UMD KNES 370 Exam 1
1/70
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Motor Development
study of changes in
motor behavior across the lifespan, the processes that underlie these changes, and the factors that influence them
Motor Control
The functioning of
the neuromuscular system to
activate and coordinate the
muscles and limbs involved in the
performance of a motor skill
Motor Learning
Relatively permanent changes in Motor skill capability associated with practice or experience
Motor Milestone
First Appearance of a type of motor behavior
Neuromaturational Perspective
Motor behavior develops as a result of maturational
processes — simple growth of nerve circuits, apparently
unfolding inevitably, and requiring no specific intervention.
Gestational Age
Time since the first day of the mothers last period (age before birth)
Chronological Age
Time since birth
Corrected Age
Time since due date (Chronological age-weeks born prematurely)
Dynamical Systems Perspective
Motor behavior emerges as a result of the interactions between the organism, environment, and task constraints
Stability
A behavior is stable if it may return to normal function following a small perturbation
Perturbation
A time varying factor that affects motor behavior
Attractor
a stable movement pattern
Types of Perturbations
internal (processing) or external (bumped into/surface variation)
Dynamical Systems vs Neuromaturational
Dynamical systems perspective emphasizes that
• The brain does not dictate behavior
• Developmental changes in other body systems are also
important
• The environment and task constraints are also important
• Changes in individual, environment
and task constraints interact
to produce developmental
changes
Constraint
a characteristic of an organism, environment, or task that limits some motor behavior while encouraging others
Individual Constraint
a characteristic of a persons unique physical and mental characteristics (height, weight, muscle size/strength)
