EXAM
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Which of the following parts of a reflex can be monosynaptic or polysynaptic?
a. Sensory receptor
b. Sensory neuron
c. Motor neuron
d. Effector
e. Integrating center
e. Integrating center
Which of the following parts of a reflex would involve the posterior root ganglion?
a. Integrating center
b. Sensory neuron
c. Motor neuron
d. Effector
e. Interneuron
b. Sensory neuron
A nerve impulse initiated at a muscle spindle has to travel through which of the following
structures to enter the integrating center?
a. Anterior root of spinal nerve
b. Posterior root of spinal nerve
c. Tectospinal tract
d. Gray commissure
e. Lateral reticulospinal tract
b. Posterior root of spinal nerve
Why is a spinal tap performed below L2?
a. The spinal cord is present ensuring there will be a subarachnoid space present.
b. The spinal meninges and spinal cord are not present, ensuring no damage to the nervous system.
c. The spinal meninges and spaces extend past the proper spinal cord, allowing fluid to be withdrawn with a minimal risk of damage to the spinal cord.
d. There is more space between the vertebrae in a flexed position below L2.
e. The supracristal line is the only way to determine placement of the needle in spinal taps.
c. The spinal meninges and spaces extend past the proper spinal cord, allowing fluid to be withdrawn with a minimal risk of damage to the spinal cord.
5. Place the reflex arc components in order from detecting a stimulus to a response
Motor neuron
Effector
Sensory neuron
Integration center
Sensory receptor
a. 51243
b. 35124
c. 35412
d. 53412
e. 21435
d. 53412
A papillary reflex is integrated into the brain stem so it classified as a ___
a. spinal; somatic
b. spinal; autonomic
c. cranial; somatic
d. cranial; autonomic
e. spinal; visceral
d. cranial; autonomic
