EXSS 288 Exam 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
1
New cards
Define Emergency medical services (EMS) system
A network of community resources and medical personnel
2
New cards
What is the purpose of EMS?
bring rapid medical care to a victim with a life-threatening injury or illness
3
New cards
The survival and recovery of critically injured or ill victims depends on:
1. Early recognition and response
2. Early activation of the EMS system
3. Care provided until more advanced medical personnel take over
4. Pre-hospital care provided by advanced medical personnel
5. Hospital care
6. Rehabilitation
4
New cards
A lay responder is:
someone who has not been professionally trained to a higher level of medical care.
5
New cards
What is the bystander effect?
The bystander effect is the social theory that states individuals are less likely to offer help to a victim in the presence of other people (great number of people, the less likely they are to help).
6
New cards
a professional responder is:
Someone who is trained with a duty to act
7
New cards
When a lay responder calls 911 to activate EMS, what information should they provide?
1. Name
2. Describe the situation
3. Number of individuals involved
4. Location and directions
5. What treatment is being given
Wait for a dispatcher to tell you what to do
8
New cards
What should you do until advanced personnel arrive?
1. Stay with the victim
2. Monitor the situation
3. Adjust care as needed
4. Inform advanced personnel
9
New cards
What are examples of professional rescuers?
police officers
Fire fighters
Lifeguards
Athletic trainers
Fire fighters
Lifeguards
Athletic trainers
10
New cards
A professional rescuer must keep what current?
Their certification
Knowledge of new issues and developments in emergency care
Knowledge of new issues and developments in emergency care
11
New cards
Who handles pre hospital care?
Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTS)
12
New cards
Describe the differences between EMT-Basic, EMT-intermediate, and paramedics
EMT-Basics are responsible for providing basic emergency treatment for respiratory, trauma, and cardiac emergencies. EMT-intermediates are trained to administer some medications and intravenous fluids. Paramedics provide advanced medical care for critical patients with sophisticated medical equipment and about 30 types of drugs.
13
New cards
Who cares for a patient when they arrive at a hospital?
Physicians, nurses, medical specialists, and other health care professionals
14
New cards
What is the purpose of rehabilitation?
Return the victim to their previous state of health
15
New cards
What are the two umbrella groupings within sports medicine?
Human performance and injury management
16
New cards
What roles fall under the human performance group of sports medicine?
Exercise physiology, biomechanics, sport psychology, sports nutrition, and sports massage
17
New cards
What roles fall under the injury management group of sports medicine?
practice of medicine
Sports physical therapy
Athletic training
Sports physical therapy
Athletic training
18
New cards
Who is most directly responsible for all phases of health care in an athletic environment?
Athletic trainer
19
New cards
What are the main roles of an athletic trainer?
injury prevention, providing initial first aid and injury management, evaluating injuries, designing and supervising rehabilitation
20
New cards
Athletic trainer works under direct supervision of a:
team physician
21
New cards
What are some roles of the team physician?
Serves to advise and supervise the athletic trainer
Compiling medical histories and conducting physical exams (pre-participation screenings)
Diagnosing an injury
Deciding on disqualifications
Compiling medical histories and conducting physical exams (pre-participation screenings)
Diagnosing an injury
Deciding on disqualifications
22
New cards
Who has the final say on when an athlete returns to competition following injury?
Team physician
23
New cards
True or false; fitness professionals exemplify the relationship between performance enhancement and injury prevention
True
24
New cards
Sports medicine team is part of the _______ in athletic settings
EMS System
25
New cards
Who works through emergency situations, as well as assisting in injury prevention and rehabilitation?
Sports medicine team
26
New cards
What are the three key things to remember in regards to an emergency action plan?
1. Provide steps and guidance for what to do in an emergency situation
2. Should be reviewed at least once per year with all involved personnel
3. Helps to ensure that the best possible care is provided in an emergency
27
New cards
What should an emergency action plan include?
1. Venue directions (map)
2. Emergency personnel
3. Emergency communication
4. Emergency equipment
5. First responder roles
28
New cards
What are blood borne pathogens?