Task constraints
Constraints outside of the organism and specific to the task (rules of the sport or properties of the equipment)
Environmental constraints
Properties of the environment not specific to the task (temperature, ground surface, sociocultural environment)
Rate limiter
a constraint that hold back or slows the emergence of a motor behavior
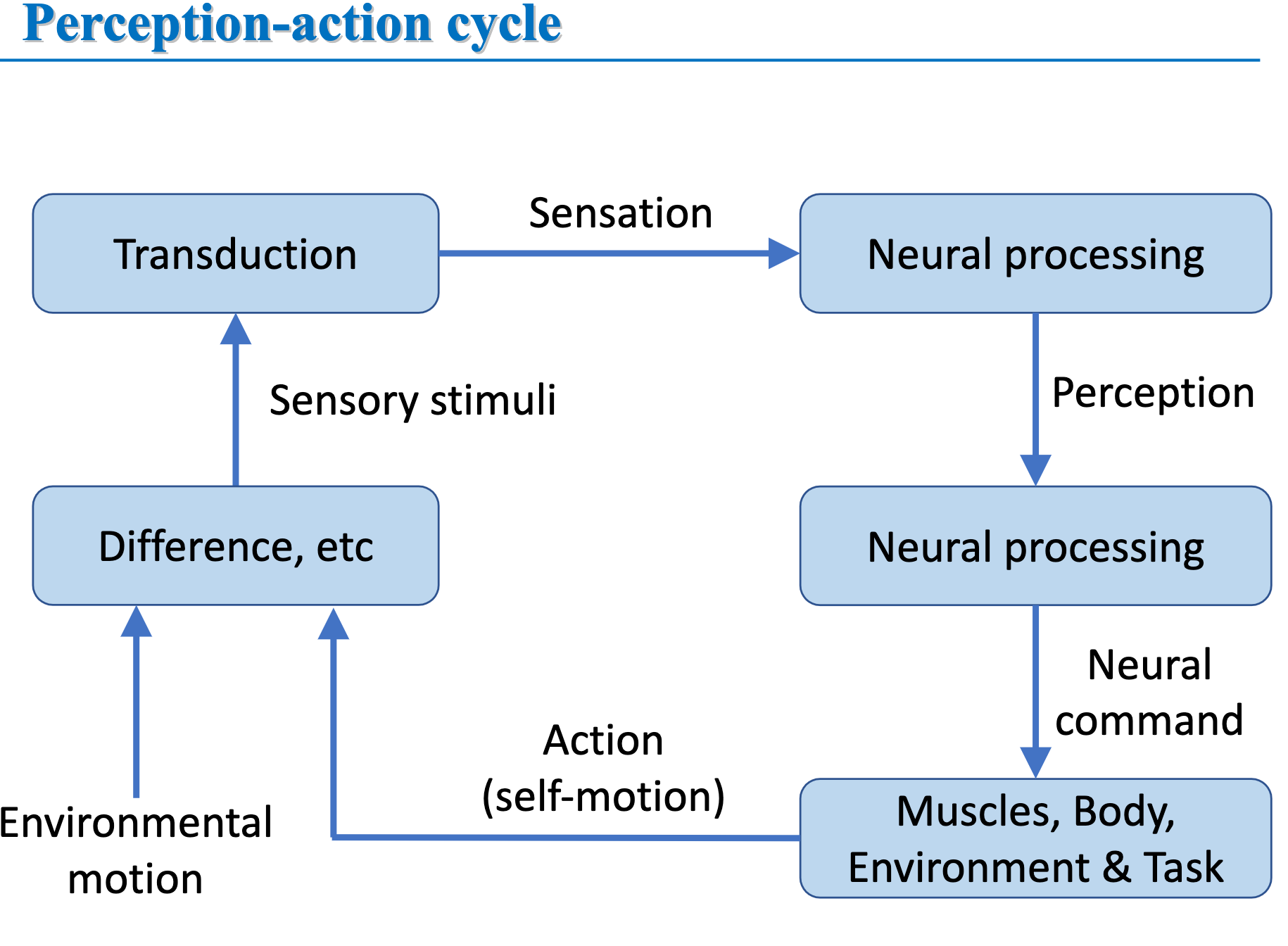
Transduction
conversion of one form of energy into another
Sensation
the initial neural activity triggered by a stimulus
Perception
Extraction of meaning from sensation (brain selecting, processing, and organizing information)
Perception-Action Cycle
Visual Acuity
Ability to perceive fine visual patterns (Bad @ birth, declines from 20-50 rapidly)
Visual accommodation
The ability to change focus between near and far objects (None @ birth, best @ 7-10 inches away, no vision past 20 inches @ birth, normal by six months)
Presbyopia
Diminished ability to focus on nearby objects
Vestibular System
-Detects rotation of head, linear acceleration, orientation of head to vertical
-Begins functioning before birth, first sensory system
-Loss of function due to aging
Cutaneous Sensation (skin)
-pressure, temp, loss of spacial acuity/pressure threshold with age
-Larger gap needed for older adults
Proprioception
-Spindles detect rate of change of muscle length, declines with age
-Decline in perception of static joint position w age
Bodily growth
-Cephacaudal growth
-Head proportion decreases, leg increases
Sarcopenia
age related muscle loss (positive feedback loop)
Myelination
-Myelin sheaths form on axons during development
-VOR reflex nerves myelinated first
Nature (Heredity)
Genetic transmission of characteristics
Environment (nurture)
factors of your environment (family, friends, education, region)
Preadaptation
The predisposition to learn specific motor skills such as crawling
Experience-Expectant Development