A patient is being examined for muscle weakness. To assess their condition, the doctor tests their knee-jerk reflex by tapping the patellar tendon with a reflex hammer and tapping their lower jaw with a finger. Both pathways are considered monosynaptic. What do they have in common?
a. They are both autonomic, cranial reflexes.
b. They both a two neuron pathway, sensory to motor
c. They are both somatic, autonomic reflexes
d. The sensory neurons exit the same segment of the spinal cord.
b. They both a two neuron pathway, sensory to motor
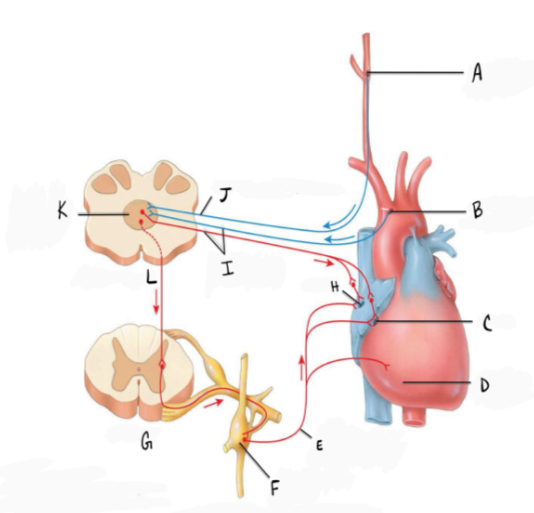
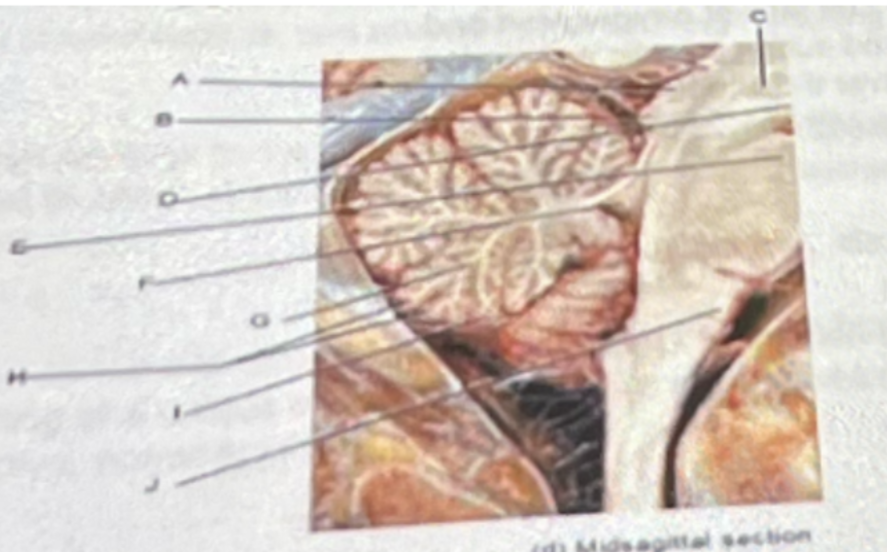
In the diagram, F represents
a. Parasympathetic ganglion
b. Sympathetic ganglion
c. Dorsal root ganglion
d. Ventral root
b. Sympathetic ganglion
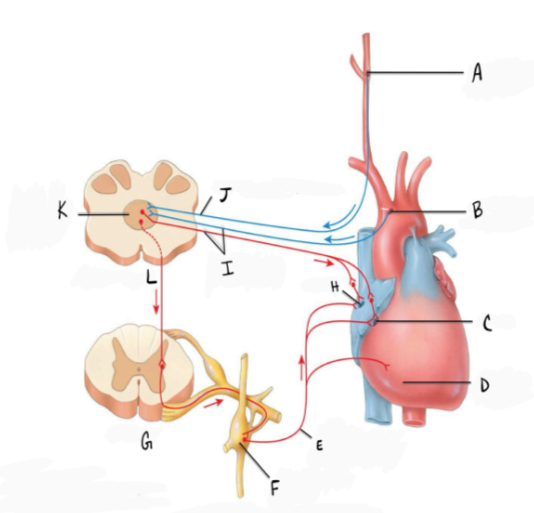
In the diagram A represents
a. a) baroreceptors in the carotid sinus
b. b) baroreceptors in the aortic sinus
c. c) baroreceptors in the brachiocephalic sinus
d. d) baroreceptors in the cerebral sinus
a) baroreceptors in the carotid sinus
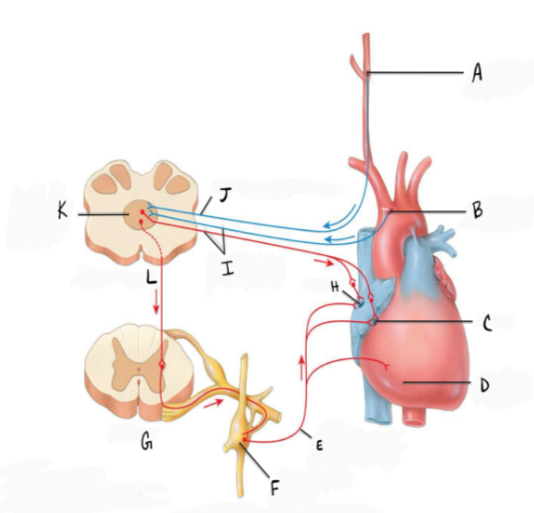
In the diagram J represents
a. glossopharyngeal nerve
b. accelerator nerve
c. vagus nerve
d. accessory nerve
a. glossopharyngeal nerve
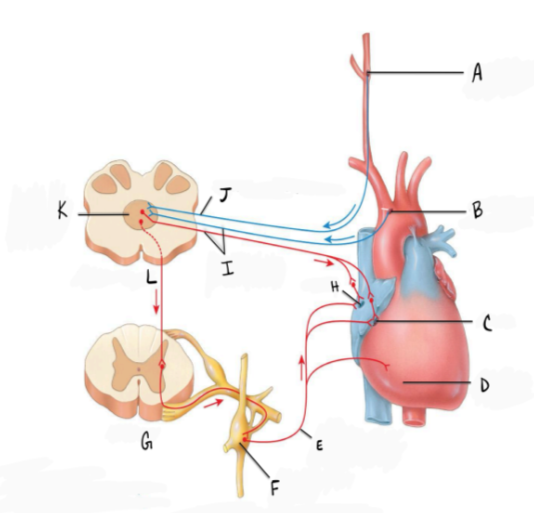
In the diagram L represents
a. spinal cord
b. pons
c. midbrain
d. medulla
e. hypothalamus
d. medulla
True or False: The latent period is the delay between the receipt of a stimulus by a motor nerve and the response to it
True
True or False: Voluntary contracting the quadriceps muscle will show a longer latent period than the reflexive action of the same muscle
True
Which part of the brain plays a major role in maintaining homeostasis by controlling the nervous system, secreting hormones, and regulating behaviors (feeding, thirst, sexual arousal)?
a. Pons
b. Medulla
c. Hypothalamus
d. Midbrain
e. Thalamus
c. Hypothalamus
Which term best describes a raised area on the surface of the cerebrum?
