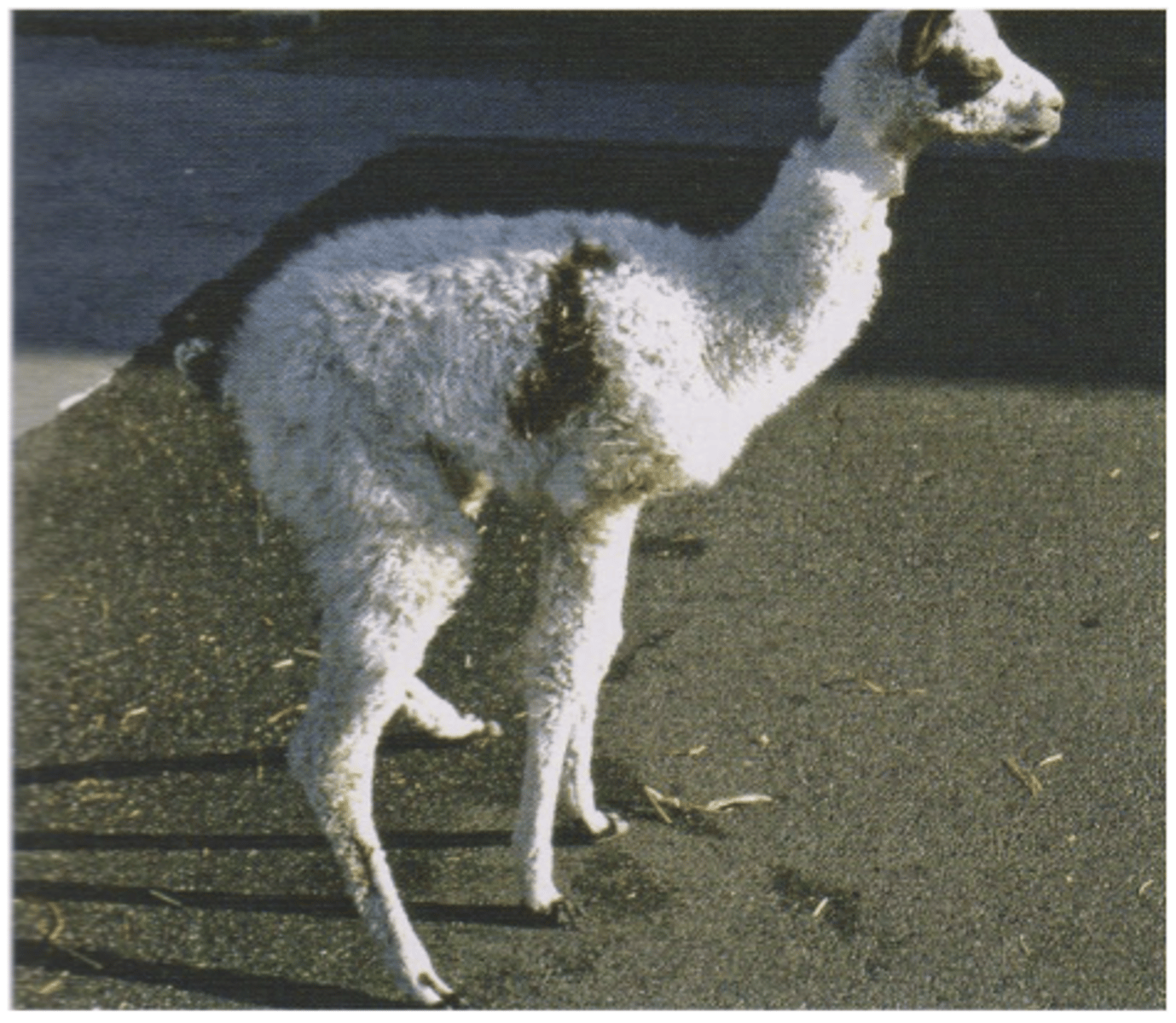
Describe Vitamin D Deficiency in Camelids in terms of:
1. Rickets
2. Aetiology
3. Signs of Deficiency
4. Diagnosis
5. Treatment/Prevention
1. Characterised by failure of mineralisation of bone osteoid and cartilage matrix in young growing animals
2. Lack of sunlight in winter, thick fleece, darker coloured animals
3. young growing animals, lameness, reluctant to move, excessive recumbency, humped back stance, swollen joints
4. History, radiographs, Serum vitamin D
5. Give young alpacas and females due to give birth in winter/early spring Vitamin D supplement in late autumn/mid winter
Describe Urolithiasis in Alpacas in terms of:
1. Causes
2. Clinical Signs
3. Prevention
1. Due to oxalates, silica, struvite crystals
2. CS = straining to urinate
3. Ensure animals have unrestricted access to water, add salt to diet to increase water intake

Describe Polioencephalomalacia (PEM) in Camelids in terms of:
1. Aetiology
2. Clinical Signs
1. Thiamine (B1) deficiency water deprivation and salt toxicity
