Milady 5-2
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

20 Terms
Infection
the invasion of body tissues by disease-causing pathogens
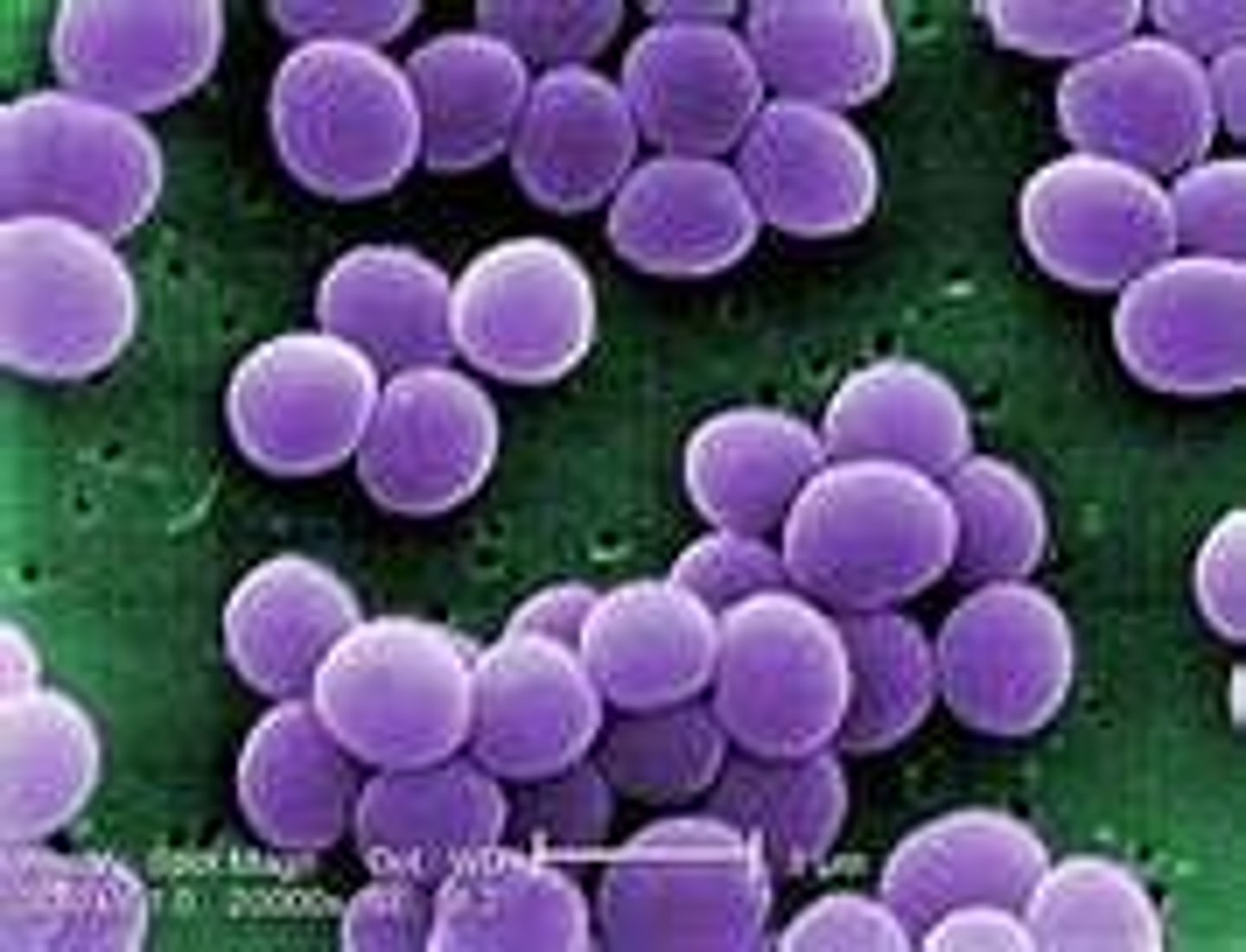
Staphylococci
pus-forming bacteria that grow in clusters like grapes. They cause abscesses, pustules, and boils.
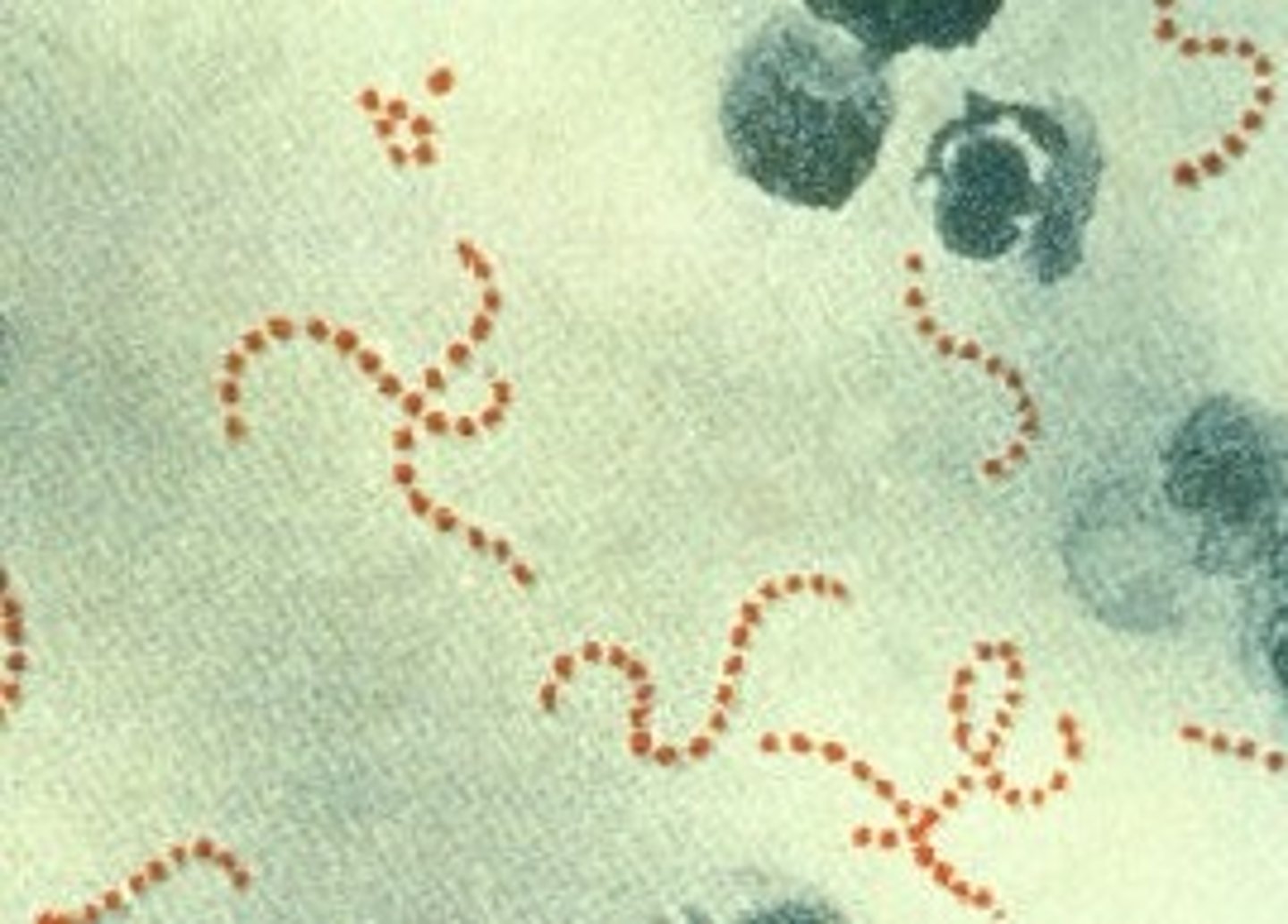
Streptococci