a. Sulcus
b. Gyrus
c. Fissure
d. Sinus
b. Gyrus
Damage to the frontal lobe (and no other lobe) will affect the ____ and cause a deficit
(inability) in ____.
a. Precentral gyrus...moving body parts
b. Precentral gyrus...sensing body parts
c. Postcentral gyrus...moving BP
d. Postcentral gyrus...sensing BP
a. Precentral gyrus...moving body parts
What type of brain tissue do you find in the cerebral cortex?
a. White matter which has myelinated axons
b. White matter which has unmyelinated axons
c. Grey matter which has myelinated axons
d. Grey matter which has unmyelinated axons
d. Grey matter which has unmyelinated axons
Myelinated neurons use ________ Than unmyelinated neurons.
a. Continuous conduction to send slower electrical impulses
b. Continuous conduction to send faster electrical impulses
c. Saltatory conduction to send slower electrical impulses
d. Saltatory conduction to send faster electrical impulses
d. Saltatory conduction to send faster electrical impulses
Which neurotransmitter is found in the synapses of the neuromuscular junction as well as in the synapses in the parasympathetic nervous system?
a. Dopamine
b. Acetylcholine
c. Serotonin
d. Oxytocin
e. Norepinephrine
b. Acetylcholine
Starting from the brain and moving outwards, which one of the following lists the meninges in the correct order?
E. brain, pia, arachnoid, dura, skull
Which part of the nervous system is stimulated during times of stress?
a. Sympathetic ns
b. Parasympathetic ns
c. Somatic ns
d. Visceral ns
a. Sympathetic ns
In which direction do electrical impulses in an afferent neuron travel at the spinal cord?
a. From the spinal cord into the PNS through the dorsal root
b. From the spinal cord into the PNS through the ventral root
c. From the PNS into the spinal cord through the dorsal root
d. From the PNS into the spinal cord through the ventral root
c. From the PNS into the spinal cord through the dorsal root
What does the “threshold” refer to?
a. the speed at which the nerve impulse travel
b. the amount of voltage change during depolarization
c. the ability of a neuron to be depolarized before it has finished repolarizing
d. the possibility that the postsynaptic neuron receive an IPSP or an EPSP
e. The voltage strength needed for an action potential
e. The voltage strength needed for an action potential
What is a ganglion?
a. A group of neuronal cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system
b. A group of neuronal cell bodies in the central nervous system
c. A group of interneurons in the central nervous system
d. A group of neural axons outside the central nervous system
e. A group of nerves exiting the same region of the spinal cord
a. A group of neuronal cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system
What is a membrane potential?
a. a sudden brief reversal of a neuron voltage in comparison to the extracellular environment
b. a wave of depolarization that begins in the axon hillock and travels down the axon to the end bulbs ( axon terminals)
c. The difference in the electrochemical gradient of the neuron when compared to the extracellular environment
d. the process in which a neuron becomes negatively charged due to the efflux of potassium
e. the phenomenon in which a chanel opens only when the neurons charge reaches threshold
c. The difference in the electrochemical gradient of the neuron when compared to the extracellular environment
What does hyperpolarization cause?
a. Excitation of an action potential
b. EPSP of a neuron membrane
c. Inhibition of an action potential
d. Excitotoxicity in a synapse
e. Sodium ions to rush inside the neuron
c. Inhibition of an action potential
What is depolarization?
a. The process of many sodium ions diffusing into a cell
b. the process of many potassium ions diffusing into a cell
c. the process of a muscle cell relaxing due to loss of cross bridges
d. the process of a cell becoming equally charged with the extracellular environment
e. the process of a cell becoming negatively charged with the extracellular environment
a. The process of many sodium ions diffusing into a cell
Prozac is an antidepressant. Which neurotransmitter is associated with its mechanism?
