carbs pt 1,2,3,6 (basics,transported,fructose,RBC,NHANES)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
carbohydrates are made up of
CHO
simple carbs include (2)
monosaccharides and disaccharides
sucrose is made up of
glucose and fructose **
lactose is made up of
glucose and galactose **
maltose is made up of
2 glucose molecules
complex carbs consist of (2)
oligosaccharides and polysaccharides
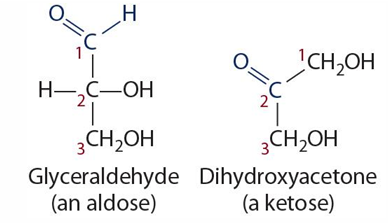
what are aldoses and ketoses
-aldoses have aldose
-ketoses have ketose group
what is chiral carbon
-assymetrical carbon
-when a carbon has 4 different atoms or groups covalently attached to it
-causes optical property **
what is stereoisomerism
the occurrence of a molecule in different espacial configuration
a straight chain monosaccharide is either _____ or ____
L or D
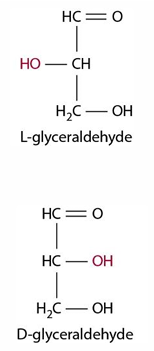
most hexoses are what configuration
D
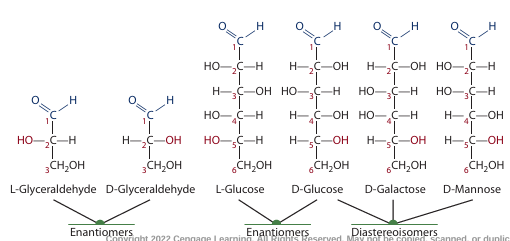
what are enantiomers **
stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other but cannot be superimposed
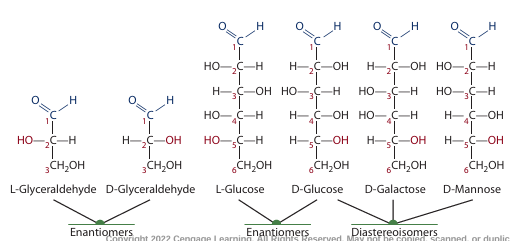
what are diastereomers
2 or more chiral carbon atoms with the same four groups attached but not mirror images of each other
what is lactose intolerance, what is it caused by ***
cannot digest lactose due to lack of lactase enzyme
what are oligosaccharides
3-10 monosaccharide chain
what are polysaccharides
more than 10 monosaccharides linked together
what are the 3 functions of polysaccharides
storage, structure, and recognition
what are the 2 types of polysaccharides (based on units)
homopolysaccharide and heteropolysaccharide
what are homopolysaccharides
a polysaccharide that contains only ONE kinds of monosaccharide
what are heteropolysaccharides
a polysaccharide that contains several kinds of monosaccharide
starch and glycogen are ______ molecules
storage
chitin and cellulose are ________ molecules
structural
cell surface polysaccharides are __________ molecules
cell recognition
starch is made up of
amylose and amylopectin
starch breaks down to _________ when digested **
glucose
where is glycogen found in the body
liver and skeletal muscle
what are the 4 functions of carbs
Carbohydrates Supply Energy
Fuel for the Central Nervous System (CNS) and Red Blood Cells
