AP Psychology Unit 0 Redesign
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Psychology
Study of behavior and mental processes

Replicability
Ability to reproduce scientific results

Critical Thinking
Examining assumptions, biases, and evidence

Hindsight Bias
Belief in predicting outcomes after learning them

Confirmation Bias
Tendency to seek info aligning with beliefs

Belief Perseverance
Clutching to beliefs despite contrary evidence

Overconfidence
Being more certain than accurate in knowledge

Scientific Method
Process for evaluating ideas with observations

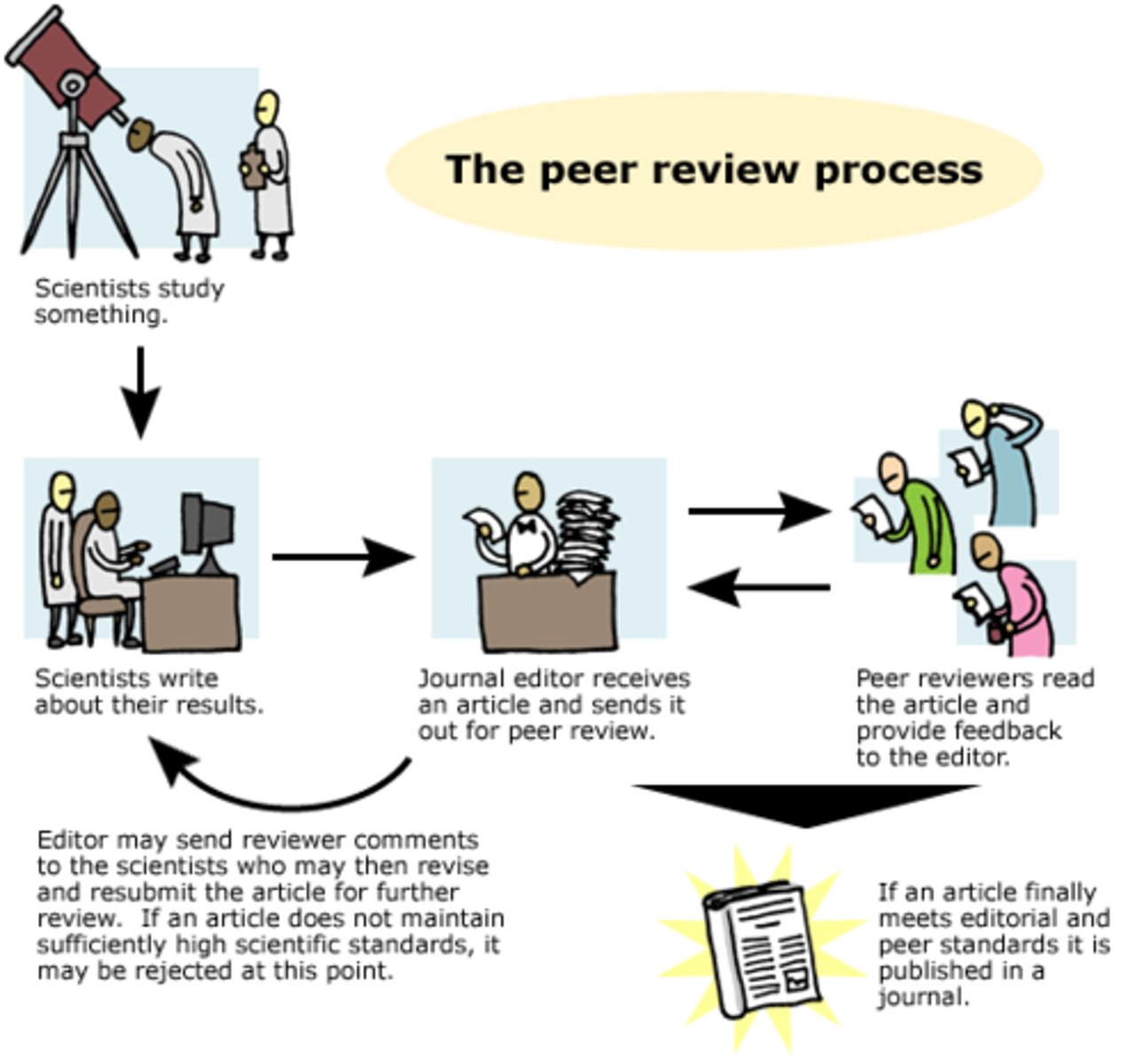
Peer Reviewers
Experts evaluating research articles
Theory
Explanation organizing observations and predicting events

Hypothesis
Testable prediction implied by a theory

Falsifiability
Idea that theories can be disproved by observation
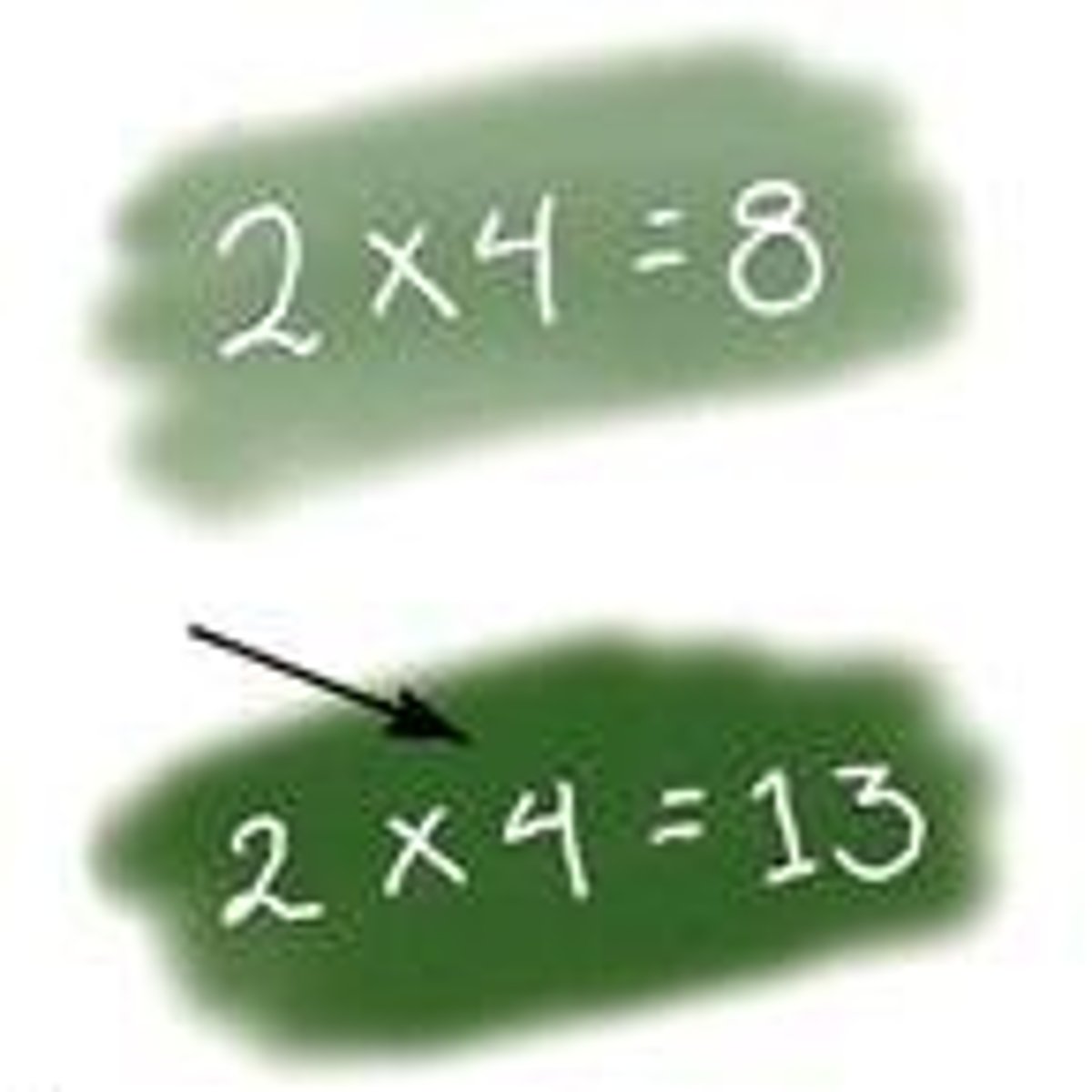
Non Experimental Methods
Techniques like case studies and surveys

