Biology Excretion
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is excretion?
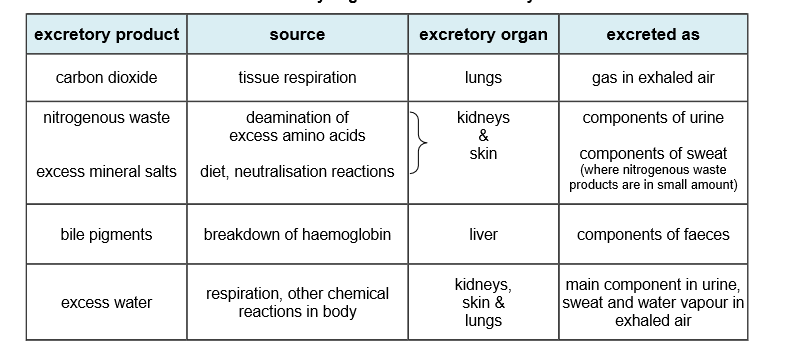
Process by which metabolic waste products and toxic substances are removed from the body of an organism
What is metabolism?
Sum total of all chemical reactions occuring in the cells of an organism
1. Anabolism --> metabolic reaction where simple molecules are built up into comples molecules with a net intake of energy
2. Catabolism --> complex molecules are broken down into simpler molecules with a net release of energy
What are metabolic waste products?
Metabolic waste products (e.g. Carbon dioxide) are unwanted substances from metabolic reactions
- they are harmful to the body if allowed to accumulae
- must be removed or deposited out of the body as harmless insoluble substances

What are the functions of a healthy kidney
1. Remove nitrogeneous waste products and excess water and mineral salts in the form of urine
2. Regulates salt and water balance of blood plasma
3. Maintain pH and composition of blood plasma
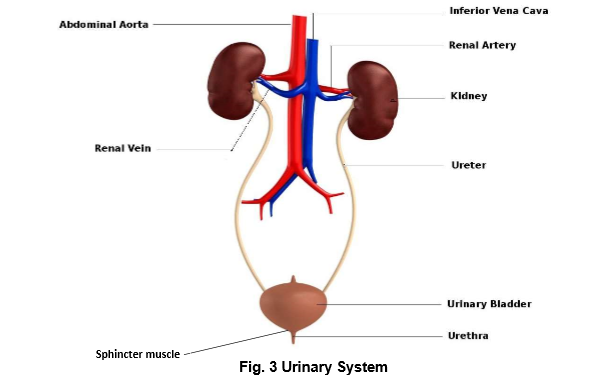
Parts of the urinary system
1. Hilum -- depression where renal artery, renal vein and nerves are connected to kidney
2. Kidney -- remove urea and excess water from the blood (urine) and keeps chemical concentration balanaced in the blood
3. Ureter -- narrow tube that emerges from the hilum, bring urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder
4. Urinary bladder -- elastic, muscular bag that stores urine
5. Sphincter muscle -- controls urine flow into and out of the urethra
6. Urethra -- duct through which urine passes out of the body
Blood vessels and kidneys
Renal arteries -- oxygenated blood containing urea and excess water from heart to kidneys
Renal vein -- deoxygenayed blood (urea and water removed) from kidney to hear
Internal structure of kidney
Cortex -- outer darker red region enclosed by fibrous capsule
Medulla -- inner, thicker paler red region + contain 12-16 structures called pyramids
Pyramids project...
into the renal pelvis which is the enlarged part of the ureter inside the kidney
Nephron
basic functional units of the kidneys -- each kidney contains about a million nephrons
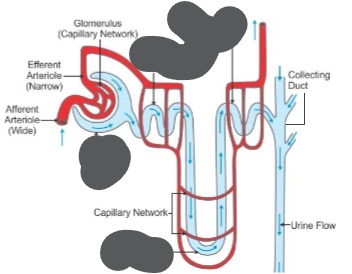
Parts of nephron
1. Bowman's capsule
2. Proximal convoluted tubule
3. loop of Henle
4. distal convoluted tubule
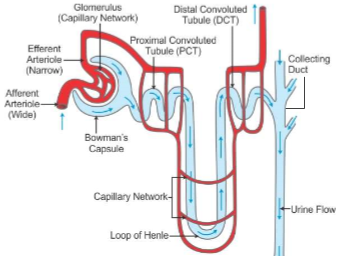
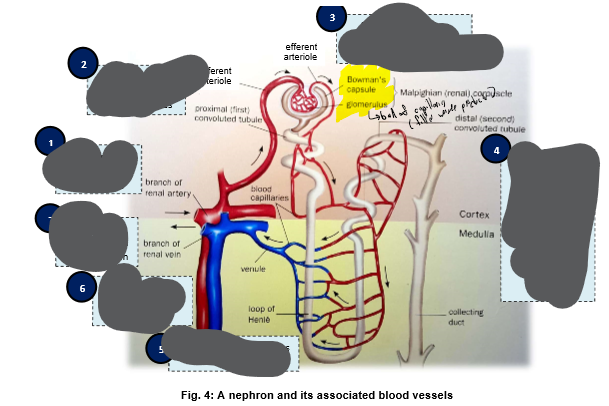
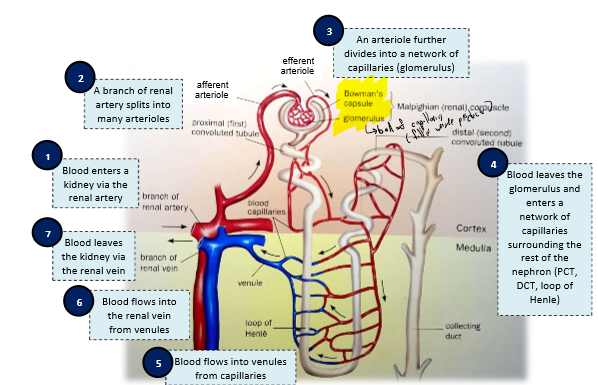
How does blood flow through the nephron?