Carbohydrates Provide Fuel for the Muscular System
Carbohydrates spare protein and prevent ketosis
NOW ONTO DIGESTION/ABSORPTION/TRANSPORT/DIFFUSION
what digestion of carbs occurs in mouth
salivary amylase breaks down starch into oligosaccharides and maltose by cleaving 1—>4 bond
what carb digestion occurs in stomach
none because amylase is inactivated by acid
what kind of digestion of carbs occurs in the small intestines
pancreatic amylase breaks down starch into oligosaccharides and maltose by cleaving 1—>4 bond
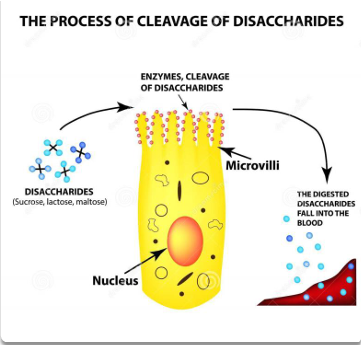
where does digestion occur in the small intestines (through what structure)
microvilli
how are carbs absorbed (what form)
as monosaccharides
(all sugars at this point are hydrolyzed into monosaccharides to be absorbed by enterocytes)
FRUCTOSE ABSORPTION TOPIC
how is fructose taken into the enterocyte (what transporter)
GLUT 5
TRANSPORT
What are the 2 main types of sugar transporters
SGLTs and GLUTs
SGLTs are what type of transport
active (rely on the movement of Na+ for energy)
what type of transport are GLUTs
facilitated transport
what transporter allows fructose to leave enterocyte and enter blood
GLUT 2
GLUT TRANSPORTERS TOPIC
GLUT isoforms are what kind of proteins
integral proteins
GLUT 1 is used for what?? (what cells and locations)
Main is blood brain barrier AND red blood cells
red blood cells and ATP (pathway to make energy) ***
-do not have mitochondria so not use TCA cycle
-make ATP through anaerobic respiration (glycolysis)
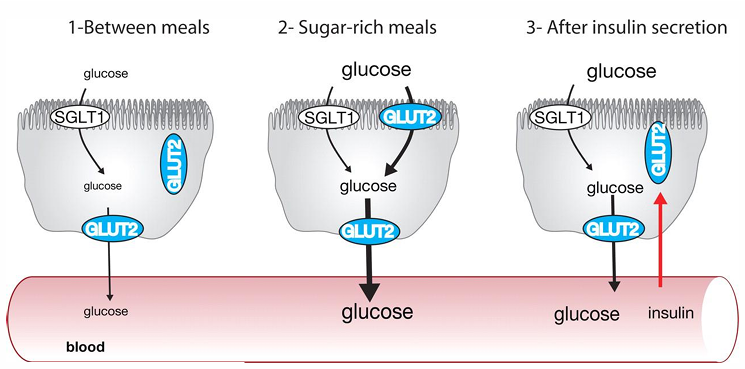
GLUT 2 transporters are found in what cells (4)
pancreas, liver, small intestines, and kidney
GLUT 2 transport what sugars
glucose and fructose
GLUT 2 works how?
GLUT 2 is always placed to allow glucose to enter the bloodstream. GLUT2 only comes to the surface of the cell to allow intake of glucose into cell when glucose is available (low affinity), so during carb rich meal. Then when insulin is released GLUT2 removes itself from the surface once again. Glut 2 however is used to move glucose from cells to blood constantly
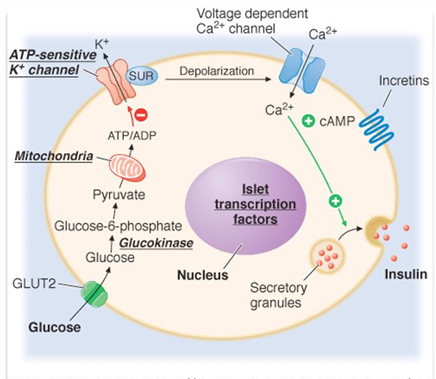
GLUT 2 is involved in release of what hormone from beta cells
INSULIN