pus-forming bacteria arranged in curved lines resembling a string of beads. They cause infections such as strep throat and blood poisoning
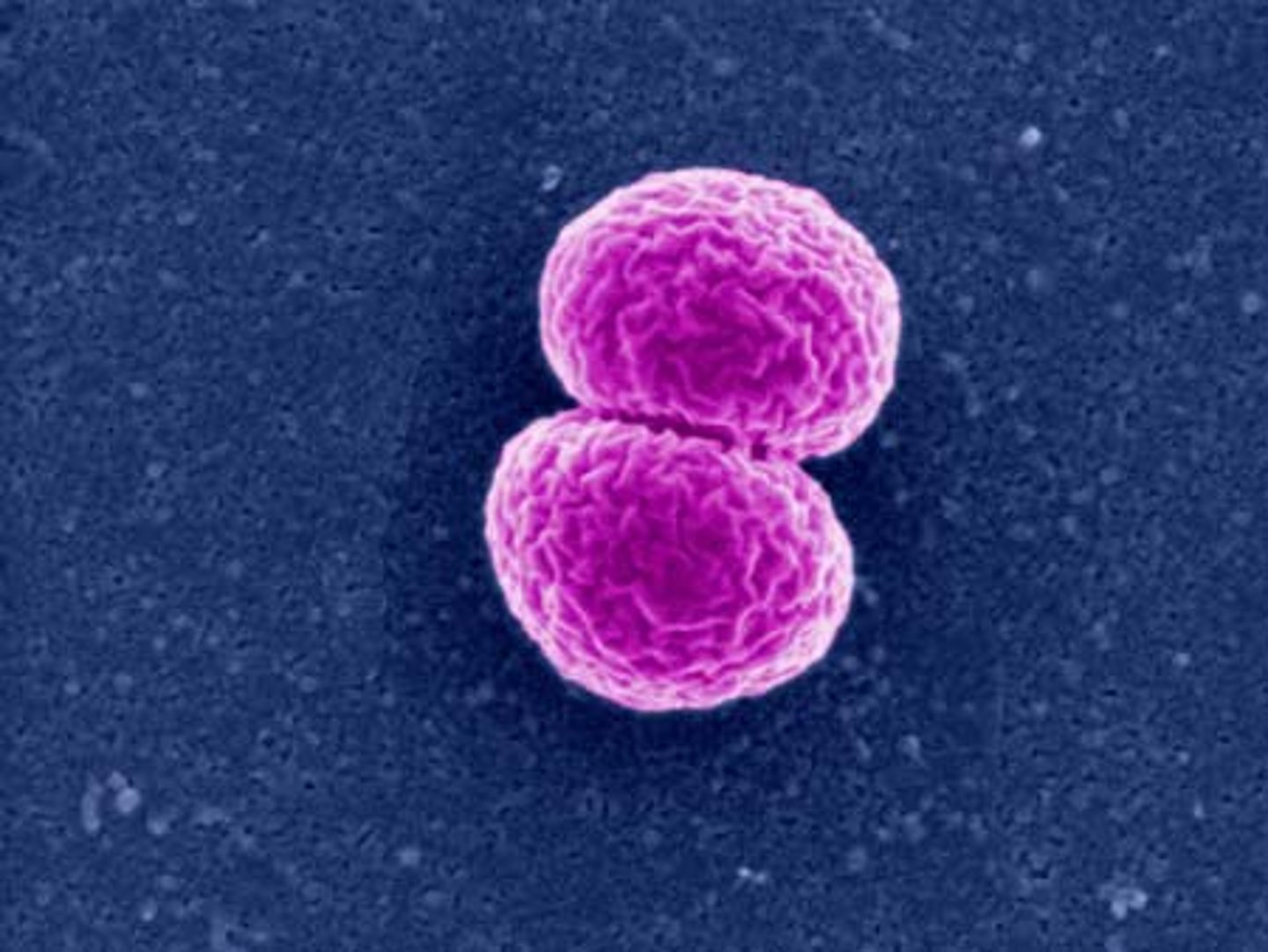
Diplococci
spherical bacteria that grow in pairs and cause diseases such as pneumonia
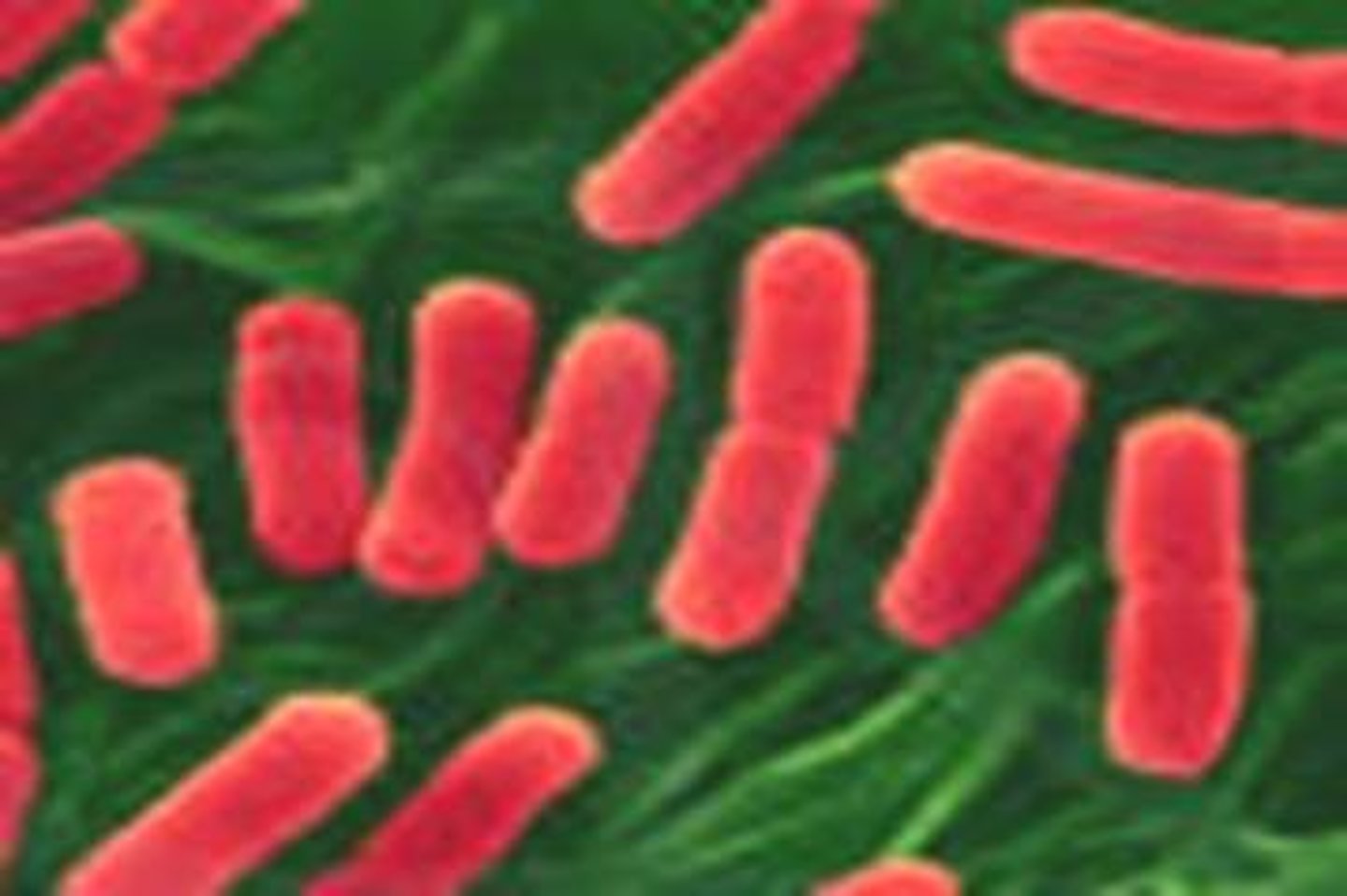
Bacilli
