Case Studies #2- Urine/Genital
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
A urine culture grew up a mixture of gram-positive and gram-negative organisms with no one organism predominant.
The culture had been inoculated with a 0.001 uL loop and five colonies of gram-positive cocci and five colonies of gram-negative rods grew.
What are the colony counts?
5,000 CFU/ML gram positive cocci and 5,000 CFU/mL gram-negative rods
20,000 CFU/mL, mixed organisms; not identified
500 CFU/mL gram-positive cocci and 500 CFU/ML gram-negative rods
>=100,000 CFU/mL mixed organisms
5,000 CFU/ML gram positive cocci and 5,000 CFU/mL gram-negative rods
A urine culture grew up a pure culture of a beta hemolytic, lactose fermenter that precipitated bile.
The plates wre so heavy with growth that individual colonies were almost impossible to see.
Testing results:
oxidase: negative
indole: positive
What would the colony count be and the most probable identification for the organism?
Colony count >=100,000 CFU/mL of Proteus vulgaris
>=100,000 CFU/mL of E. coli
>=100,000 CFU/mL of Serratia Marscensens
>=100,000 CFU/mL of Proteus mirabilis
>=100,000 CFU/mL of E. coli
Results of a catheterized urine culture incubated at 35C for 18 hours from a 16 year-old female:
Sheep blood agar (BAP):
Isolate # 1: >= 100,000 CFU/mL beta-hemolytic, yellowish colonies.
gram stain = GPC
Catalase = positive
Isolate # 2: 9,000 CFU/mL non-hemolytic, gray colonies
gram stain = GPC
Catalase = negative
Isolate # 3: 3,000 CFU/mL non-hemolytic, mucoid gray colonies
gram stain = GNB
What is the next step?
Perform identification and susceptibility on isolates #1, #2, and #3
Perform identification and susceptibility on isolates #1 and #2
Perform identification and susceptibility on isolate # 1
No further work up of culture is necessary
Perform identification and susceptibility on isolate # 1
Either two or three organism types with predominate growth of one organism type and <10,000 CFU/mL of the other organism type(s)
ID and Susceptibility for the predominating organism; description of other organisms
A swab for Neisseria gonorrhoeae is collected on Wednesday afternoon at the physician's office. The swab missed the final transport to the lab for the day, so the nurse placed the swab in the refrigerator, so it could be picked up the next day. The swab arrives at the lab on Thursday afternoon. What should the lab do with this specimen?
Reject the specimen
Set up the specimen on Modified thayer-Martin media and incubate at 35C in ambient air
Set up the specimen on chocolate agar and incubate at 35C in 5% CO2
Perform a gram stain and set up the specimen on sheep blood agar.
Reject the specimen
Swabs for gonococci must be transported at room temperature within 24 hours. Refrigeration kills Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
A doctor expects a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis and orders a vaginal gram stain on the patient. If this diagnosis is correct what is expected in the gram stain?
A. Many gram-positive rods resembling Lactobacillus
B. Many WBC's
C. Rare to few gram-positive rods resembling Lactobacillus
D. Predominate amounts of curved, gram variable rods and tiny gram variable rods and gram negative coccobacilli
E. Large amounts of epithelial cells covered with gram negative and gram variable rods or coccobacilli
C, D, and E
C, D, and E
In bacterial vaginosis, Lactobacilli are decreased and there is an increase in clue cells which are epithelial cells coverd with gram negative coccobacilli and gram variable rods.
You are working on a vaginal culture from a 27 year old female. The culture grows moderate growth of Lactobacillus, Strep. viridans, Coag Negative Staph, and Heavy growth of beta-hemolytic Streptococcus.
The Beta Strep types as Group B.
How should this culture be reported?
Heavy Growth Normal Vaginal Flora
Heavy Growth Group B Streptococcus and Moderate Growth Normal Vaginal Flora
Negative
Heavy Growth Lactobacillus, Strep species, Coag Negative Staph
Heavy Growth Group B Streptococcus and Moderate Growth Normal Vaginal Flora
In childbearing age women Group B Strep is considered a pathogen as it can infect the baby.