Bacteria and viruses present in blood and bodily fluids, which can cause disease in humans
29
New cards
What are the 3 most common blood borne pathogens?
1. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
2. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
3. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
30
New cards
What is hepatitis B?
* liver infection resulting in swelling, soreness, and loss of normal liver function
* Signs include flulike symptoms, fatigue, weakness, nausea, headache, fever, possible jaundice
* Prevented by 3 part vaccination process over 6 months
* Signs include flulike symptoms, fatigue, weakness, nausea, headache, fever, possible jaundice
* Prevented by 3 part vaccination process over 6 months
31
New cards
What is hepatitis C?
* liver disease caused by the Hep C virus
* Most common blood borne infection in the US (3-5 million cases, 67% infected with HCV develop liver disease)
* No vaccinations or treatment
* Most common blood borne infection in the US (3-5 million cases, 67% infected with HCV develop liver disease)
* No vaccinations or treatment
32
New cards
What percentage of Hep C victims show no symptoms?
80%
33
New cards
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV):
* virus that causes AIDS
* No vaccine, currently treated with “drug coctails”
* No vaccine, currently treated with “drug coctails”
34
New cards
What are the 4 conditions that must be met for a pathogen to spread?
1. Pathogen is present
2. Pathogen passes through correct entry site
3. Person is susceptible to pathogen
4. Sufficient quantity is present to cause disease
35
New cards
What are 3 ways a pathogen can spread?
1. Direct contact: infected bodily fluids from one person enter another’s body
2. Indirect contact: person touches and object that contains bodily fluid from an infected person
3. Droplet and vector borne transmission: person inhales droplets (like from a cough/sneeze), or skin is penetrated by an infections source (bite, sting, etc)
36
New cards
Who created universal precautions to protect against the spread of blood borne pathogens?
OSHA
37
New cards
What are the universal precautions to prevent blood borne pathogens?
1. Hand hygiene
2. Personal protective equipment (PPE)
3. Work practice controls
4. Equipment cleaning and disinfecting
38
New cards
What is the most effective measure to prevent the spread of infection?
Hand washing
39
New cards
When should you use alcohol based sanitizers?
1. When soap and water are not available
2. Hands are not visibly soiled
40
New cards
What are examples of personal protective equipment?
* disposable gloves
* Gown
* Mask
* Protective eyewear
* Breathing barriers
* Gown
* Mask
* Protective eyewear
* Breathing barriers
41
New cards
What are the workplace controls for blood borne pathogens?
1. Disposing of sharps in puncture resistant, leakproof, labeled containers
2. Avoid splashing, spraying, and spattering of infectious materials
3. Removing and disposing of soiled protective equipment
4. Cleaning and disinfecting all soiled equipment and surfaces
5. Not eating, drinking, smoking, applying cosmetics, or touching body area in environments where exposure is possible
6. Isolating contaminated areas
42
New cards
Define liability
The state of being responsible for harm
43
New cards
What is the scope of Practice?
The treatment that someone is allowed to provide based on their state and professionally dictated qualifications
44
New cards
True or false: The certification for CPR/AED for adult, child, and infant is different.
True
45
New cards
What is the standard of care?
The minimum level of care: communicate proper info to prevent injury, recognize the victim in need, attempt to rescue, and provide emergency care
46
New cards
What is negligence?
When you fail to do something someone with your same level of certification would do.
47
New cards
In order for there to be negligence, these 3 need to be in play:
1. Duty of care: you have a legal responsibility as you are certified and able to provide care
2. The standard of reasonable care was not met (ex within scope of practice, feel short to prevent further injury)
3. Damages; harm. This is the most important part if someone is being sued for negligence
48
New cards
What are the 3 types of torts?