A- Dopamine
B- Acetylcholine
C- Norepinephrine
D- Serotonin
E- Glutamine
D- Serotonin
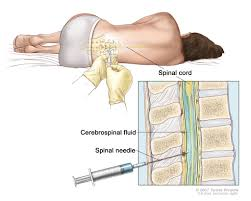
list the sequence of the above test in the proper order) spinal tap picture
A- arachnoid mater
B- dermis
C- dura mater
D- epidermis
E- epidural space
F- hypodermis
G- subarachnoid space
H-msubdural space
d,b,f,e,c,h,a,g
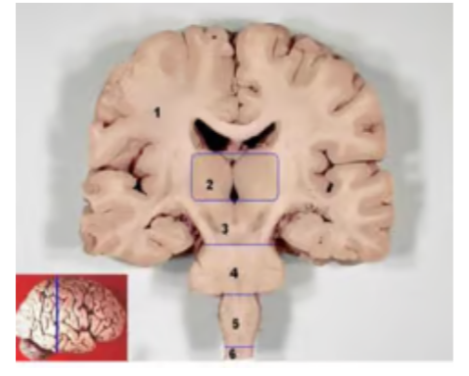
Number 2 above represents?
a. Hypothalamus
b. Epithalamus
c. Thalamus
d. Pons
e. Medulla oblongata
Thalamus
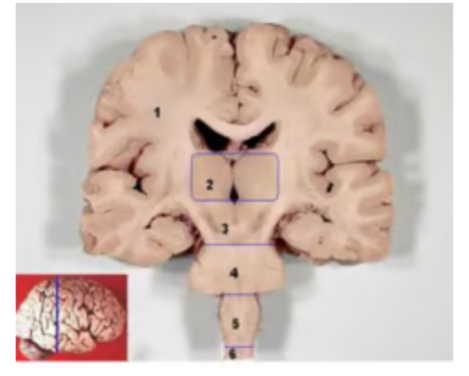
Number 1 represents?
a. cerebrum
b. cerebral cortex
c. white matter
d. lateral ventricles
b. cerebral cortex
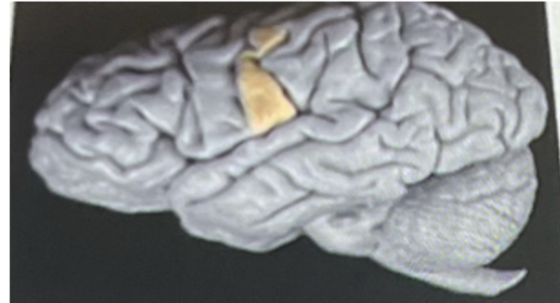
The highlighted section above if damaged will interfere (postcentral gyrus highlighted)
a. motor functions
b. sensory perception such as feeling pain
c. spinal reflex
d. visual functions
e. auditory functions
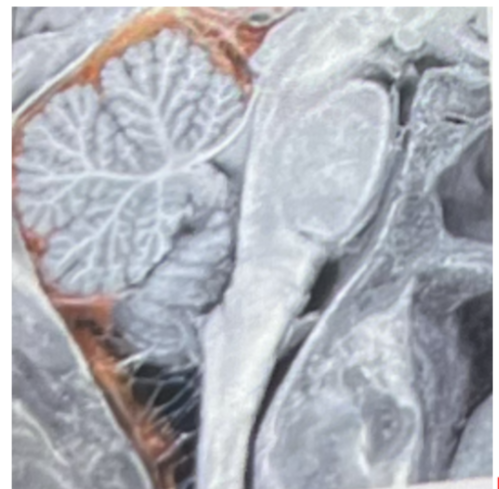
The highlighted space above represents
a. The third ventricle
b. epidural space
c. the 4th ventricle
d. subarachnoid space
e. cerebral aqueduct
subarachnoid space
The colored region below is the
A- Pons
B- thalamus
C- hippocampus
D- medulla
E- Midbrain
E- Midbrain
What condition is this?
hydrocephalus
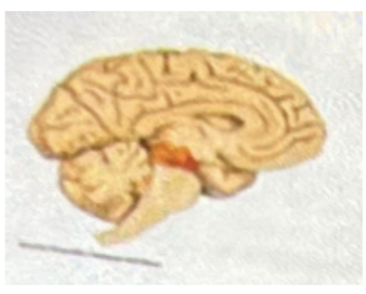
A B and C above represent
A- Pons
B- cerebellum
C- midbrain
D- hippocampus
E- hypothalamus
C- midbrain
Waves of electromagnetic radiation are sent through the patient’s head and create images on a film as a result of tissues of varying densities
CAT scan
A transductor emits high-frequency sound waves to the brain and spinal cord. When they bounce back off these tissues, the transducer detects these waves and the computer determines the location and size of the structure
ultrasound
Body fluids and tissues change the direction of their spin when exposed to a magnetic high-energy field. A pulse of resonating radio waves is emitted when the protons return to their original position of spin
MRI
Skin electrodes that are placed on the scalp detect electrical signals in the brain’s cerebrum
X-ray
Glucose is tagged with a radioactive isotope and is injected into the patient. The patient is given certain mental tasks to complete, and the different levels of glucose in the brain highlight the metabolically active parts of the brain on a computer screen.