Experimental Methods
Involving manipulation of variables
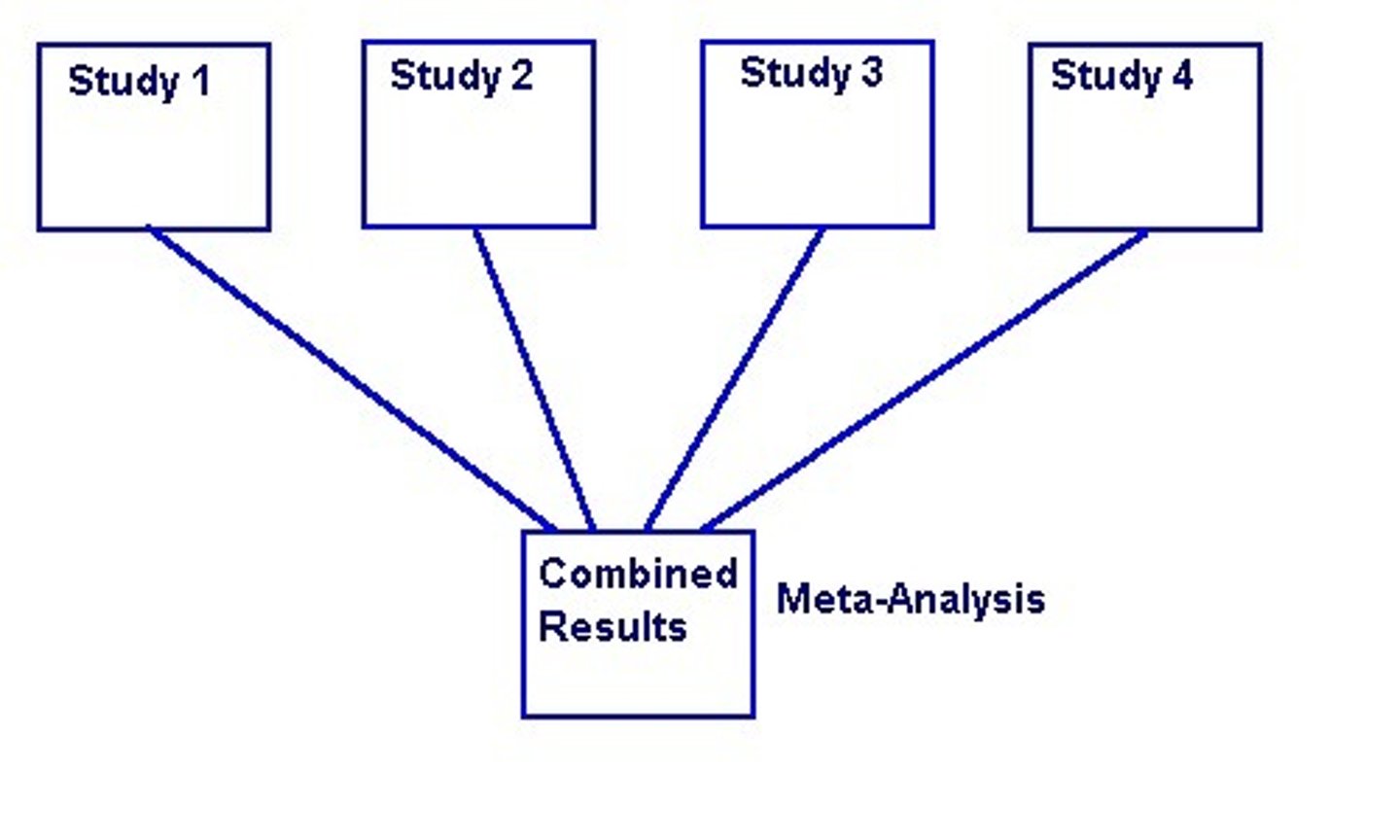
Meta Analyses
Studying results of multiple studies for conclusions
Correlational Research
Describing relationships between variables
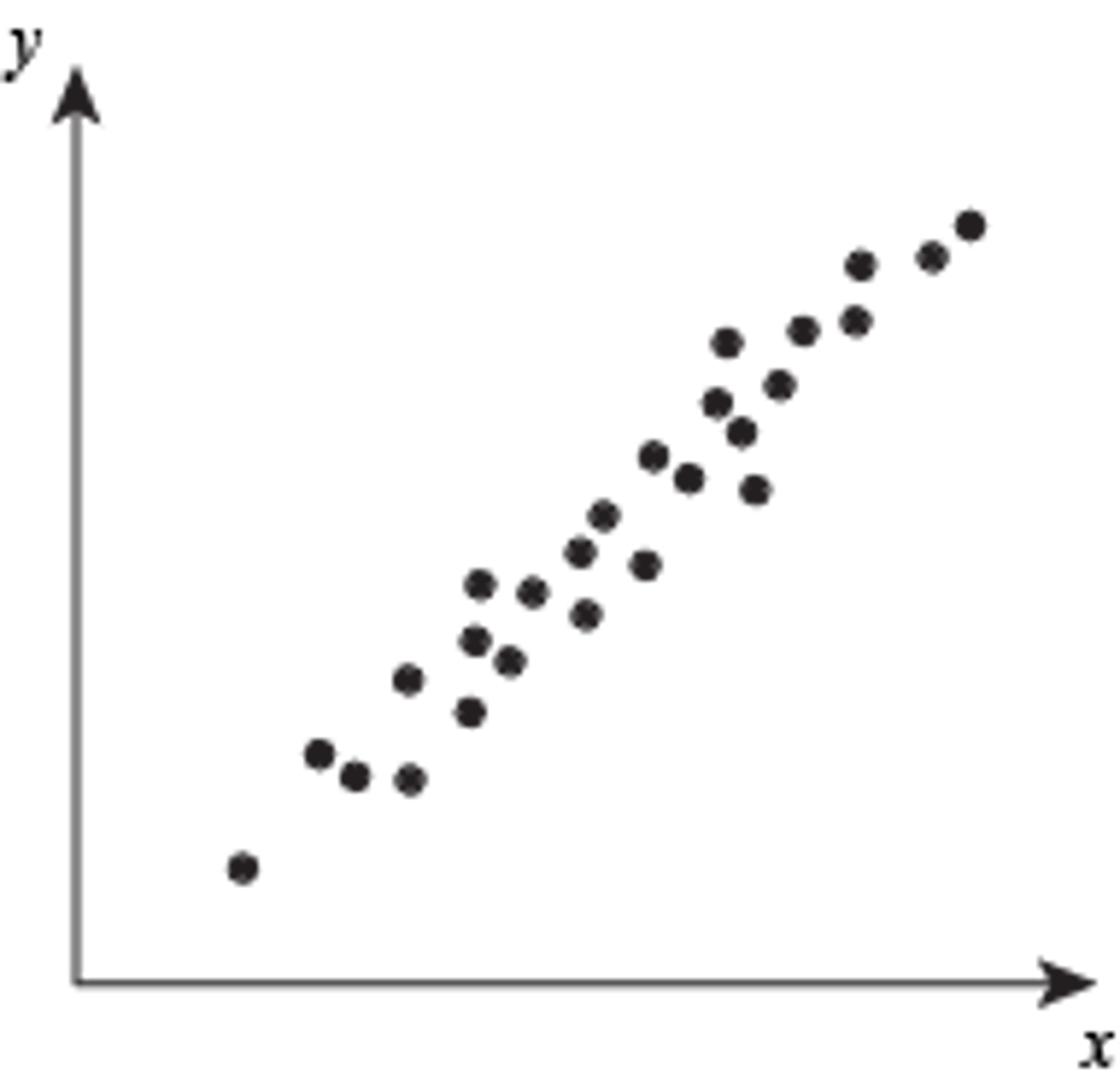
Correlation Coefficient
Measures strength of relationship between variables