short, rod-shaped bacteria. They are the most common bacteria and produce diseases such as tetanus, typhoid fever, tuberculosis, and diphtheria
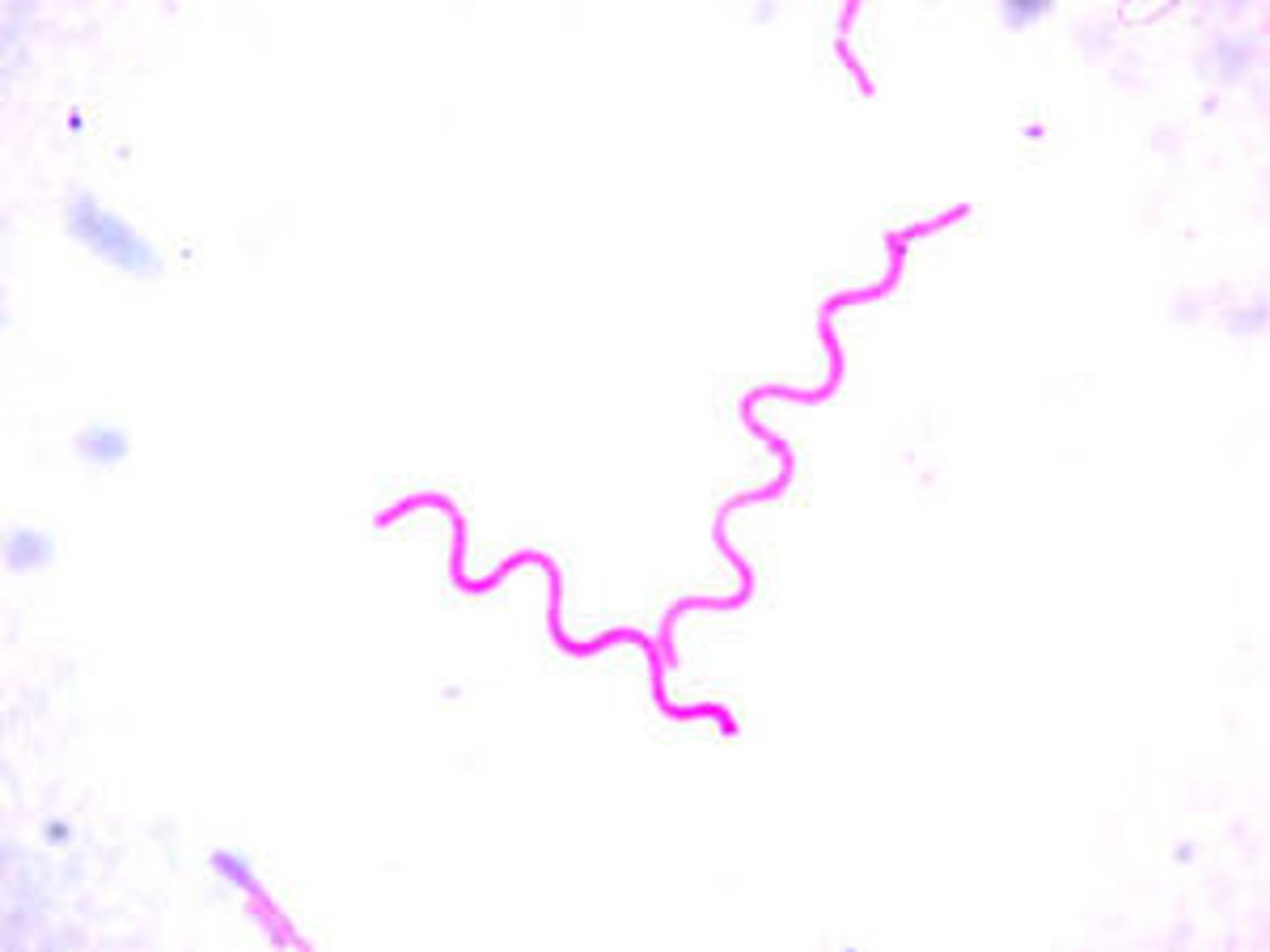
Spirilla
spiral or corkscrew-shaped bacteria. They are subdivided into subgroups such as syphilis and Lyme disease
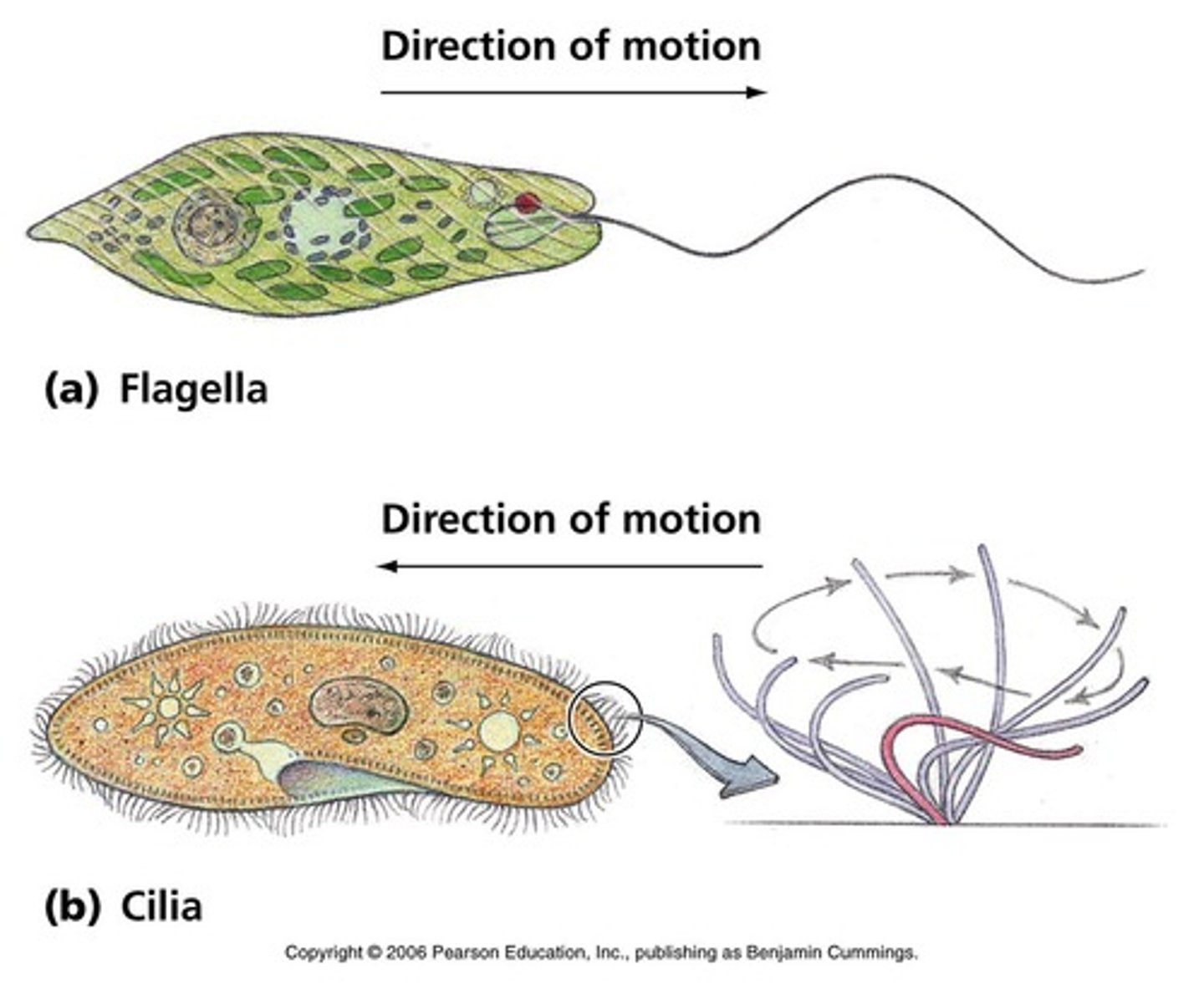
Motility
the term used to describe self-movement
Flagella
