Exam 1 Kidneys Ultrasound
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Are the kidneys retro or intraperitoneal?
retroperitoneal
The kidneys lies in a protective sac better known as
Gerota's fascia
Briefly describe the main functions of the kidney
Get rid of metabolic waste
The average adult kidney measure is
9-12cm
What is the main functional unit of the kidneys?
nephrons
Where does filtration of the blood occur?
glomerulus
renal corpuscle
The structures between the medullary pyramids are known as the
columns of bertini
Where do the renal veins drain into?
inferior vena cava
What position is the renal artery in relation to the renal vein?
posterior to IVC
What is the area between the right kidney and right lobe of liver known as? What might we find here?
Morison's pouch
ascites
List some lab values relative to the urinary system.
BUN
Protein
creatine
GFR
Briefly describe prominent columns of bertin
Hypertrophied, invaginates towards renal sinus
Briefly describe a dromedary hump
Found on left kidney
Briefly describe a junctional parenchymal defect
a triangular or linear hyperechoic structure in the anterosuperior or posteroinferior surface of the kidney
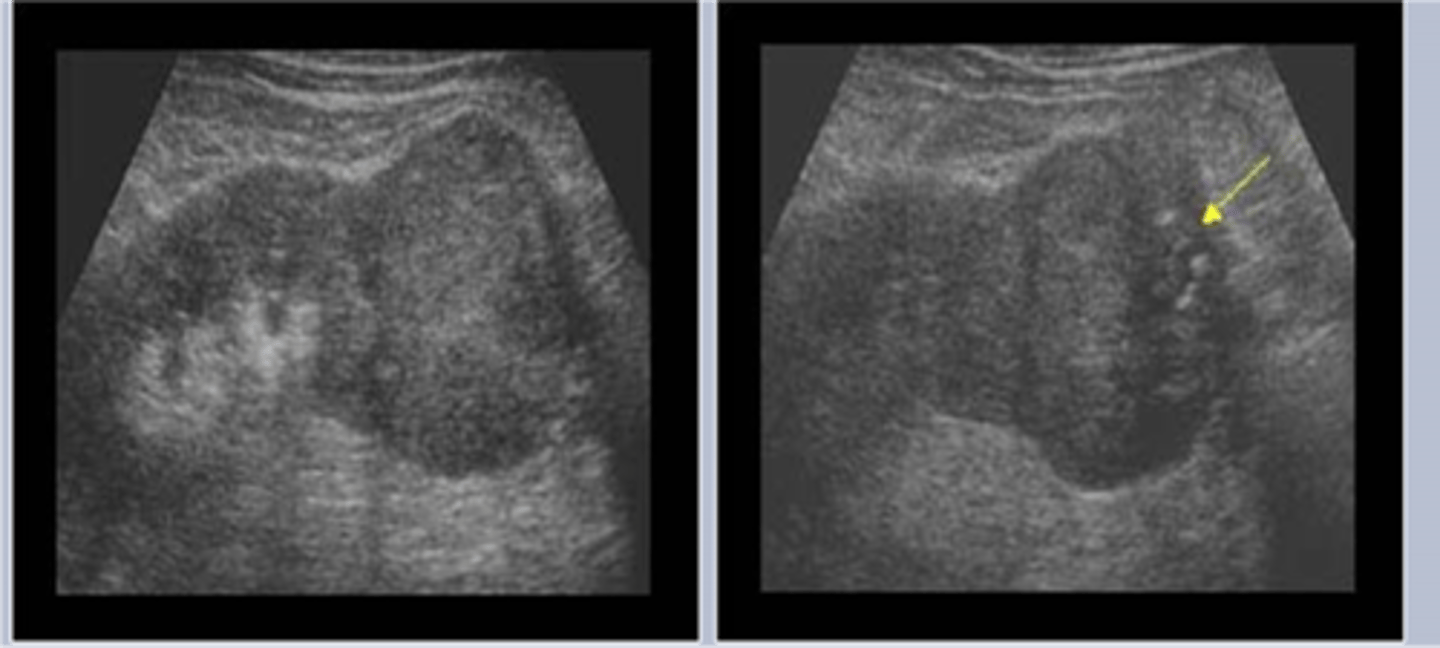
What is a stricture?
narrowed opening
Briefly describe fetal lobulations
an uncommon condition that causes the surface of the kidney to appear as several lobules instead of smooth, flat and continuous.
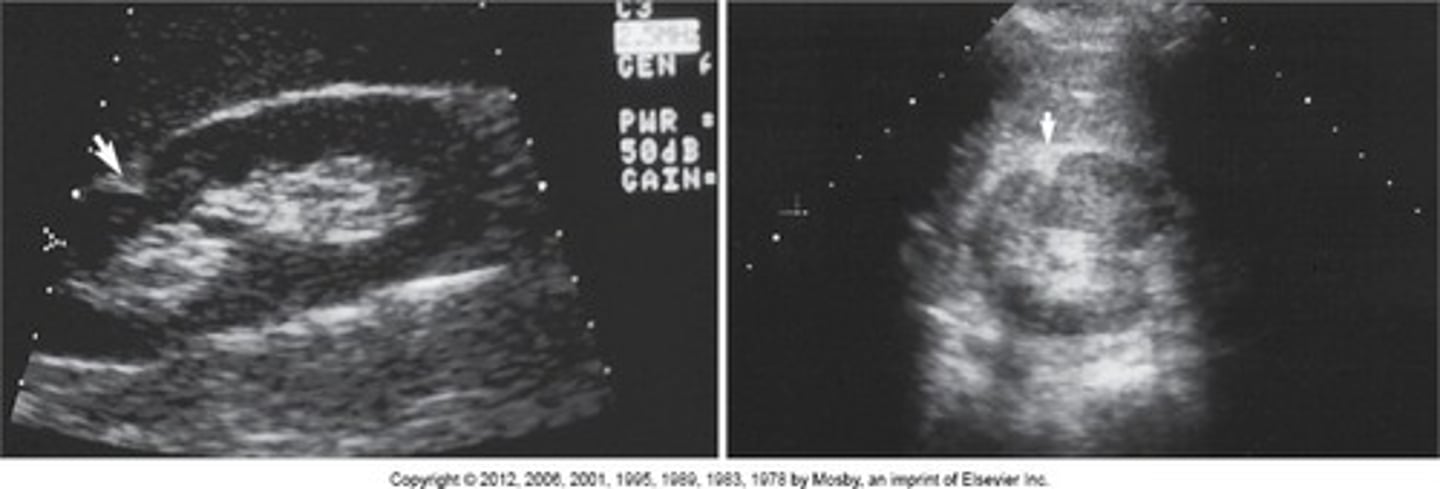
Sinus Lipomatosis
Thinning of the cortex WNL: >1cm
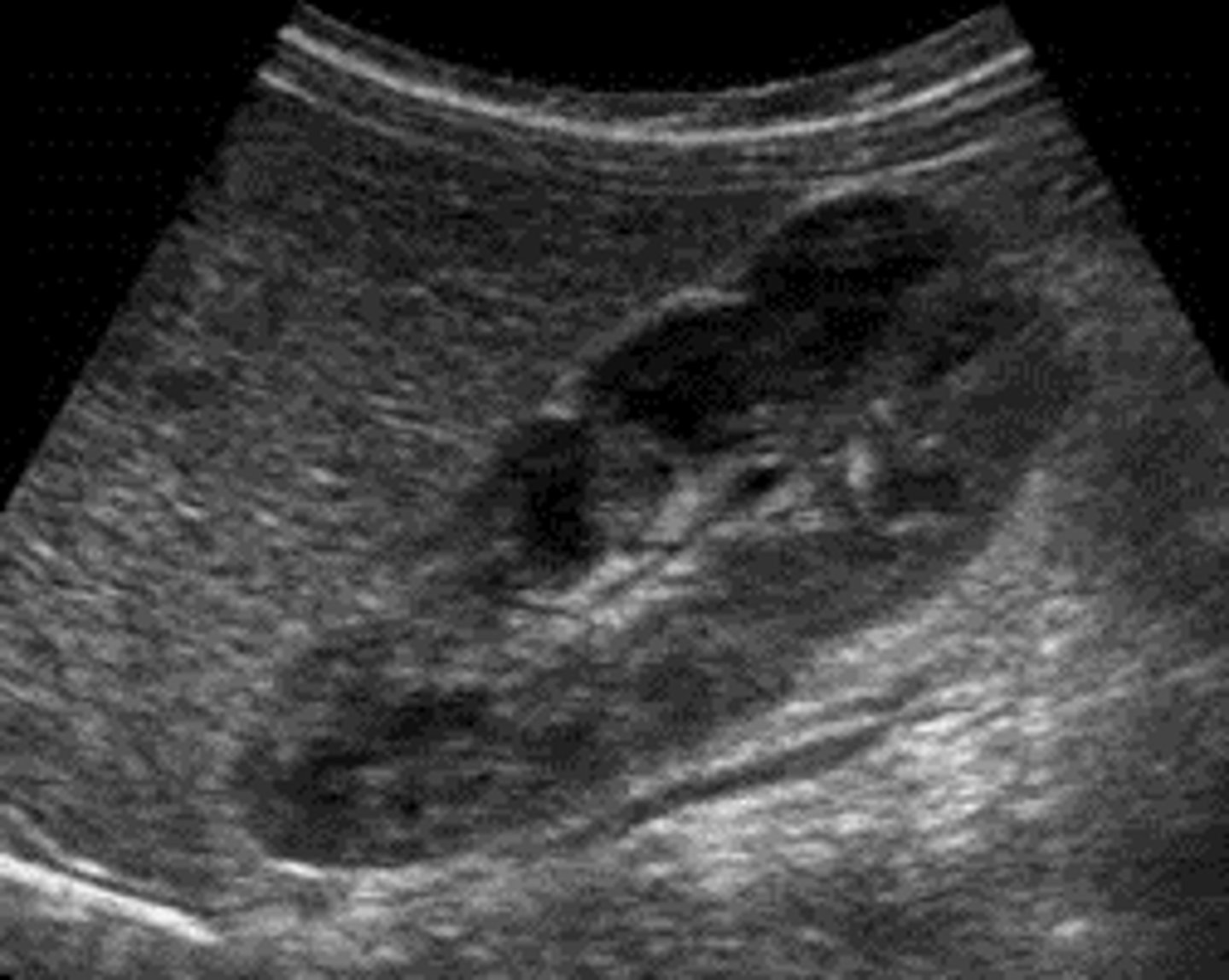
Extrarenal pelvis
Extends outwards of the renal sinus
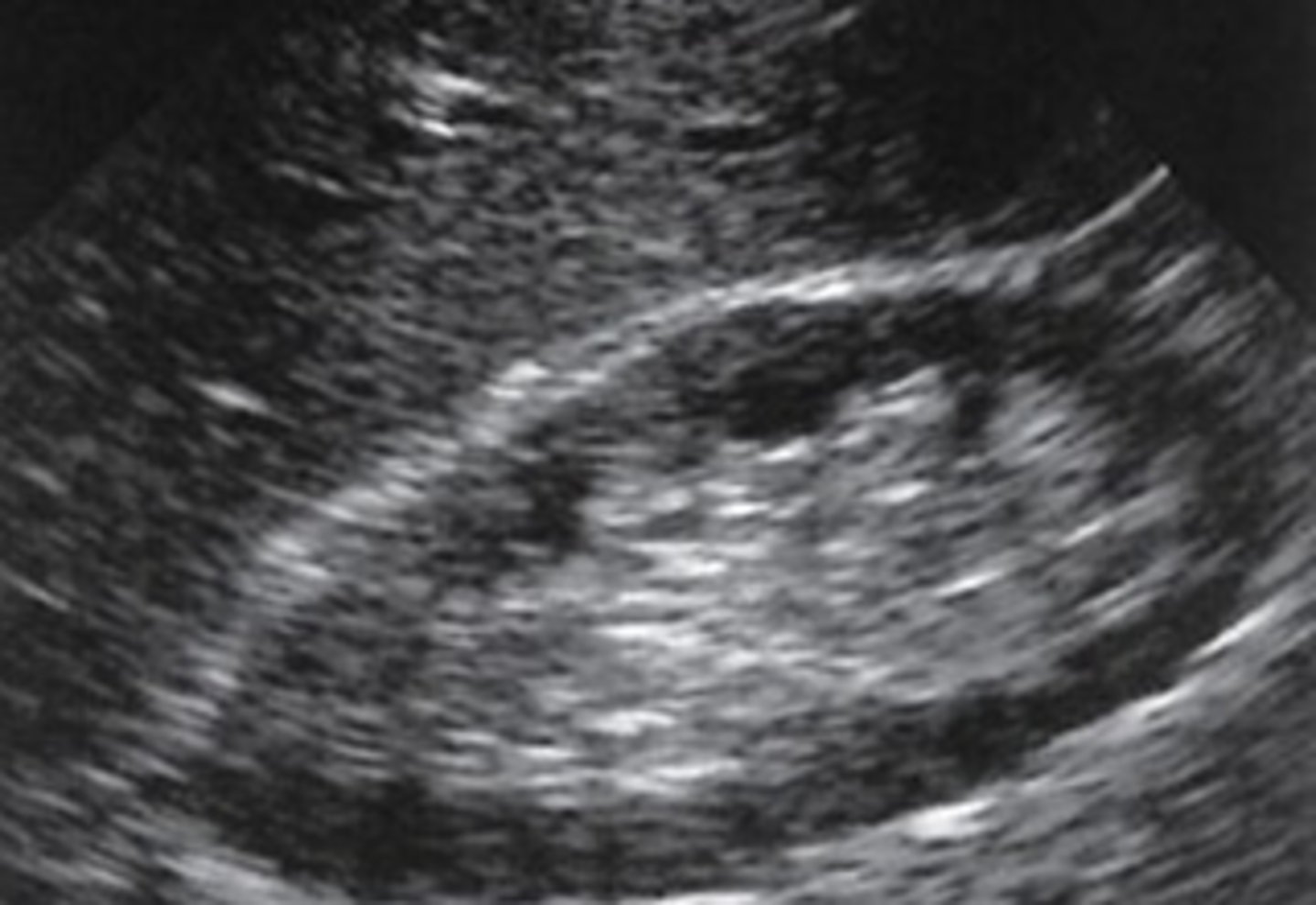
What is stricture?
narrowing
uterocele
herniation of the uterus (25-30cm)
1. The patient showed kidneys were fused at the lower pole. What is this better known as? 2. What pediatric renal tumor is associated with this condition?