Scatterplot
Graph showing relationship between two variables
Directionality Problem
Inability to determine cause and effect between variables
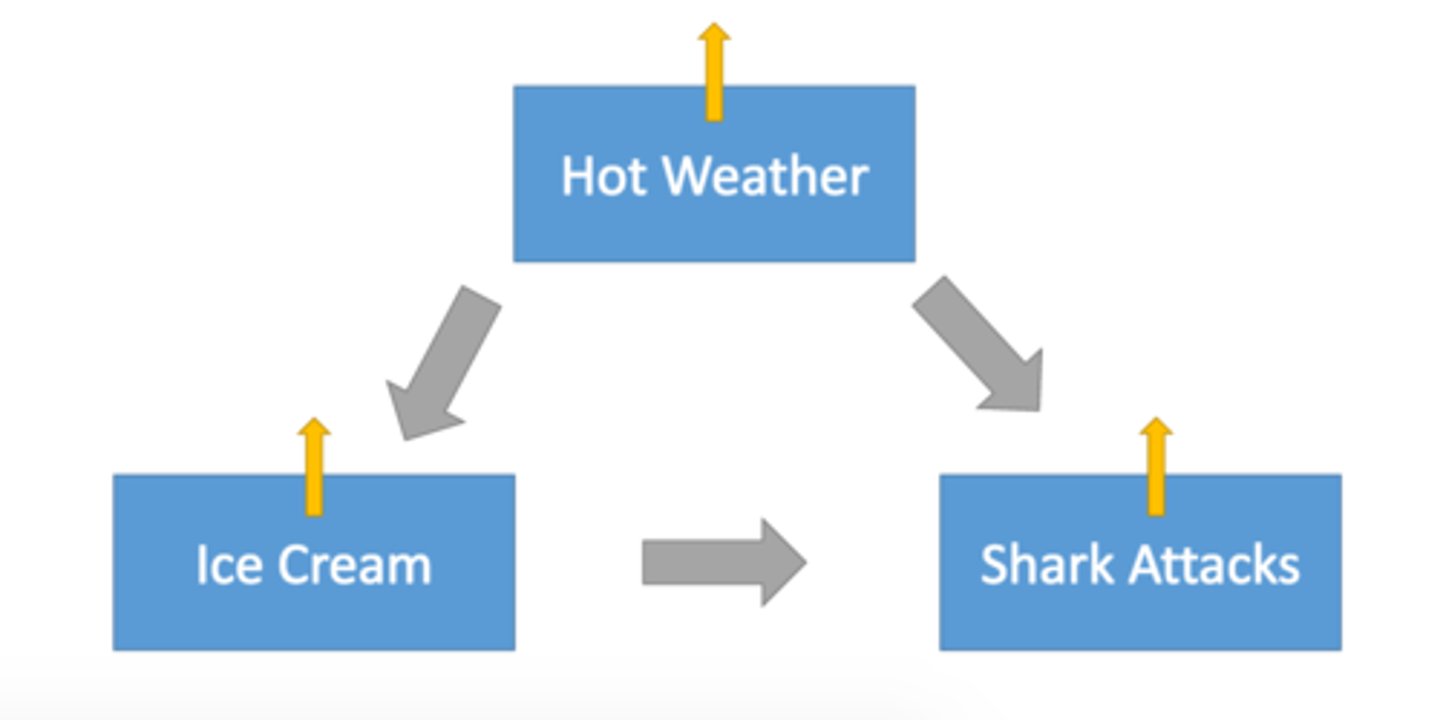
Third Variable Problem
Hidden variable impacting studied variables
Illusory Correlation
False belief in a relationship between variables