hair-like extensions for locomotion
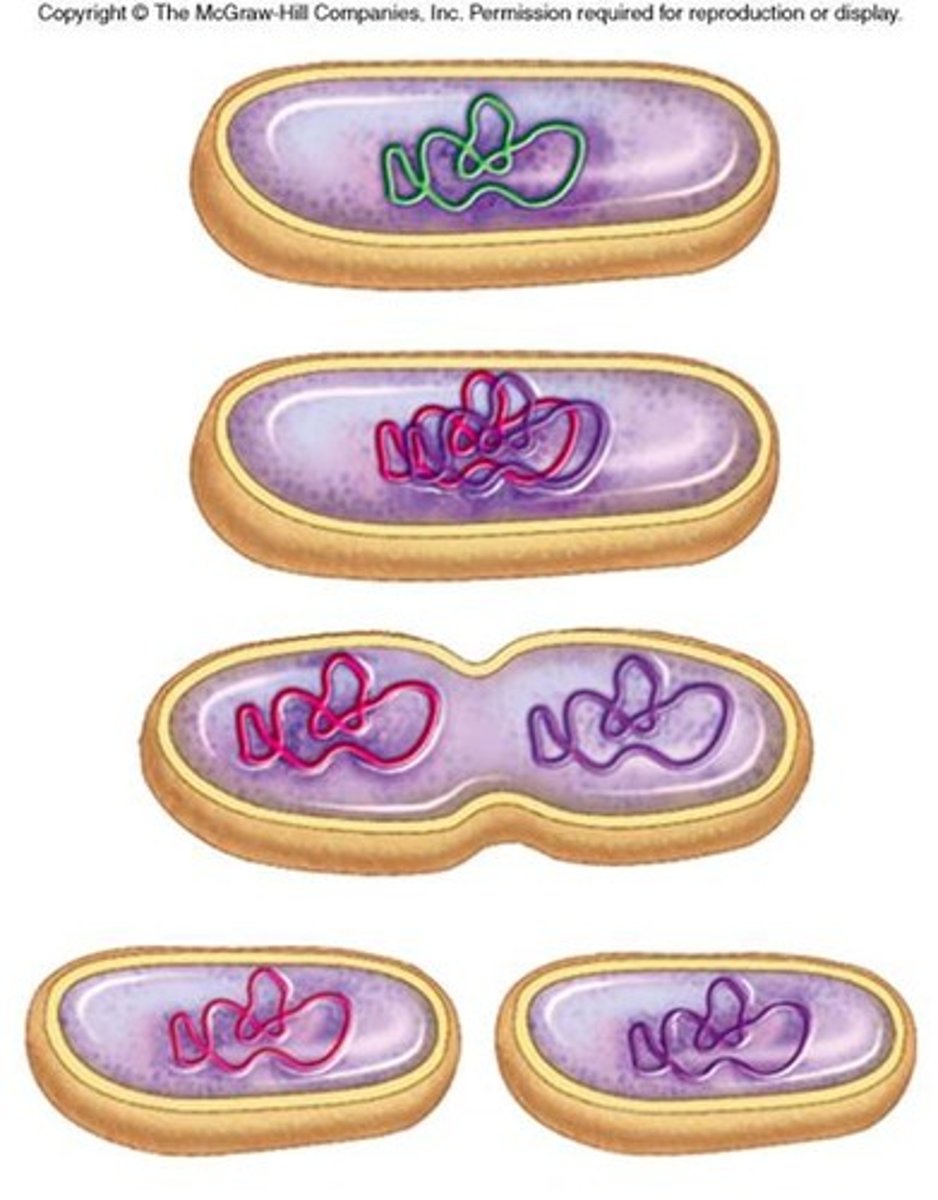
Binary Fission
the division of cells into new cells, called daughter cells
Bacterial spore
the ability of certain types of bacteria to form a hard keratin coating that will protect it until the environment is more favorable
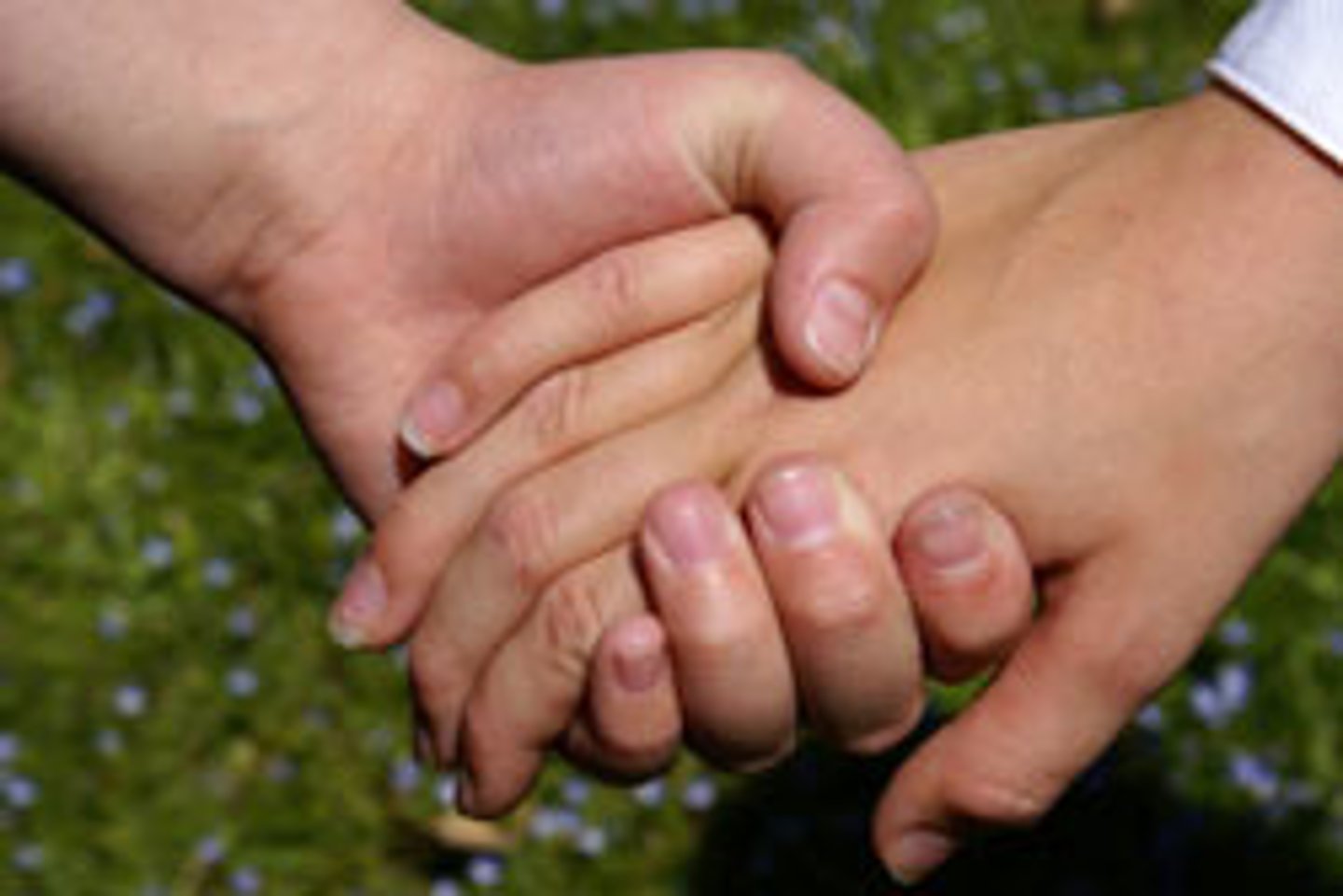
Direct Transmission
