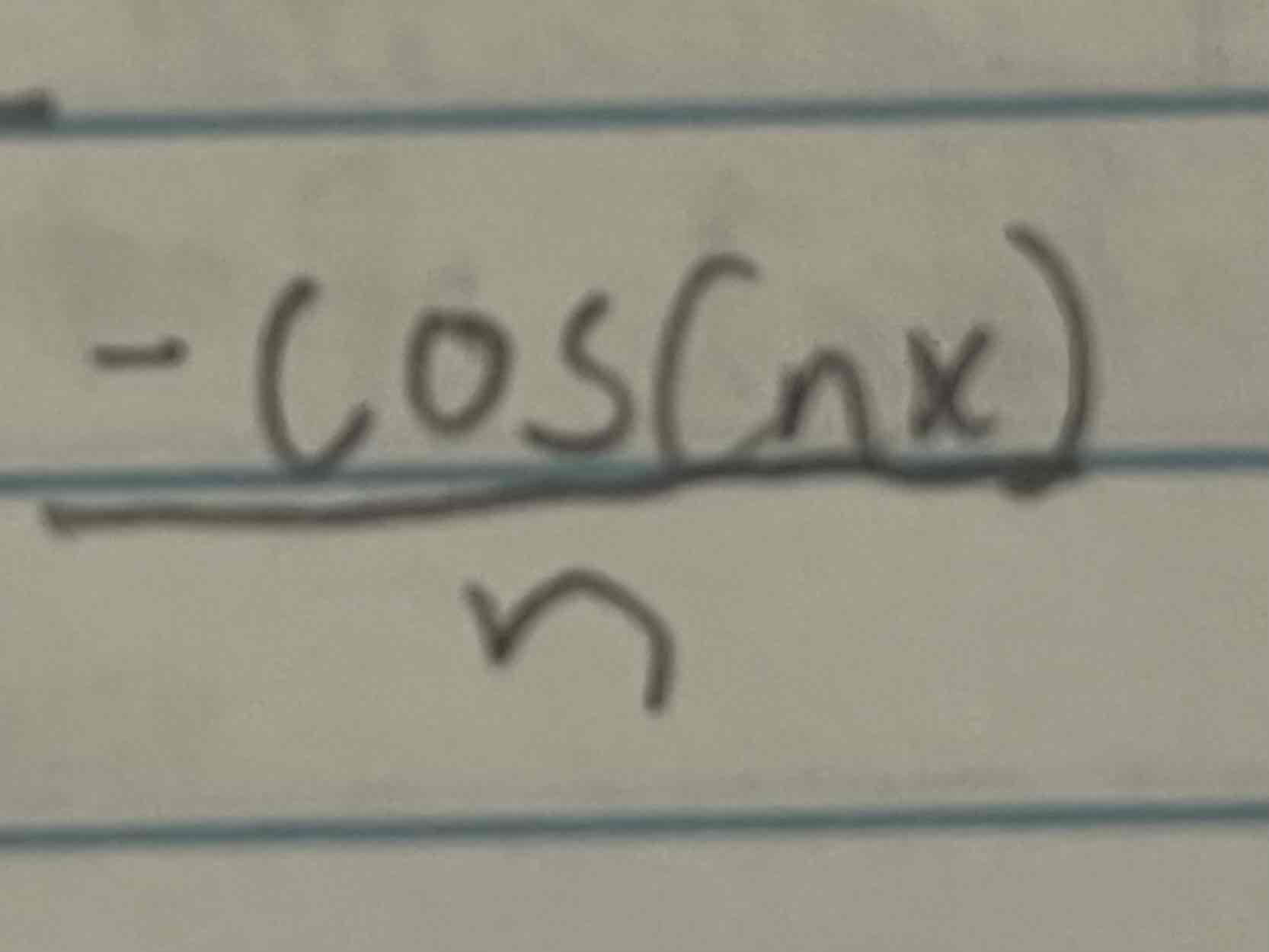Calc BC
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Definition of a derivative
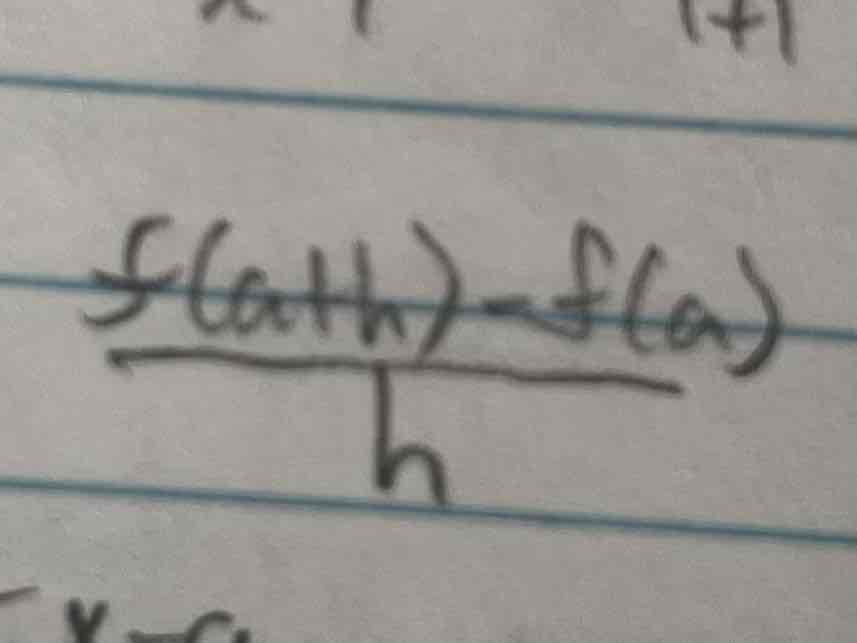
Product Rule
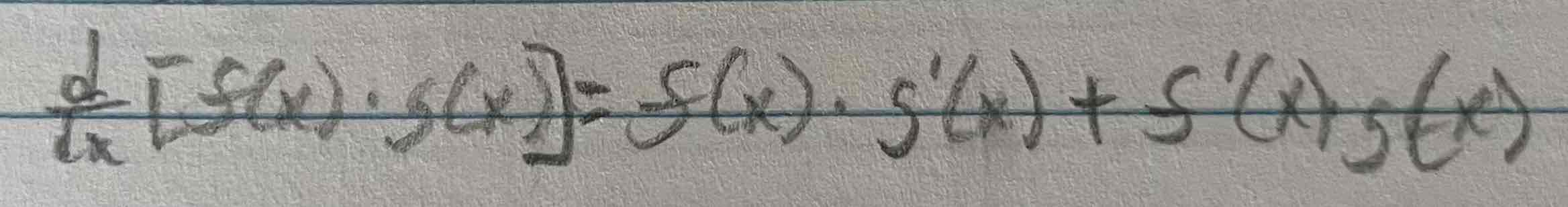