1. Its horseshoe kidney
2. Nephroblastoma aka wilms
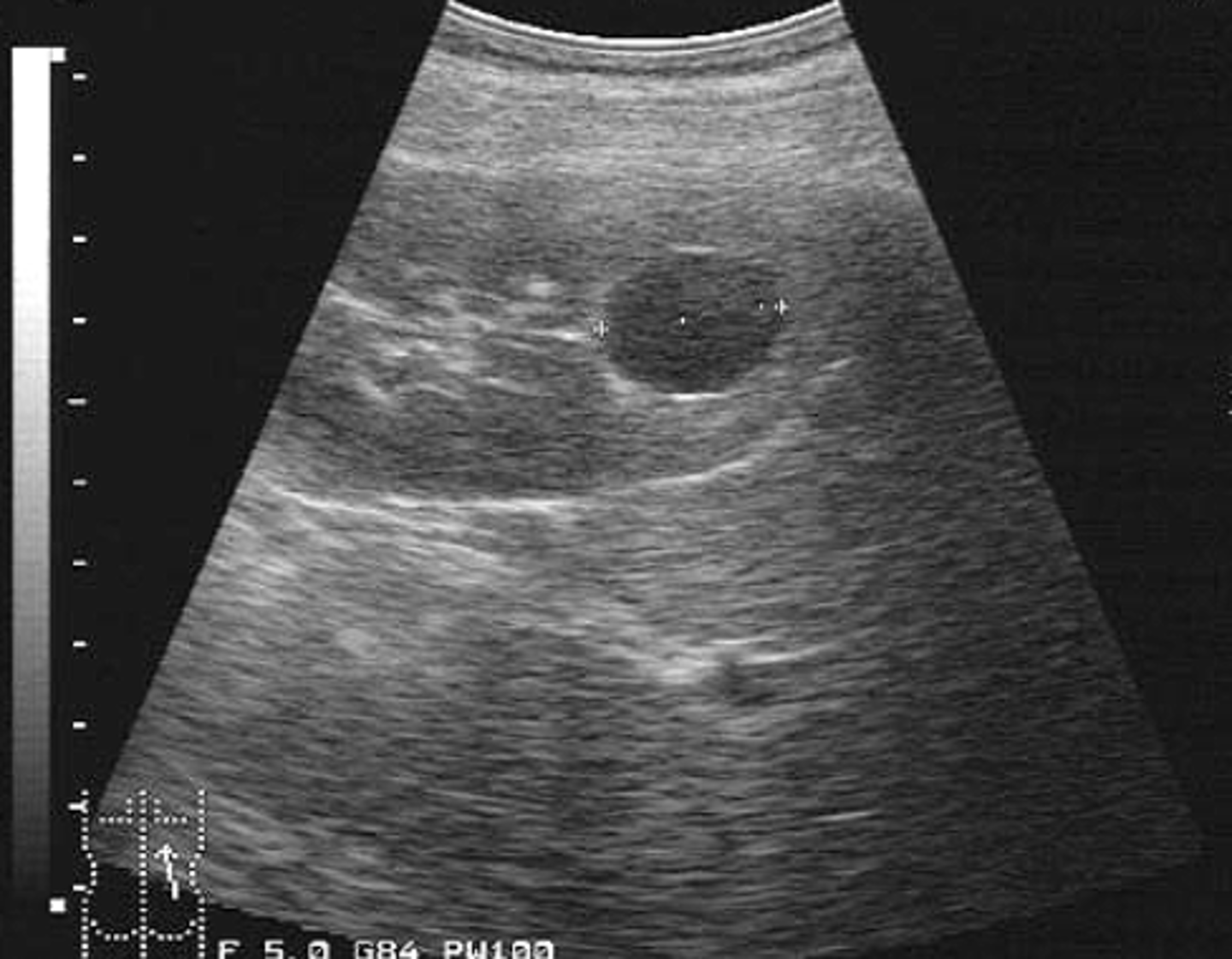
1. How would you describe the above structure in the kidney? 2. Should we assume all kidney masses are benign?
1. Its anechoic
2. No
The above kidney was shown to have autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. What does autosomal recessive mean and what type of patient is this form of cystic disease seen in?
a rare genetic disorder that affects 1 in 20,000 children. A fetus or baby with ARPKD has fluid-filled kidney cysts that may make the kidneys too big, or enlarged. ARPKD can cause a child to have poor kidney function, even in the womb.
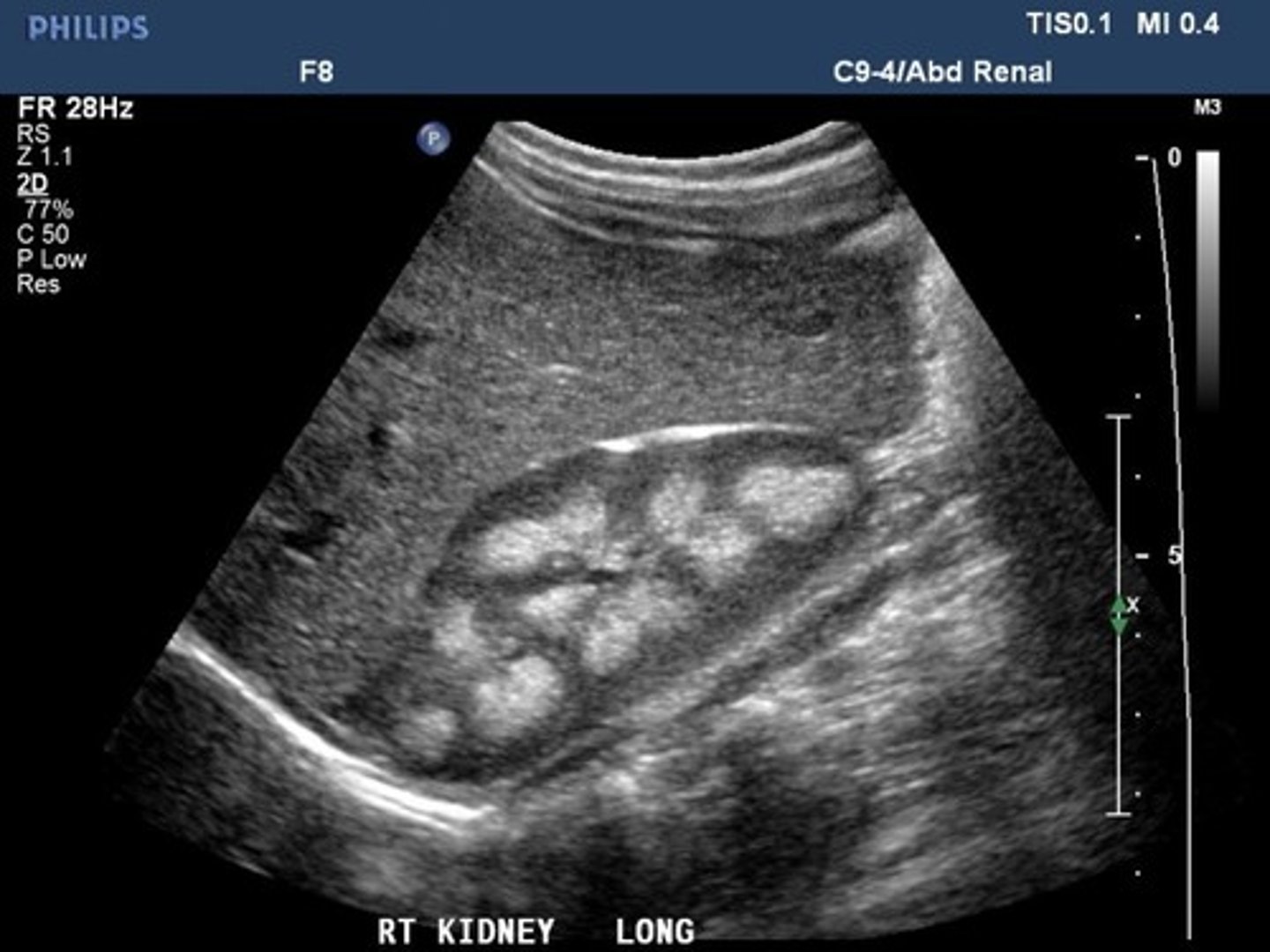
The above kidney shows cysts of varying size. The patient was a 40 year old male. 1. What type if cystic disease is this? 2. Is it bilateral?
1. ADPKD by one parent
2. Its bilateral
The above kidney shows a disease known as metacystic dysplastic kidney disease. what is a common cause of this? what type of patient does it effect? what of both lodmeys
In utero obstruction
fetus
MCKD not compatible with life
Briefly describe medullary sponge kidney
ducts of bellini- dilatation
The above image shows renal cell carcinoma. List some risk factors related to this tumor.
Long term dialysis
VHL
Cysts
Tumor
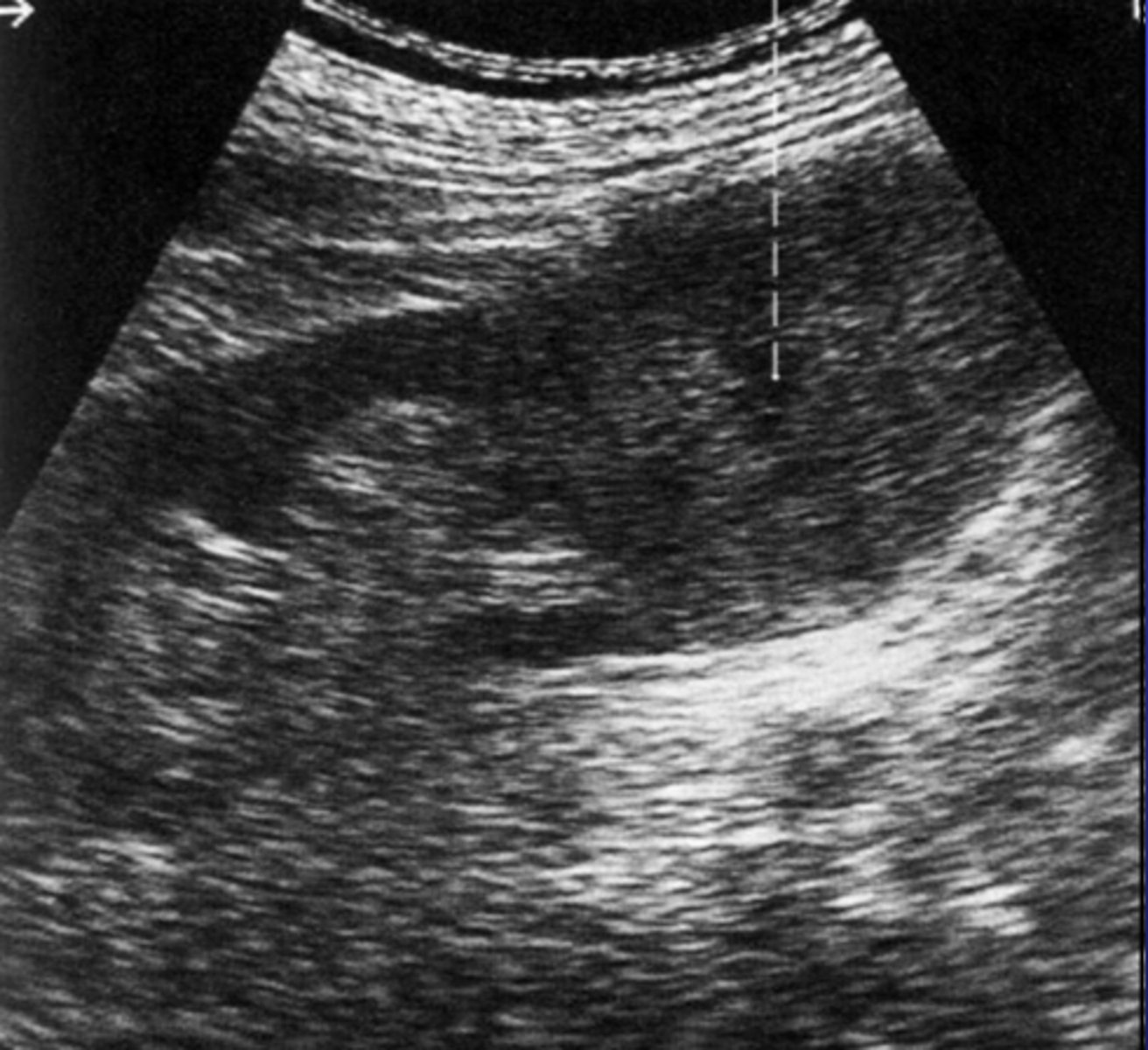
The above mass was biopsied and turned out to be a transitional cell carcinoma. 1. Where do these tumors commonly originate? 2. Briefly describe the difference between a flat and papillary TCC.
1. Originates in the bladder
2. Flat is more aggressive and TCC
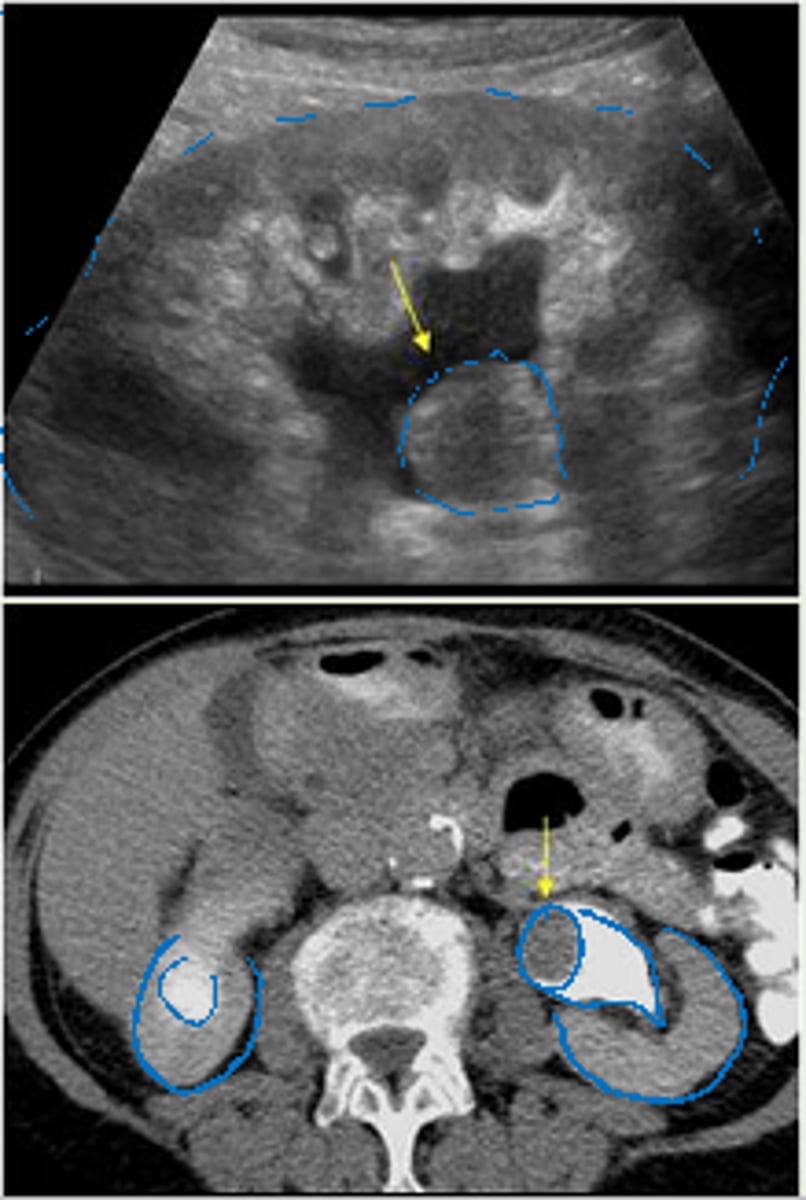
The above image is a nephroblastoma. 1. What type of patient is this seen in. 2. Is it deadly?
