Septal Defects - Right side of Heart
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
ASD stands for?
Atrial Septal Defect
What is an Atrial Septal defect?
Defect or discontinuity within the atrial septum
What are the different types of ASDs?
Secundum
Primum
Sinus venosus
What is the ASD: Secundum?
Most common but most difficult one to see
Located in central arterial septum and near the foramen ovale
Absence of foramen ovale flap is noted
What is the ASD: Primum?
Found lower in the septum, near krux of the heart
Cleft in mitral valve is found which will cause mitral regurgitation
The ASD, Primum is associated with…
Atrial ventricle septal defect malformation
Other abnormalities of the arterial ventricular valve
Trisomy 21
What is the ASD: Sinus Venosus?
Least common,
Near entrance of SVC into the RA
The ASD, Sinus Venosus is associated with…
Parietal anomalis pulmonary venous return
ASDs are common in ______ _________ and associated with…
Down Syndrome
PDA
VSD
Pulmonary stenosis
Transposition of great vessels
Tetralogy of flow
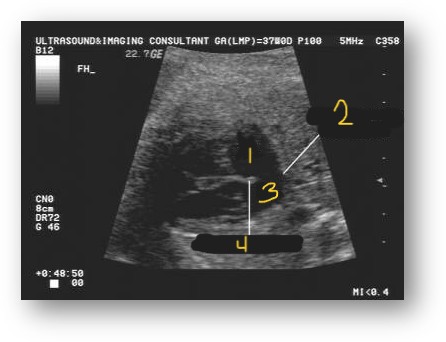
Label this image
Right atrium
Absent septum secundum
Left atrium
Septum primum
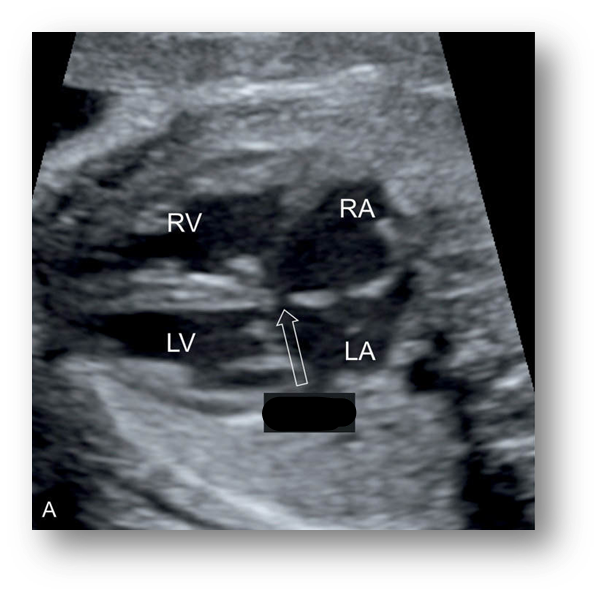
ASD
What does VSD stand for?
Ventricular Septal Defect
What is a Ventricular Septal defect?
Interruption of interventricular septum
May be large or small
What is the most common CHD?
VSD
30% of structural heart defects
The ventricular septum may be __________ or ___________.
Muscular
Membranous
What is a muscular VSD?
Found lower in septum and typically small, multiple holes
Spontaneously close after birth
What is a membranous VSD?
Most common, just below aortic leaflets.
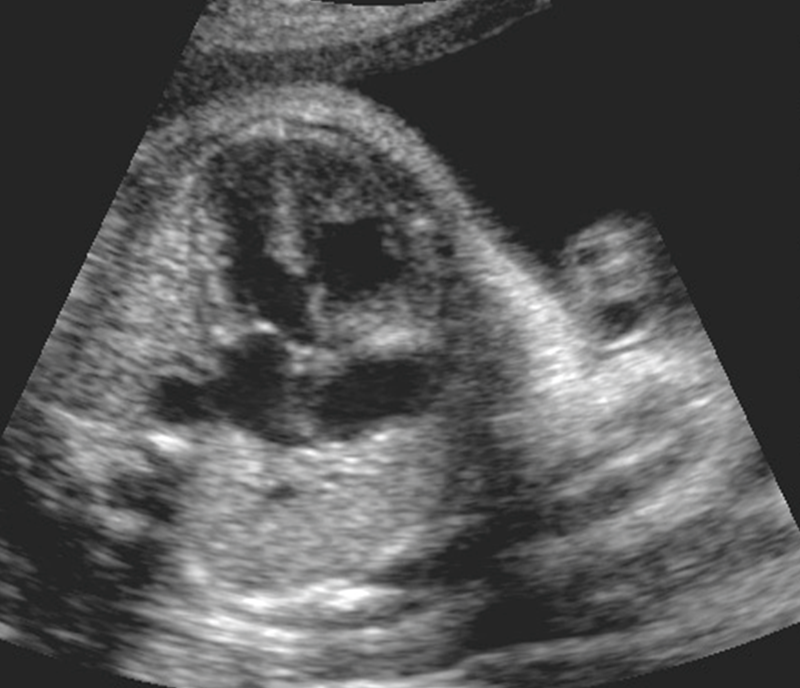
VSD
What is the best view to see VSDs in?