Quotient Rule
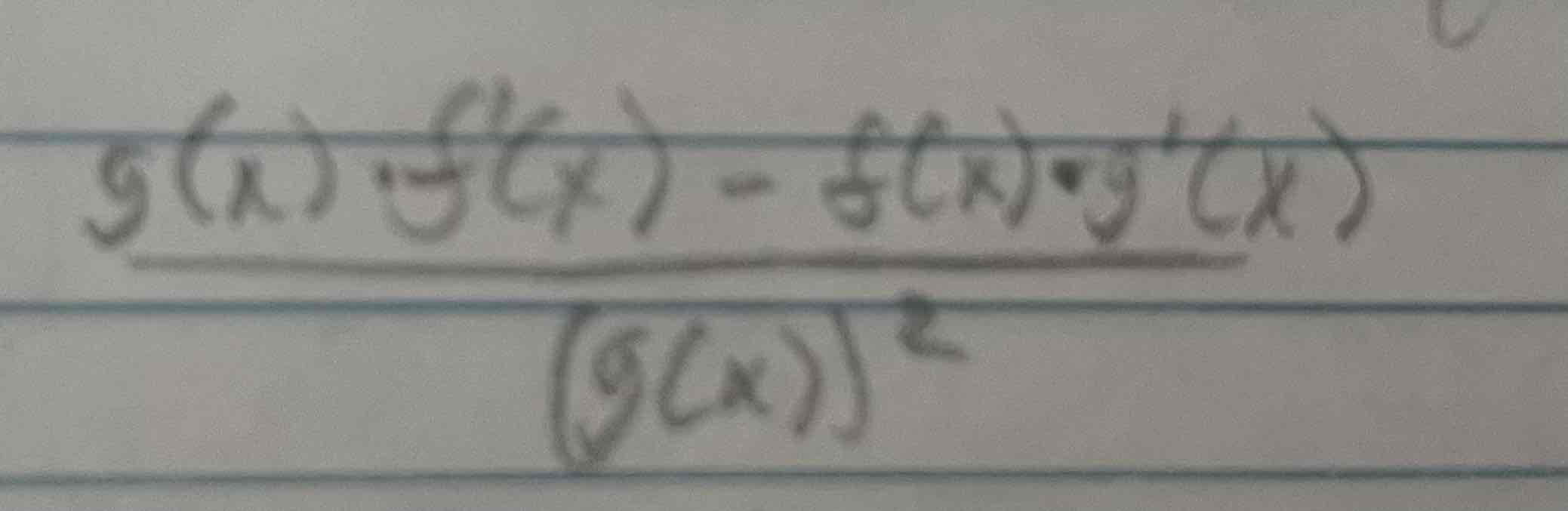
derivative of sin(x)
cos(x)
Derivative of cos(x)
-sin(x)
Derivative of tan(x)
sec²(x)
Derivative of sec(x)
sec(x)*tan(x)
Derivative of csc(x)
-csc(x)*cot(x)
Derivative of cot(x)