Ultrafiltration
Occurs in glomerulus
Mechanical filtration to remove small molecules from the blood
Most of the blood plasma is forced out of glomerulus blood capillaries into the Bowman’s capsule to form glomerular filtrate
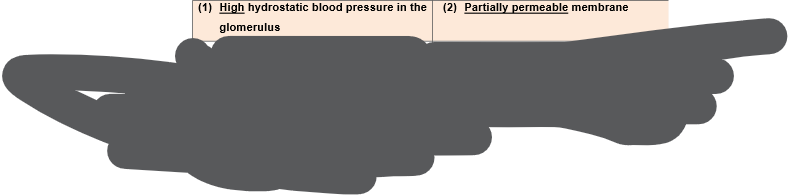
Conditions for ultrafiltration
ultrafiltration
1. High hydrostatic blood pressure in the glomerulus
- Difference in diameter between the afferent and efferent arterioles creates high hydrostatic blood pressure in glomurulus
- afferent arteriole wider than efferent arteriole
- main force for ultrafiltration
2. Partially permeable membrane
- basement membrane have small pores so only allows water and very small molecules to pass throughultrafiltration
Purpose for ultrafiltration
1. Water, mineral salts, glucose, amino acids and nitrogeneous waste products (urea) are filtered off during ultrafiltration
2. Blood cells, platelets and large molecules are not filtered
Selective reabsorption
Some subs reabsorbed from filtrate during ultrafiltration
Occurs through walls of tubule into surrounding blood capillaires

Parts involved (tubule) with selective reabsorption
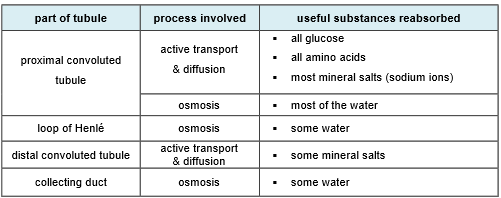
What happens to the rest of the waste products after going through selective reabsorption?
Excess water, mineral salts, nitrogeneous waste products, uric acid and creatine pass out of collecting duct into reval pelvis -- urine
Kidney failure common causes
high blood pressure, diabetis, alchohol abuse, accidents damaging kidney, complications during surgery
How to deal with failed kidney
Kidney transplant (requires suitable donor), haemodialysis (device to stimulate excretion mechanism of kidneys) and peritoneal dialysis
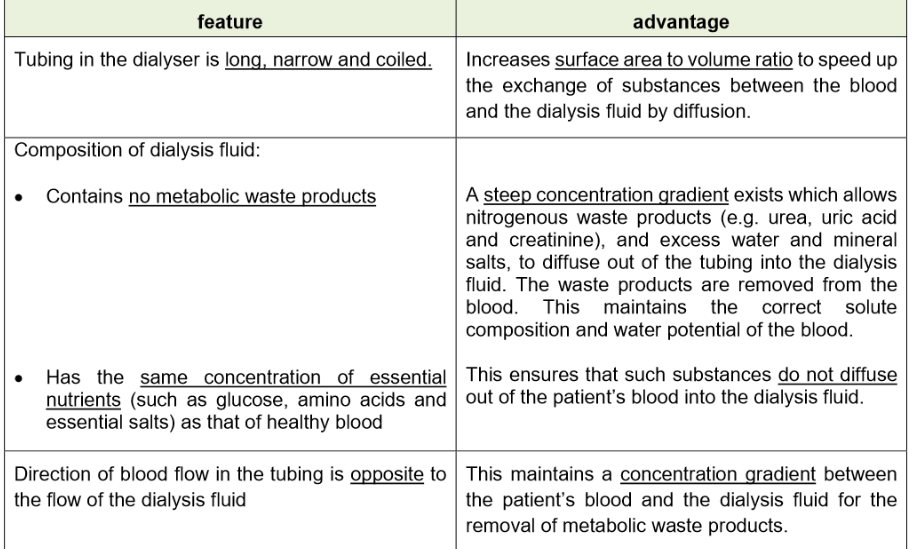
What happens during haemodialysis
Blood is chanelled from the vein into the dialyser of a dialysis machine
Blood flows into the tubing of the dialyser. Tubing is bathed in controlled dialysis fluid
Walls of tubing is partially permeable
Small molecules like urea and other metabolic waste products diffuse out of tubing into dialysis fluid
Bloocells and platelets and large molcules remain
Features of dialysis machine