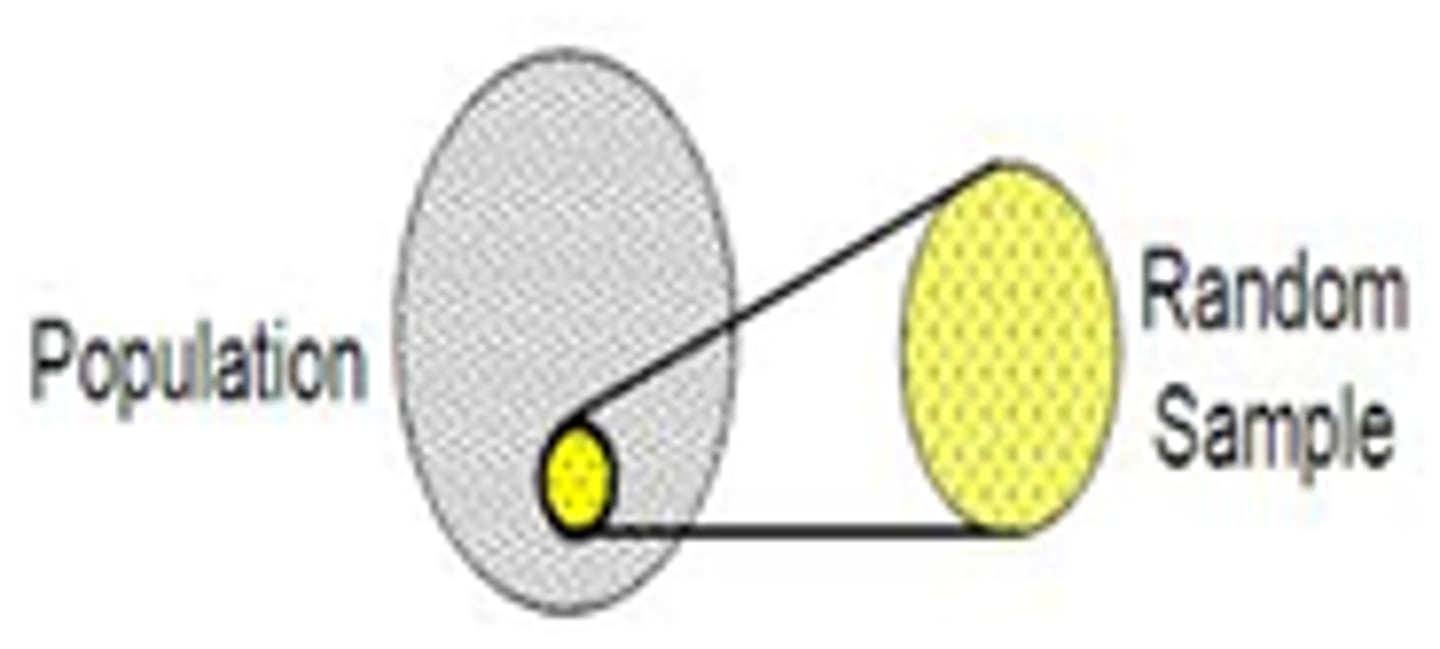
Random Sampling
Selecting a sample from a population randomly
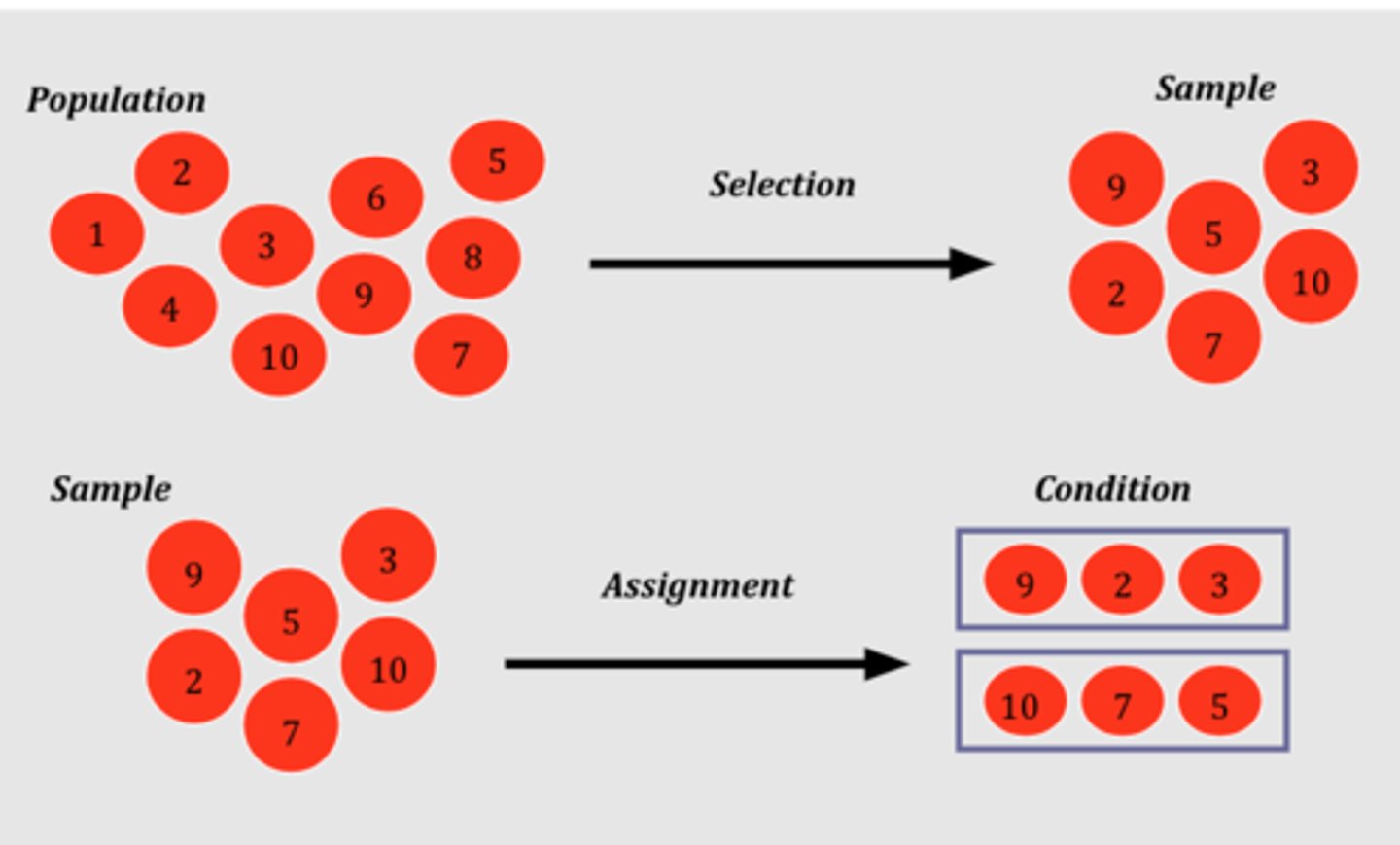
Random Assignment
Assigning participants to groups randomly
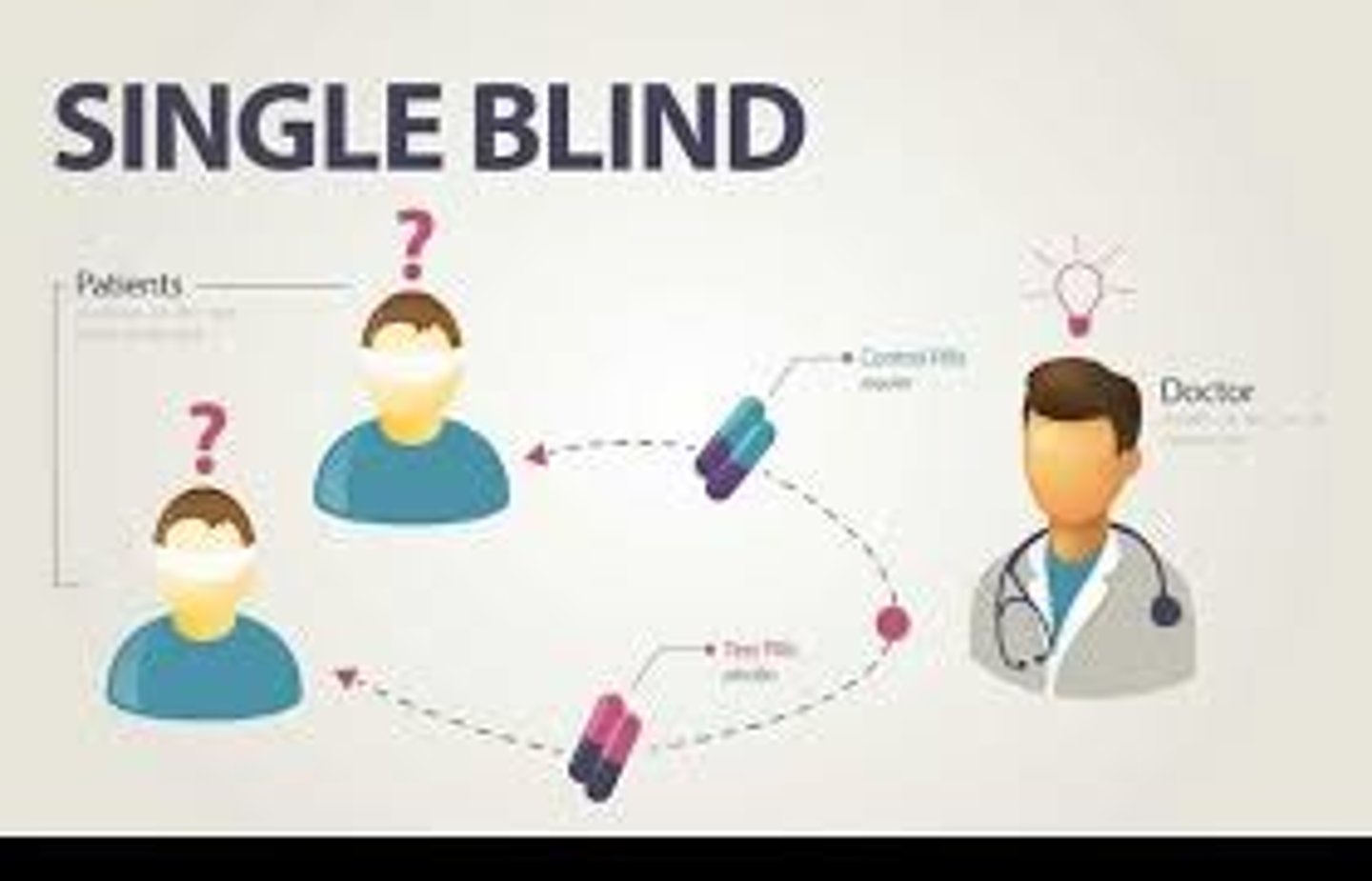
Single-Blind Procedure
Participants unaware of their group assignment
Double-Blind Procedure
Both researchers and participants unaware of group assignments

