Honors anatomy test 1 Plasma membrane
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Plasma membrane
A selectively permeable barrier that surrounds the cell, regulating the passage of substances in and out of the cell. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that facilitate communication and transport.
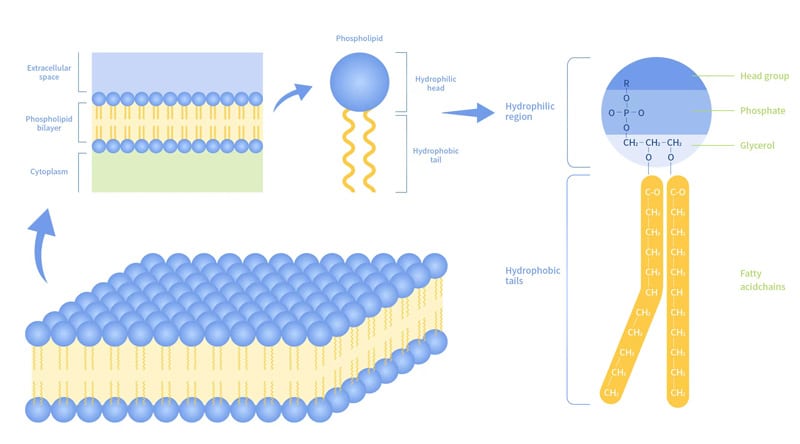
Phospholipid
A type of lipid molecule that forms the bilayer of the plasma membrane, consisting of hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
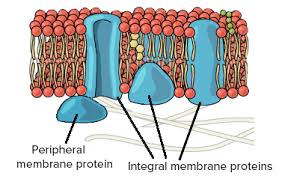
