DNA Sequencing (9/6-9/11)
1/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Sanger DNA Sequencing
Determination of the sequence of nucleotides in a particular piece of DNA
Sanger Sequencing Output (Hint: 2)
700-800 nt of a single molecule
Highly accurate (>99%)
Sequencing by Synthesis
Determine the sequence by synthesizing a strand of DNA
Template
The piece of DNA to be sequenced
Primer
A short (18-22 nucleotides) single stranded piece of DNA that is complimentary to one strand of the template
Oligonucleotide
Another name for a primer
DNA Polymerase (Hint: 2)
Catalyzes the addition of dNTPs to the 3’-OH of the growing daughter cell
Synthesizes DNA in the 5’ → 3’ direction only
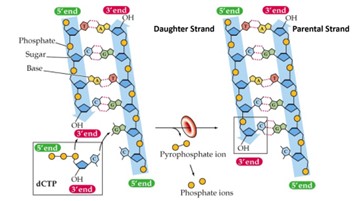
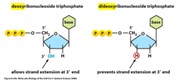
Di-deoxy nucleotides (ddNTPs) (Hint: 2)
Block DNA synthesis; Lack an -OH group at the 3’ position
DNA polymerase cannot add a nucleotide to a ddNTP
Chain Termination (Hint: 2)
Another name for Sanger Sequencing
A technique for DNA sequencing based upon the selective incorporation of chain-terminating dideoxy nucleotides (ddNTPs) by DNA polymerase
Read
The sequence of a single molecule
Shotgun Sequencing
Random sequencing of small portions of a genome and reassembly by overlapping
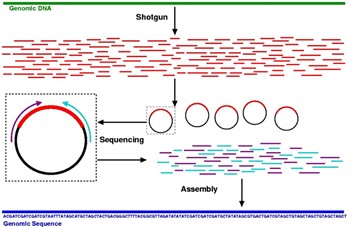
Genomic Library (Hint: 3)
Genome is sheared and cloned randomly into plasmids which are transformed into E. coli
Individual colonies are selected the plasmid purified, and the genomic fragment sequenced
Sequence overlaps are assembled into the genome by computer algorithms
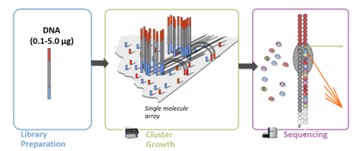
Illumina Sequencing (Hint: 5)
Generated by ligating sequence specific adaptors
Individual molecules made into clusters by bridge amplification
400 million 300 bp reads (short)
Total Output: 120 Gb
Highly accurate (>99.9%)
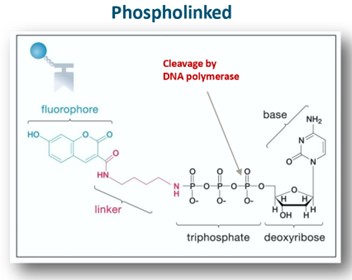
PacBio Sequencing (Hint: 10)
Real-time sequencing by synthesis produces long reads
Fluorophore clipped off by polymerase
DNA synthesized is natural
No steric hindrance or accumulation of background signal
All four nucleotides added at once
Up to 8 million reads
10-15 kb average read length (long)
Total output: Up to 200 GB
Low single read accuracy (86%)
Consensus read accuracy >99%
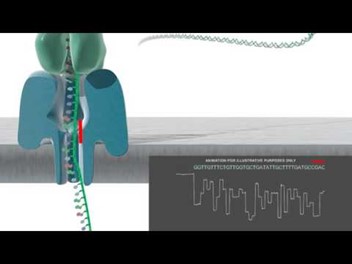
Oxford Nanopore Sequencing (Hint: 5)
Detects electrochemical differences between the base pairs passing through a small protein pore in a membrane
10-15 kb average reads with some ultra long reads (>100 kb)
Total output is unlimited
Low single read accuracy (85%)
High consensus accuracy (>99%)
RNA-seq
Sequence all of the RNAs expressed in a cell
Transcriptome
The collection of RNA transcripts in a cell, tissue, or organism
ChiP-seq (Hint: 2)
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
Identify protein binding sites in entire genome
DNA Sequencing
A laboratory technique that determines the order of the four bases that make up DNA
How is the primer labeled?
Labeled with 32P at the 5’ end
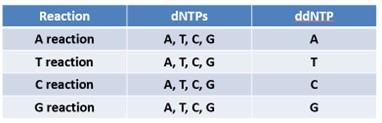
How many reactions are used to do chain termination? What is different in each reaction?
4 sequencing reactions
What ddNTP is added
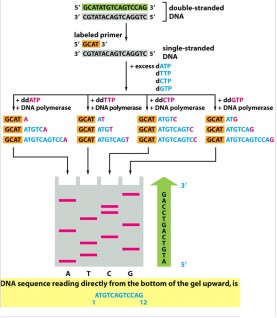
How are the fragments produced in Sanger sequencing separated and visualized? (Hint: 3)
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is used to visualize the results of the sequencing reaction
Denature the DNA
Run each reaction in a separate lane
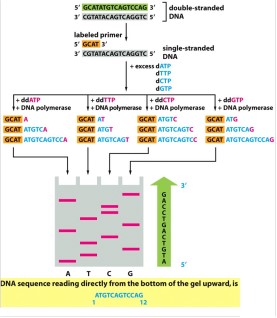
How do you read a sequencing gel?
From the bottom
How is automated Sanger sequencing different from classic Sanger sequencing? (Hint: 4)
All 4 reactions carried our in one tube
Use ddNTPs fluorescently labeled with 4 different colors
Sequence of colored bands is detected automatically with a laser
Produces a sequence trace file from which you can call bases and build the sequence
Where is sequencing data stored in the United states?
GenBank
Housed at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)
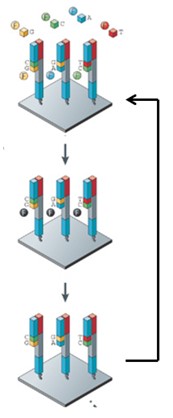
What is the Illumina sequencing cycle? (Hint: 5)
Add 4 labeled nucleotides and DNA polymerase
3’ Reversible terminator ensures that only 1 nucleotide is added per cycle
Take thousands of pictures across the flow cell
Call the nucleotide incorporated at each spot
Remove terminators and dyes