Aka Wilms tumor
1. Its a pediatric patient
2. Its deadly and can be treated (cancerous)
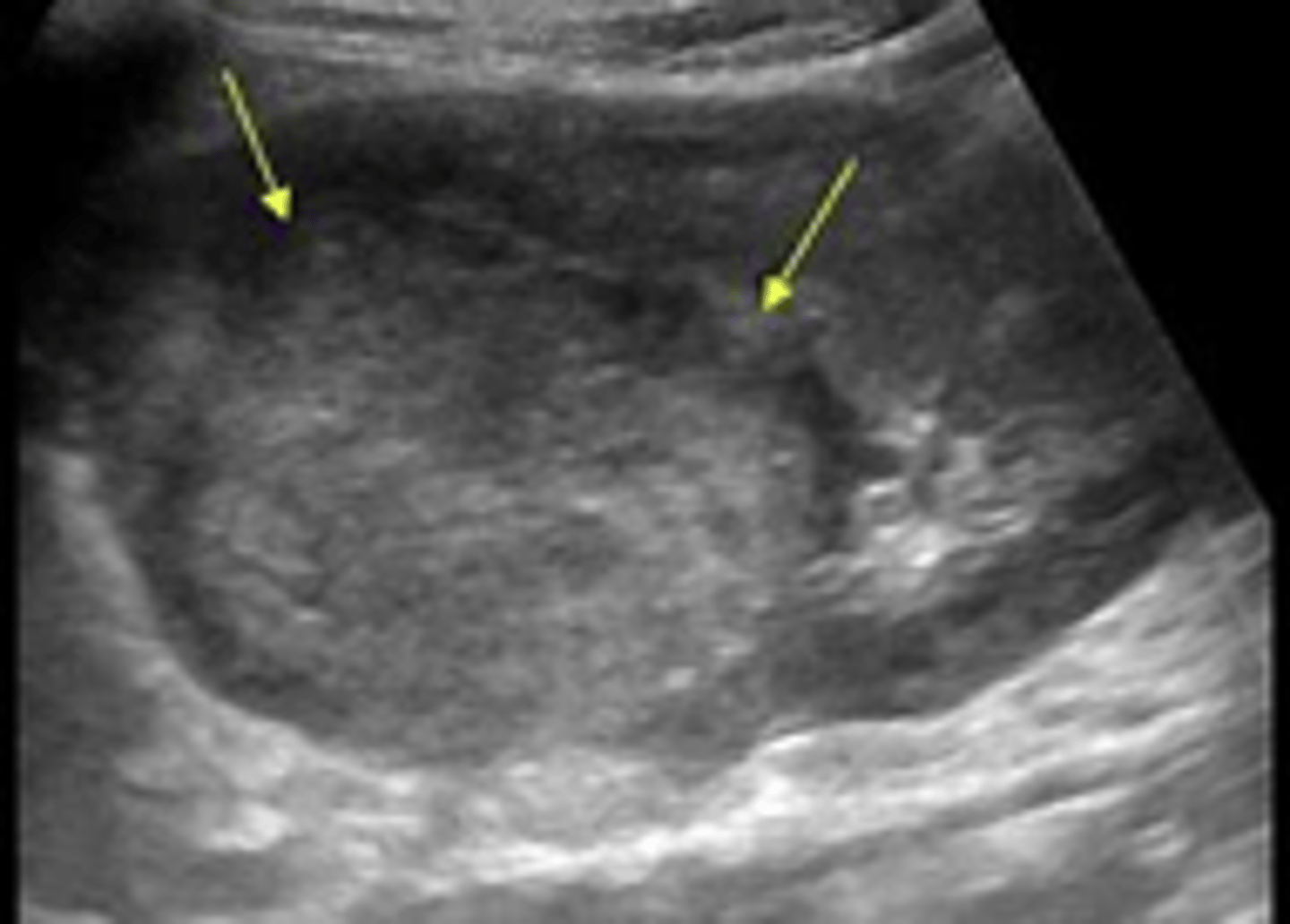
What is papillary necrosis and what can cause this condition?
1. Happens at the apex of the kidney, dead tissue
2. Diabetes, sickle cell anemia, poison
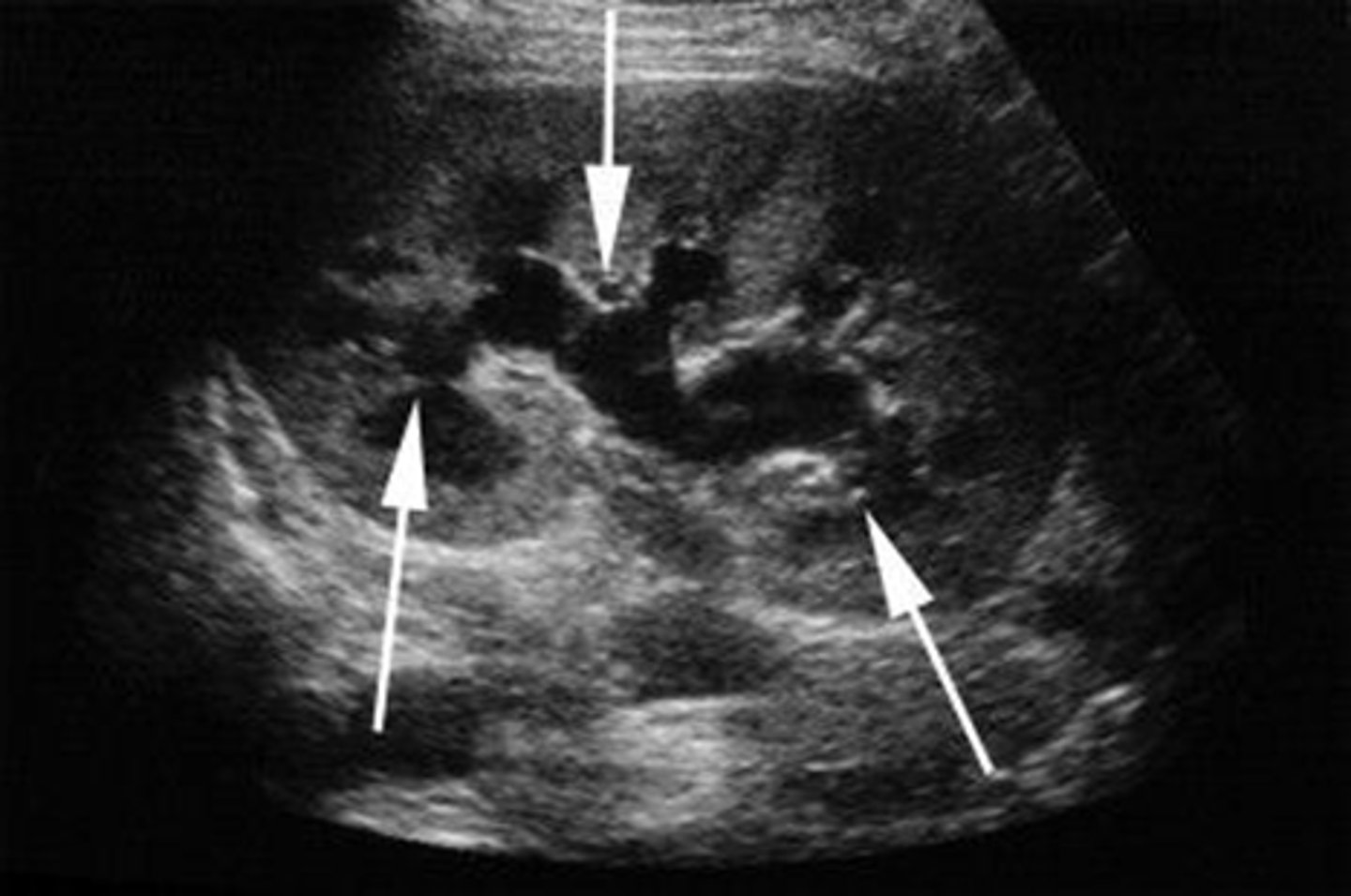
Briefly describe lupus nephritis
A disease that occurs when your body's immune system attacks your own tissues and organs
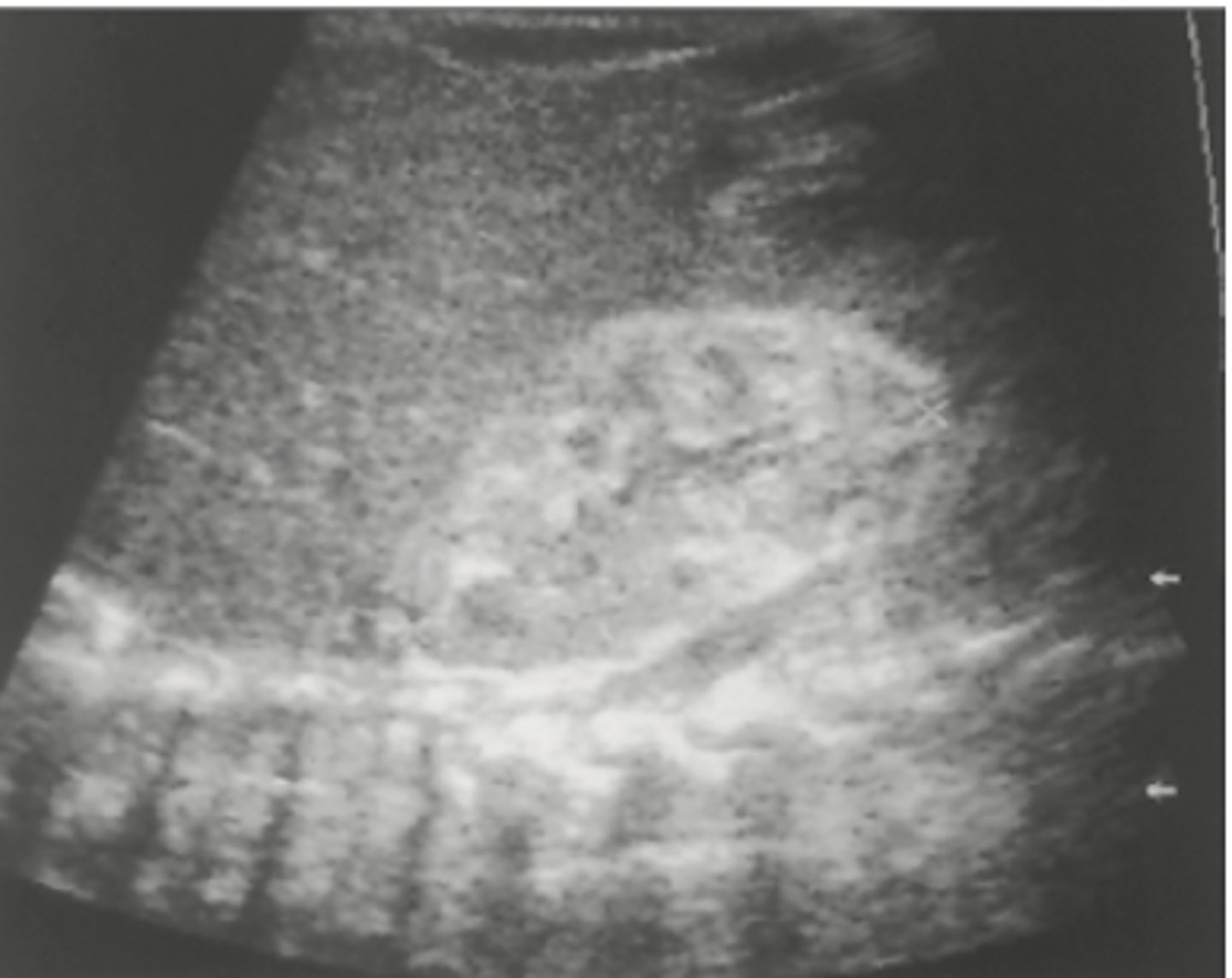
What is the most common form of renal lymphoma? Does it commonly affect one or two kidneys?
