Cell biology exam 1
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Centrifugation
a technique used to separate molecules or cellular components based on their physical properties, primarily through the use of centrifugal force
Ion exchange chromatography
method used to separate proteins based on their surface charge
Gel-filtration Chromatography
also known as size-exclusion chromatography, is a technique that separates proteins based on their size
Affinity chromatography
technique used to purify specific proteins from a complex mixture based on their unique binding properties.
Native gel electrophoresis
separates proteins based on their size, charge, and shape while maintaining their native structure and interactions
SDS-Page electrophoresis
a technique used to separate proteins based primarily on their molecular weight. It involves the use of the detergent to denature proteins and give them a uniform negative charge
(IEF) Isoelectric focusing
a type of electrophoresis that separates proteins based on their isoelectric point (pI), which is the pH at which the protein has no net electrical charge
Western blotting
is a technique used to detect specific proteins within a sample after they have been separated by gel electrophoresis
Co-immunoprecipitation
a technique used to identify protein-protein interactions by using an antibody to pull a specific protein (and its binding partners) out of a complex mixture
Epitope tagging
adding a short, known peptide sequence (the epitope tag) to a protein of interest
Affinity tagging
adding a specific peptide sequence (the affinity tag) to the protein of interest. This tag is designed to bind to a specific substrate
Forward genetics
begins with a phenotype of interest and works towards identifying the gene
Reverse Genetics
begins with a specific gene and works towards identifying the phenotype
Population genetics
a way of studying genetic variation within and between populations, and can be used to infer how genes are associated with certain traits or diseases
Amphiphilic
a molecule that has both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and lipophilic (or hydrophobic, water-repelling) domains
Phospholipid Bilayer
structure formed by two layers of phospholipid molecules, which is the basic structure of biological membranes
lipid rafts
dynamic, specialized microdomains within the cell membrane that are characterized by a distinct lipid composition and may have specific functions in cell signaling and membrane protein localization
Integral membrane proteins
a type of protein that is permanently attached to the cell membrane
Peripheral membrane proteins
a type of protein that is temporarily associated with the cell membrane or with other membrane proteins, but it is not embedded within the lipid bilayer
(FRAP) Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching
a technique used to study the mobility of molecules, particularly proteins, within a cell membrane It involves using fluorescence microscopy and photobleaching to track the movement of fluorescently labeled molecules
Homeoviscous adaptation
a process by which cells maintain the fluidity of their membranes by altering the composition of their lipids in response to temperature changes
Microfilaments
also known as actin filaments, are a major component of the cytoskeleton
G-Actin
G-actin, or globular actin, is the monomeric form of actin that, when assembled, forms microfilaments also known as F-actin
F-Actin
F-actin, or filamentous actin, refers to the polymeric form of actin that makes up microfilaments, a major component of the cell's cytoskeleton
Nucleation
the initial step in the formation of a new actin or microtubule filament, and is generally considered the rate-limiting step
Polymerization
the process by which monomers are added to a growing filament, and is a key step in the formation of both actin microfilaments and microtubules
Treadmilling
dynamic process observed in actin filaments where G-actin monomers are added to the plus end of the filament while other G-actin monomers are simultaneously removed from the minus end
Profilin
a key regulatory protein that plays a significant role in actin polymerization by promoting the addition of G-actin monomers to the plus end of actin filaments
Thymosin
a regulatory protein that plays a role in actin dynamics by binding to G-actin monomers and preventing them from being added to actin filaments
Formin
a class of proteins that play a crucial role in actin polymerization by working in conjunction with profilin to promote both the nucleation and elongation of actin filaments
CapZ
a regulatory protein that controls actin filament length by preventing the addition or loss of monomers at the plus end of actin filaments
Tropomodulin
a regulatory protein that controls actin filament length by preventing the addition or loss of monomers at the minus end of actin filaments
Cofilin
a regulatory protein that plays a crucial role in actin dynamics by promoting the disassembly of actin filaments
Tropomyosin
regulatory protein that plays a crucial role in stabilizing actin filaments by binding along their length
Arp2/3
a protein complex that plays a crucial role in actin dynamics by initiating actin filament branching and nucleation
Microtubules
a key component of the cytoskeleton, and they are involved in a variety of cellular processes. They are more rigid and less flexible than intermediate filaments, and they are different from actin filaments, which are also part of the cytoskeleton