-csc²(x)
Chain Rule
F(x) = f(g(x)); f’(g(x)) * g’(x)
Derivative of a^x where a is a constant
a^x * ln(a)
Derivative of inverse sin(x)
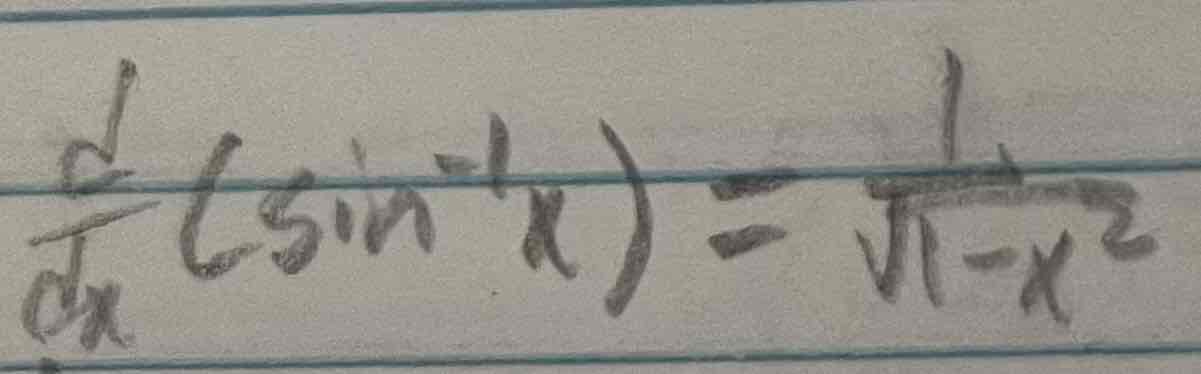
Derivative of inverse cos(x)