Hodgkin's lymphoma
Non Hodgkin's lymphoma
Will involve both kidneys
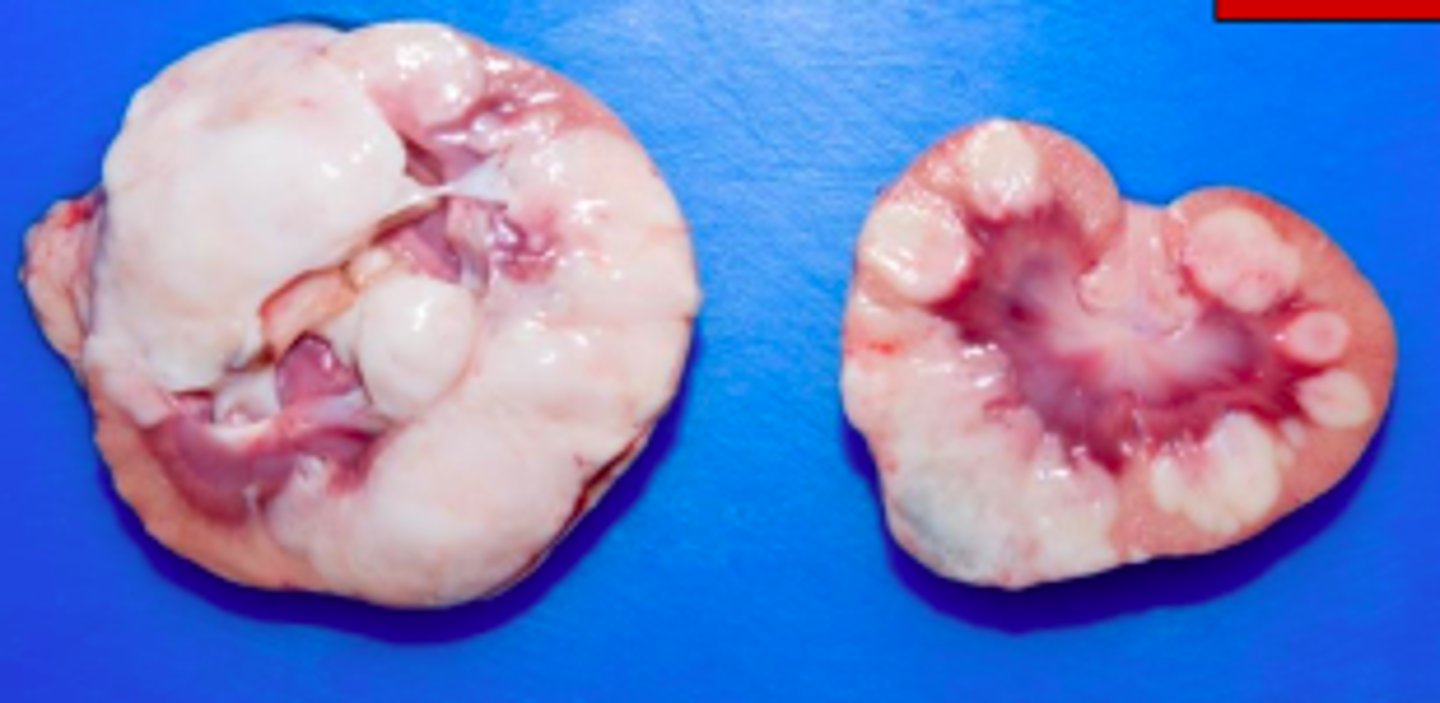
List some benign renal tumors. Which is the most common?
Angiomyolipoma
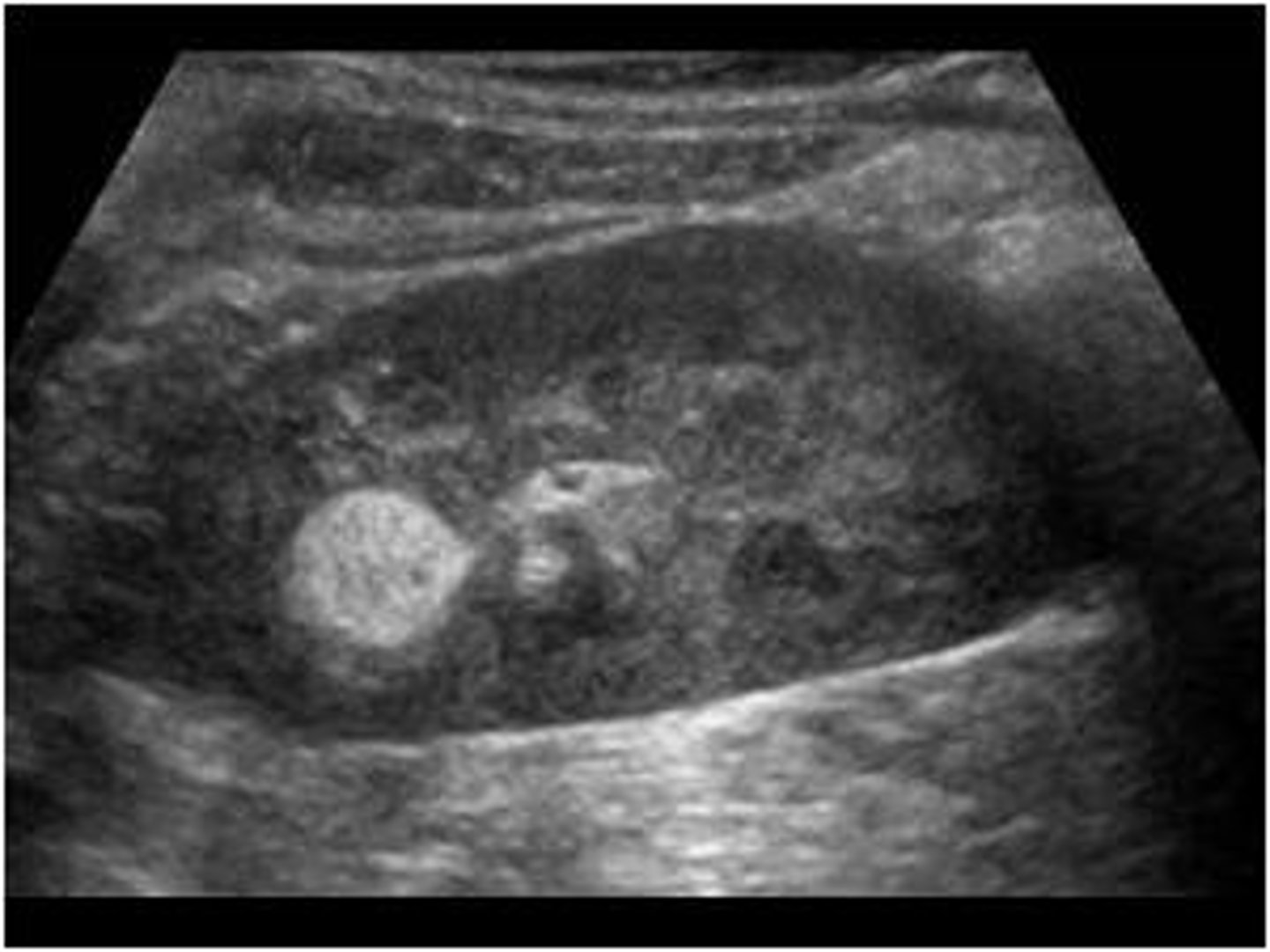
Briefly describe an oncocytoma and lipoma.
Oncocytoma- spokes on a wheel, central scar artifact
Lipoma- fatty tumor located just below the skin
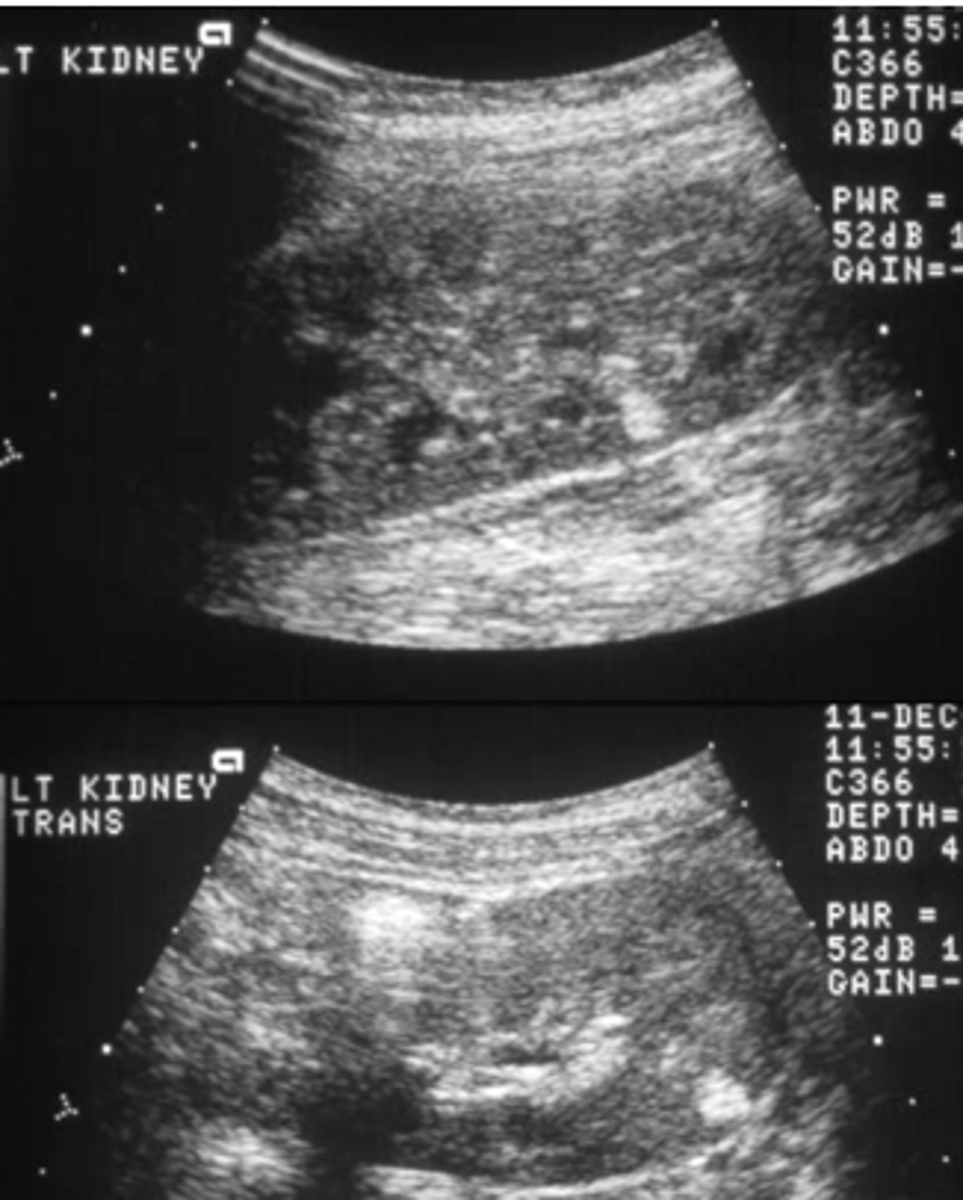
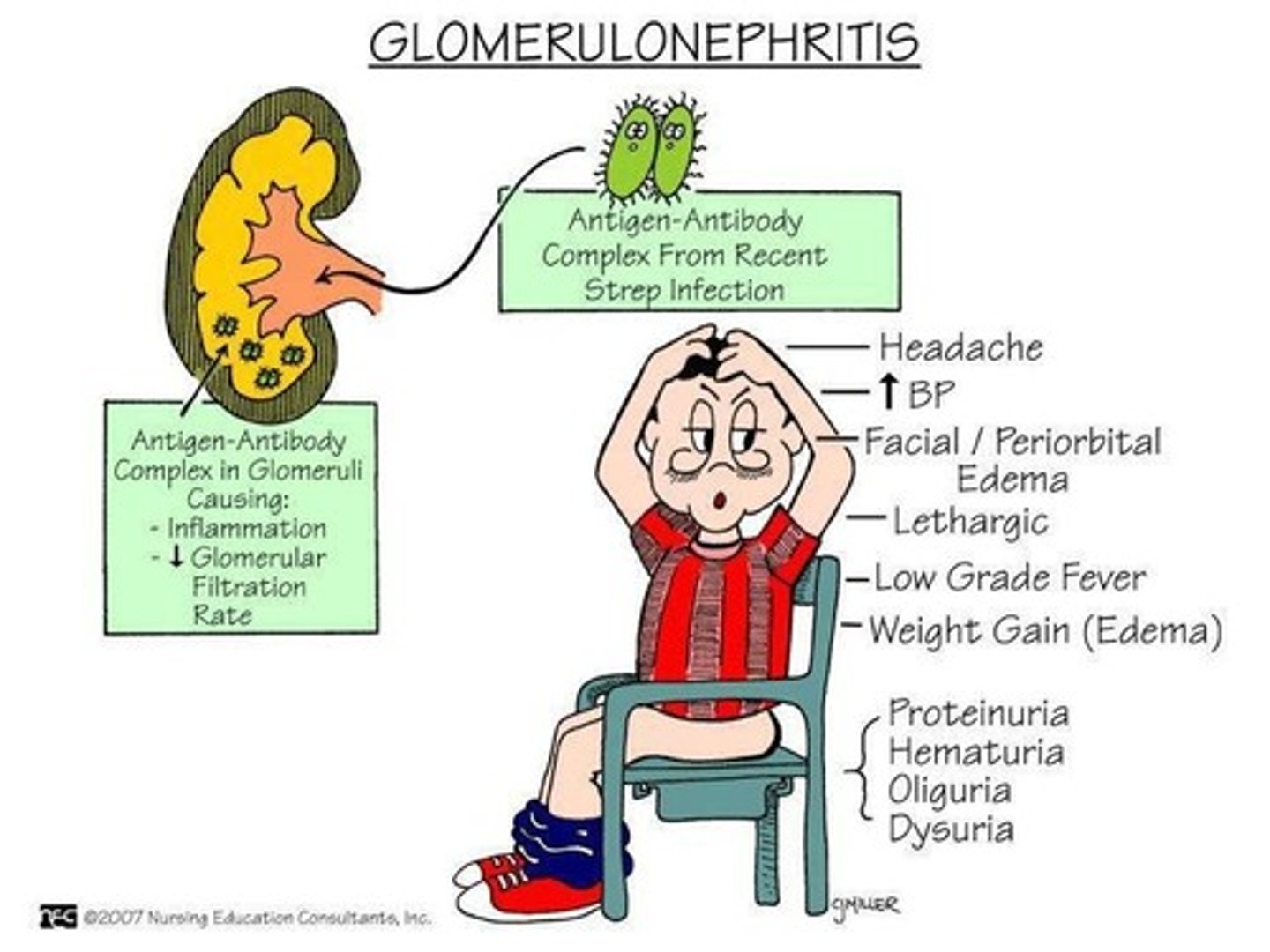
What is glomerulonephritis and what diseases is it commonly related with?
1. inflammation of the tiny filters in the kidneys (glomeruli)
2.Toxins or medicines.
Viral infections, such as HIV, hepatitis B and C viruses.
Lupus-related kidney inflammation.