transmission of blood or body fluids through touching, kissing, coughing, sneezing, and talking

Indirect Transmission
transmission of blood or body fluids through contact with an intermediate contaminated object, such as a razor, extractor, nipper, or an environmental surface

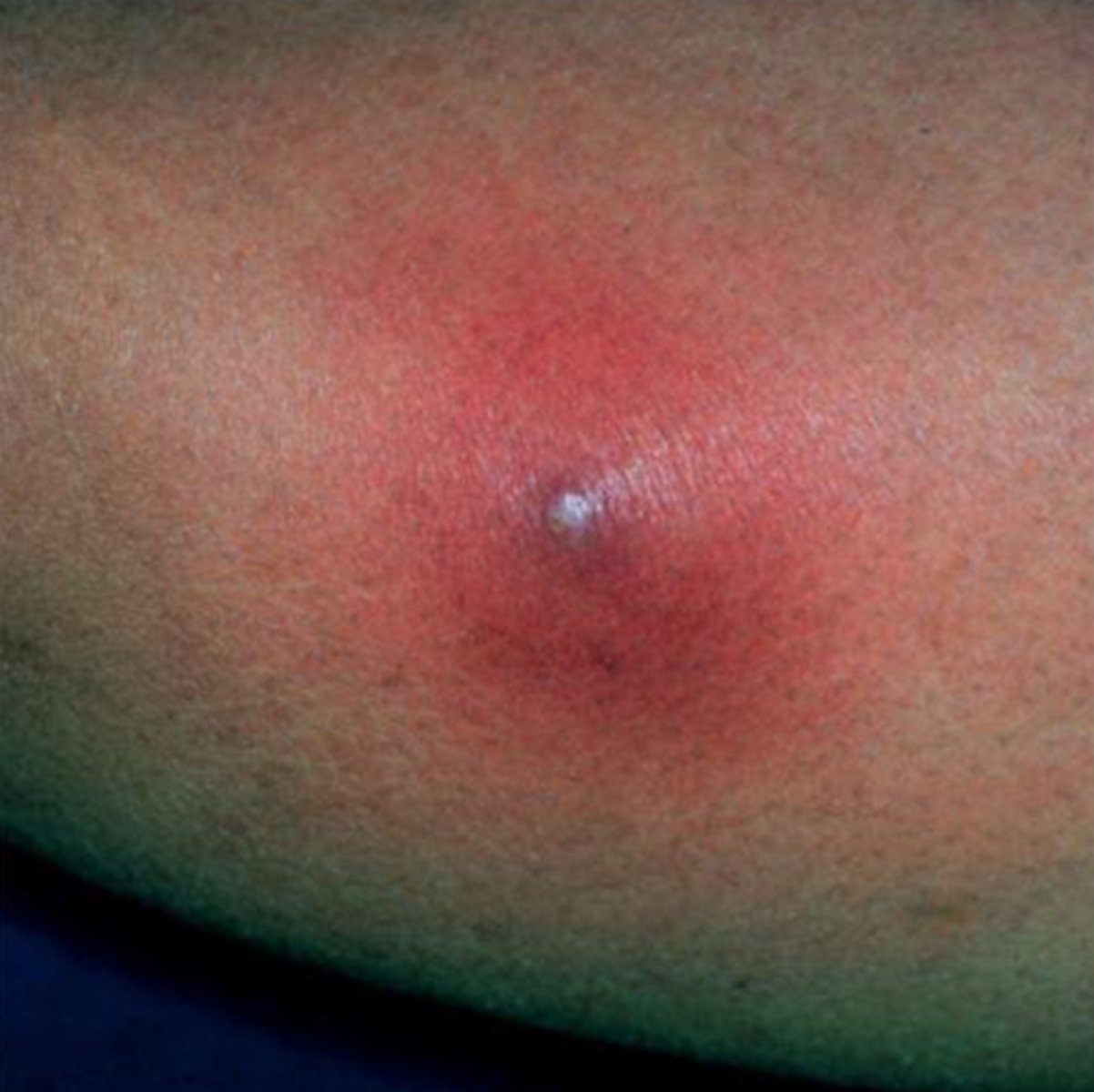
Inflammation
