Edexcel igcse biology paper 2
1/273
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
274 Terms
What characteristics do all living organisms share?
Movement respiration sensitivity nutrition excretion reproduction growth
Organelles in both animal and plant cells?
Cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus. ribosomes, mitochondria
What are the organelles that plant cells have that animal cells dont have?
Chloroplast, vacuole, cell wall
What does the nucleus do?
Controls activity of the cell
What does the cell membrane d
Controls entry and exist of substances into the cell like oxygen, water, carbon dioxide but do not allow larger molecules like glucose, sucrose, proteins, and starch to enter
What does the cytoplasm do?
It is where chemical reactions take place
What does mitochondria do?
Where aerobic respiration takes place to release energy
What do ribosomes do?
Protein synthesis (where proteins are made)
What is the role of vacuoles?
Filled with cell sap contains dissolved sugars and mineral ions
What is the role of chloroplasts?
To carry out photosynthesis
What is the role of cell wall?
To protect and support the cell which is made out of cellulose in plant cells
What are the 2 types of cells
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic
What does eukaryotic mean
It has membrane bound organelles e.g. animal cells have mitochondria, chloroplasts, nucleus
What does prokaryotic mean?
No membrane bout organelles, e.g. bacteria and viruses
What features does a bacterial cell have?
Cytoplasm, cell membrane, cell wall made of peptidoglycan, cell capsule, mitochondria, nucleoid (circular strand of DNA/Chromosome), plasmid (rings of DNA) , flagellum
What is a pathogen?
A microorganism that causes disease
Some bacteria are pathogenic, which?
Pneumococcus (responsible for pneumonia), tuberculosis (coughing up blood)
What bacteria are useful?
Lactobacillus (yoghurt)
Are viruses bigger or smaller than bacteria?
Smaller and made of DNA or RNA, envelope, Protein coat
What do viruses not do?
Excrete respire grow, eg flue cold hiv
What does tobacco mosaic virus do in plants?
Causes discolouration in plant leaves due to prevention of chloroplast formations
Examples of protoctists?
Chlorella and algae (both have chloroplasts), amoeba (dont have cell wall or chloroplasts), plasmodium (pathogenic because it causes malaria via mosquitos)
Are protoctists unicellular or multicellular?
Both
What is cell wall in fungi made of?
Chitin
Examples of fungi?
Mucor, mushrooms
What do fungi have?
Thread like structures called hyphae that form a network called mycelium
What nutrition to fungi carry out?
Saprotrophic nutrition which is the extracellular secretion of enzymes onto dead matter to break down and absorb as food
What fungi is used in yeast and bread making?
Yeast, for anaerobic respiration o break down glucose into ethanol and CO2 (ethanol is needed for beer, CO2 is needed for bread rising)
What are the 5 kingdoms?
Plants, animals protoctists, bacteria, fungi
How are carbohydrates stored in animals fungi plants
glycogen, glycogen starch
What is a cell?
A group of organelles working together to perform the same function
What is a tissue?
A group of cells working together to perform the same function
What is an organ?
A group of tissues working together to perform the same function
What is an organ system?
a group of organs working together to perform the same function
What are all the organ systems in the body named?
Digestive system, endocrine system, reproductive system, circulatory system, respiratory system, nervous system, excretory system
What organs make up the digestive system?
Stomach, oesophagus, pancreas, large intestine, small intestine,
What is a zygote?
When the sperm and egg meet at fertilisation you form 1 cell called a zygote which has to divide to form the embryo. It divides by mitosis 2 cells —>3—>8—>16….
What is differentiation?
The process by which cells become specialised, e.g nerve cells
What is a stem cell?
A cell that has the ability to divide many times without becoming differentiated.
What are the 2 types of stem cells?
Embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells
What can embryonic stem cells do?
Embryonic stem cells can differentiate into any type of cell, e.g. if you have a damaged liver, they can make you a new liver. This means it can treat many diseases
What can an adult stem cell do?
It doe snot have the ability to differentiate or specialise into any type of cell, it’s stuck to only making 1 type of cell so it has limited use such as making bone marrow
What does leukaemia do?
It affects the blood by destroys white blood cells?
How do you fix leukemia?
Chemotherapy, which uses chemicals do destroy cancer cells but an issue is that it can also affect healthy cells and kill them, But the thing that stem cell therapy then does is that it can replace those damaged cells with new cells
What is the disadvantage of stem cell therapy?
The ethics because they come form aborted fetuses, miscarried fetuses
What elements are found in carbohydrates?
Carbon hydrogen oxygen
What elements are found in proteins?
carbon hydrogen oxygen nitrogen
what elements are found in lipids
3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol
What is an enzyme?
It is a biological catalyst which means it speeds up the rate of a reaction without being used up
Enzymes and the active site image?
this
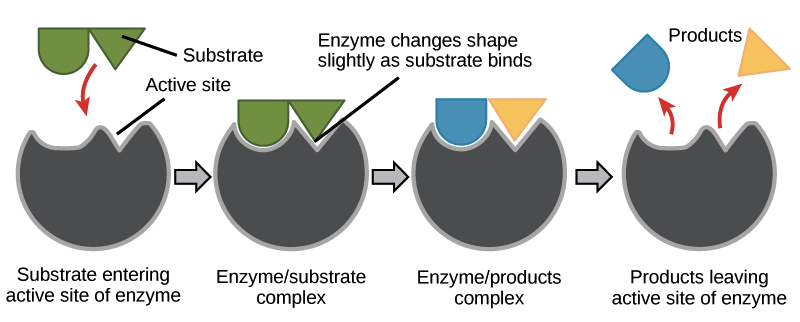
What do enzymes usually end in?
ase
Amylase is an enzyme, what is it made in?