PET
The computer analyzed BOLD signals. The ratio of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood levels is analyzed during specific activities. This information is superimposed over the image of the brain. Metabolically active parts of the brain are highlighted on a computer screen.
fMRI
Contrast dye is injected into blood vessels and X-rays are taken
Angiogram
A sample of CSF is removed and analyzed in this test
lumbar puncture
It can be used to detect brain death, seizures, and levels of unconsciousness (including coma) based on electrical impulses
C-EEG
It produces sharp, detailed images of soft and hard tissues. It is used to diagnose the location of structures, fractures, tumors, edema, and inflammation. It cannot be used on an individual with a metal pacemaker, metal defibrillation, or artificial metal joint
D-MRI
It produces images of soft and hard tissues. However, the soft tissues are slightly more blurry than those in the previous question. Unlike the previous question, this technique can be used on an individual with metal.
E- X-ray
It is used to detect vascular blockage and aneurysms, and the effectiveness of fibrinolytic therapy by measuring the amount of reperfusion
Angiography
Which one of the following uses ionizing radiation? (multiple choice)
A- X-ray
B- Ultrasound
C- MRI
D- fMRI
E- EEG
A- X-ray
It can be used to identify structural disorders in the nervous system of a developing fetus, such as conjoined twins, spina bifida, or other skill or spinal column defects, and offers continuous imaging during fetal surgery
A- Ultrasound
It can be used to diagnose or rule out meningitis or infection. It can also be used to administer certain medications such as anesthesia or chemotherapy.
B-lumbar puncture
It can be used to detect anatomical areas of the brain that are functioning at a unique metabolic level. This helps to identify areas that are hyperactive, normoactive, or inactive
C-fMRI
The abnormal protein associated with A in the photo____
A- synuclein
B- amyloid
C- myelin
D- Tau
E E- Actin
D- Tau