When glucose enters the pancreatic cell through GLUT2 transporter is causes triggers that depolarize the cell which causes insulin to be released
GLUT 3 is expressed where (1)
neurons
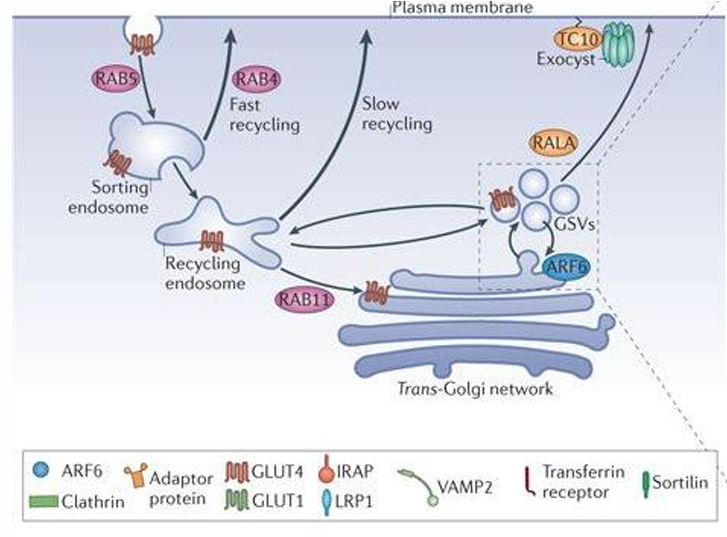
GLUT 4 is found where in the body **
MUSCLE and adipose tissue
GLUT 4 is dependent on what hormone **
INSULIN
When insulin is not present, GLUT 4 is stored where
in GSVs (GLUT 4 storage vesicles)
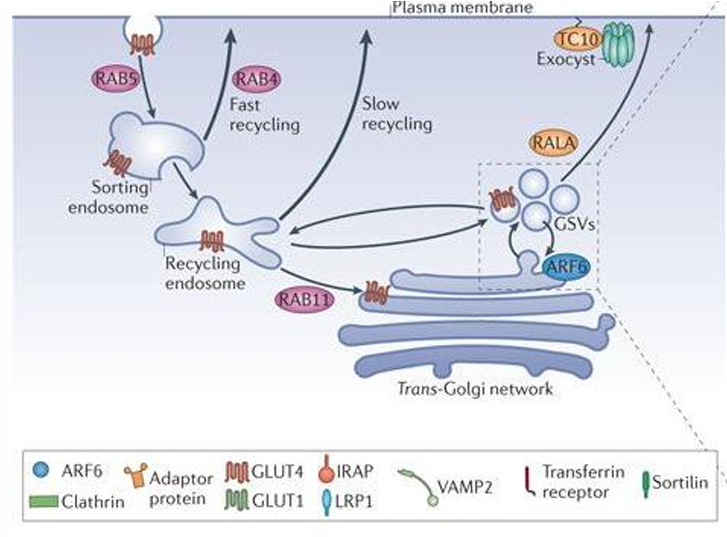
how does GLUT 4 move to the surface of cell to allow glucose into muscle and adipose tissue
When there is insulin, the GSVs are stimulated and transported by elements of the cytoskeleton. They dock with the plasma membrane for fusion and their lipid bilayers fuse. Glut 4 becomes part of the cell membrane and is available for transporting glucose into the cell.
When there is no insulin, GLUT4 stays in the GSVs and its presence in the cell membrane is reduced.
GLUT 5 is used for transport of what sugar ***
FRUCTOSE
Fructose is not found where and why (hint: systemic) ***
not in systemic circulation because it is efficiently removed and metabolized by the liver
GLYCEMIC RESPONSE TOPIC
what 2 hormones are involved in blood glucose concentration**
insulin and glucagon
what pathway is involved in blood glucose concentration
glycogenesis
define glycemic index
increase in blood glucose during 2-hour period after consuming a contain amount of CHO compared with equal CHO from reference food
cons of Glycemic Index
-depends on prep, ripeness of the CHO source
-affected if CHO eaten with other things
-tells us nothing about nutritional value
-doesnt reflect amount we would actually eat of the food
define glycemic load
considers the quantity and quality of CHO in a food
-GI x grams of CHO in typical food portion
PERSPECTIVE (WHAT DO AMERICANS EAT) TOPIC
what do we use to assess the health and nutritional status of adults and children in the US?
NHANES!!!
What has NHANES discovered/found for us (like what has its findings been used for) (4)
Determine the prevalence of major diseases and risk factors for diseases.
Assess nutritional status and its association with health promotion and disease prevention.
Basis for national standards for such measurements as height, weight, and blood pressure.
Used in epidemiological studies and health sciences research