Development that depends on typical interactions with the environment (sensory stimulus to mature senses)
Experience-dependent devlopment
development that depends on interactions withs ones environmental surroundings which are not the same for all
Johnny and Jimmy Study
-Fraternal twins with different motor stimulus each day
-Johnny had more motor exposure, developed more skills
-study flawed by non-identical twins, low sample size, and the twins shared a home experience
Blind Vs. Sighted infants
Blind reach milestones significantly later only for raising self up and walking across room alone
Sensitive Period
a time during development where specific stimuli is needed for optimal or typical development to occur
Sleeper effect
When evidence for a sensitive period emerges only long after the sensitive period ends
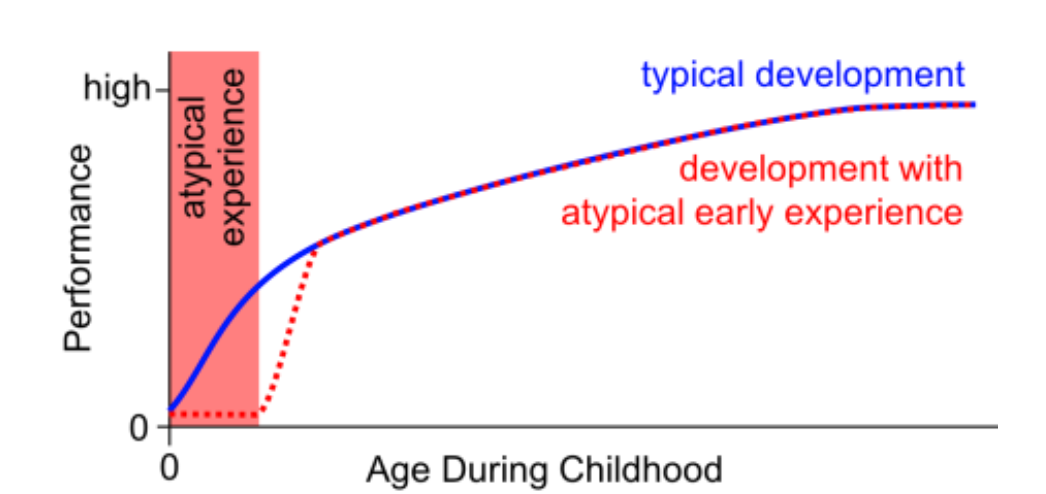
No sensitive period
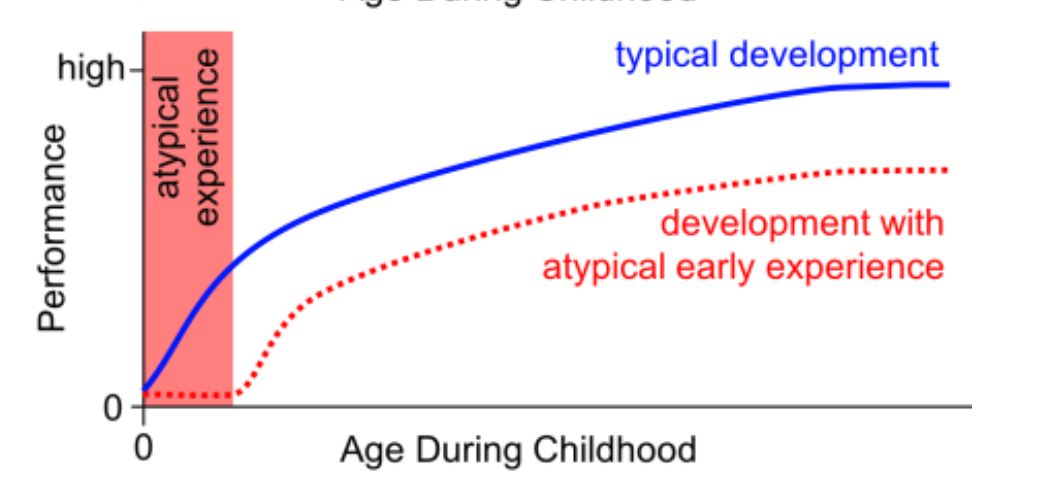
Sensitive Period with no sleeper effect
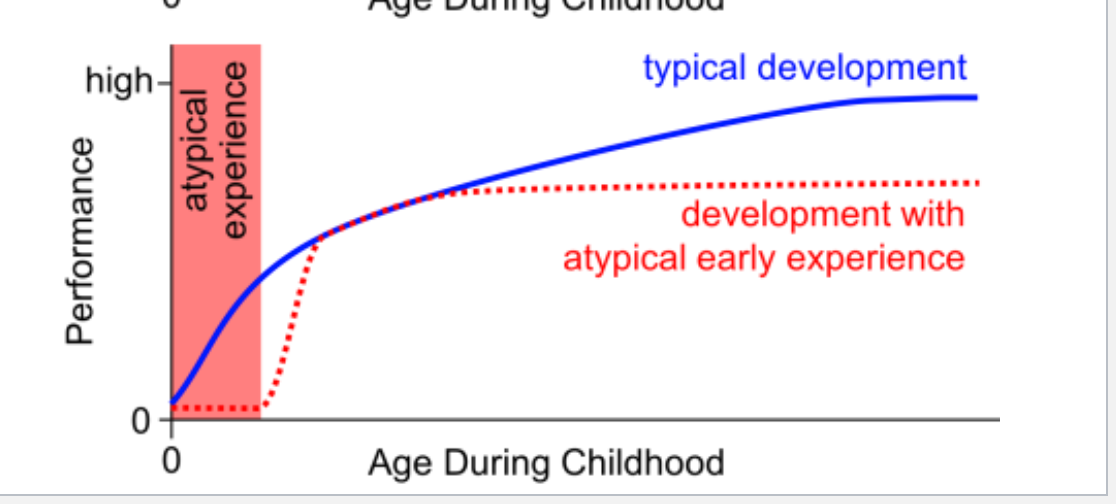
sensitive period with sleeper effect
Kokwet infants were not taught to___? But, they ___ earlier than US infants.
Kokwet infants were not taught to roll over or crawl. But, they sat, stood, and walked earlier than US infants.
True or False: Jamaican infants tended not to crawl before walking at higher rates than English infants
True
True or False: active exercise practices led to quicker achievement of walking and longer retention of walking reflex in infants
True
Compensation period
time in motor development where an individual compensates for adverse change in an individual constraint (ex:injury)
Types of compensation
Injury or age associated
Age related changes after young adulthood follow what acronym
Cumulative, Universal, Progressive, Intrinsic, Deleterious (CUPID)
Attributes of successful aging
Free of disease, socially engaged, productive, high cognitive and physical levels