The abnormal protein associated with inclusions, from substantia nigra
A- synuclein
B- amyloid
C- myelin
D- Tau
E E- Actin
A- synuclein
Identify the Meningioma below
Glioma
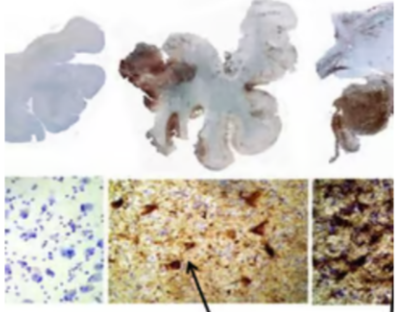
The brain slides above with neurofibrillary tangles from what condition?
A- alzheimer
B- parkinsons
C- stroke
D- CTE
E- TIA
D- CTE
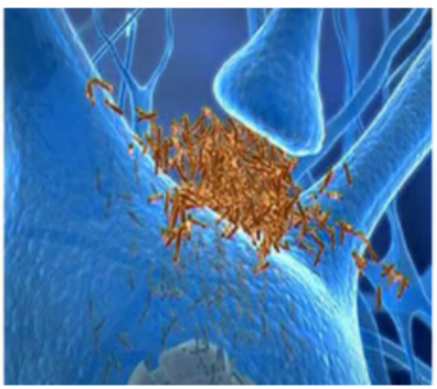
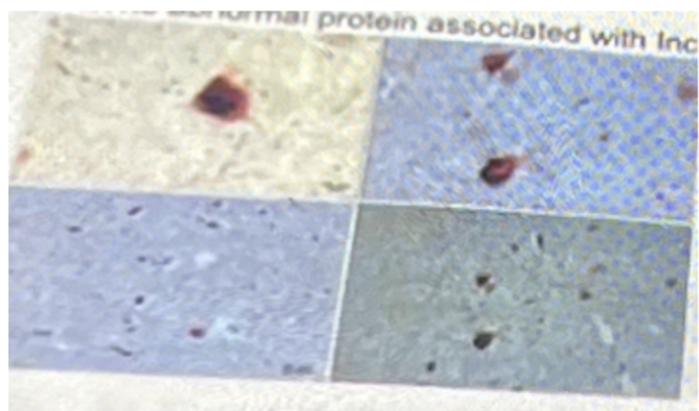
In the synapse which item(s) is/are indicated? (use blue synapse photo)
A- TAU
B- Lewy bodies
C- amyloid
D- synuclein
E- Myelin
C- amyloid
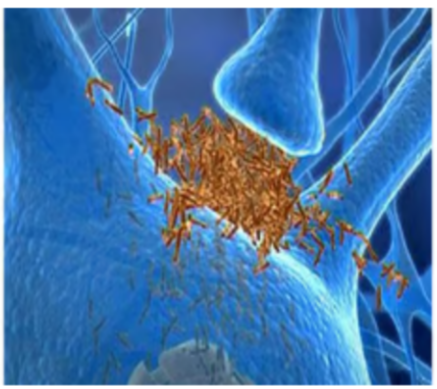
Which neurotransmitter is being interfered with? (use blue synapse photo)
A- Dopamine
B- serotonin
C- glutamate
D- ach
E- norepinephrine
D- ach
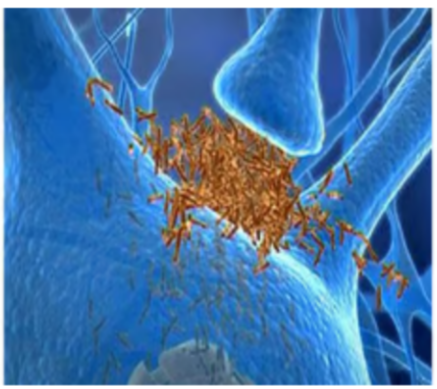
Which enzyme is responsible for the above problem?
A- choline acetyltransferase
B- beta secretase
C- alpha secretase
D- monoamine oxidase
E- superoxide dismutase
B- beta secretase
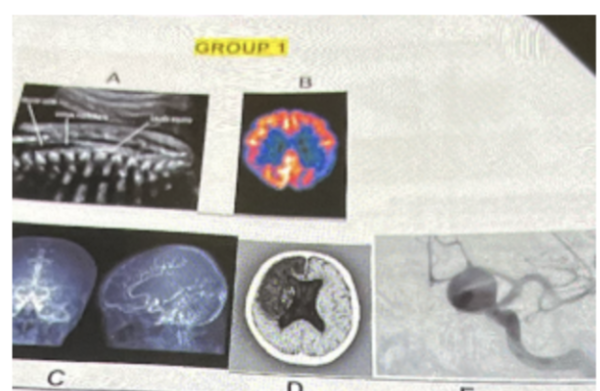
Which is the PET scan? (use group 1 of photos)
B
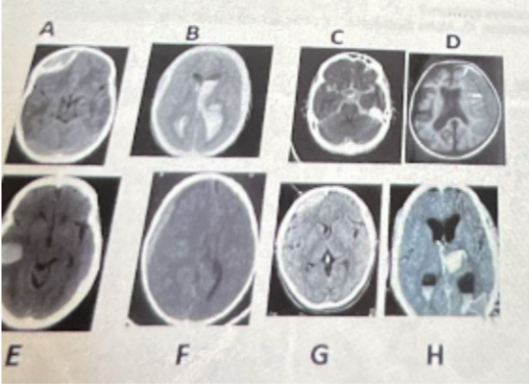
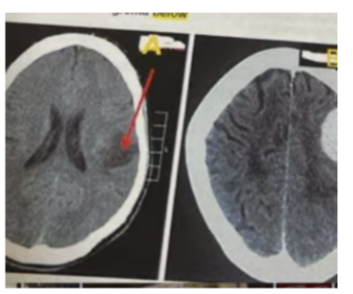
What is photo D?
a. intracerebral hemorrhage
b. subdural hemorrhage
c. intracerebral/ subarachnoid hemorrhage
d. epidural hemorrhage
b. subdural hemorrhage
Smoking is considered a common
A- sign
B- Symptom
C- risk factor
D- syndrome
E- differential diagnosis
C- risk factor
Brain tumor is considered a common
A- sign
B- Symptom
C- syndrome
D- risk factor
E- differential diagnosis
A- sign
Pain is considered a common
A- sign
B- Symptom
C- risk factor
D- syndrome
E- differential diagnosis
B- Symptom
Vomiting is considered a
A- sign
B- Symptom
C- risk factor
D- differential diagnosis
E- syndrome
A- sign
All are non-pharmacological management for Alzheimer’s disease EXCEPT?
a. Exercise
b. Estrogen replacement therapy
c. Psychoeducation
d. maintain socialization of the patient
e. computer courses
b. Estrogen replacement therapy
Which differential diagnosis below can mimic Alzheimer’s disease, but can be ruled with MRI (MRA?)
