ecosystems
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Energy in ecosystems
Sun is a source of energy for ecosystems
Energy is trapped + fixed in the ecosystems by green plants in the process of photosynthesis
Energy is trapped by chlorophyll + used to chemically combine water (soil) and CO2 (air) to form carbohydrate + O2 (released to air)
Green plants occupy trophic level → AUTOTROPHS/ PRODUCERS
All subsequent/ later trophic levels get their energy directly/ indirectly from green plants
They can’t photosynthesise - Heterotrophs
TL2 herbivores TL3 carnivores TL4 omnivores
What are decomposes
Decomposers e.g bacteria/ fungi operate at each trophic level by breaking down dead organic matter + releasing nutrients to soil,
What is biomass
Dry weight of living matter usually expressed as Kg/ m2
Why does energy decrease with each trophic level
used by organism for movement respiration, digestion etc
Bones, teeth, fur, nut shells are not eaten
Biomass that can be supported decreases and number of organisms decreases.
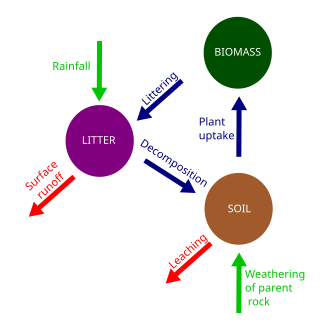
The nutrient cycle
One small scale case study of how an Ecosystem Functions
Breenwood Co. Antrim
What is the type of ecosystem at breenwood Co Antrim
Deciduous woodland- mainly oak trees
Where is Breenwood located
6 miles from ballycastle, in County Antrim
Abiotic relief aspect of Breenwood
North facing slope of a valley 130-190m above sea level
Abiotic climate of Breenwood
High annual rainfall around 1600mm (high)
January - 4oC , July - 15oC
Very cloudy most days, winter frost common
Short growing season of 7 months
Abiotic soil in Greenland
Formed from basalt a podzol
Low in nutrient soil, thing rocky, acidic pH 4.5
Thin humus layer bleached
What is the autotrophs/ producers
Trophies level 1
Dominant species is oak but they are stunted. Also downy birch in Canopy
Shrub layer - rowan hazel Holly
Field layer - bilberry bramble fern
Soil surface mosses ferns
On branches and trunks of living n dead trees - mosses, lichen, ferns
Early spring - before tree gets leaves there are bluebells and anemones.
Primary consumers herbivores TL2
Insects, butterflies (orange tip) red squirrels
Secondary consumers TL3 carnivores
Blue tits + gold crest are birds that eat seeds + insects
Tertiary consumers TL4 herbivore
sparrow hawks + buzzards feed on smaller birds
Badger feeds on small birds + fruits + nuts
Stoat - squirrels + birds
All TL decomposers
Earthworms fungi insects
Why is the biomass large
Biomass is the largest store because it’s a mature deciduous woodland that’s an ASSI, so it’s protected
reasons for small litter
The trees lose their leaves in the autumn and it can take take years for them to break down in this hostile (cold and acidic) environment
Why soil stores are low
Because the parent material is basalt which is very low in nutrients . Pod soil is also heavily leached because precipitation is high at 1600mm and rates of evapotranspiration are low as temperatures are 4oC to 15oC, so the overall movement of soil water is downwards .
Why is the uptake pathway low
Because there is a 7 month growing season which is very short and this is not a dense forest due to the harsh climate conditions.
Why is the fallout pathway high
Every autumn deciduous trees lose their leaves, so there is an annual contribution of dead organic matter to little
Why is the decay pathway
The dead organic matter breaks down slow because of the low temperatures (4-15oC) and acidic environment - which renders decomposers less effective.
the inputs of breenwood
Input if nutrients from precipitation (1600mm/yr) is higher that that from weathering of basalt. Precipitation is high in this upland areas, whereas the basalt is low in nutrients
Output of nutrients
From runoff and leaching is high as there are high rainfall totals (1600mm) and low temperatures.
The ecosystem is on a slope which is also contributes to the high loss of nutrients