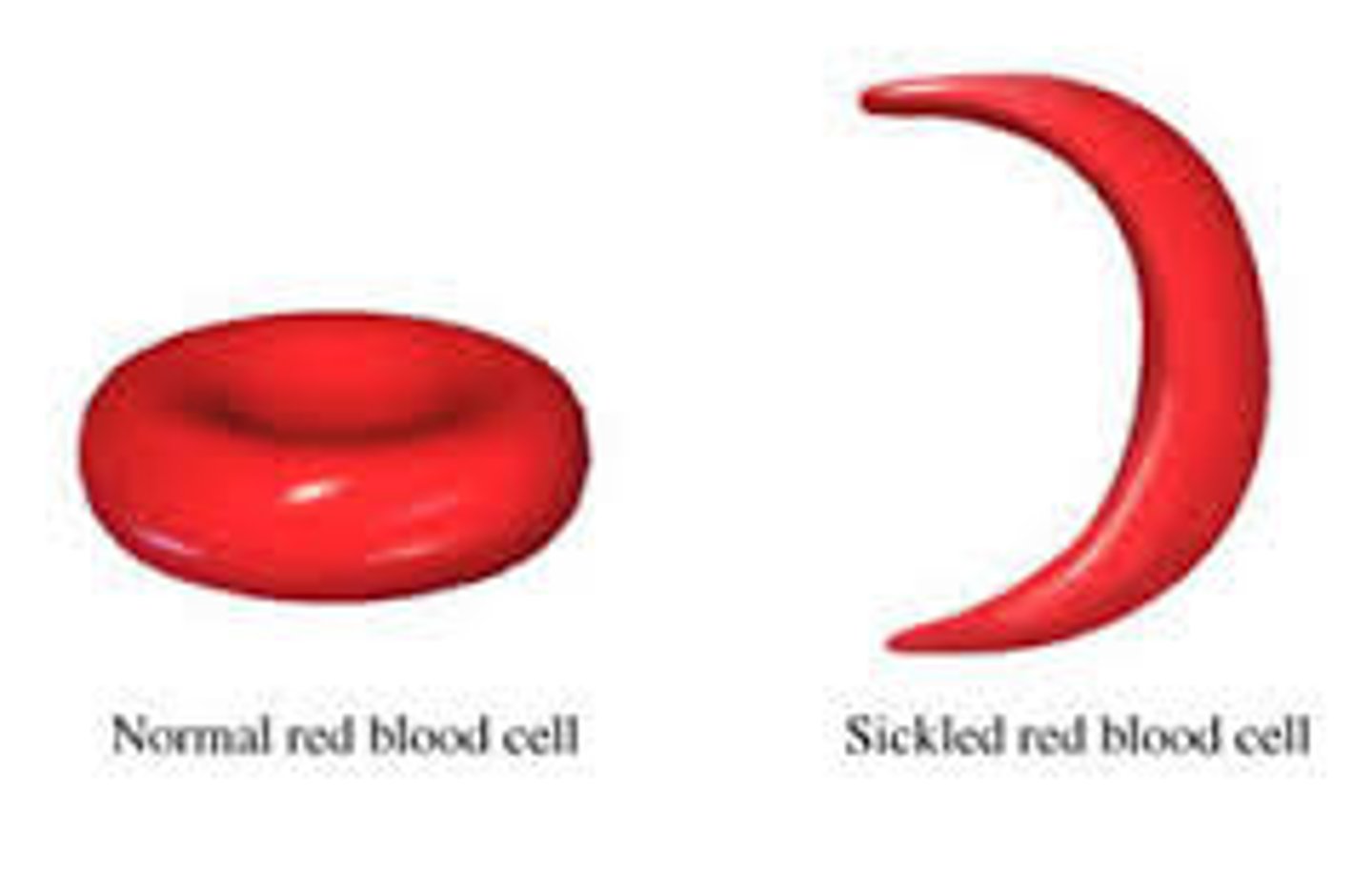
Describe sickle cell disease
- mutation in hemoglobin.
- look "sickled" & are easily damaged.
- may get stuck in narrow vessels & block oxygen from getting to tissues.
List some causes of renal failure.
Blood or fluid loss.
Blood pressure medications.
Heart attack.
Heart disease.
Infection.
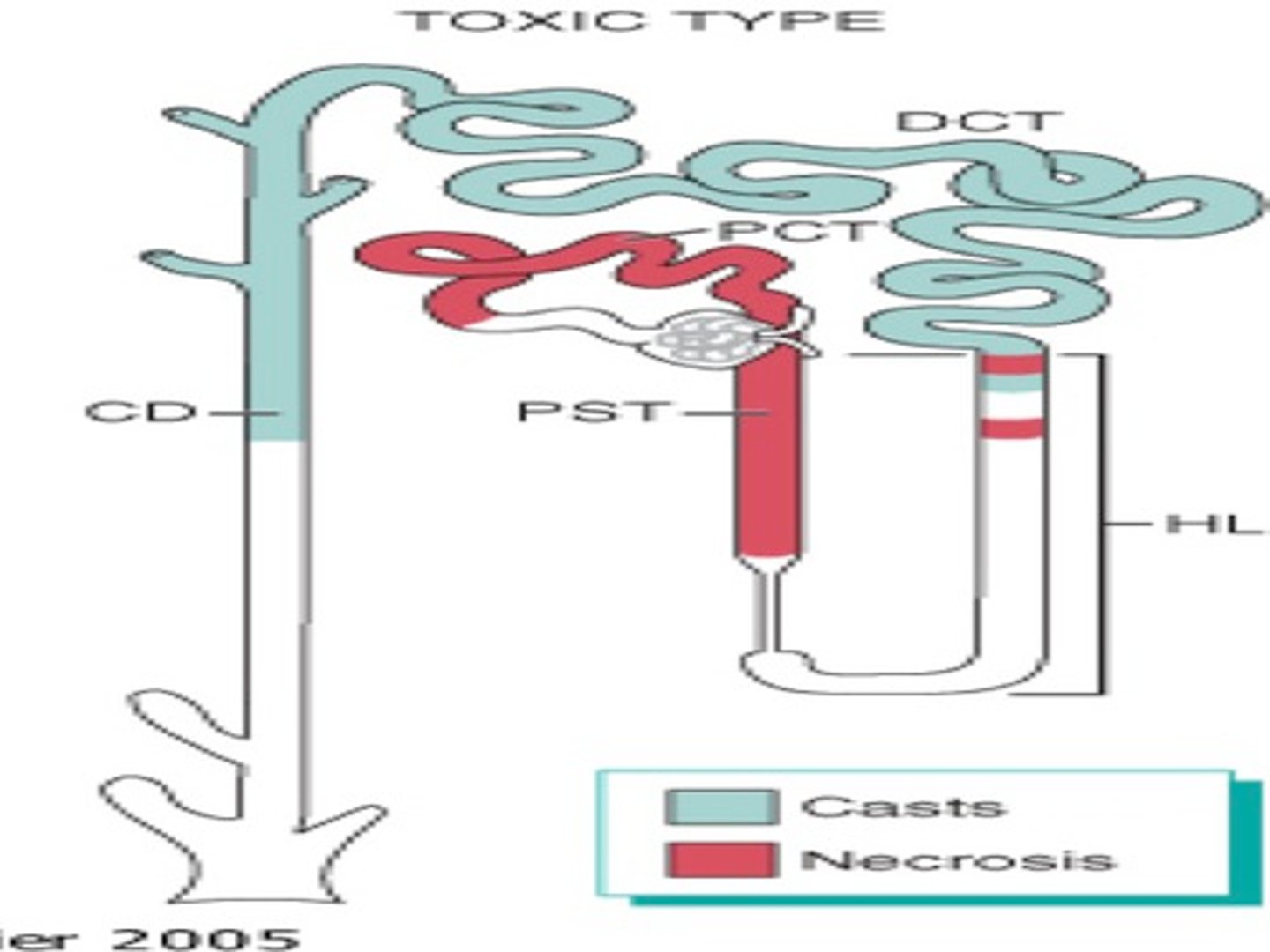
Briefly describe acute tubular necrosis.
a kidney disorder involving damage to the tubule cells of the kidneys, which can lead to acute kidney failure
What is pyonephrosis and what is it associated with?
1. urologic emergency (pus in kidney), a suppurative infection of the upper urinary system (need to be on IV, and antibiotics)
2. An infection
What is Emphysematous Pyelonephritis and what causes it?
1. A severe, necrotizing infection of the renal parenchyma
2. Air is infiltrated which causes bacteria growth
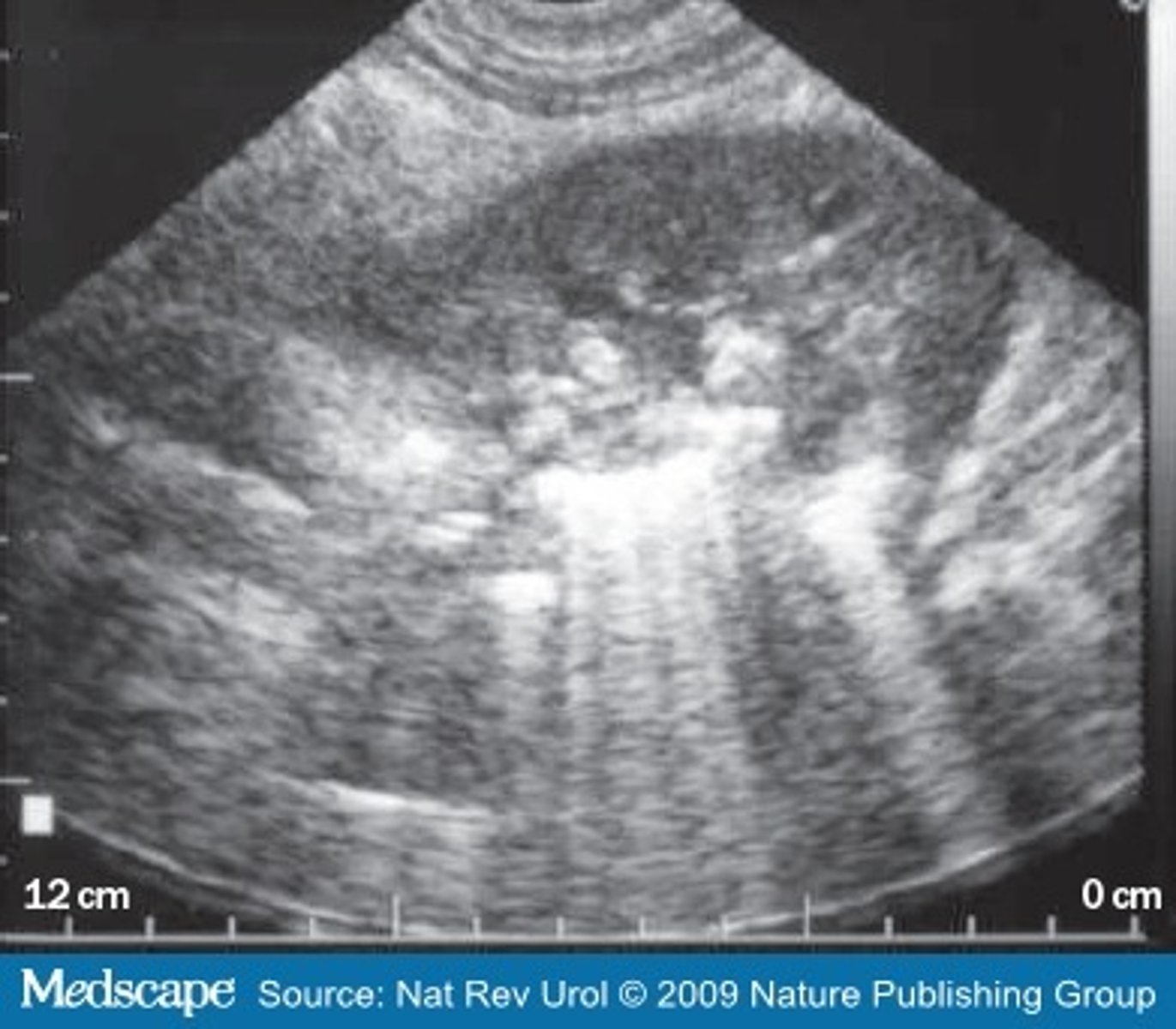
Briefly explain Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis
A rare, serious, chronic inflammatory disorder of the kidney characterized by a destructive mass that invades the renal parenchyma
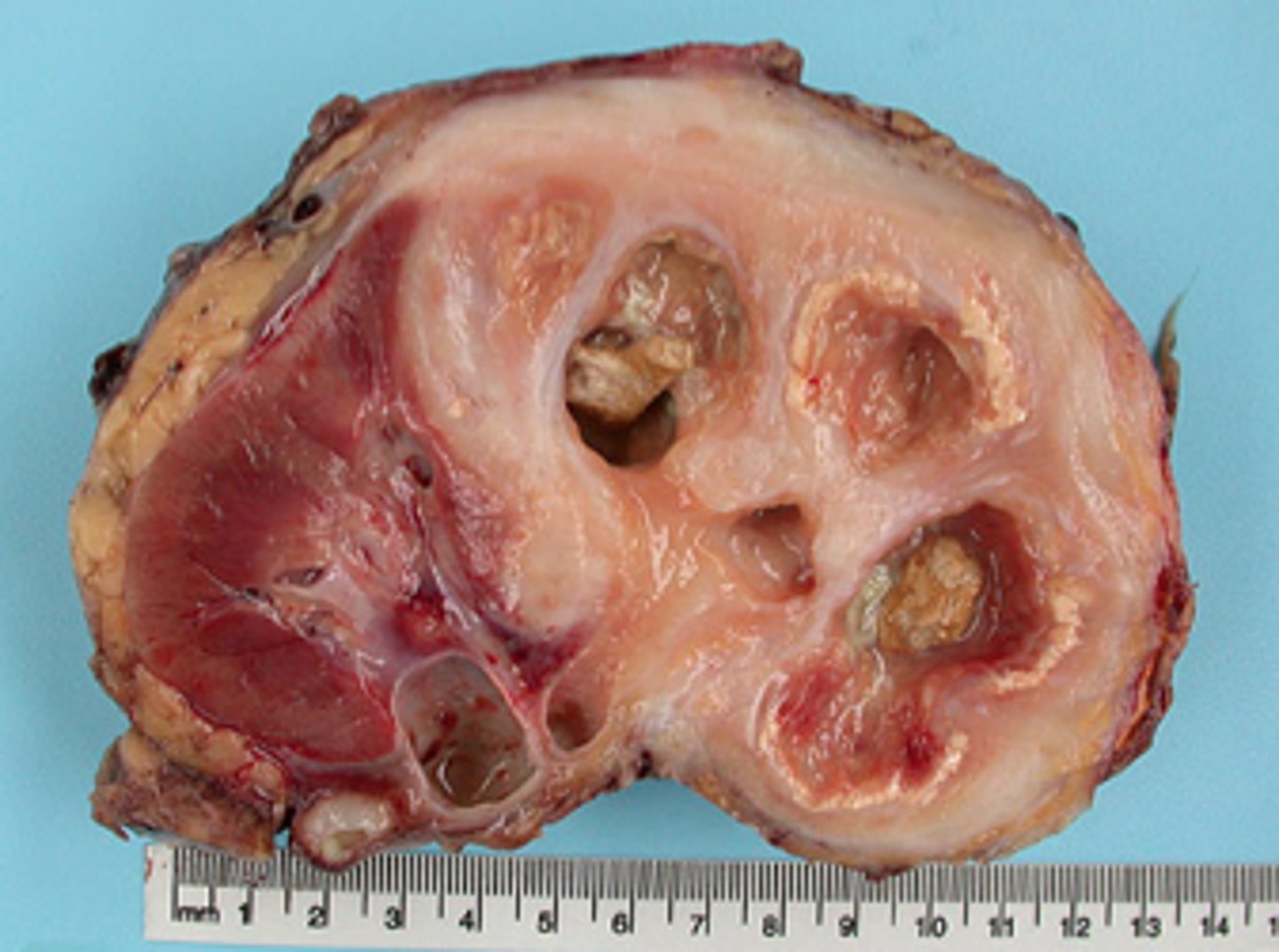
What is Nephrocalcinosis?