a. Parkinson's disease
b. Lewy body dementia
c. frontol-temporal dementia
d. cerebrovascular infarction
d. cerebrovascular infarction
All are risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease EXCEPT?
a. female gender
b. monitored use of NSAIDS
c. Smoking
d. Multiple TBI’s (traumatic brain injuries )
b. monitored use of NSAIDS
When discerning dementia versus delirium it can be noted that:
a. delirium is an irreversible impairment of cerebral oxidative metabolism and/or various neurotransmitter abnormalities.
b. delirium is an acquired impairment of executive function in one or more cognitive domains ( like memory, language, and attention )
c. delirium is a transient , usually acute, reversible cause of cerebral dysfunction with confusion that manifests clinically with a wide range of neuropsychiatric abnormalities.
d. delirium is a form of chronic dementia
e. delirium and dementia have exactly the same pathophysiology
c. delirium is a transient , usually acute, reversible cause of cerebral dysfunction with confusion that manifests clinically with a wide range of neuropsychiatric abnormalities
Which non-plaque protein is involved in neurofibrillary tangles causing Alzheimer’s disease?
Tau
Alzheimer’s disease is
a. the only cause of dementia
b. a condition of cognitive deficits not caused by psychiatric, neurogenic or systemic disease
c. a condition of cognitive deficits always caused by psychiatric, neurogenic or systemic disease
d. one of many forms of dementia
e. b and d are correct
e. b and d are correct
In Alzheimer’s disease, plaques and tangles are found in the cerebral cortex and:
a. substantia nigra
b. optic chiasma
c. Hippocampus
d. medulla oblongata
e. corpora quadrigemina
c. Hippocampus
The leading cause of death of AD patients is:
a. space occupying lesions, like brain tumors
b. Pneumonia especially succumbing to food aspiration due to difficulty swallowing
c. Down syndrome
d. Suicide
e. febrile seizure
b. Pneumonia especially succumbing to food aspiration due to difficulty swallowing
In the early stage of AD, prodromal with MCI (mild cognitive impairment) there is hope that we can improve neural ___ with the help of ___ as an imaging technique
a. elasticity/ ultrasound
b. Plasticity/ MRI
c. Repolarization/ MRI
d. Hyperpolarization/ CT Scan
e. Regrowth/ X-ray
b. Plasticity/ MRI
Which of the following is a sign of late-stage Alzheimer’s disease?
a. Dysphagia or Aphasia
b. forgetting familiar words or names
c. Wandering
d. misplacing keys, glasses and hearing aids
e. delusions and hallucinations
a. Dysphagia or Aphasia
The BEST imaging technique to rule out a brain tumor as a differential diagnosis for AD
A- EEG
B- PET scan
C- Plain X-ray
D- CAT scan
E- ultrasound
D- CAT scan
Which of the following is not a warning sign of Alzheimer’s disease
a. Depression
b. problems communicating
c. mental confusion
d. all of above are warning signs for AD
d. all of above are warning signs for AD
In Alzheimer’s disease, cleavage by which enzyme leads to a generation is insoluble
plaques?
a. Acetylcholinesterase
b. gamma secretase
c. beta secretase
d. carbonic anhydrase
e. choline acetyltransferase
c. beta secretase
With Alzheimer’s disease, the cortical atrophy and loss of neurons is mostly seen
a. frontal and temporal lobes
b. parietal and temporal lobes
c. occipital and temporal lobes
d. cerebellum and temporal lobes
e. midbrain and basal ganglia (nuclei)
a. frontal and temporal lobes
Which of the following is not a drug involved in the treatment of AD?