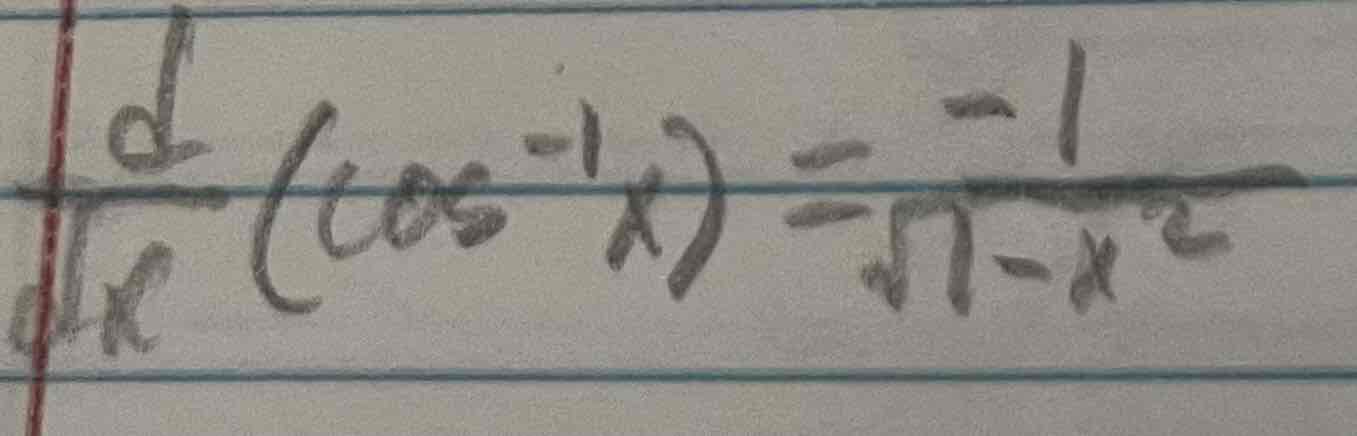
Derivative of inverse tan(x)
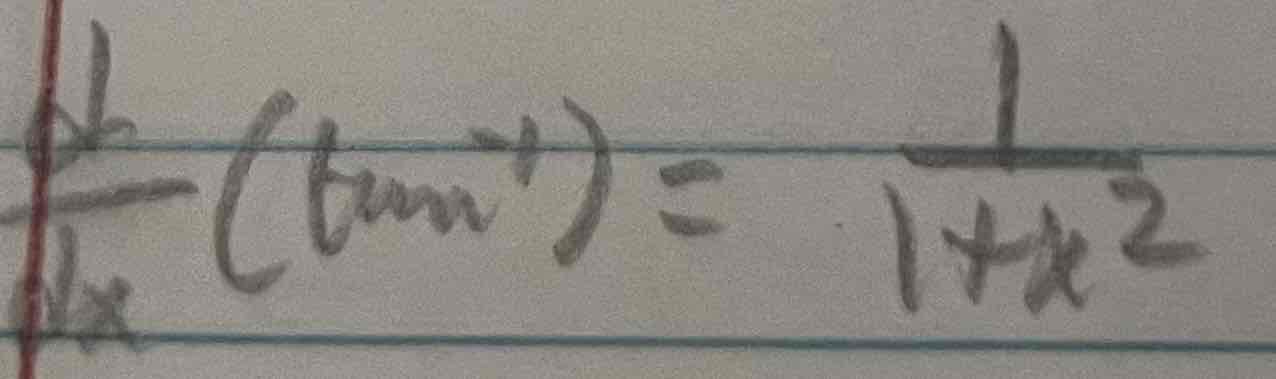
Derivative of inverse csc(x)
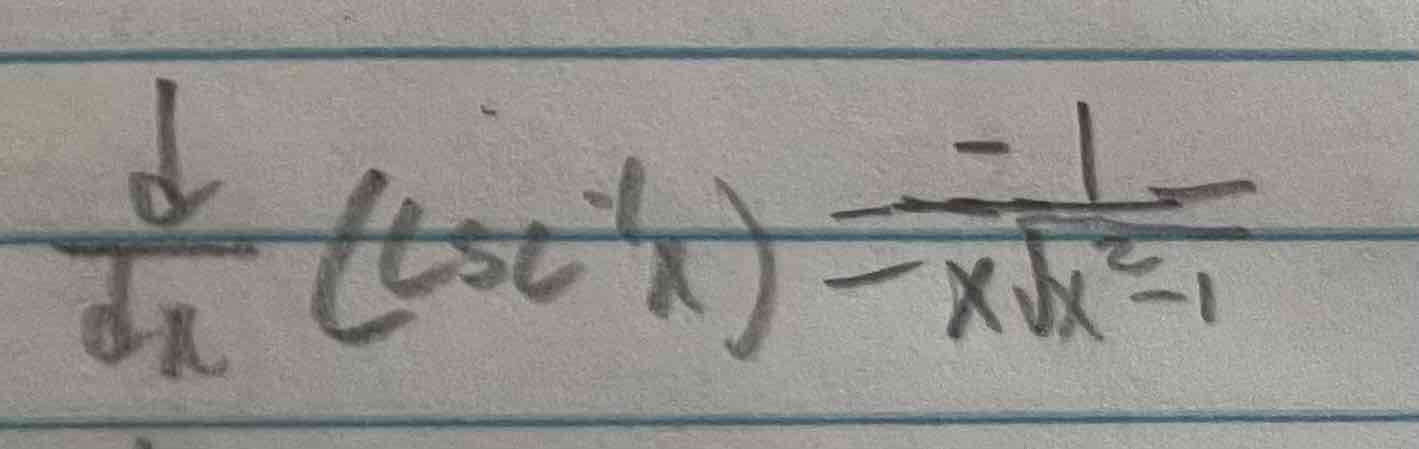
Derivative of inverse sec(x)
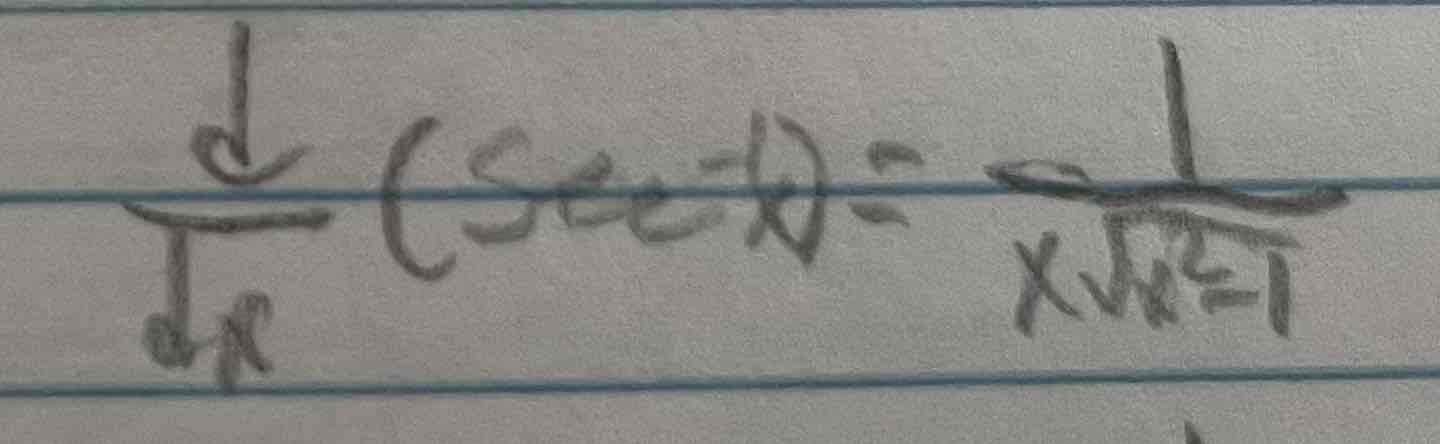