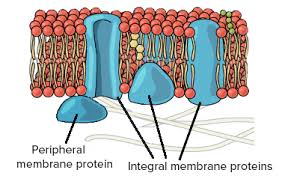
Integral protein
membrane-associated protein that spans the entire width of the lipid bilayer
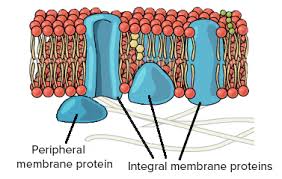
Peripheral protein
a protein that is loosely attached to the exterior or interior surfaces of the plasma membrane, playing roles in signaling and maintaining the cell's shape.
Protein channel
A type of integral protein that forms a pore in the plasma membrane, allowing specific molecules to pass through the membrane.
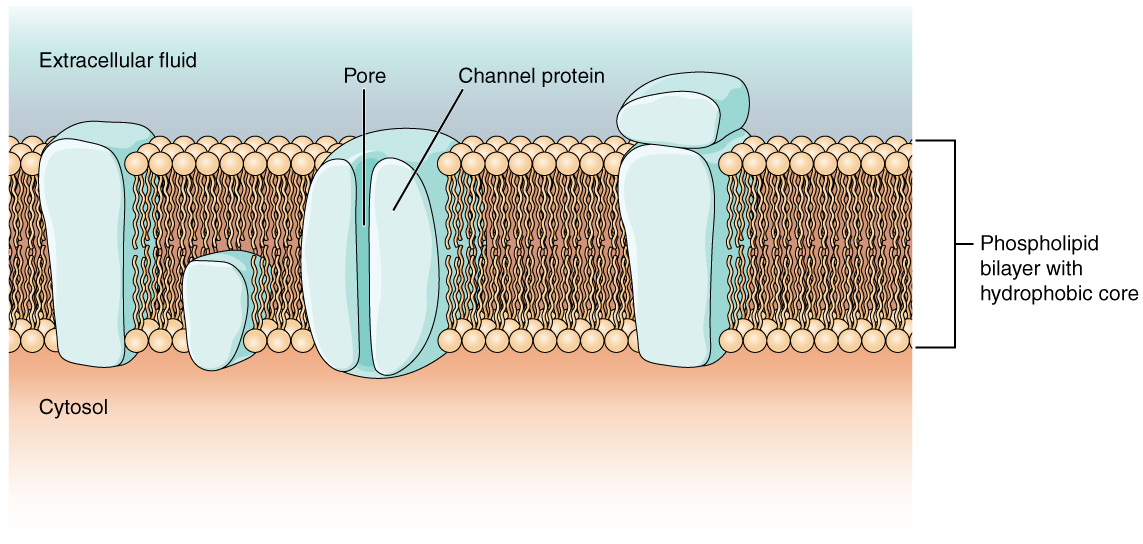
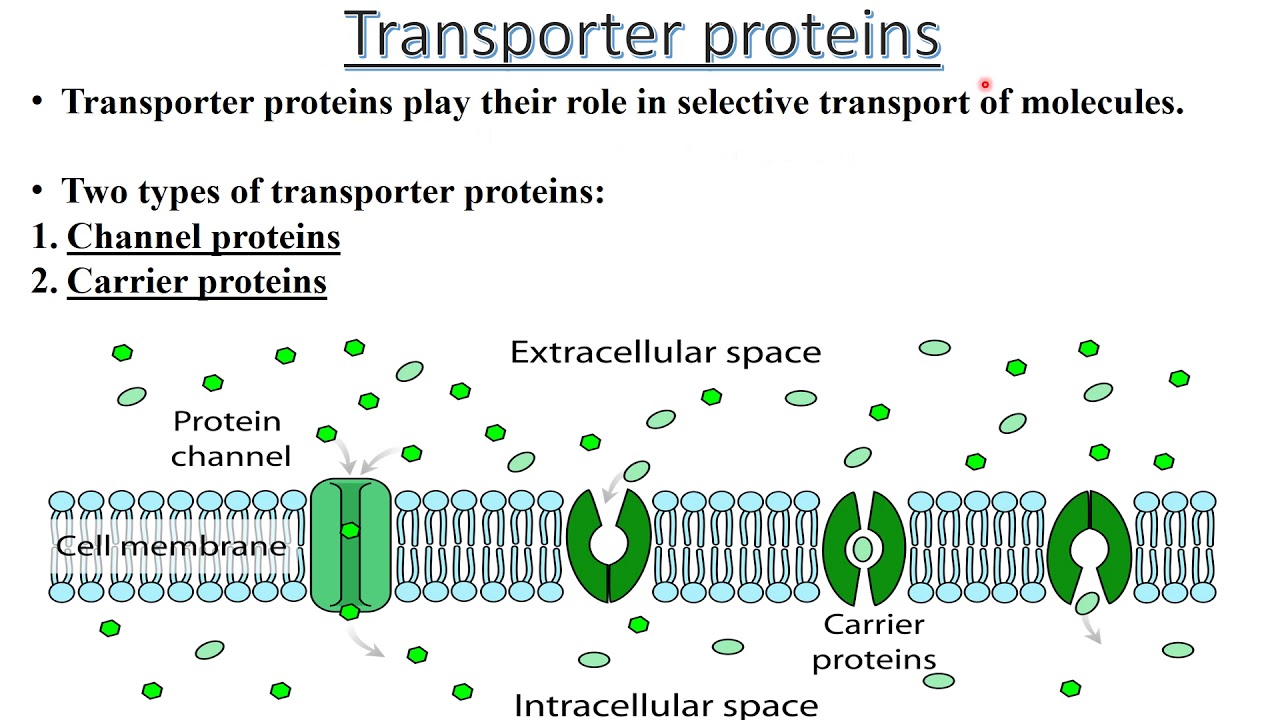