Long axis
Short axis
4-chamber
5-chamber
What are the US findings of a VSD?
Found just below aortic leaflets
Defects smaller than <2mm not normally detected on a fetal echo
May not see shunting of flow, pressure between ventricles are going to be similar
What is the prognosis of VSDs?
Pretty good unless associated with other anomalies. Can have surgery after birth
What does ASVD stand for?
Atrioventricular septal defect
What is the most common type of AVSD?
Endocardial cushion defect
Where is the Endocardial Cushion found?
Area where the valves, atria, and ventricles come together
Central portion of heart, where the Cruz of the arterial and ventricular septum grow centrally together
What is the seen with an incomplete AVSD?
Communication between LV & RA
Membranous VSD & Primum ASD
Abnormal Tricuspid valve
Cleft Mitral valve
What is a cleft mitral valve?
Anterior part of leaflet is divided into 2 parts (medial & lateral)
What is the seen with a complete AVSD?
Single large AV valve stretching across both of the ventricles
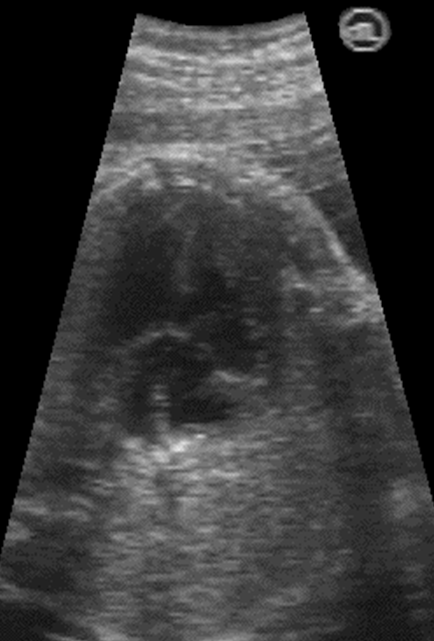
Systole AVSD [different sizes of atrium]
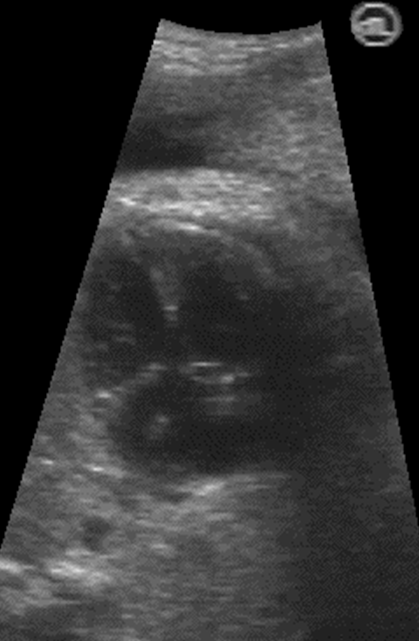
Diastole AVSD
AVSD is associated with:
Coarctation of the aorta
Pulmonary stenosis
Atresia
Increase incidence with Trisomy 21
What is the best view to see AVSDs in?
Long axis
Short axis
4-chamber view
Right ventricular inflow disturbance type is considered…
Tricuspid Atresia
Where is the Tricuspid valve located?
In between Right atrium and Right ventricle
Where is the Mitral valve located ?
In between the Left atrium and Left ventricle
What is Tricuspid Atresia?
Interruption of growth of tricuspid leaflet
Causing valve to be hypoplastic or atresia
With Tricuspid Atresia, the ________ portion of the _______ ventricle has failed to form.
Inflow
Right
Leading to Hypoplastic RV
What plane can Tricuspid Atresia be visualized in?
4-chamber view
The _____ and ____ will be diminished in size when looking at Tricuspid Artesia.
RVOT
PA
Ultrasound findings of Tricuspid Atresia.
Large, left ventricles
Small, underdeveloped right ventricle
Echogenic tricuspid annulus & no valvular movement
Use color doppler

Tricuspid Atresia
When a small right ventricle is seen, what should the sonographer suspect?
Pulmonary atresia
Tricuspid atresia
Aortic stenosis or insufficiency
Underdeveloped
Pulmonary and Tricuspid Atresia can be seen with and without any _______ ________.