a condition in which the body reacts to injury, irritation, or infection
may be characterized by redness, heat, pain, and swelling
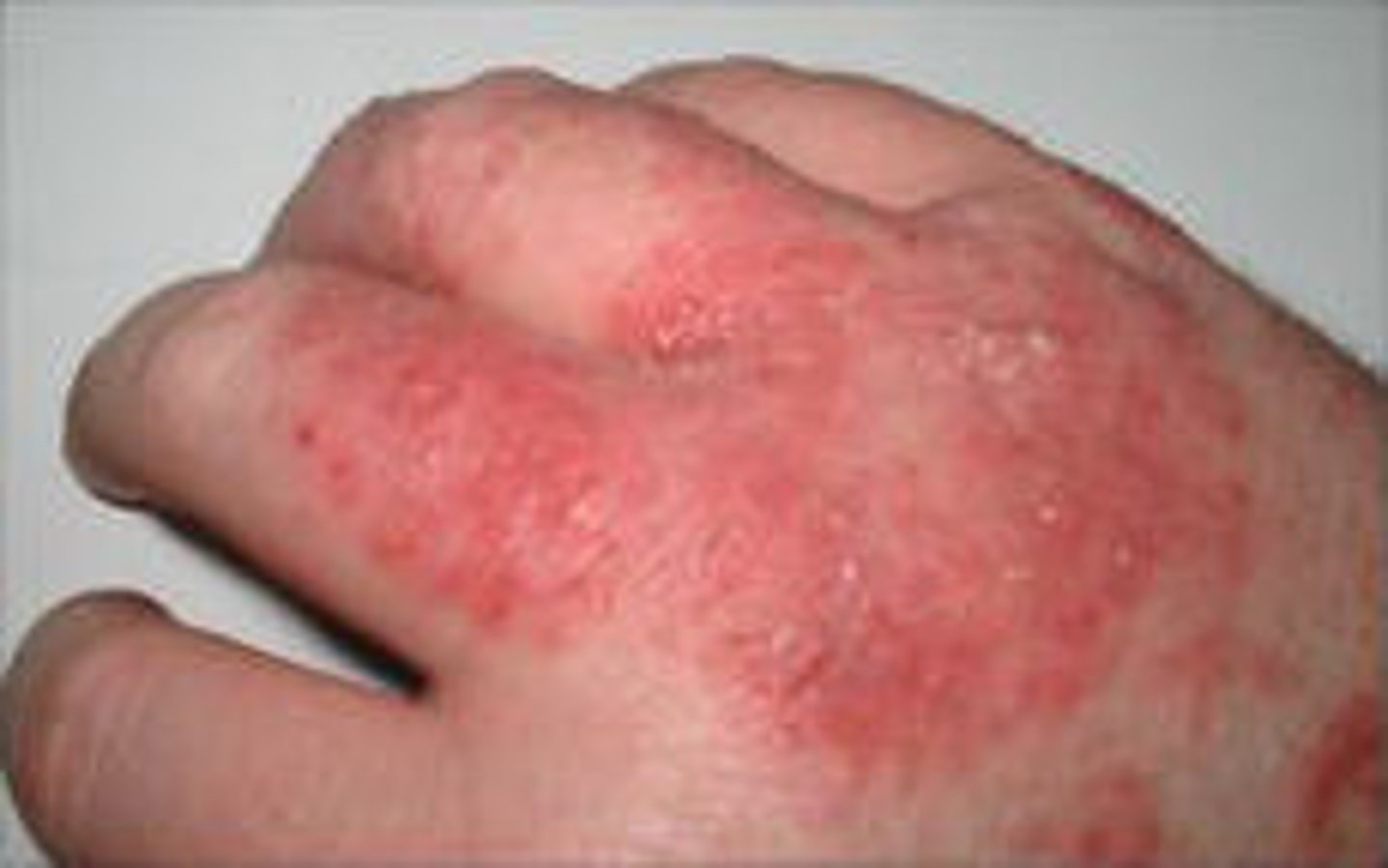
Pus
a fluid containing white blood cells, bacteria, and dead cells, and is the byproduct of the infectious process
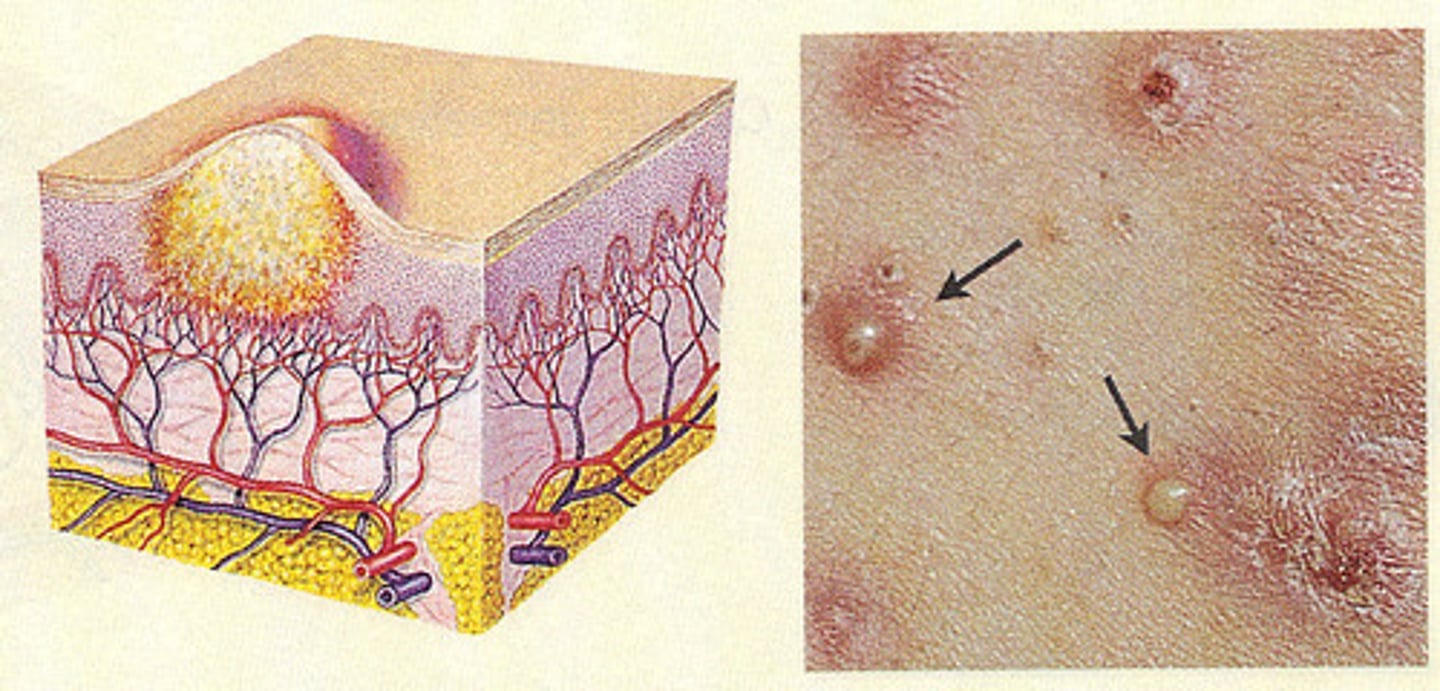
MRSA
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