2. neurological signs (depression, head pressing, central blindness, incoordination,
Describe Facial Eczema in Camelids in terms of:
1. Aetiology
2. Clinical Signs
1. Hepatogenous photosensitisation Caused by ingestion of sporodesmin, a toxin produced by pithomyces chartarum (fungus). Grows on dead plant material (Usually in late summer/autumn
2. Irritation, restlessness, rub face, seek shade, skin swelling,
Describe Ryegrass Staggers in Camelids in terms of:
1. Aetiology
2. Clinical Signs
1. Caused by ingestions of mycotoxin lolitrem B, produced by perennial ryegrass endophyte fungus
2. Tremours, incoordination, mostly seen when stressed
Describe Internal Parasites of Camelids in terms of:
1. Aetiology
2. Treatment
1. Have host specific intestinal parasites + cattle/sheep/goat parasites. Very susceptible to liver fluke (Treat with triclabendazole/albendazole)
2. no registered antiemetics. Only use oral/injectable drugs, pour ons not recommended (skin to thick – wont absorb). Use short acting, multi-dug compounds
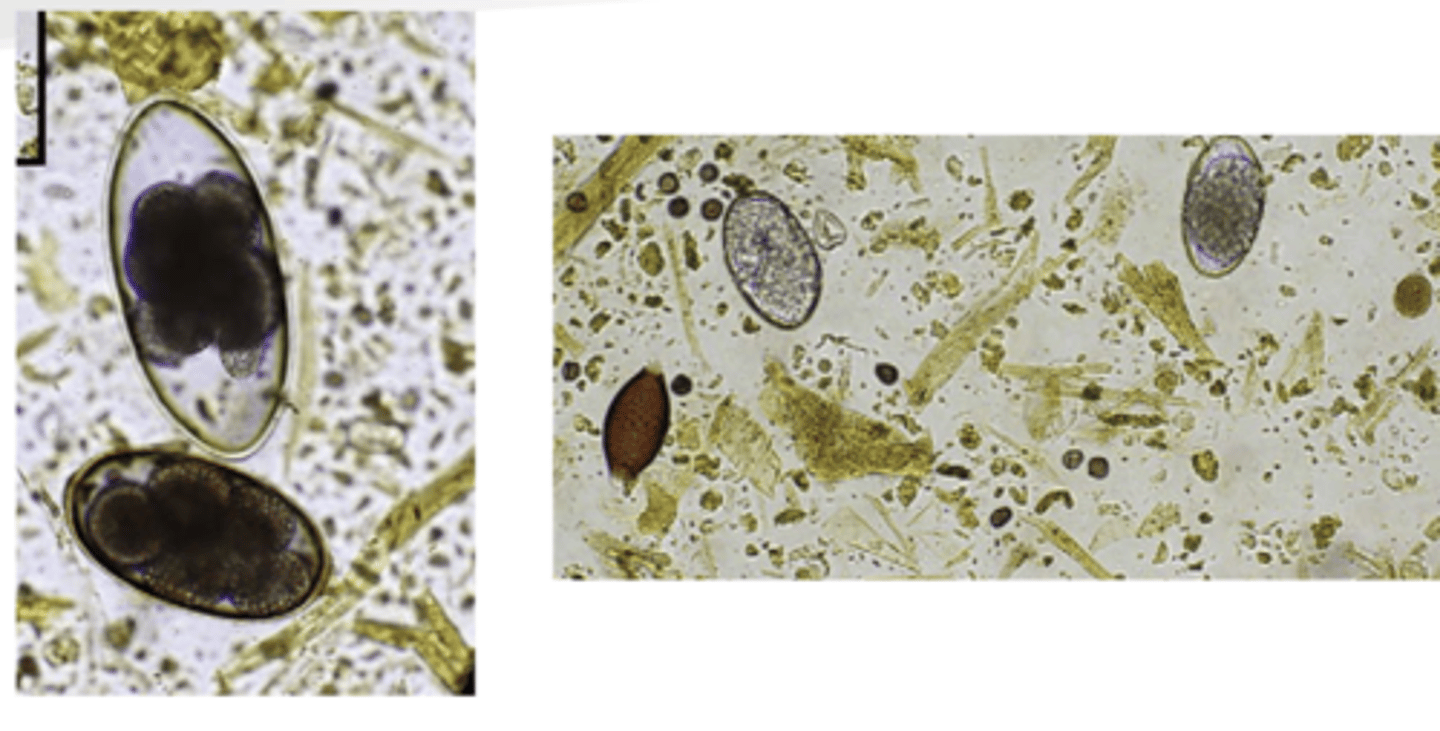
Describe Coccidiosis (Eimeria) in Camelids in terms of:
1. Aetiology/Camelids Susceptible
2. CS
3. Treatment
4. Control
1. Camelids under 7 Weeks of age. Associated with overcrowding and poor hygiene
2. May cause enteritis and dirhoea with bloods/ pieces of intestinal mucosa with weight loss.
4. Sulphonamides, Toltraxzuri, DO NOT USE MOMENSIN
5. Good hygiene and reduce stressors
Describe Diarrhoea in Crias (Baby Camelid) in terms of:
1. Nutritional Causes
2. E.Coli
1. Over feeding milk to bottle fed neonates
2. Accompanied by septicaemia, seen with decreased colostrum and poor hygiene
DEscribe Biting Lice in Camelids in terms of:
1. Transmission
2. CS
3. Treatment
1. Spread requires close contact
2. Rubbing/biting at fleece – matting of coat and fibre loss – reduced fleece value
3. Treat with shower/plunge dip with Spinosad

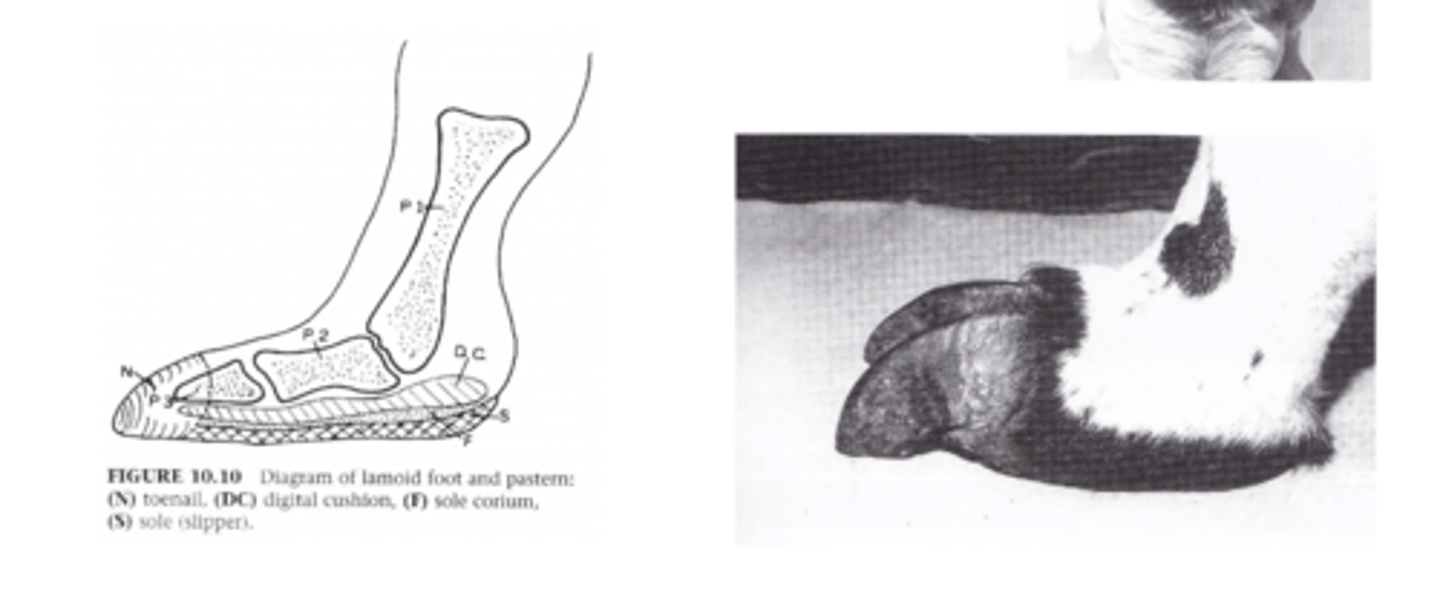
Describe the Feet of Alpacas
- Modified digitigrade, padded foot (like dogs) with toenail
- Trim toenails as required