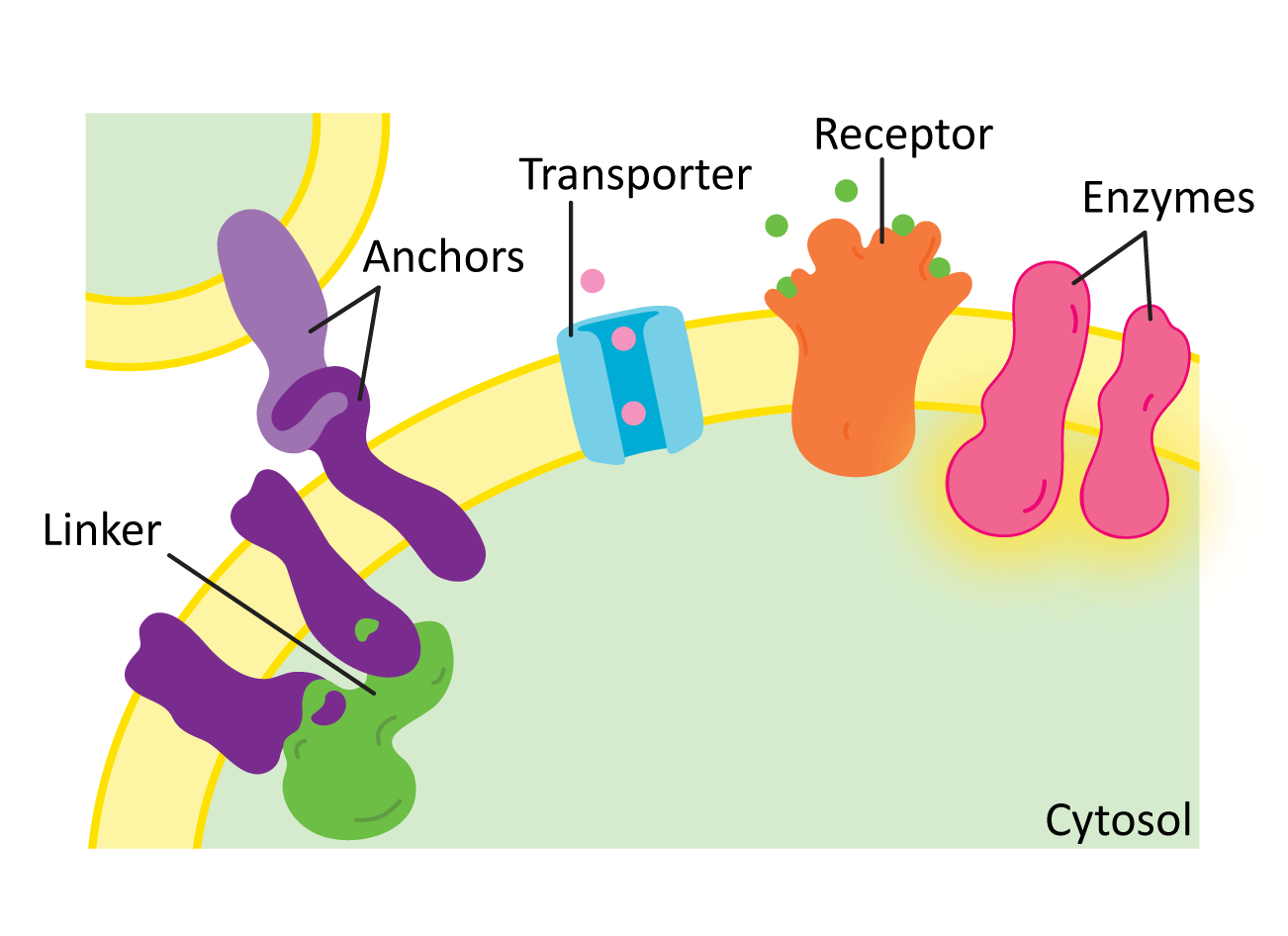
Transporter protein
is a specialized protein that moves substances like ions, molecules, and other macromolecules across cell membranes
Cholesterol
sterol molecule with a rigid ring structure and a hydrocarbon tail. It inserts itself between the phospholipids in the cell membrane, forming a fluid mosaic pattern.
Receptor protein
allows for attachment of substances, such as hormones, to the membrane. is an integral protein embedded in the cell membrane that receives signals from the external environment by binding to specific molecules called ligands.