An infectious staph bacteria that is highly resistant to conventional treatments
occurs frequently among persons with weakened immune systems or among people who had undergone medical procedures
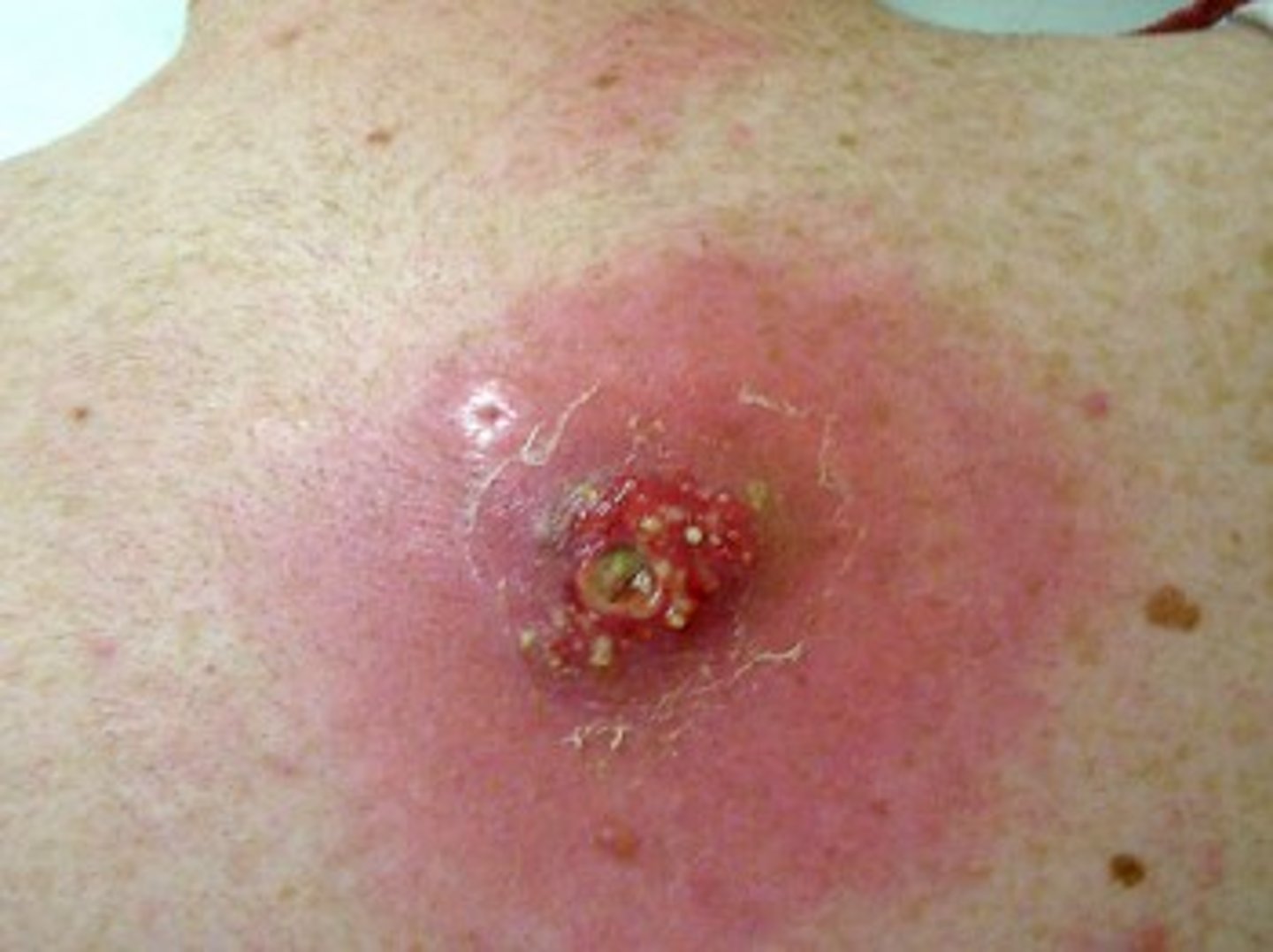
Systemic Infection
Affects the whole body, disease is carried through the blood or lymphatic systems.
Local Infection
Infections confined to a particular part of he body, a lesion containing pus (pimple or abscess)
Infectious
Caused by or capable of being transmitted by infection.
Contagious Disease
Disease spread from one person to another (common cold, pinkeye, viral infections)
Mycobacterium fortuitum
Microscopic germs found in tap water in very small numbers.