Placebo
Inert treatment given to the control group

Placebo Effect
Behavior change due to expectations from an inert substance

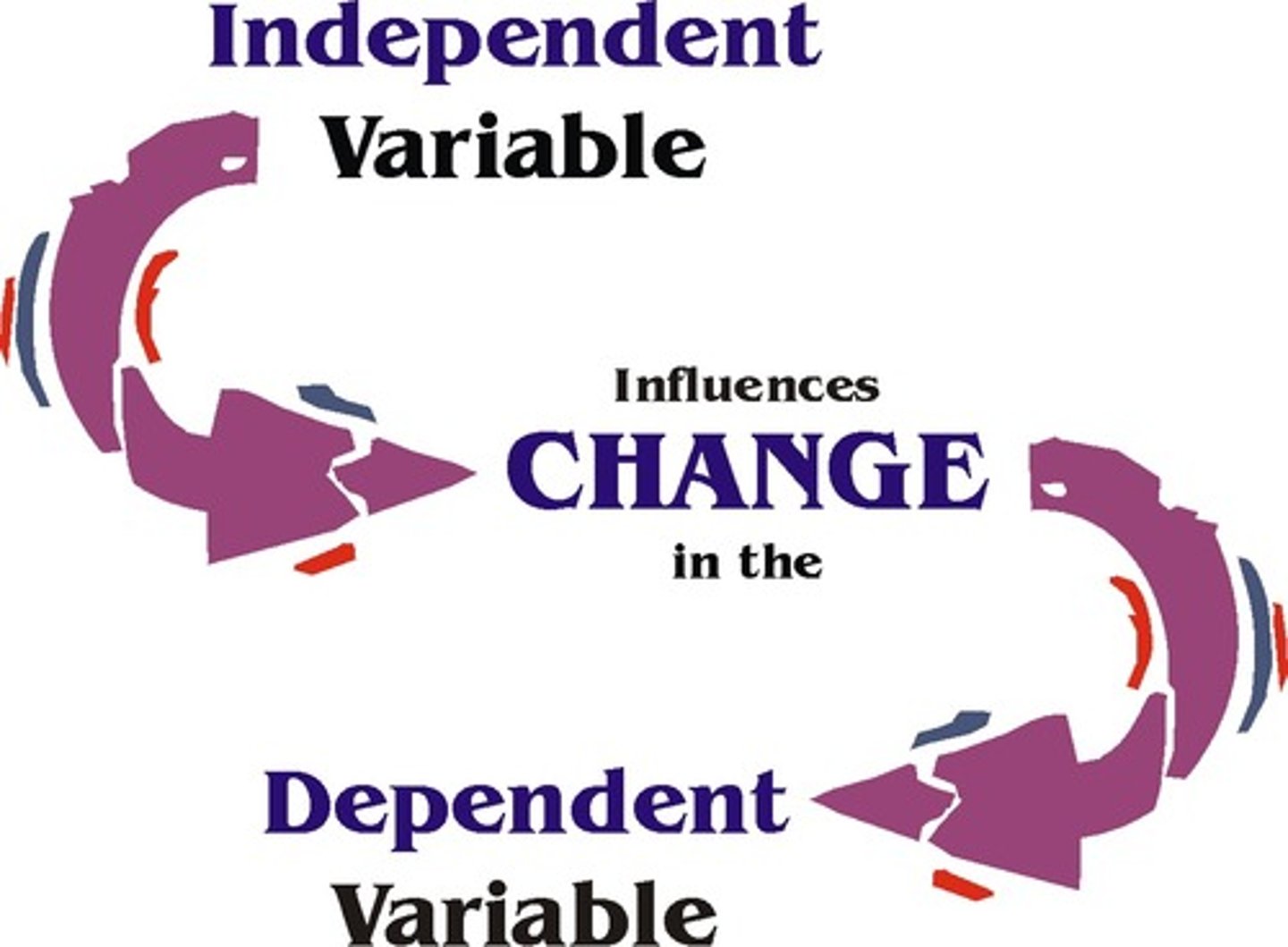
Independent Variable
Manipulated variable in an experiment
Confounding Variable
Factors influencing study outcomes other than the IV
Social Desirability Bias
Subjects altering results to please researchers

Experimenter Bias
Researchers unintentionally skewing results to match beliefs

Dependent Variable
Measured outcome variable in an experiment

Operational Definition
Specifies procedures to manipulate IV and measure DV

Validity
Experiment testing what it's supposed to

Quantitative Research
Using numerical data to represent variables

Qualitative Research
Relies on narrative data, not numerical
APA Guidelines for Animal Research
Mandates humane care, healthy conditions, and minimal discomfort
Deception in Research
Temporary deception justifiable with thorough debriefing

Informed Consent
Subjects must agree to participate after being informed
Protection in Research
Ensuring protection from harm, discomfort, and confidentiality
Institutional Review Boards
Comprised of scientists, non-scientists, and community reps to screen ethical concerns