* Nonfeasance: act of omission; forgetting to do something
* Malfeasance; act of commission; committing an act that is not under your qualification or certification
* Misfeasance; incorrect; doing something improperly, even when you have the qualifications to do it
* Malfeasance; act of commission; committing an act that is not under your qualification or certification
* Misfeasance; incorrect; doing something improperly, even when you have the qualifications to do it
49
New cards
True or false; training supersedes the Good Samaritan law
True
50
New cards
What is the Good Samaritan law?
encourages those with no duty to provide care to help in an emergency situation. They must
* act within their scope of practice
* Act in good faith
* Not be negligent
* Not expect anything in return
* act within their scope of practice
* Act in good faith
* Not be negligent
* Not expect anything in return
51
New cards
Duty of Care is a:
legal responsibility
52
New cards
What must you state when obtaining consent from a conscious adult or parent of a minor?
1. Name
2. Level of training
3. Ask permission to help
4. Explain suspected condition
5. Explain plan of care
53
New cards
What do you have if the victim is unconscious or a parent is not available to gain consent?
implied consent
54
New cards
What do you do if someone refuses care?
1. Call EMS and document!
2. Inform victim why they need care and what might happen if they don’t receive it
3. Always stay with them (don’t touch them)
4. May lead to battery if you do something despite their refusal
5. If the victim falls unconscious, implied consent will allow you to act
55
New cards
You could be held responsible for abandonment, unless:
1. The scene becomes unsafe