α-tubulin
a key protein that, along with β-tubulin, forms the basic building block of microtubules
β-tubulin
a key protein that, along with α-tubulin, forms the basic building block of microtubules
γ-Tubulin
a crucial protein involved in the nucleation of microtubules at the Microtubule Organizing Centers (MTOCs), or centrosomes
γ-TuRC (gamma-tubulin ring complex)
a crucial protein complex that plays a key role in the nucleation of microtubules at the Microtubule Organizing Centers (MTOCs) It is essential for the proper organization of the microtubule network within the cell
Catastrophe
a term that describes a key aspect of microtubule dynamics. It refers to the rapid shrinking of a microtubule due to the hydrolysis of GTP on β-tubulin
Rescue
a term that describes a key aspect of microtubule dynamics, referring to the process where a shrinking microtubule switches back to a growth phase. This is crucial for the dynamic instability of microtubules, allowing them to perform their various cellular functions
Microtubule Organizing centers (MTOCs) or centrosomes
also known as the centrosome, is a crucial structure in the cell that serves as the primary site for the nucleation of microtubules
Centrioles
proteinaceous structures that are a key component of the Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC), also known as the centrosome, and play a crucial role in cell division and the organization of the microtubule network
Intermediate filaments
a major component of the cytoskeleton, distinct from actin filaments and microtubules, and are best thought of as cellular ropes that provide mechanical strength and flexibility to cells and tissue
Molecular motors
proteins that undergo conformational changes to catalyze effects, especially movement, within a cell, Cytoskeletal motors are a specific class that move along actin filaments or microtubules, and include myosins, kinesins, and dyneins
Myosin
a class of actin-binding molecular motors that use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to generate force and movement. They play crucial roles in various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, vesicle transport, and cell motility
Myosin I
primarily involved in vesicle transport. It is characterized as a non-processive, plus-ended motor
Myosin II
primarily known for its role in muscle contraction, but also participates in other cellular processes. It is characterized as a non-processive, plus-ended motor
Myosin V
primarily involved in vesicle transport. It is characterized as a processive, plus-ended motor
Myosin VI
primarily involved in vesicle transport. It is unique among myosins as it is a processive, minus-ended motor
Kinesin
a type of microtubule-binding molecular motor protein that is primarily involved in intracellular transport. Kinesin is a processive, plus-ended motor protein
Dynein
a type of microtubule-binding molecular motor protein that is primarily involved in intracellular transport. It is characterized as a processive, minus-ended motor protein
Processive motor
a molecular motor that remains attached to its cytoskeletal filament as it moves, allowing it to take multiple steps without detaching
Non-processive motor
a molecular motor that detaches from its cytoskeletal filament during its movement, meaning it must repeatedly bind, move, and then release the filament as it transports cargo
Cadherin
a family of cell-cell adhesion proteins that play a crucial role in the organization of tissues and in development
Adherens junctions
a type of cell-cell junction that are primarily responsible for the adhesion of cells to one another through the binding of cadherin proteins
Desmosomes
a type of cell-cell junction that provide strong adhesion between cells through connections with intermediate filaments. They are critical for maintaining the structural integrity of tissues that experience mechanical stress.
Integrins
Focal Adhesions
Hemidesmosomes
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Tight junctions
Gap Junctions
Nucleolus
snoRNPs
heterochromatin
Euchromatin
Nuclear Envelope
Nuclear Lamina
LINC Complex (Linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton)
Dimer
a structure formed by two subunits of a molecule, often a protein, that are bound together
Fusion protein
How to make polyclonal antibodies
How to make monoclonal antibodies
Antigen
Antibody
Widefield Microscopy
Confocal Microscopy
Distance is equal to?
λ/2
2 limitations of light microscopy
Resolution, lack of detail
3 ways to label proteins
Antibodies, Fusion proteins, Epitope tagging
Constant region (antibody)
Variable region (antibody)
Antibody structure
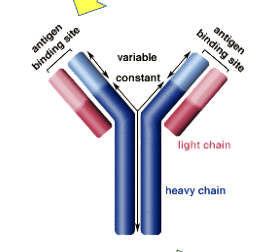
Secondary antibody
GFP
Cell Fractionation
Velocity Sedimentation
Beta-mercaptoethanol and DTT
GST binds with
Glutathione
His binds with
Cations (Nickel)
Biotin binds with
Streptavidin
3 ways phospholipids differ
Tail length, Saturation, head groups
Why does a phospholipid bilayer membrane require no energy to form?
Energetically favorable, Steric hindrance
3 things that affect membrane fluidity
Temperature, Cholesterol, and fatty acid saturation (unsaturation increases fluidity)
How many amino acids does it take to traverse the membrane
~20
hydrophathy plot
4 ways to limit protein mobility
Bind “scaffolding” proteins, fences, binding to other cells, and lipid rafts.