A condition of calcium deposits within the renal parenchyma
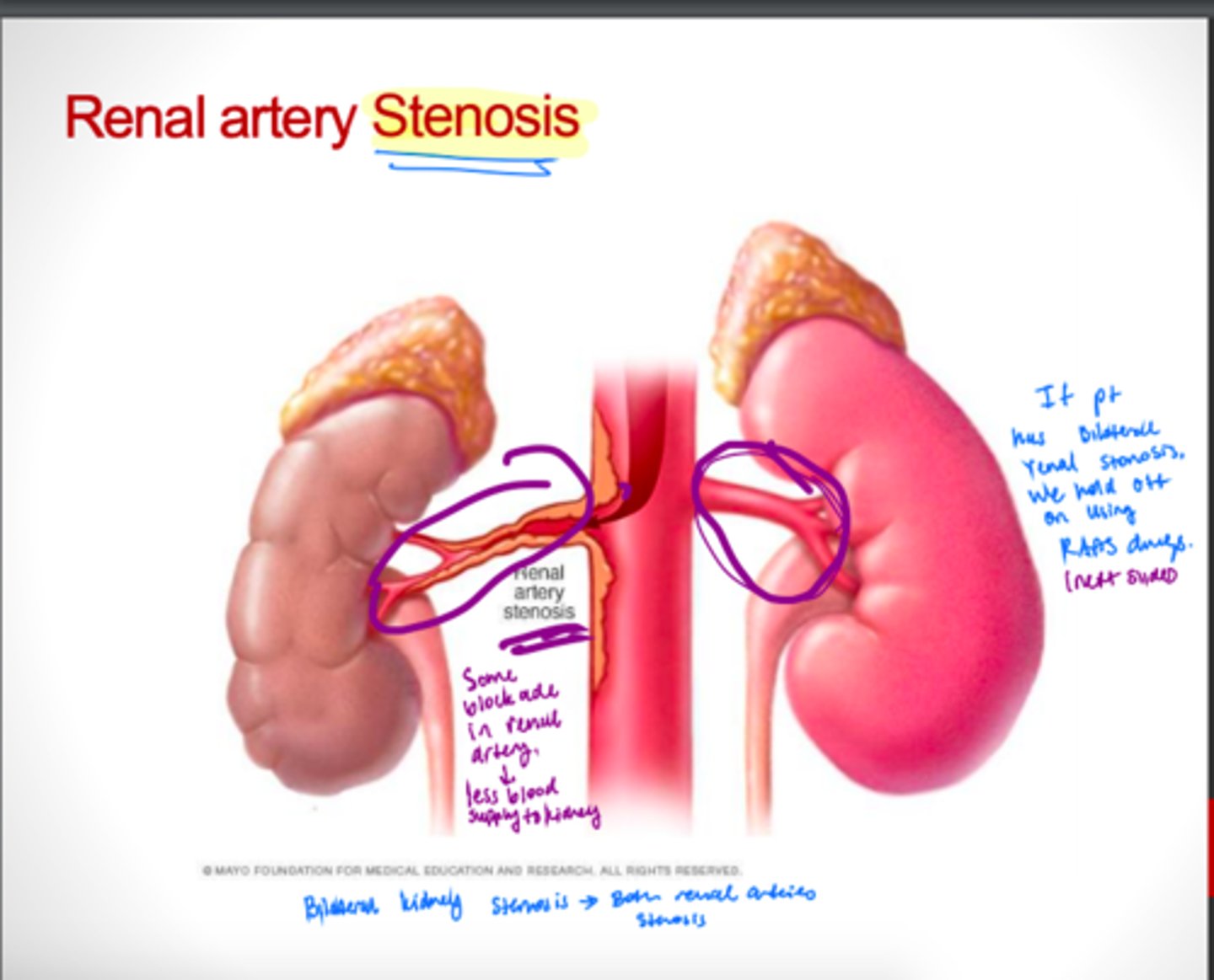
Briefly explain Renal artery stenosis.
Correctable cause of HTN
The narrowing of one or more arteries that carry blood to your kidneys
Columns of Bertin
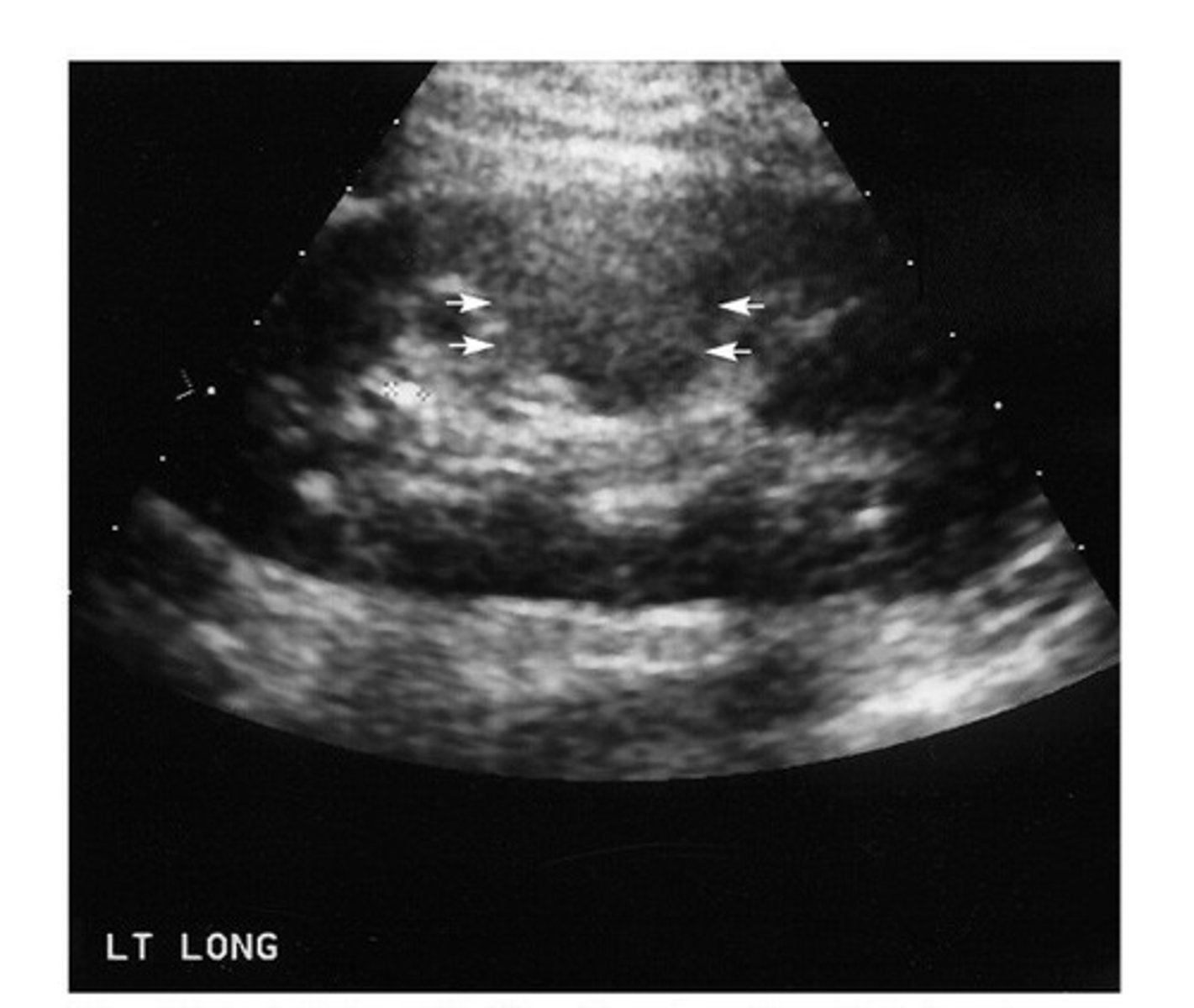
dromedary hump
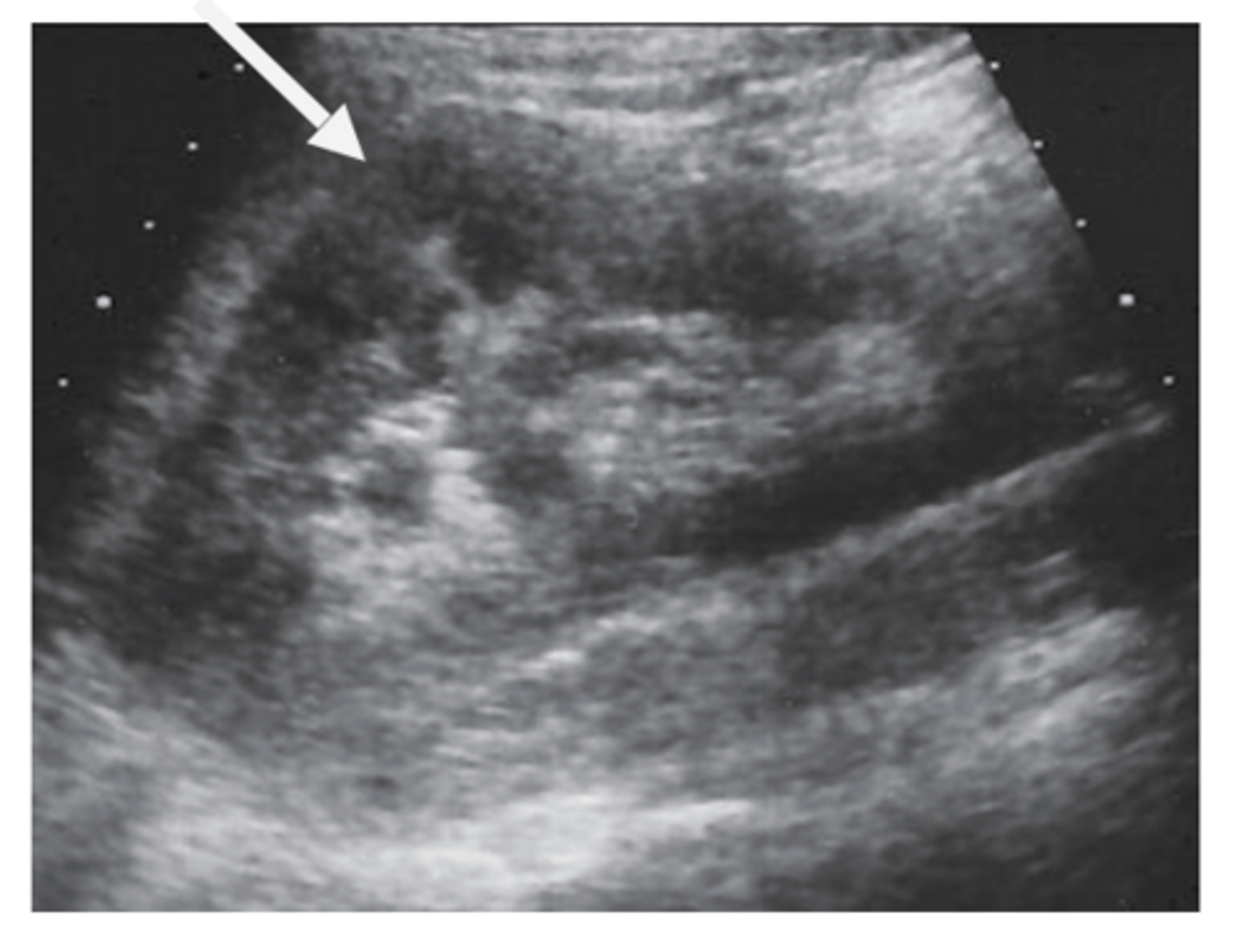
JUNCTIONAL PARENCHYMAL DEFECT