2. You are too tired to continue
3. The victim shows obvious signs of life
56
New cards
What is the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996?
HIPAA protects individually identifiable health information such as name, DOB, medications, test results, address, SSN, etc. Do not share any information regarding physical/mental health, providing or payment for health care that could identify a person.
57
New cards
Why should you always document everything?
* helps medical personnel treat a patient following your care
* Help create future preventative plans and protocols
* Can protect you in the case of a lawsuit
* Help create future preventative plans and protocols
* Can protect you in the case of a lawsuit
58
New cards
Who should you ask for forms to protect yourself agains a lawsuit following emergency care?
Hospital or EMS
59
New cards
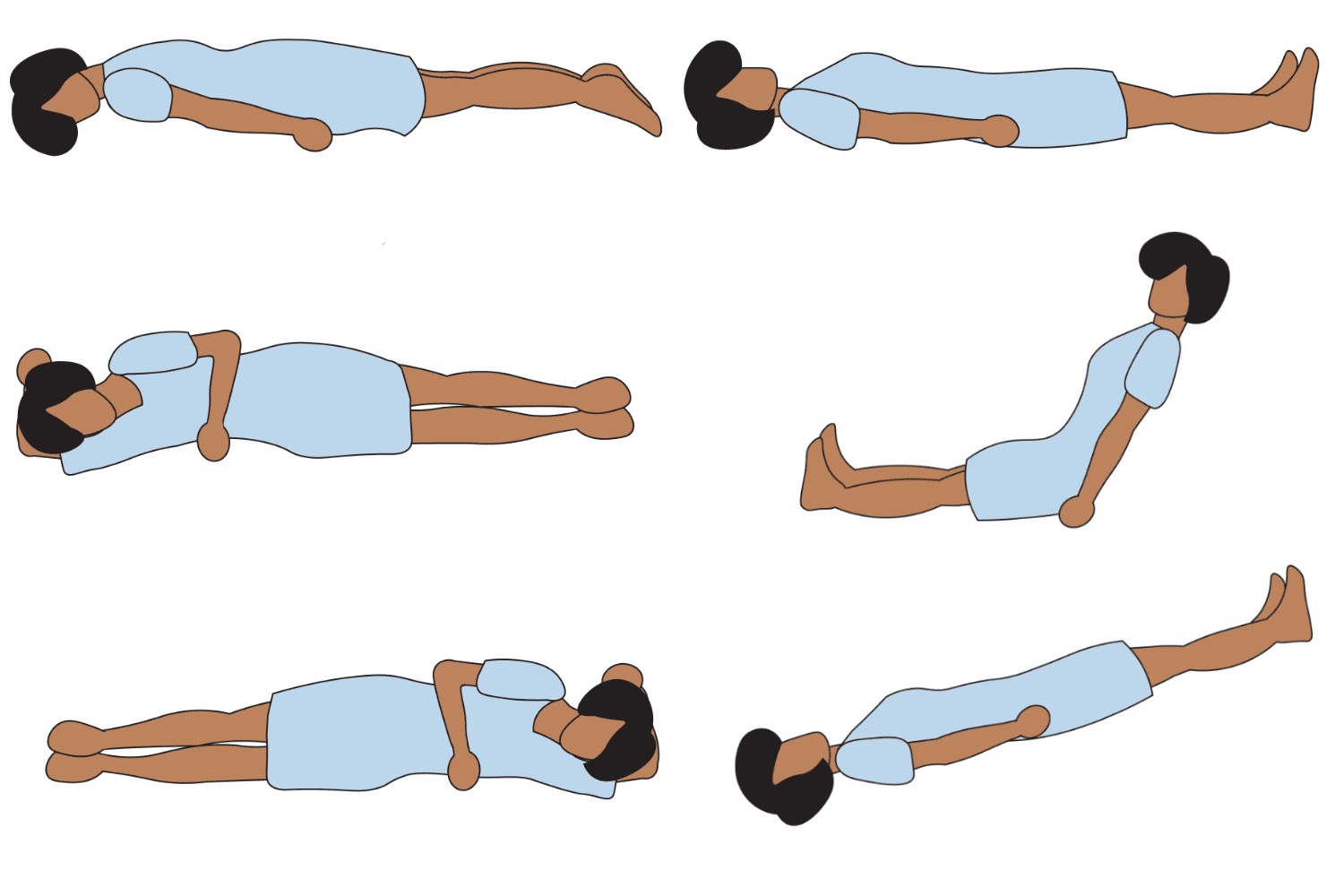
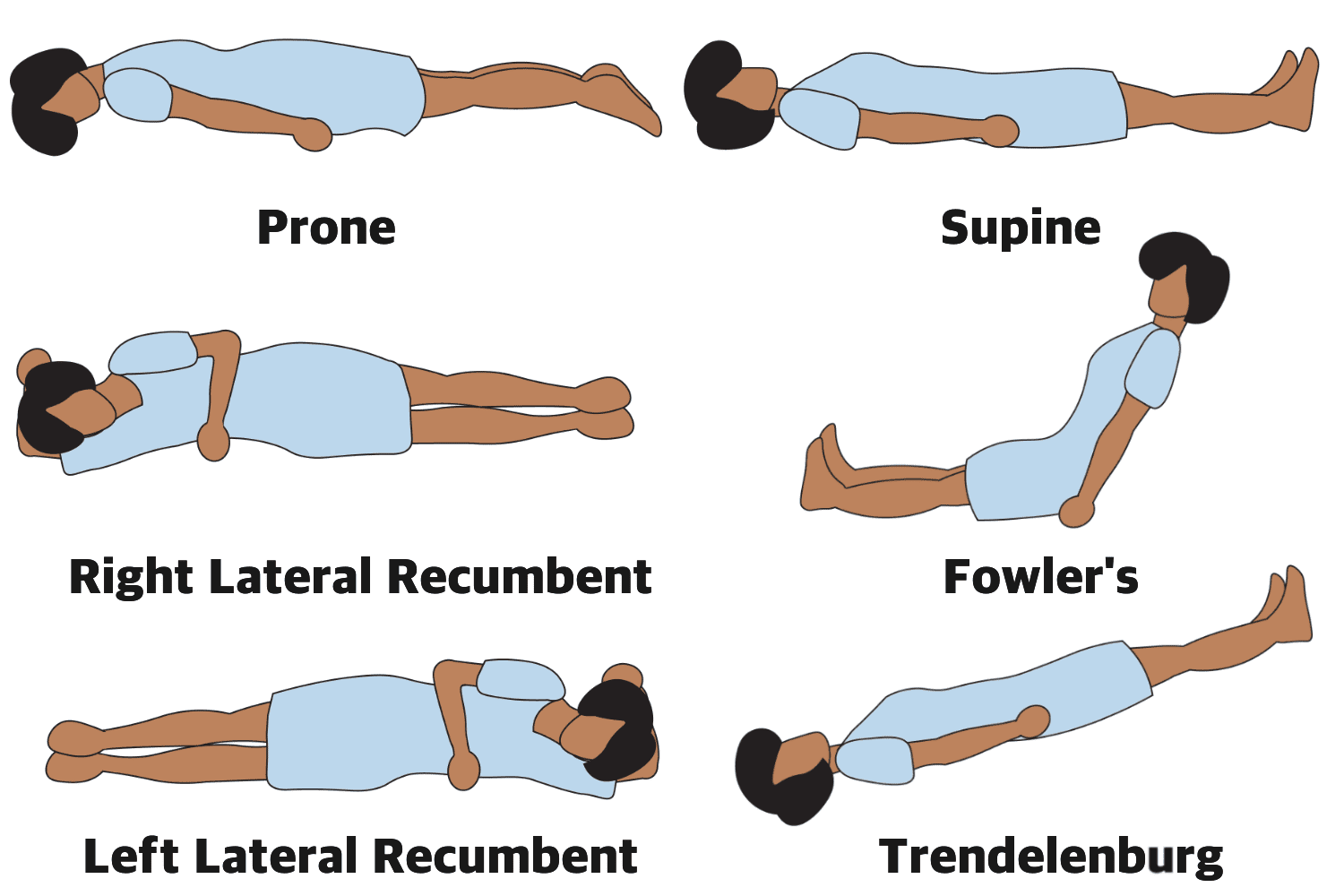
60
New cards
What are the 5 major body cavities?
* cranial
* Spinal
* Thoracic
* Adbominal
* Pelvic
* Spinal
* Thoracic
* Adbominal
* Pelvic
61
New cards
What is the purpose of the respiratory system?
To allow oxygen into the body and release CO2
62
New cards
What is the normal respiration rate for a resting adult and a resting child?
12-16 per minute for an adult
18-30 per minutes for a school aged child
18-30 per minutes for a school aged child
63
New cards
What is the purpose of the circulatory system?
carrying oxygenated blood throughout the body
64
New cards
What is the purpose of the nervous system?
Transmit signals, and regulate the body
It is the most complex of all the body‘s systems
It is the most complex of all the body‘s systems
65
New cards