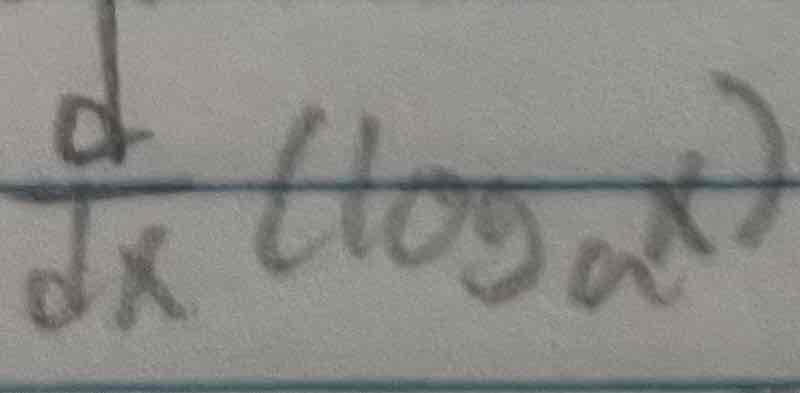
Derivative of log a of x
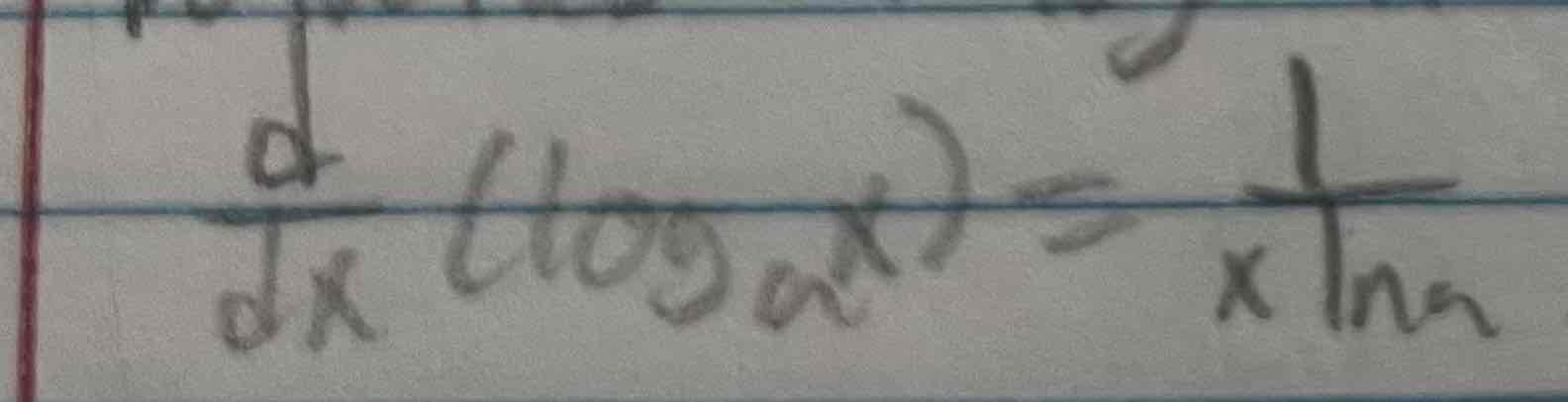
Derivative of ln(x)
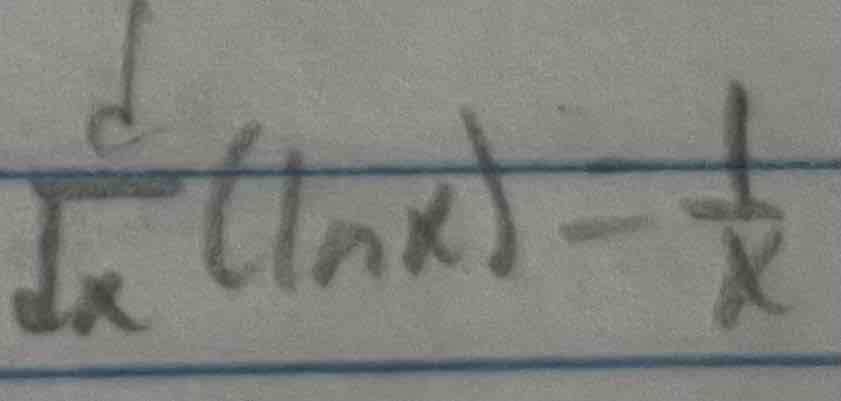
Rolle’s Theorem
Let f satisfy…