Descriptive Statistics
Measuring and describing characteristics of a study group
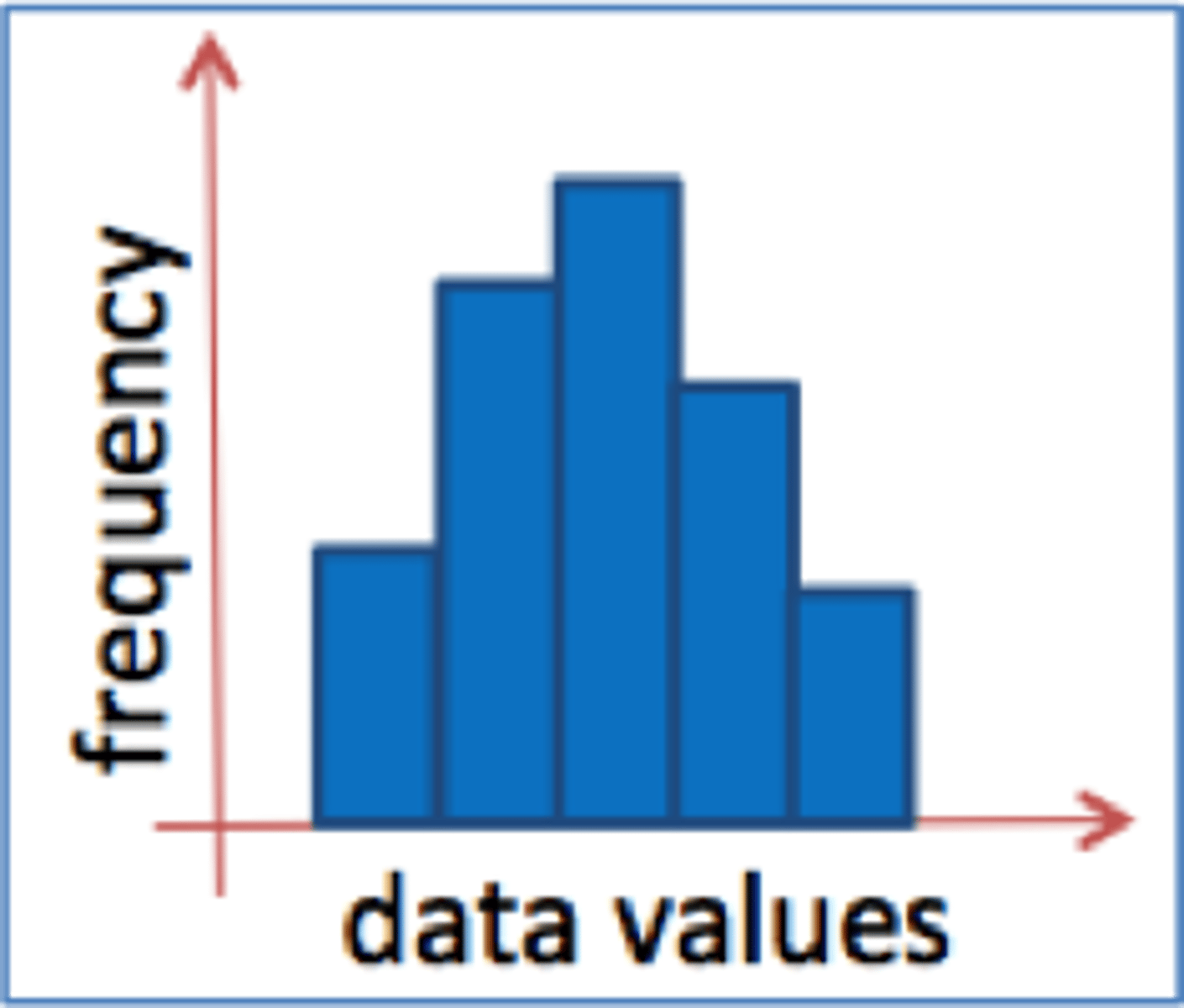
Histogram
Bar graph displaying frequency distribution
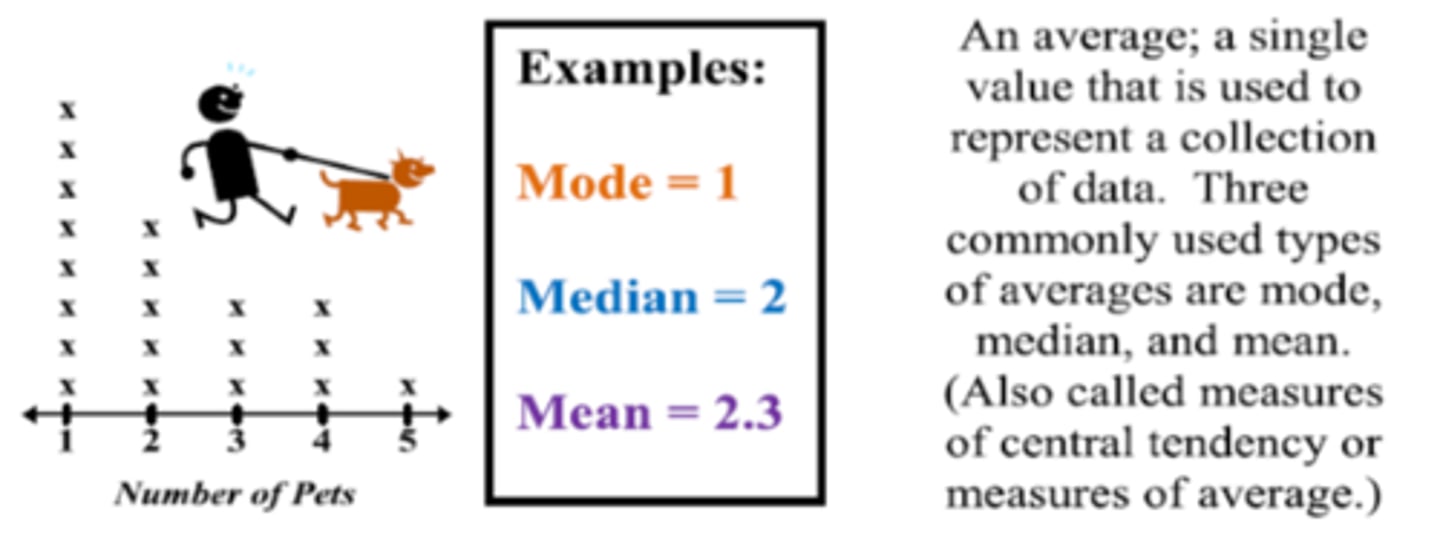
Measures of Central Tendency
Mean, mode, median - describe distribution characteristics
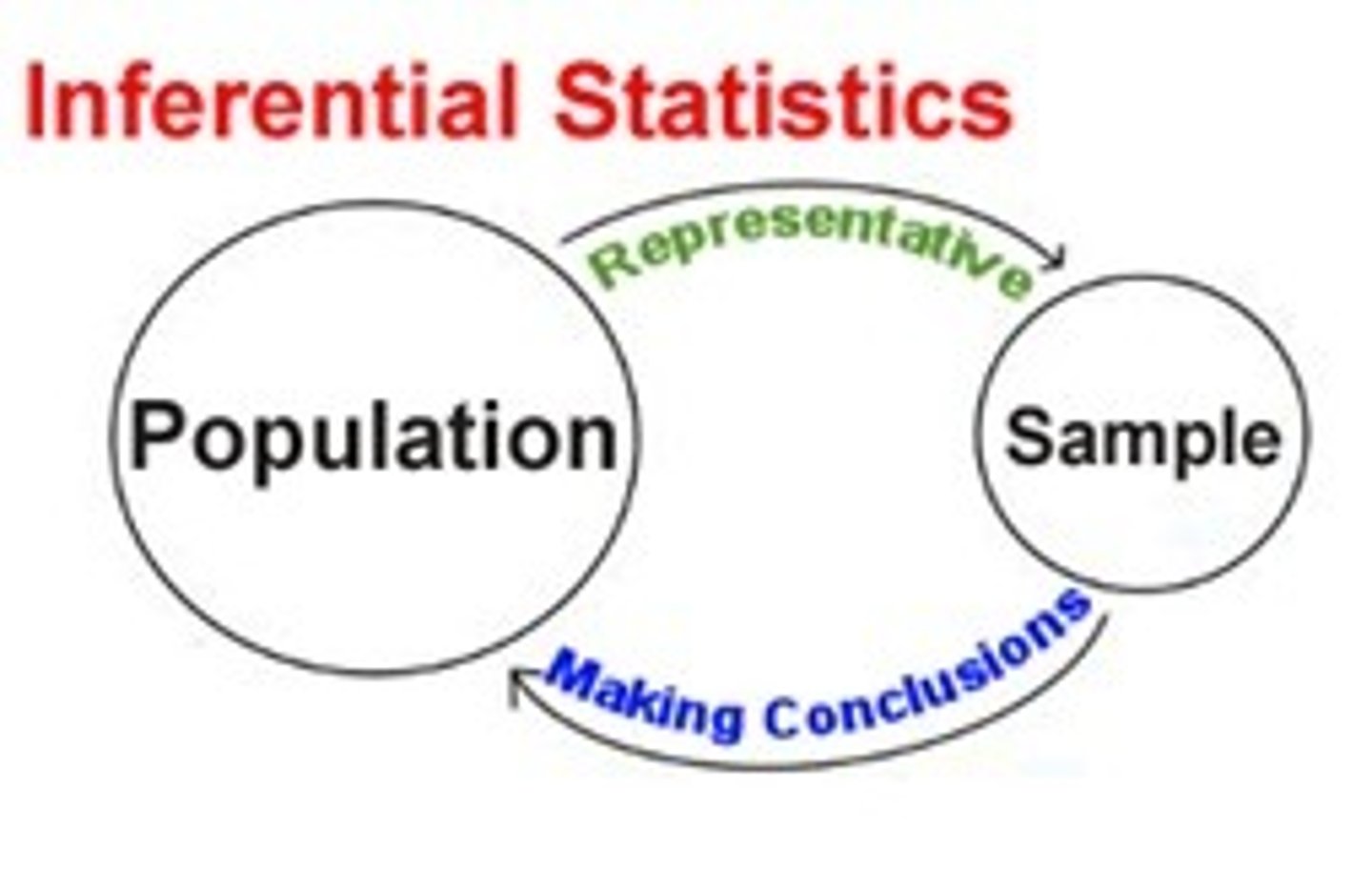
Inferential Statistics
Data allowing generalization from sample to population
Case study
an observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
positive correlation
A correlation where as one variable increases, the other also increases, or as one decreases so does the other. Both variables move in the same direction.
negative correlation
the relationship between two variables in which one variable increases as the other variable decreases
naturalistic observation
observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation
Replication
repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding extends to other participants and circumstances
standard deviation
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
percentile rank
the percentage of scores below a specific score in a distribution of scores
mean
the arithmetic average of a distribution, obtained by adding the scores and then dividing by the number of scores
Median
the middle score in a distribution; half the scores are above it and half are below it
Mode
the most frequently occurring score(s) in a distribution
range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
normal curve
