3.1 - Prokaryotes
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary terms related to prokaryotes, including their characteristics, processes, and impact on the environment and humans.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Prokaryotes
Unicellular organisms that lack internal organelles and are characterized by their simple structure.
Binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in prokaryotes where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
Halobacterium
An archaean prokaryote that survives in hyper-saline environments and pumps potassium ions to balance osmotic pressure.
Peptidoglycan
A large polymer that forms the cell wall of bacteria, composed of sugars and amino acids.
Gram-positive bacteria
Bacteria that have a thick peptidoglycan layer and stain purple during Gram staining.
Gram-negative bacteria
Bacteria that have a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane, staining pink during Gram staining.
Capsule
A sticky layer of polysaccharides or proteins surrounding the cell wall of some prokaryotes, aiding in adhesion.
Endospore
A highly resistant structure formed by some bacteria in response to harsh conditions, allowing survival for extended periods.
Conjugation
The process by which genetic material is transferred between prokaryotic cells through direct contact.
Antibiotic resistance
The ability of bacteria to survive and grow in the presence of antibiotics, often due to genetic mutations and selection.
Nitrogen fixation
The process by which some prokaryotes convert atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3), making it usable for plants.
Chemoheterotrophs
Organisms that obtain their energy and carbon by consuming organic compounds from other organisms.
Facultative aerobes
Prokaryotes that can survive in both aerobic and anaerobic environments.
Extremophiles
Prokaryotes that thrive in extreme environmental conditions, such as high temperatures or salinity.
Microbiome
A community of microorganisms, including bacteria, that inhabit a specific environment, such as the human gut.
Prokaryotic phylogeny
The evolutionary history and relationships among the different groups of prokaryotes.
Why do lakes turn pink?
Very high salt concentration
Most prokaryotes are
Unicellular
Have no internal organelles
Have many shapes
Small
Common prokaryotes shapes
Spherical
Rod-shaped
Spiral
Prokaryotes cell wall
Provides protection against osmosis stress
Bacterial cell walls contain
Peptidoglycan
What do some prokaryotes cell wall have
Some have naked cell walls, others have an additional cell membrane on top of the cell wall
What is the cell wall surrounded by in many prokaryotes
Capsule
Capsule
In many prokaryotes, the cell wall is surrounded by a sticky layer of polysaccharide or protein
Fimbriae
Hairlike appendages in some prokaryotes cell wall
Prokaryotes structural adaptations
Endospore, flagellum
Endospore
Highly protective, multilayer coat forms around the chromosome, water removed, metabolism stops
How is the endospore formed?
When faced with harsh conditions
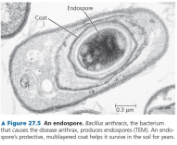
Name
Endospore
Flagellum
Allows prokaryotes to move
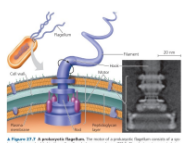
Name
Flagellum
Genetic diversity in prokaryotes main factors
Rapid reproduction, mutation and genetic recombination
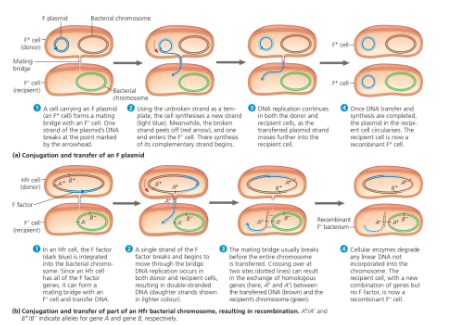
Name
Conjugation and recombination
Obligate aerobes must…
Use O2 for cellular respiration
Obligate anerobes are…
Poisoned by O2, and either use another terminal electron acceptor or only conduct fermentation
Facultative aerobes
Very flexible and can work in either aerobic or anaerobic environments
What is nitrogen essential for?
The production of amino acids and nucleic acids in all organisms
Nitrogen fixation
Some prokaryotes incorporating N2 from atmosphere into ammonia
Five clades based on molecular data
Proteobacteria, chlamydias, spirochetes, cyanobacteria, gram-positive bacteria
Proteobacteria
Very diverse clade including nitrogen fixing bacteria
Chlamydias
Parasitic bacteria, survive only in animal cells, depend on host for resources as basic as ATP
Spirochetes
Spiral, most free-living, some pathogenic parasites
Cyanobacteria
Only prokaryotes with plant-like oxygen-generating photpsynthesis
Gram-positive bacteria
Very diverse clade, include streptomyces
Archaea
Share traits with bacteria and eukarya and some are unique
Archaea include
Extremophiles, methanogens
Extremophiles
Grow in extreme salt or temperature environments
Methanogens
Decomposers
Chemical recycling
The process by which essential elements are reused in the ecosystem, typically involving decomposition and transformation of organic materials by microorganisms.
Ecological relationships parts
Mutualist, commensal, parasitic
How prokaryotes affect humans?
Mutualistic bacteria (+/+)
Pathogenic bacteria