a. Aricept
b. Memantine
c. Exelon
d. L-Dopa
e. Lecanemad
d. L-Dopa
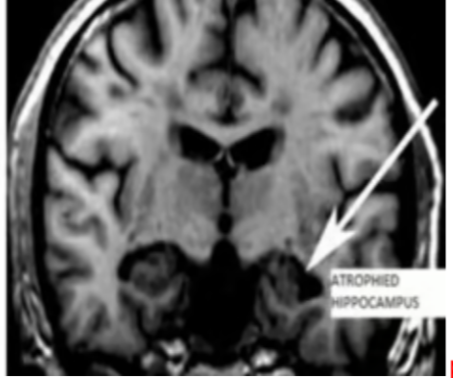
The image above most likely is from a patient with
Alzheimer
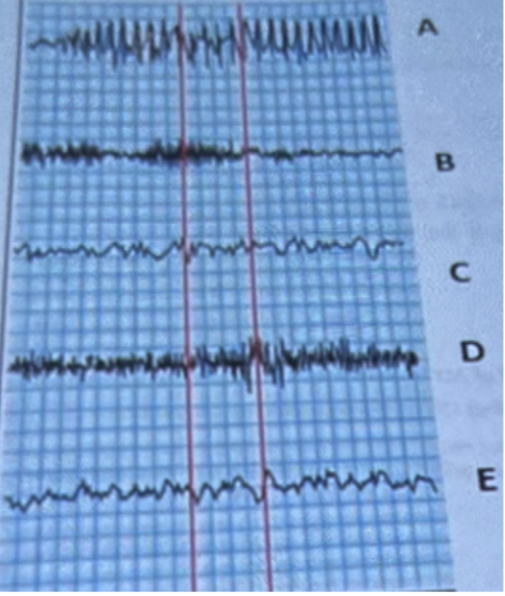
Which letter in the above shows a recording from a patient with cerebral embolism?
E

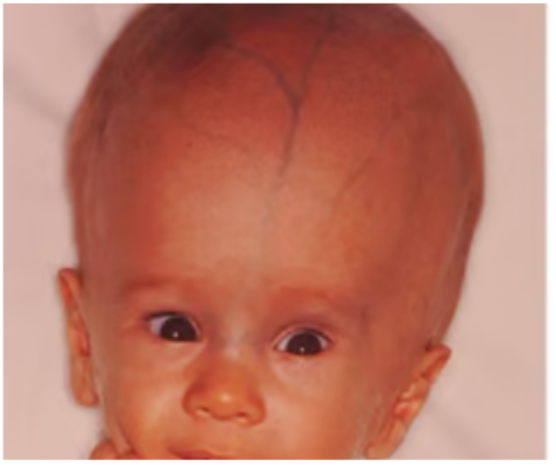
The above photo shows
a. Hydrocephalus
b. Microcephaly
c. Acrania
d. anencephaly
c. Acrania
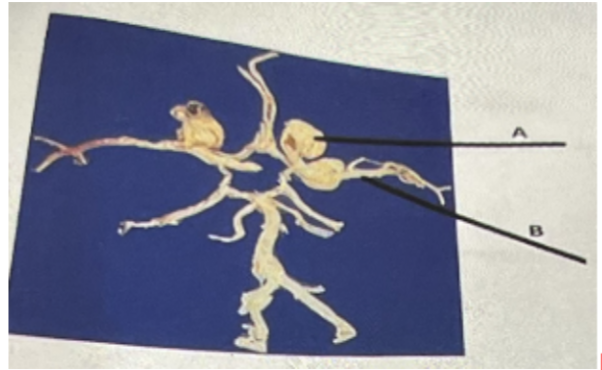
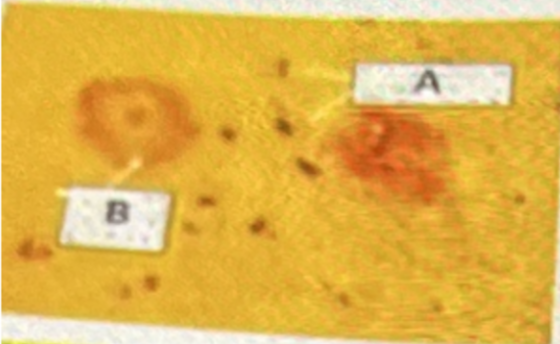
In the above photo, A represents
a. A tumor
b. Cancer
c. Aneurysm
d. Edema
c. Aneurysm
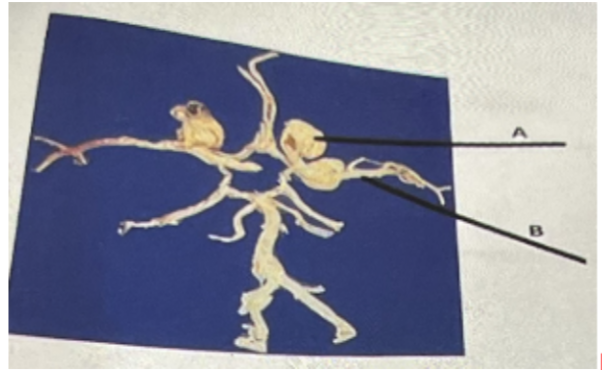
B in the above photo represents
a. Cerebral artery
b. Common carotid artery
c. Cerebellar artery
d. Internal carotid artery
Internal carotid artery