What are the components of blood?
Red blood cells
White blood cells
Platelets
Plasma
White blood cells
Platelets
Plasma
66
New cards
What is the purpose of the musculoskeletal system?
* support the body
* Protect the organs
* Allow movement
* Store minerals
* Produce RBC
* Produce heat
* Protect the organs
* Allow movement
* Store minerals
* Produce RBC
* Produce heat
67
New cards
What is the purpose of the integumentary system?
(Skin)
Protection
Cooling
Protection
Cooling
68
New cards
What is the purpose of the endocrine system?
* regulatory system
* Pituitary gland regulates growth
* Thyroid regulates metabolism and nervous system
* Pancras is responsible for insulin
* Adrenal gland regulates sympathetic nervous system through hormone release
* Pituitary gland regulates growth
* Thyroid regulates metabolism and nervous system
* Pancras is responsible for insulin
* Adrenal gland regulates sympathetic nervous system through hormone release
69
New cards
What is the purpose of the digestive system?
Provides the body with electrolytes, water, and energy
Eliminates waste
Eliminates waste
70
New cards
What is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure?
systolic pressure is the maximum pressure the heart exerts while beating, while diastolic pressure is the amount of pressure in the arteries between beats.
71
New cards
What is the age range of a victim by age for respiratory trauma?
Adult is 12 and over
Child is 1-12
Infant is below 1
Child is 1-12
Infant is below 1
72
New cards
What is the age range of a victim by age for cardiac/AED trauma?
Adult is 9 and above
Child is 1-8
Infant is below 1
Child is 1-8
Infant is below 1
73
New cards
What are the 3 important steps to follow in an emergency?