Septal defects
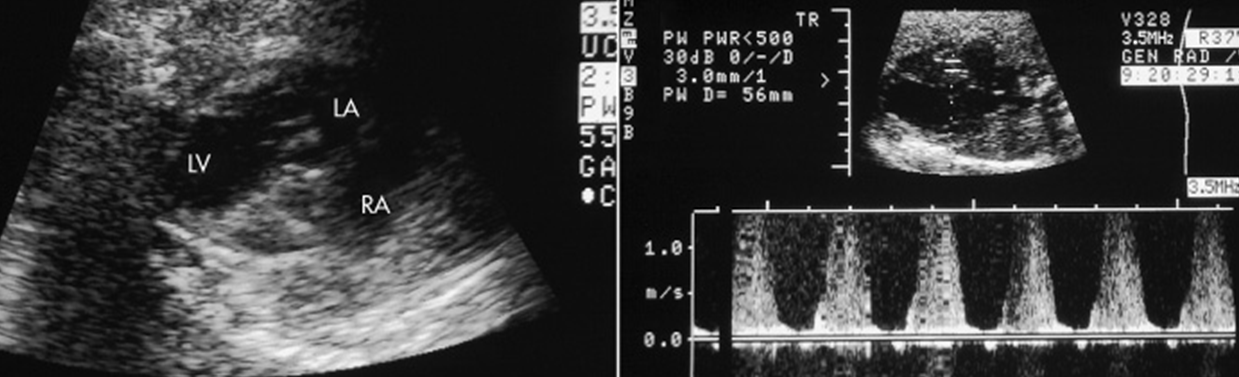
What is Ebstein’s anomaly of Tricuspid Valve?
Abnormal displacement of septal leaflet of tricuspid valve toward apex of right ventricle creating malformed tricuspid valve
How does the heart function with Ebstein’s Anomaly of the Tricuspid Valve?
Arterialized Chamber
Reduced capacity of pumping action of the right ventricle
What does ‘Atrialized chamber’ mean?
Portion of the right ventricle that becomes a receiving chamber with the right atrium pressure
US findings found with Ebstein’s Anomaly of Tricuspid Valve.
Apical displacement of Tricuspid valve leaflet
Arterialized right ventricle
Right ventricular dysfunction
Right atrium is massively dilated
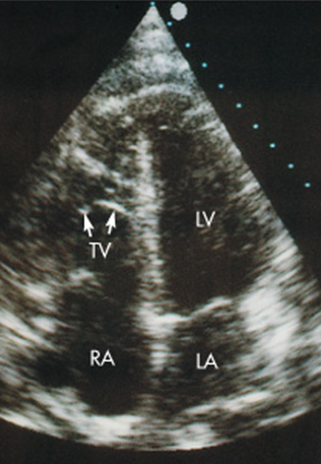
Ebstein’s Anomaly of Tricuspid Valve
Ebstein’s Anomaly of Tricuspid Valve
When an enlarged right atrium is seen, what should the sonographer suspect?
Ebstein anomaly
Tricuspid dysplasia
Tricuspid regurgitation without inferior displacement of the valve
Summary describing Ebstein’s Anomaly.
Malformation of tricuspid valve
Valves are displaced inferiorly
Enlarged right atrium
Right ventricular outflow disturbance type is considered…
Hypoplastic Right Heart
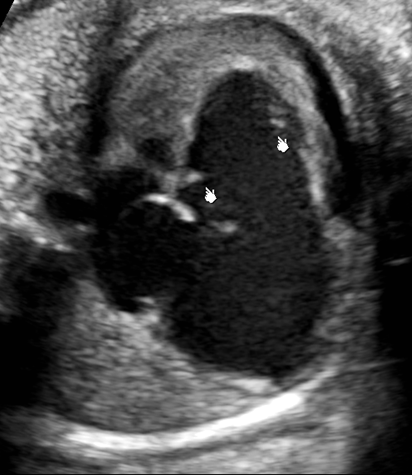
What is Hypoplastic Right Heart?
Underdeveloped right heart from obstructed RVOT
Secondary to pulmonary stenosis
Hypoplastic Right Heart will have multiple structures that are small, what are they?
Tricuspid valve
Right ventricle
Pulmonary artery
Hypoplastic Right Heart
Don’t confuse Hypoplastic Right Heart with….
Hypoplastic Left Heart
Know situs & chamber locations
When something is found in the wrong place, what should the sonographer suspect?
Teratology of Fallot
Most common form of cyanotic heart disease [blue at birth] in infants and children.
Tetralogy of Fallot
What is the differential diagnosis for Tetralogy of Fallot?
Double outlet right ventricle
What is double outlet right ventricle?
Both great vessels, AO and PA arise from right ventricle
What is the prognosis of Tetralogy of Fallot?
Good with surgery after birth
Pulmonary atresia or absent pulmonary valve may worsen prognosis
What 4 things are assoc with Teratology of Fallot?
High, membranous VSD
Overriding Aorta
Pulmonary stenosis
Hypertrophy of right ventricle
The severity of Tetralogy of Fallot depends on the ________ _________.
Pulmonary Stenosis
In utero the ventricles may still be _________, Hypertrophy of right ventricle happens over time.
Symmetrical
Tetralogy of Fallot is associated with…
Trisomy 21, 18, and 13
What is an Overriding Aorta?
Large, anteriorly displaced aorta, which overrides the septal defect
Form of RVOT obstruction?
Pulmonic Stenosis
Where is the Pulmonic valve found?
Between RV & PA has 3 semilunar cusps
When a pulmonic stenosis is present, what is seen on US.
Cusps become thickened
Less mobile
Domed (in diastole)
When a Pulmonic Stenosis, what else may be seen?
Hypoplastic or may have poststenotic dilation
May see dilated RA & RV