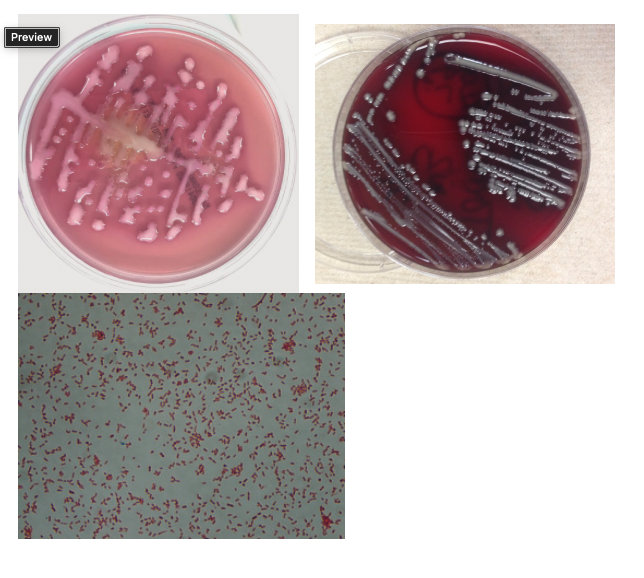
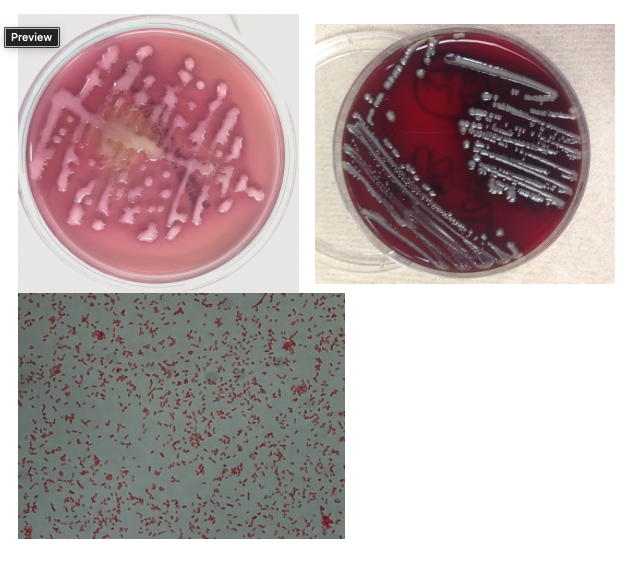
A 38 year old man with history of bladder disease presented to the ED with fevers, chills, and weakness. Clinical evaluation revealed hypotension and leukocytosis concerning for sepsis. His urinalysis was positive for 3+ blood, 1+ leukocyte esterase and positive nitrites. Urine and blood cultures grew bacteria with the below gram stain and morphology:
What is the colony count on the MAC plate image (urine was plated with a 0.001uL loop)?
10,000 cfu/mL
1,000,000 cfu/mL
>100,000 CFU/mL
4+ growth
>100,000 CFU/mL
Based on the growth and gram stain what is your next step in working up the urine culture?
Perform a spot indole and if positive call it E. coli
Set up an identification panel and susceptibility
This is an isolate that needs a full identification panel and susceptibility.
Perform a catalase
No work up, this is not a significant isolate
Set up an identification panel and susceptibility
This is an isolate that needs a full identification panel and susceptibility.
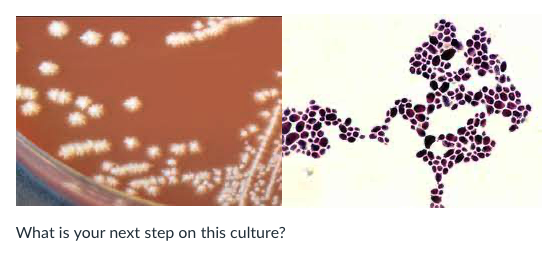
A vaginal culture grew the following organism:
What is your next step on this culture?
Report as normal flora
Set up a germ tube to identify the yeast
Report as possible Neisseria isolated
Report as gram positive cocci isolated
Set up a germ tube to identify the yeast
Germ tube test will help to identify this yeast as C. albicans. Also note that 'feet' on the chocolate agar colonies indicates this is C. albicans.
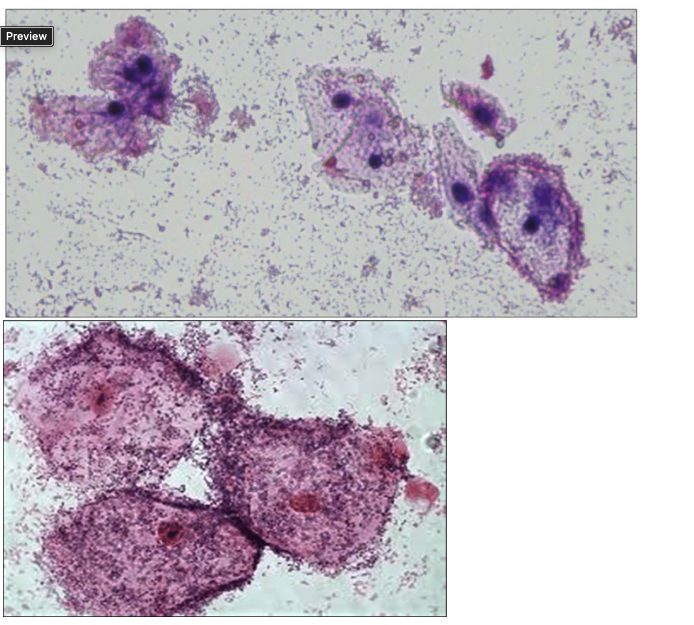
The following images are from a vaginal gram stain:
What are these cells called and what infectious condition are they associated with?
normal squamous epithelial cells; no condition
White Blood Cells; Cervicitis
Clue Cells; Bacterial Vaginosis
None of the above
Clue Cells; Bacterial Vaginosis
The urine culture from a pregnant 28-year-old female at 26 weeks gestation grows 110 colonies of beta-hemolytic (soft), gray colonies that prove to be catalase negative, PYR negative, and hippurate hydrolysis positive.
There is no growth on the MacConkey agar. A 0.001 mL calibrated loop was used to inoculate both agars. This organism should be reported as:
>1,000 CFU/mL of Streptococcus agalactiae
>100,00 CFU/mL of Streptococcus pyogenes
>100,000 CFU/mL of Streptococcus agalactiae
110,00 CFU/mL of Streptococcus pyogenes
110,000 CFU/mL of Streptococcus agalactiae
>100,000 CFU/mL of Streptococcus agalactiae