It is made in salivary glands and small intestines and pancreas, what it does it catalyses the breakdown of starch into glucose, in this case, starch is the substrate (the thing entering the amylase enzyme) and the product is glucose, amylase has been broken down into a small simpler sugar named glucose
What does protease do?
It breaks down proteins into amino acids, it is found in your stomach, small intestine, pancreas
What is lipase?
It breaks down lipids into fatty acids and glycerol and is made in small inestine and pancreas
What happens as you increase temperature of enzymes?
enzyme activity increases because enzymes are colliding more often, when it reaches its peak, the enzymes and substrates are coming together more frequently, after this temperature of 37 degrees usually, there is a massive decrease in enzyme activity because they have become denatured (pH also does this)
What are the 3 types of transport?
Diffusion, osmosis and active transport
What is the definition of diffusion?
The net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration, diffusion doesn’t require energy
Definition of osmosis?
The net movement of water molecules from an area of high water potential to an area of low water potential across a partially permeable membrane, it doesnt require energy
What is active transport?
It requires energy, the net movement of particles from an area of low concentration to high concentration
Wht is diffusion quick in amoeba (small organism)?
They are single celled and have a high surface area to volume ration so diffusion occurs quickly
Why is diffusion too slow in multicellular organisms (large organisms)?
Because they have a small surface area to volume ration so diffusion is too slow whhich is why they have a circulatoiry system
What is photosynthesis?
It is carried out in chloroplasts of the plant which absorb light to carry it out
What is the photosynthesis equation?
Carbon dioxide + water—> glucose + oxygen, this is good because lots of O2 is created
What are the limiting factors of photosynthesis?
CO2, light intensity, temperature
Definition of limiting factor?
A factor in a reaction which is in the shortest supply and a lack of this factor is why the rate of reaction no longer increases
In the morning, why is a temperature and light intensity a limiting factor?
It means enzymes have little kinetic energy
What is the limiting factor of photosynthesis at midday?
CO2 levels
At night what do plants do?
Because they can’t photosynthesise due to lack of sunlight, it will just be respiring so more Oxygen enters the leaf than exit
What are the adaptions of leaf?
large surface area, thin (so gases don’t need to diffuse too far), flat
Structure of a leaf image?
this
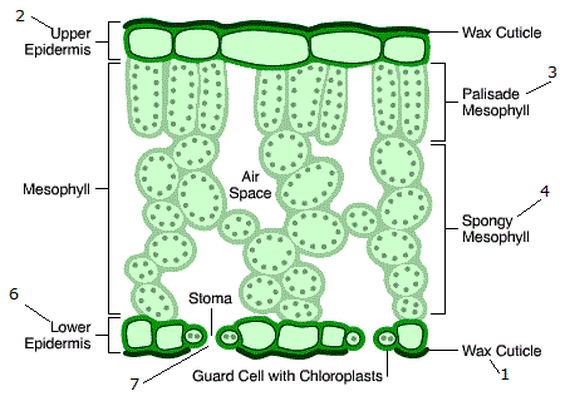
What is waxy cuticle for?
Prevent transpiration (loss of water form the leaf)
What is the upper epidermis for?
Transparent to allow light to enter the leaf
What is palisade mesophyll for?
Contains lots of chloroplasts which absorb light in photosynthesis
What is spongy mesophyll for?
it has air spaces to allow gases to diffuse (Co2 and O2)
What is the vein containing xylem and phloem for?
the xylem brings water to the leaf, the phloem removes sugar
What is guard cells for?
Controlling opening and closure of stomata
What is stomata for?
Allowing CO2 into the leaf and oxygen out
What is glucose in photosynthesis used to make
Proteins, fats, cellulose for cell wall, starch for storage
What are mineral ions absorbed for the soil by?
Active transport into the root hair cell (magnesium and nitrates)
What is magnesium used to makee?
Chloroplasts
What does magnesium deficiency look like?
Yellow leaves
What does nitrate defficiency look like?
Stunted growth in plants
What is the definition of digestion?
The break down of large insoluble molecules into smaller soluble ones (so that it can be absorbed through the walls of the small intestine)
What is mechanical digestion?
It takes place in the mouth teeth when food is broken into smaller chunks, (chemical digestion is when amylase digests starch into glucose), The food then passes through the osoeephagus through peristalsis (muscular contractoins push the bolus of food down the oesophagus) down into your stomach, in stomach the muscular linings of the stomach help churn the food, in stomach HCl is also secreted o break down he food and kill pathogens
What is a pathogen?
A microorganism which causes disease
What is bile?
A greeen liquid made in liver, stored in gall bladder, released into small intestines to emulsify large fat droplets into smaller droplets to create a much larger surface area so that lipase can work more easily on the lipd molecules, bile also neutralises the stomach acid (HCl)
How is the small intestine adapted for its role?
It has large SA provided by villi and microvilli, lots of capillaries, thin wall for short diffusion distance, lacteals for absorptions of fats
After food passes the small intestine what does it do in th large intestine?
Water is reabsorbed into the blood
Where are faeces stored?
Rectum before the leave the body via the anus (this is named egestion)
Do you extrete or egest faeces?
You egest them
What is excretion definition?
The removal of waste products of metabolism
What is ingestion definition?
The process of taking in food to the mouth
What is metabolism definition?
The rate at which chemical reactions take place
What is the definition of assimilation?
The build up of large molecules from small ones
What does a balanced diet contain?
carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, fibre, water
What are carbs an important source of?
Energy
What is protein good for?
The growth and repair of muscles
What is the disease form lack of protein?
Kwashiorkor (stomach comes out very far)
What are fats?
A very concentrated source of energy, also used for insulation
Where is vitamin C found and what is it food for?
Citrus fruits, important for repair of tissues