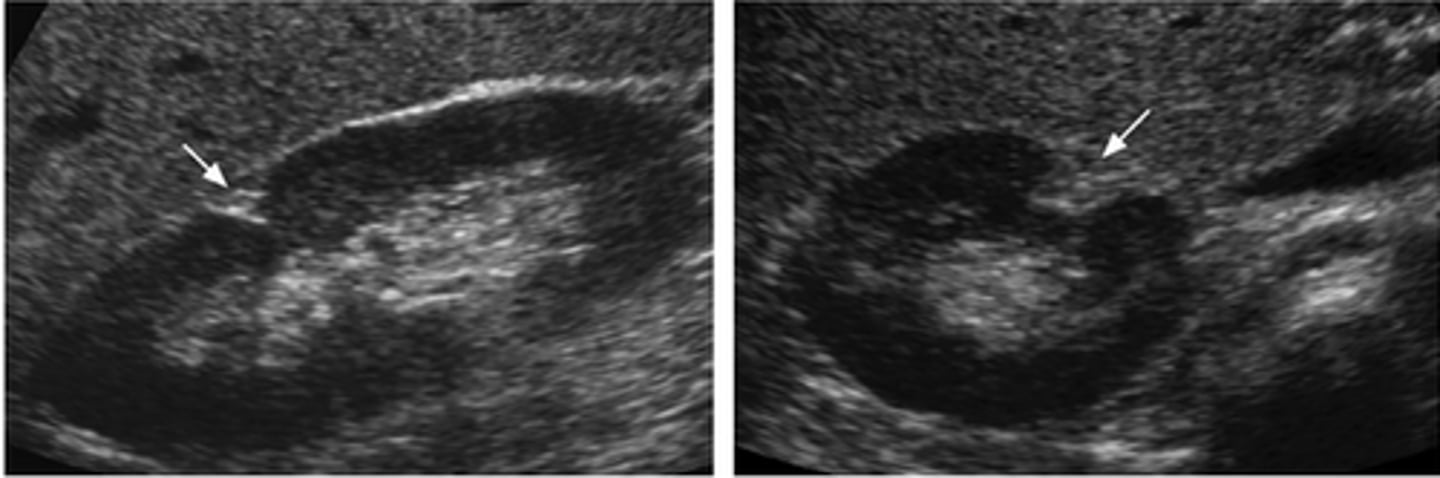
fetal lobulation
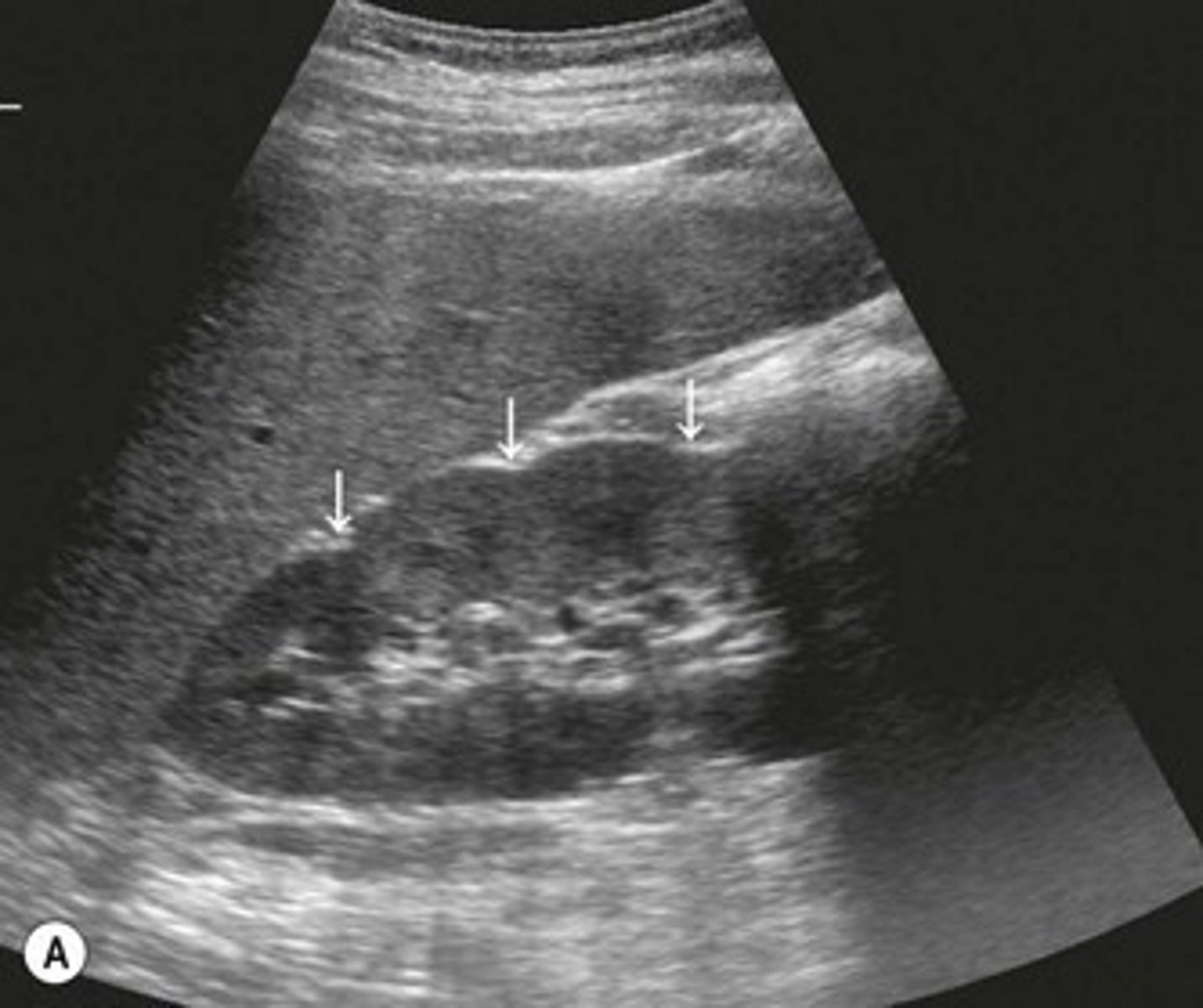
Sinus Lipomatosis
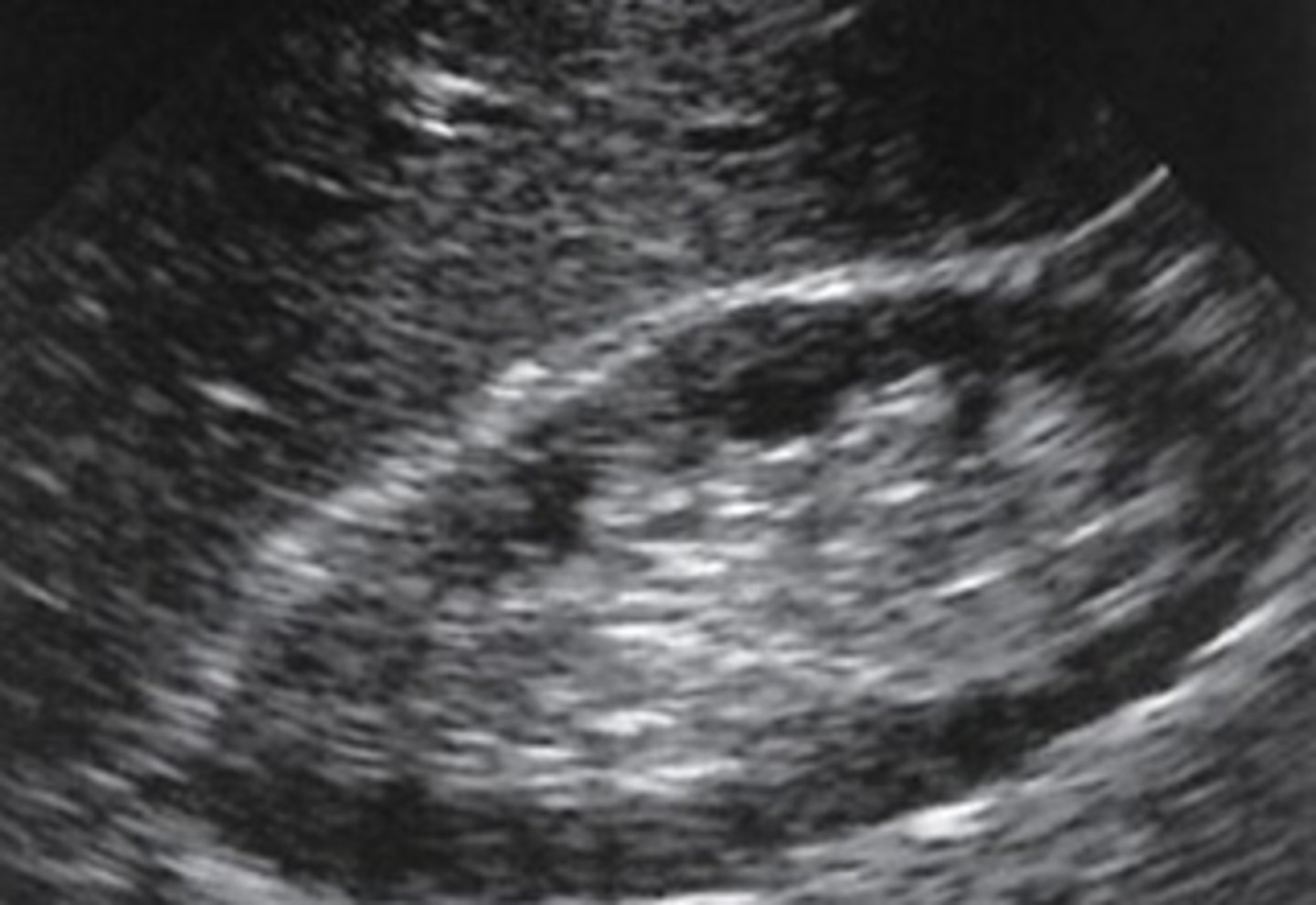
EXTRARENAL PELVIS
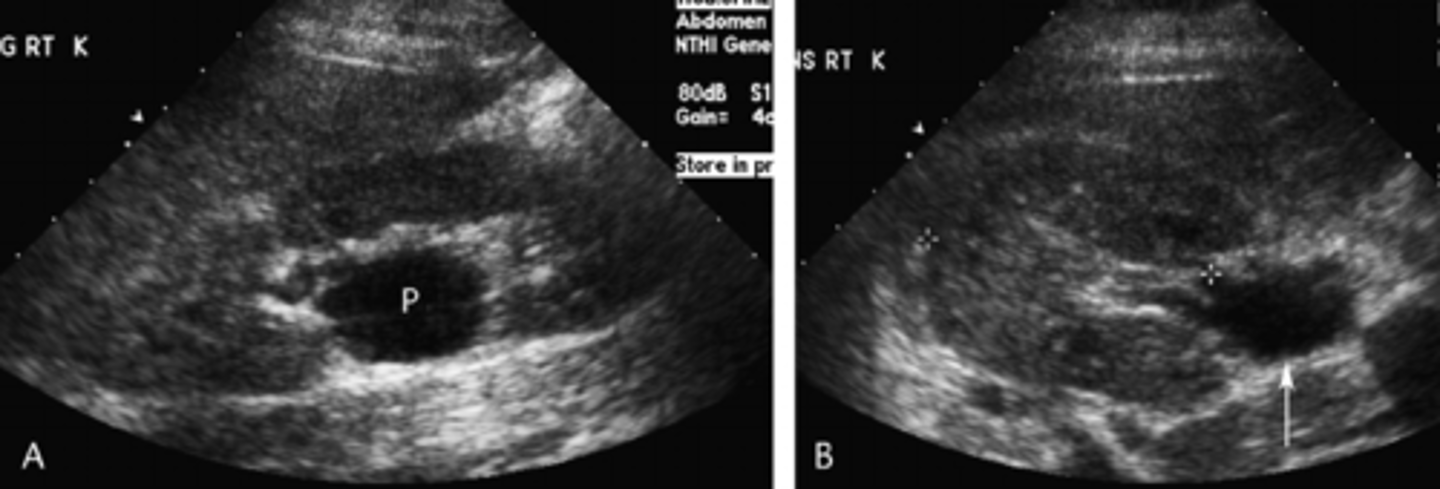
HORSESHOE KIDNEY
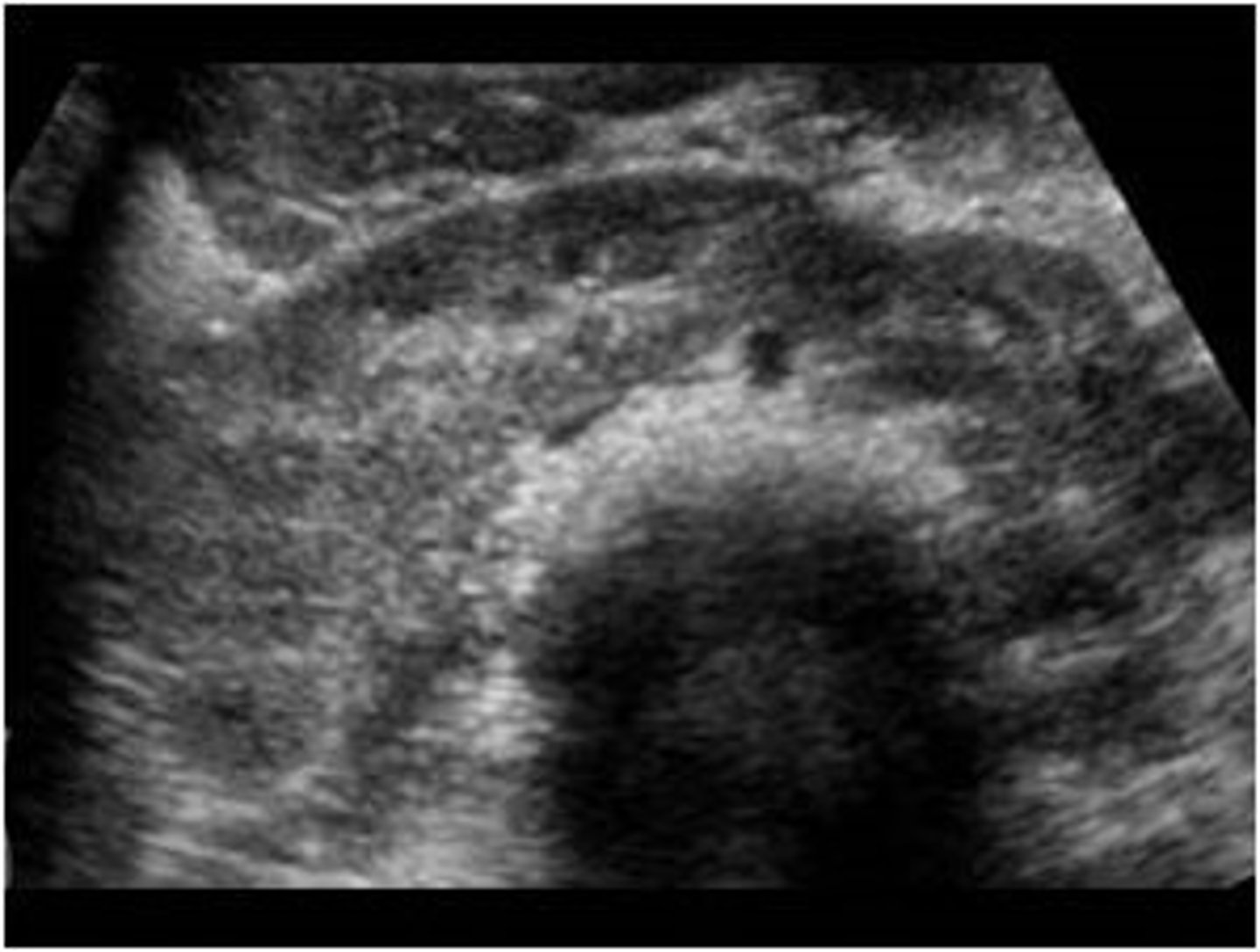
SIMPLE RENAL CYSTS
COMPLEX RENAL CYSTS
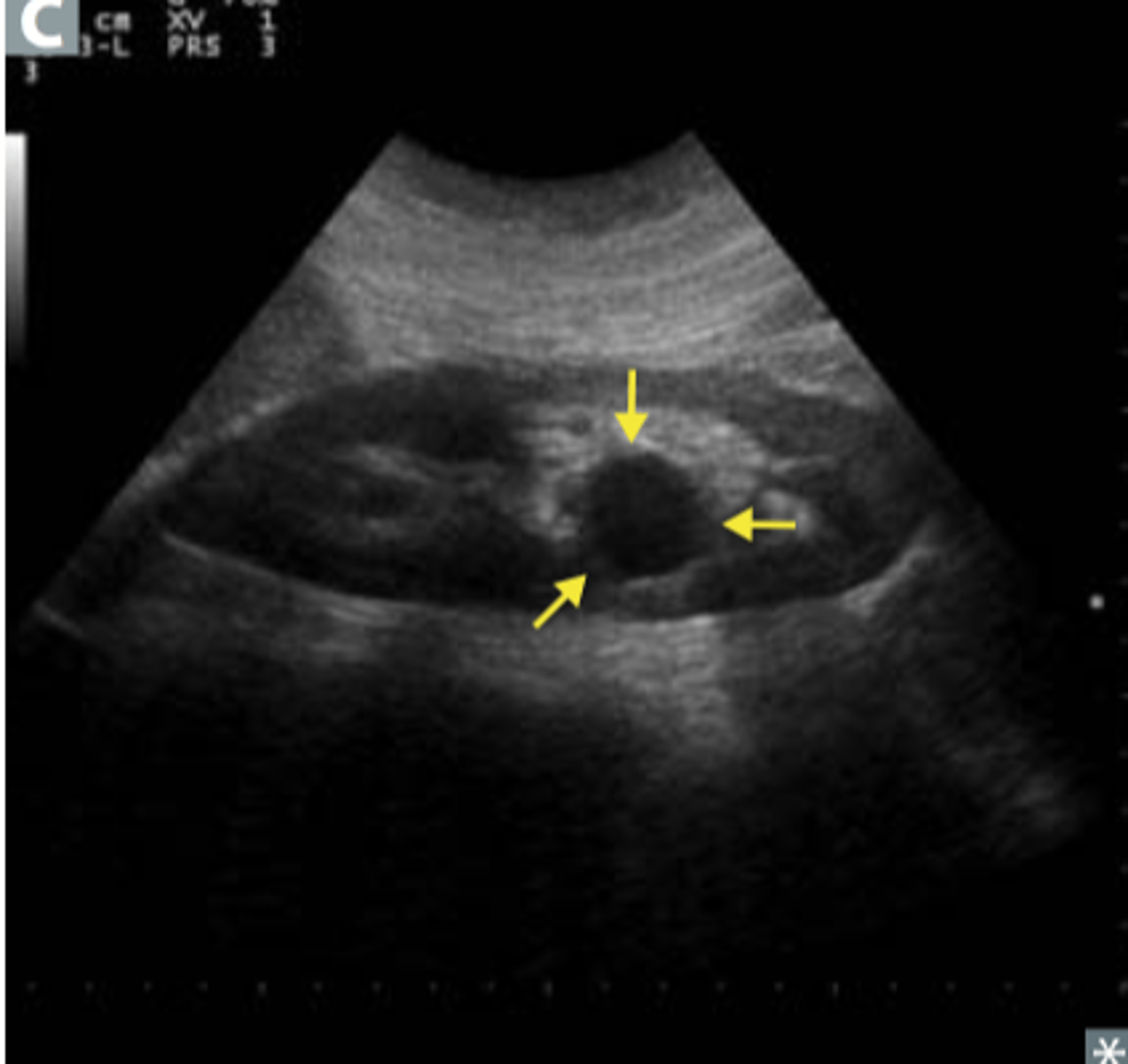