the symmetrical bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many physical and psychological attributes. Most scores fall near the average, and fewer and fewer scores lie near the extremes.
positively skewed distribution
A distribution where the scores pile up on the left side and taper off to the right.
negatively skewed distribution
A distribution in which most scores pile up at the high end of the scale.
bimodal distribution
a distribution with two modes
regression towards the mean
the tendency for extreme or unusual scores to fall back (regress) toward their average.
Sample
A relatively small proportion of people who are chosen in a survey so as to be representative of the whole.
population
a group of similar things that a scientist is interested in learning about
representative sample
a sample that accurately reflects the characteristics of the population as a whole
random sampling
a sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
convenience sampling
using a sample of people who are readily available to participate
Generalizing
the ability to apply the findings of a particular research project to larger segments of society
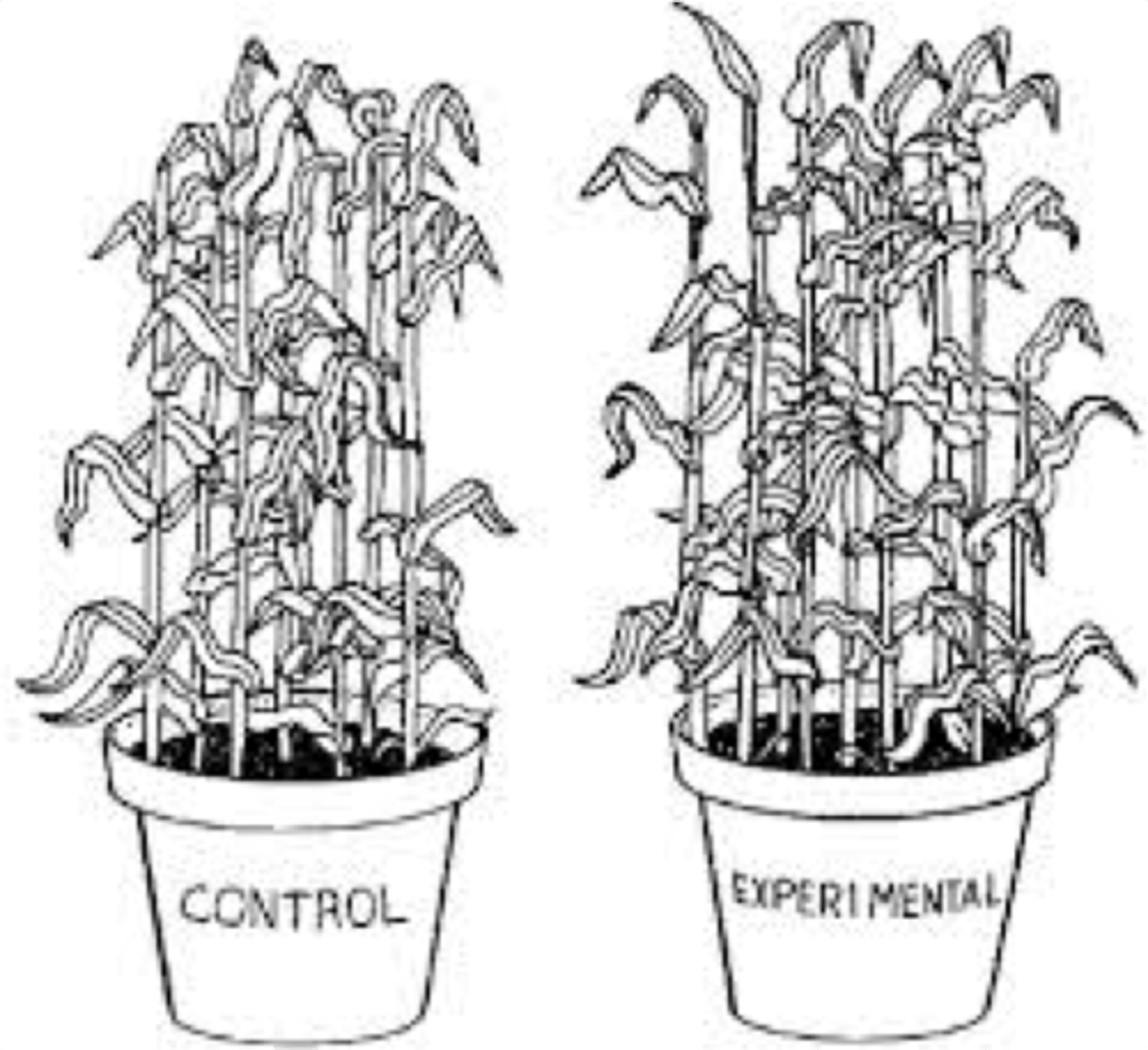
experimental group
In an experiment, the group that is exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable.
control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
structured interview
a research procedure in which all participants are asked to answer the same questions
Likert scales
ordinal-level scales containing seven points on an agree or disagree continuum