Early motor development involves what changing constraints?
Change from amniotic fluid and uterine walls to full gravity without uterine walls
Spontaneous movements
movements not elicited by any known external stimulus
Rhythmic Stereotypies
Spontaneous rhythmic movements
Patellar tendon reflex (knee jerk) is a __ reflex
lifetime
Reflex
Stereotypical response to a stimulus
Palmar grasp reflex is a ___ reflex
primitive
The primitive babinski reflex is characterized by what?
Fanning of the toes from stroking of the sole
The primitive galant reflex is characterized by what?
curving of body to the side being stroked while held in the air
The primitive moro reflex is characterized by what?
arm extension and retraction from suddenly falling backwards
The primitive rooting reflex is characterized by what?
Opening the mouth and turning to stroking near lip
The primitive sucking reflex is characterized by what?
sucking when the lips make contact with an item
The primitive asymmetric tonic neck reflex is characterized by what?
Limb extension on the face side and limb flexion on the opposite when the head turns
The primitive symmetric tonic neck reflex is characterized by what?
arm extension and leg flexion when head is extended, reverse when head is flexed
Locomotor Relexes
Moving in place reflexes (often disappear before real motor skill occurs)
The locomotor stepping reflex is characterized by what?
Feet “walking” when held up and touching floor
The locomotor swimming reflex is characterized by what?
Swimming like movements when placed horizontal or in water
Postural Reflex
Helps maintain posture and often evolves cumulatively
The postural labyrinthine righting reflex is characterized by what?
Infant moving head to upright position when angled
The postural parachute reflex is characterized by what?
Extending the legs or arms to balance themself when falling
The postural landau reflex is characterized by what?
Head up, feet up, head down, feet down