AUTOSOMAL-RECESSIVE POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE(ARPKD)
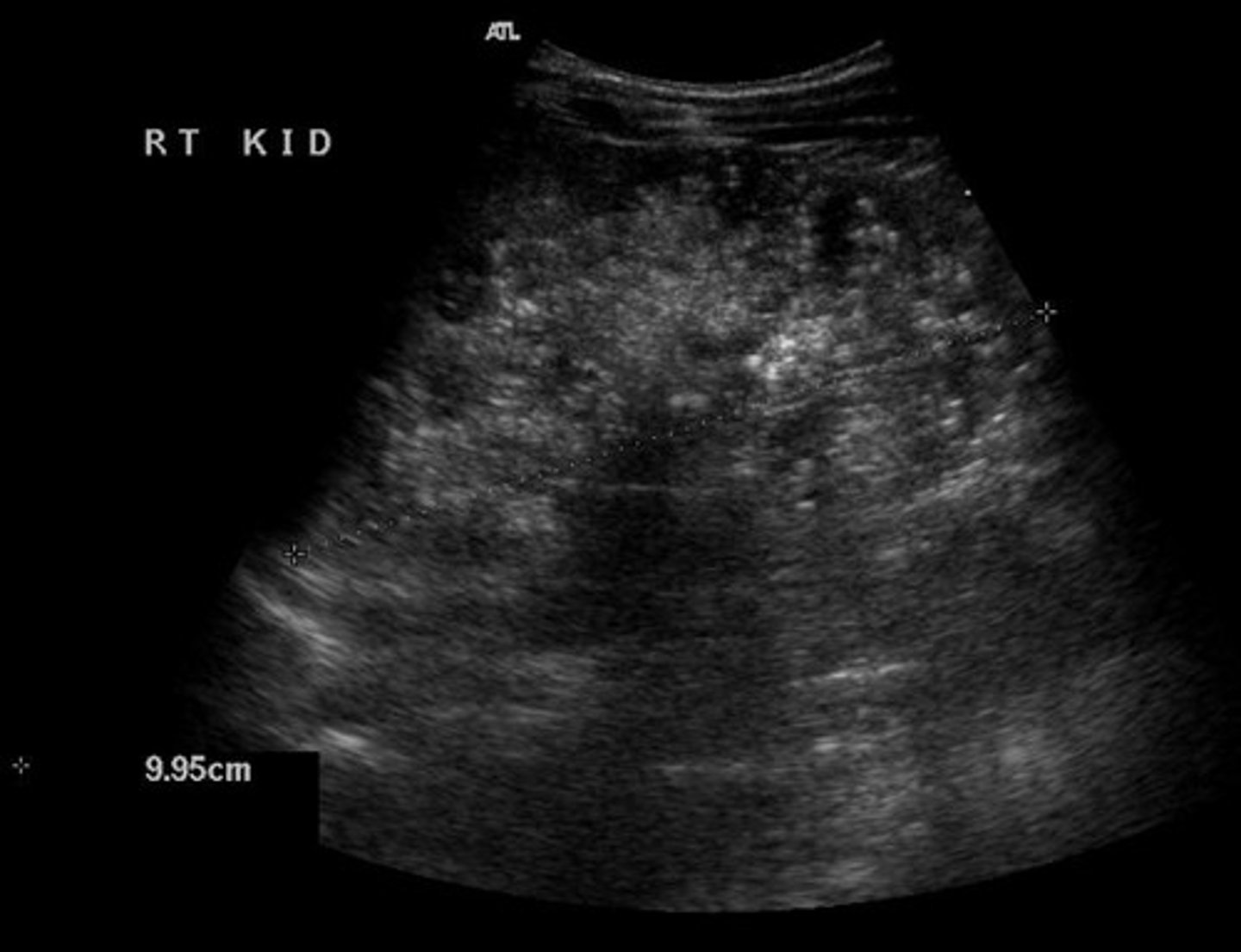
AUTOSOMAL-DOMINANT POLYCYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE(ADPKD)
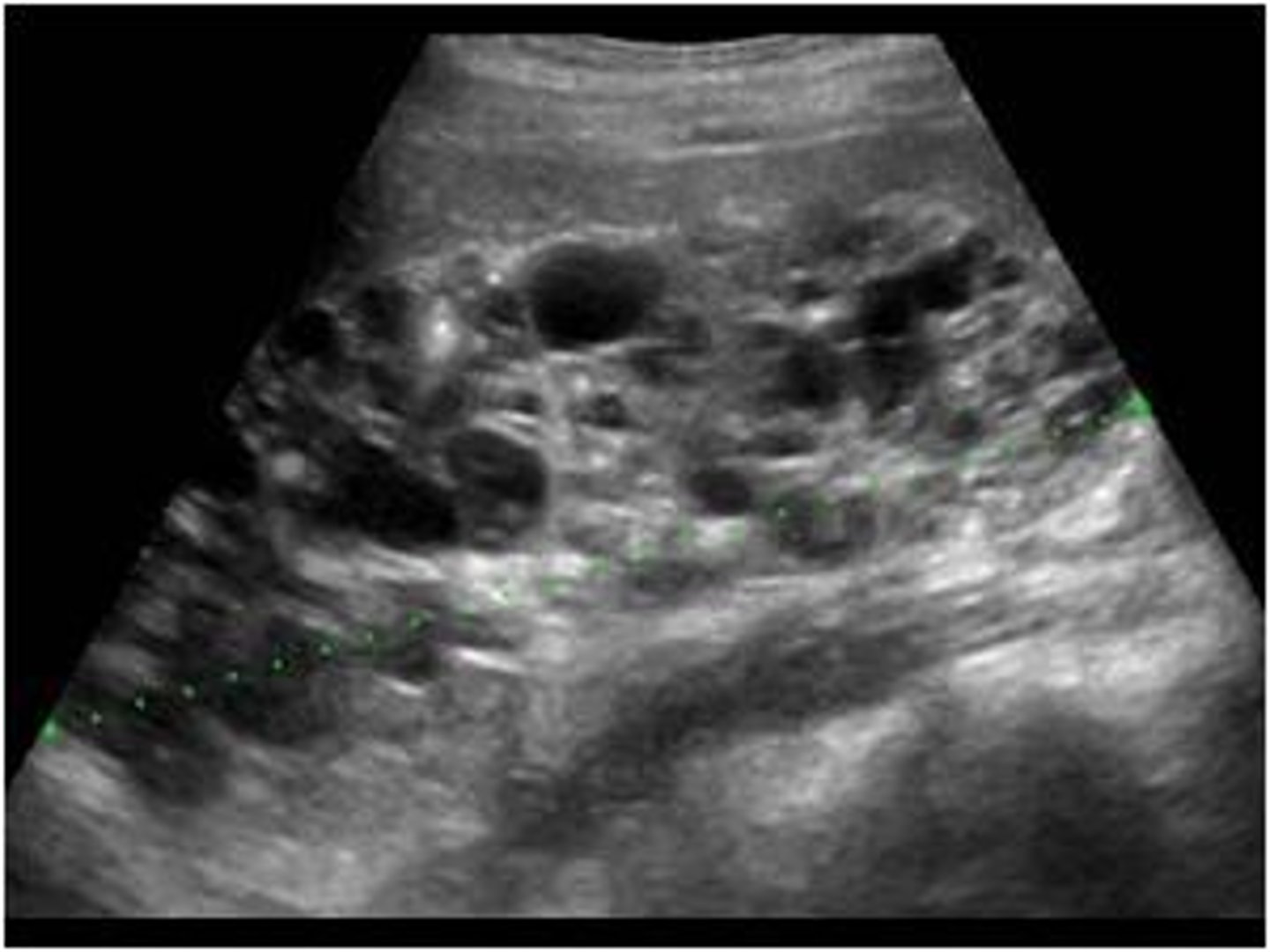
MULTICYSTIC DYSPLASTIC KIDNEY (MCDK)
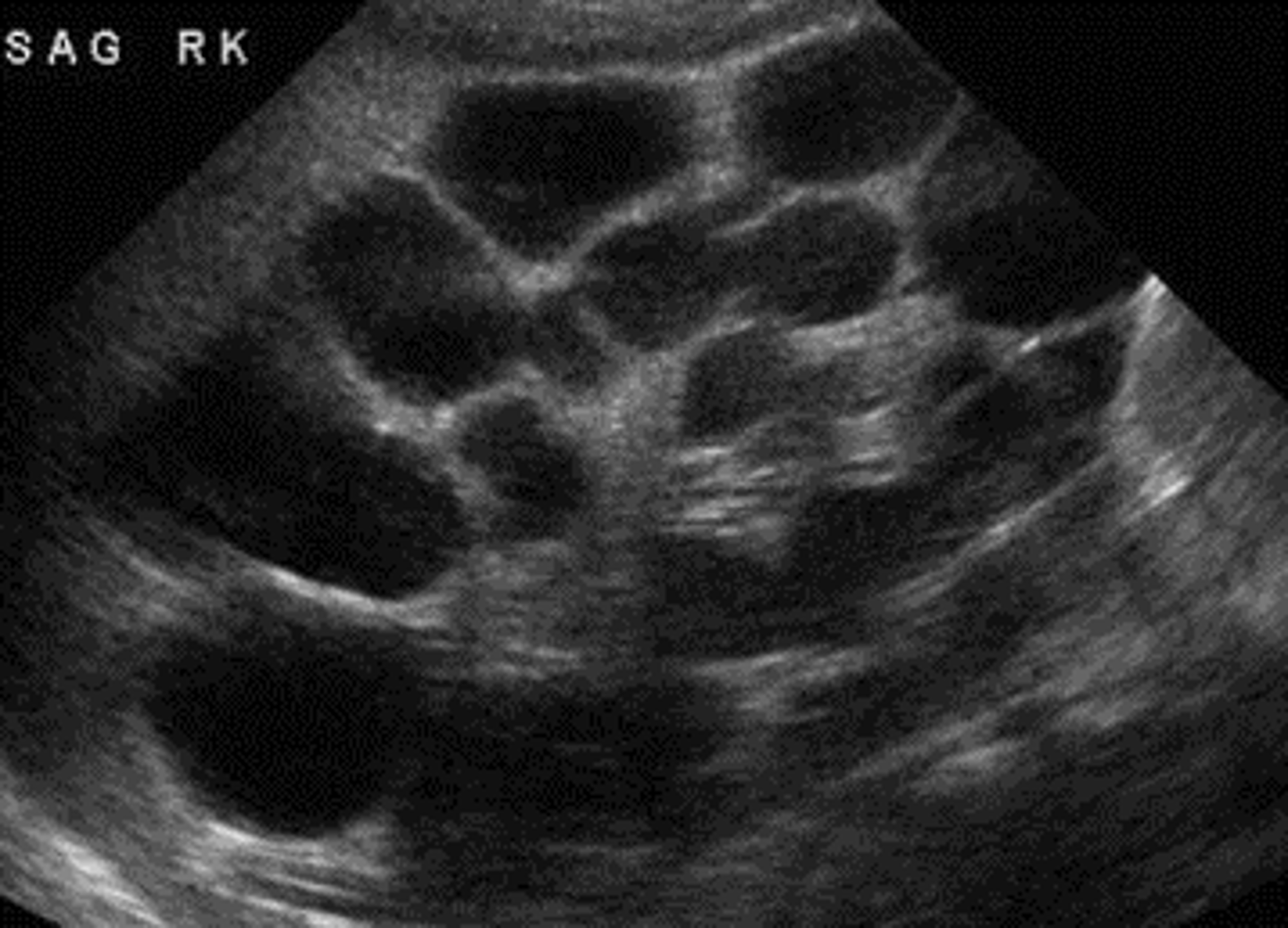
MEDULLARY CYSTIC DISEASE (MEDULLARY SPONGE KIDNEYS)
renal cell carcinoma