f is continuous on closed interval [a,b]
f is differentiable in open interval (a,b)
f(a) = f(b)
Then there is a number d such that f’(d) = 0
Fermat’s Theorem
If f has a local max or min at d and f’(d) exists, f’(d) = 0
Closed Interval Method
This finds extreme minimums and maxes of continuous functions on interval [a,b]
Find values of f at critical values of interval
Find values of f at endpoints on interval
Largest value of steps 1 and 2 is absolute max and smallest is absolute min
Integral of 1/x
ln(x): d in absolute value
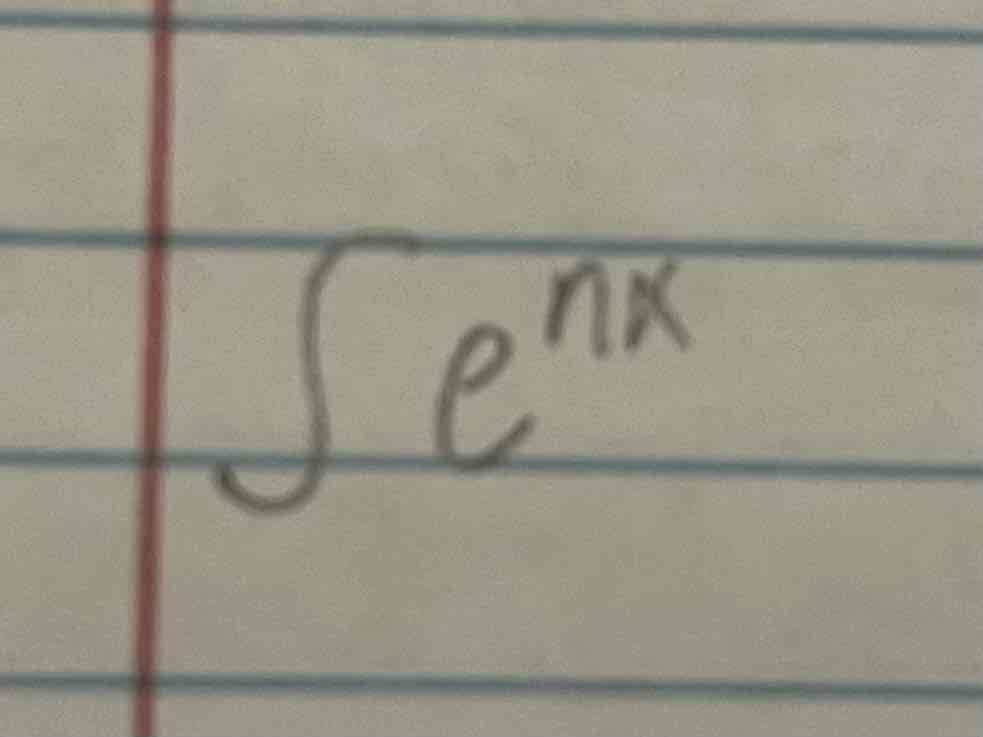
Integral of e^nx
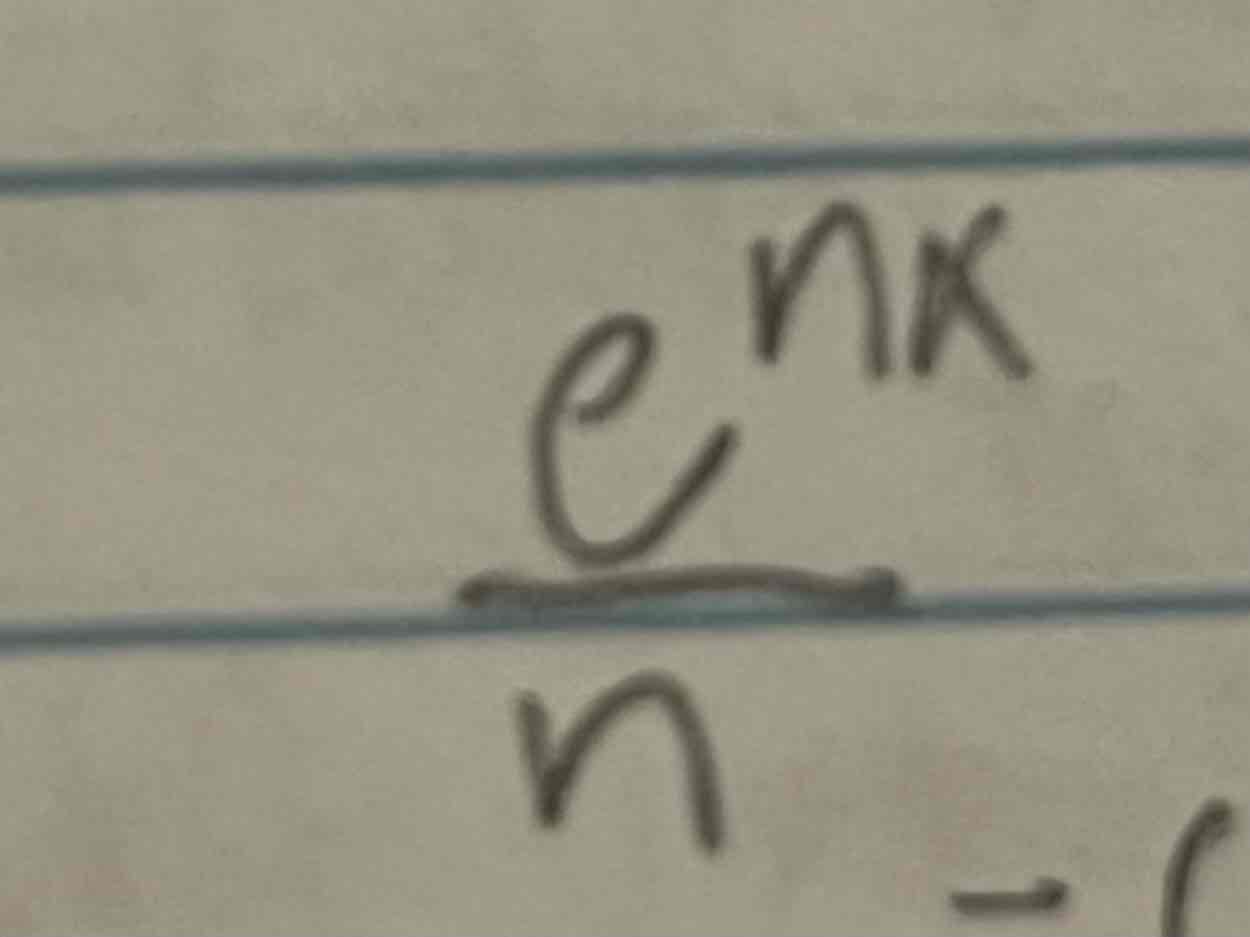
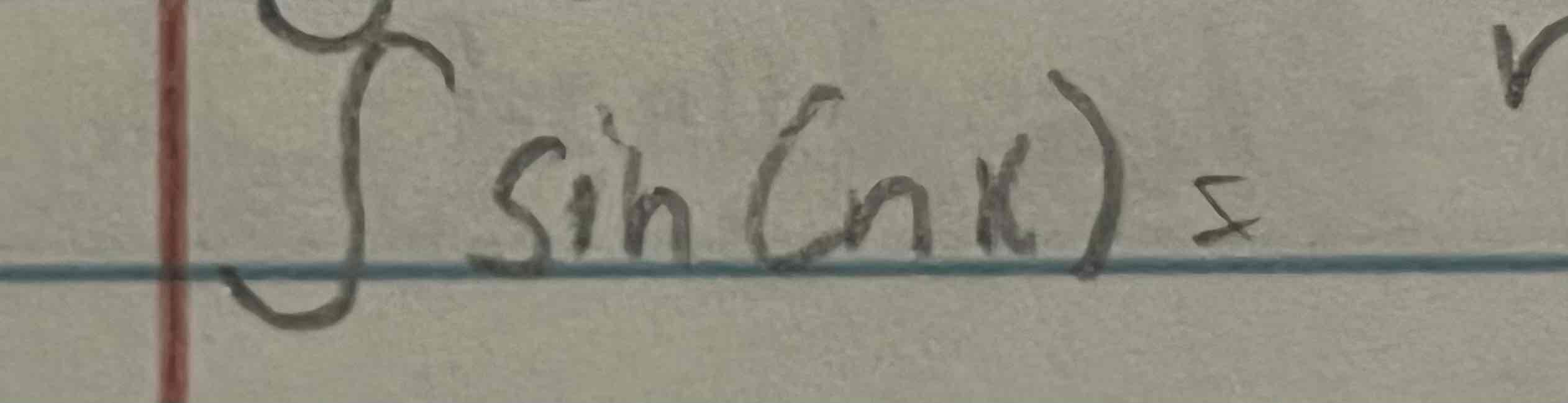
Integral of sin(nx)