1. Size up the scene
2. Perform a primary assessment
3. Summon advanced medical professional
74
New cards
True or false: care is the same for all ages of victim
False
75
New cards
What should you do when sizing up a scene?
use a careful and systematic approach that utilizes all of your senses quickly
1. Ensure safety
2. Identity necessary PPE
3. Determine MOI
4. Determine number of victims
5. Identify if helps is necessary
1. Ensure safety
2. Identity necessary PPE
3. Determine MOI
4. Determine number of victims
5. Identify if helps is necessary
76
New cards
What is a primary assessment?
used to assess and correct life threatening situations
Activate EMS
Activate EMS
77
New cards
What are the ABCs ?
airway
Breathing
Circulation
Breathing
Circulation
78
New cards
What are things to note in a primary assessment for an unconscious athlete?
1. Position
2. Responsiveness
3. Equipment considerations
4. ABCs
5. Provide care as determined
79
New cards
True or false: you should always remove equipment from an injured athlete to treat them
False; if possible, always leave equipment on
80
New cards
What are the 4 steps of performing a primary assessment?
1. Are the conscious?
2. Are they breathing?
3. Do they have a pulse?
4. Is there bleeding and is it severe?
81
New cards
How should you check for alertness?
Tap, shout, tap
AVPU
AVPU
82
New cards
What is the AVPU scale?
a scale used to assess alertness
Alert
Verbal
Painful
Unresponsive
Alert
Verbal
Painful
Unresponsive
83
New cards
What are the two ways to open an airway?
1. Head tilt chin lift
2. Jaw thrust (for when there is a suspected head/neck/spine injury?
84
New cards
True or false: when in doubt, assume there was a head, neck, or spinal injury.
True
85
New cards
How long should it take you to check for breathing?
No longer than 10 seconds
86
New cards
True or false: agonal gasps count as breathing
False
87
New cards
What are agonal gasps indicative of?
a cardiac issue
88
New cards
What pulse points should be used for adults and children?
carotid/radial for adult/children
Brachial for infants
Brachial for infants
89
New cards
What type of victims should be given two ventilations if found not breathing?
1. Drowning victims
2. Victims of hypoxia (low levels of oxygen)
3. Children and infants
90
New cards
What are the steps of giving ventilations?
1. Position and seal the resuscitation mask
2. Open the airway and blow into the mask
91
New cards
How often should ventilations be given?
For an adult, 1 every 5 seconds
For a child, 1 every 3
Ventilation should last about 1 second and make the chest clearly rise and fall
For a child, 1 every 3
Ventilation should last about 1 second and make the chest clearly rise and fall
92
New cards
What are 3 recovery positions?
1. Face up (maintain open airway)
2. Modified HAINES (High arm in endangered spine)
3. Infant recovery position
93
New cards
When should you call before giving care?
* if there is any cardiac condition
* Time dependent
* Unconscious adult
* Unconscious infant/child with a cardiac condition
* Time dependent
* Unconscious adult
* Unconscious infant/child with a cardiac condition
94
New cards
When should you provide care before calling?
* breathing emergency
* Drowning
* Cardiac arrest
* Drug overdosE
* Drowning
* Cardiac arrest
* Drug overdosE
95
New cards
When should you move a victim?
1. When the scene becomes unsafe
2. Reaching another victim
3. Need to provide proper care elsewhere
96
New cards
What is a normal BPM for a resting adult or child?
60-80 for adults
80-100 for children
80-100 for children
97
New cards
What is a normal respiration rate for a child and adult?
12 per minute for adults
20-25 for children
20-25 for children
98
New cards
What vital signs do you need to check for in a secondary assessment?
1. Pulse
2. Respiration
3. Blood pressure
4. Temperature
5. Skin color
6. Pupils
7. State of consciousness
99
New cards
How do you measure blood pressure?
with a sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff)
100
New cards
What is a normal blood pressure?
115-120 mmHg over 60-80 mmHg