peer review
a review by people with similar professional qualification

effect sizes
a measure of the strength of the relationship between two variables or the extent of an experimental effect
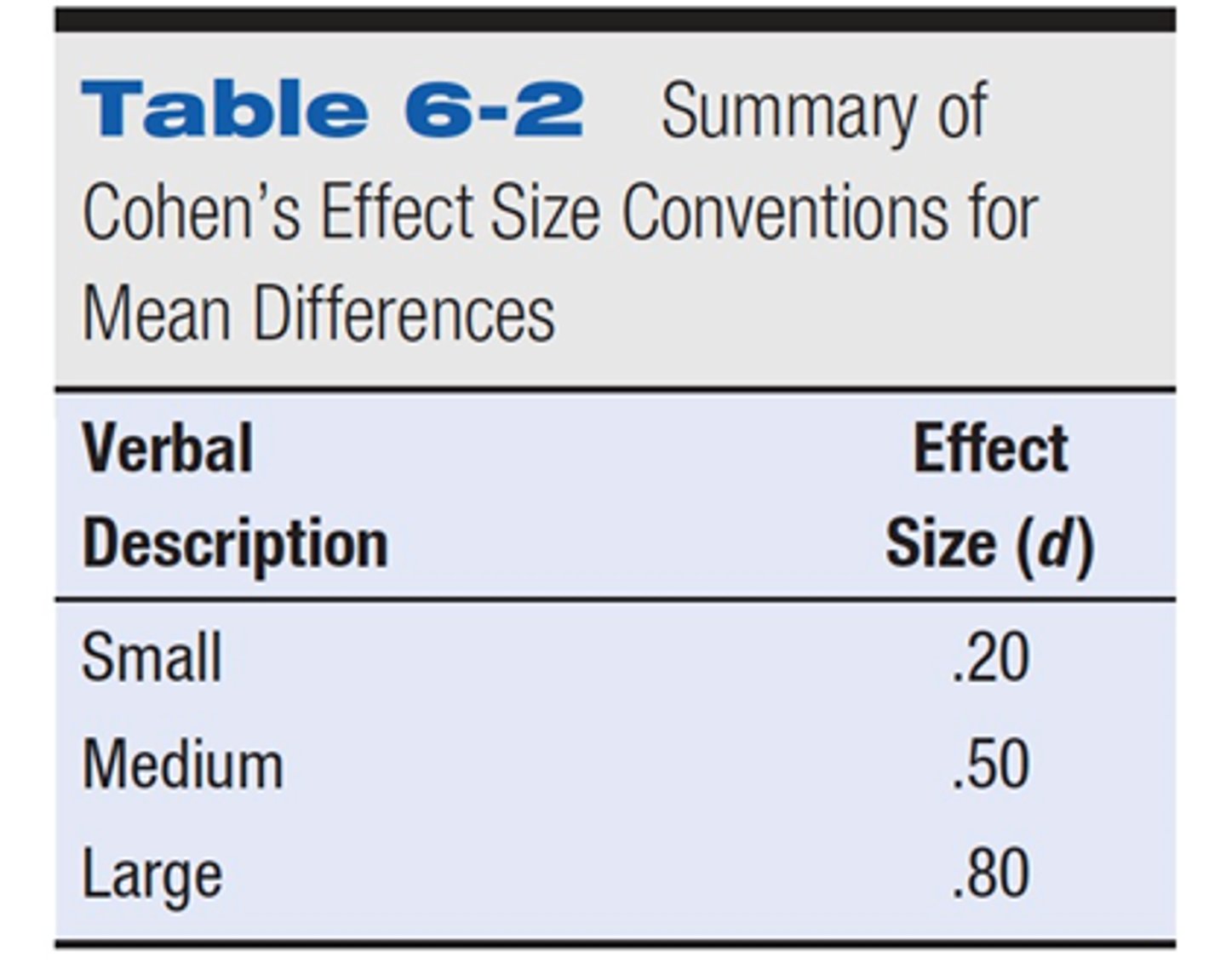
statistical significance
a statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance

Confidentiality
Respecting the privacy of both parties and keeping details secret

Debriefing
the post-experimental explanation of a study, including its purpose and any deceptions, to its participants

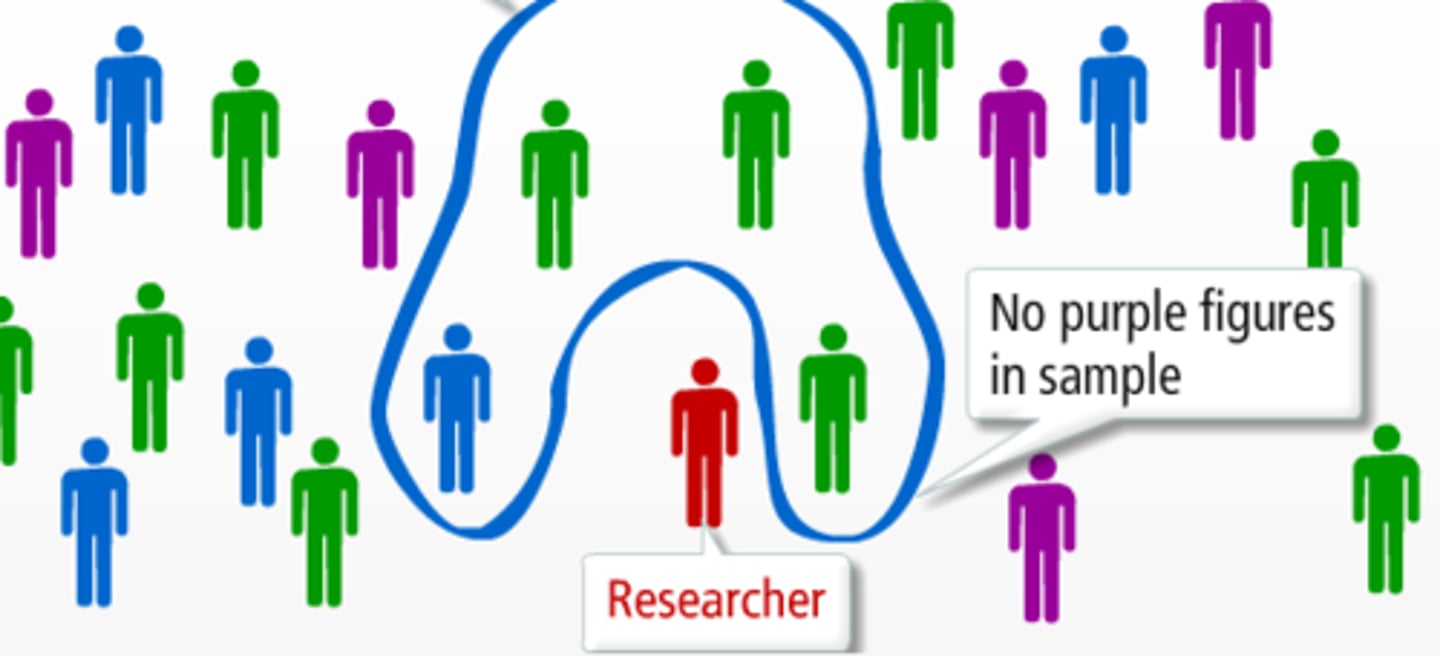
sampling bias
A problem that occurs when a sample is not representative of the population from which it is drawn.
Placebo Group
A control group of participants who believe they are receiving treatment, but who are only receiving a placebo.
Survey
a non-experimental technique for obtaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of the group.
Framing
the way an issue is posed; how an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgements.
Social Desirability Bias
bias from people's responding in ways they presume a researcher expects or wishes.
Self-report bias
bias when people report their behavior inaccurately.
Informed assent
Participant's agreement to participate in the absence of full understanding and commonly applies to individuals who have not attained legal majority and/or capacity (under 18)
Confederates
in psychological and social research, a confederate is a person who is working with the experimenter and posing as a part of the experiment, but the subjects are not aware of this affiliation