Lecture: Single Species Population Growth
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
population and communities Lecture one
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
: What does population ecology study?
Changes in population size and structure and the mechanisms behind them.
What defines a population in ecology?
A group of individuals of the same species sharing a location, interacting (competing, breeding, cooperating), and experiencing the same environment.
What are the main ways to characterize populations?
Abundance, biomass, density, age/size structure, genetic structure, growth rate.
Why is genetic structure important?
It affects evolution and long-term survival.
What characterizes exponential growth?
Constant growth rate, independent of population size.
What's the limitation of exponential growth models?
They are only realistic short-term; they ignore resource limits.
What is logistic growth?
Growth slows as population nears carrying capacity (K).
What does the logistic equation show?
Growth rate decreases as population size approaches K.
Orthologistic Growth (Positive Density Dependence)
Q: When does orthologistic growth occur?
When growth accelerates with increasing population size due to cooperation.
What does a simple exponential growth program for bacteria illustrate?
Exponential growth becomes unrealistic without limits—it could "fill the oceans."
What’s the lesson from exponential bacterial growth?
Real-world factors must cap growth.
What's the difference between discrete and continuous models?
Discrete: step-based; Continuous: smooth/infinitesimal time steps.
What are pros and cons of discrete models?
Pros: Easy to simulate. Cons: May overshoot or oscillate.
What did Darwin show with elephants?
Even slow breeders would overpopulate Earth without checks.
What does this support in population theory?
Natural limits like death and limited resources are essential.
What happens with delayed feedback in population systems?
Populations overshoot and oscillate.
What is the "driving blind" analogy about?
Delayed feedback leads to instability—like driving with eyes closed periodically.
What does plotting population vs. time reveal?
Growth type—exponential, logistic, or chaotic.
What can plots of individual reproduction rates show?
How individual behavior changes with population size.
What is chaos in population dynamics?
Sensitive dependence on initial conditions causing unpredictable outcomes.
What makes a chaotic system unique?
It’s deterministic but behaves unpredictably.
What is a bifurcation diagram?
A visual showing system behavior (stable, periodic, chaotic) as parameters change.
What happens to population behavior as the growth rate increases?
It can shift from stability to periodic cycles to chaos.
What are key properties of chaos in population models?
Deterministic but unpredictable
Infinitely many patterns
Sensitive to initial conditions
What does chaos suggest about simple models?
They can produce complex, unpredictable behaviors.
Who introduced chaos to different scientific fields?
Henri Poincaré: Math
Edward Lorenz: Weather
Robert May: Population models
Ian Stewart: Recognized the logistic equation's significance
What is the main conclusion from population dynamics studies?
Simple internal rules and feedbacks can cause complex population fluctuations without external influences.
factors influencing growth
limits to growth
starting population
how fast it grows
K strategists
type 1
live to old age
few offspring
high parental care
Both K and R
type 2
constant survivorship
many offspring
some parental care
R strategists
type 3
low early and high late survival
many offspring
no parental care or little
discrete exponential growth equation
N(t+1)=N(t)xR
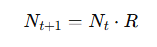
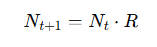
discrete exponential growth equation (after multiple time steps):
N(t)=N(0)xr^t
N(0) = initial pop size
t=number of timesteps
continuous exponential equation
dN/dt=rN