Linker protein
helps stabilize the plasma membrane and attach cells together. connects the cell's internal cytoskeleton to the external environment or other parts of the cell.
Glycolipid
are lipids with attached carbohydrate chains found exclusively on the outer leaflet of the cell membrane. They are crucial for cell recognition, acting as markers for immune responses and cell adhesion
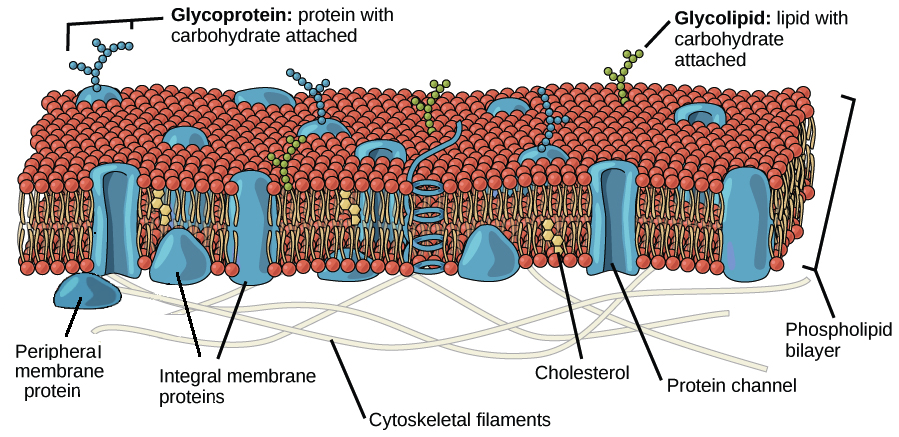
Glycoprotein
is a protein that has carbohydrate molecules attached, which extend into the extracellular matrix.
G-protein coupled receptor
large family of proteins on the cell surface that act as sensors for external signals, such as hormones, light, and odorants
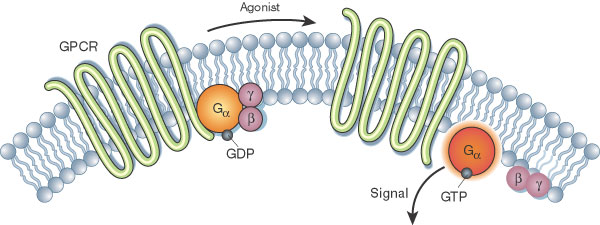
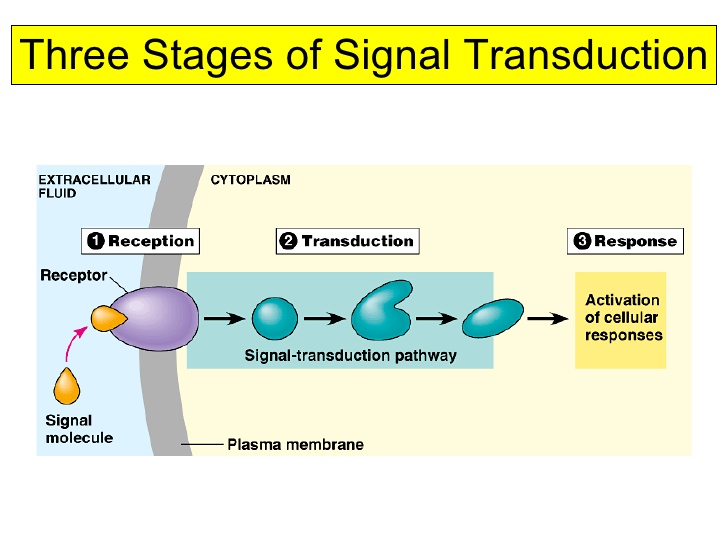
Cell signaling
the process by which cells communicate with each other and respond to external cues. It involves the transmission of signals between cells, which can trigger specific cellular responses.
Ligand
is the specific molecule that binds to and activates a receptor.
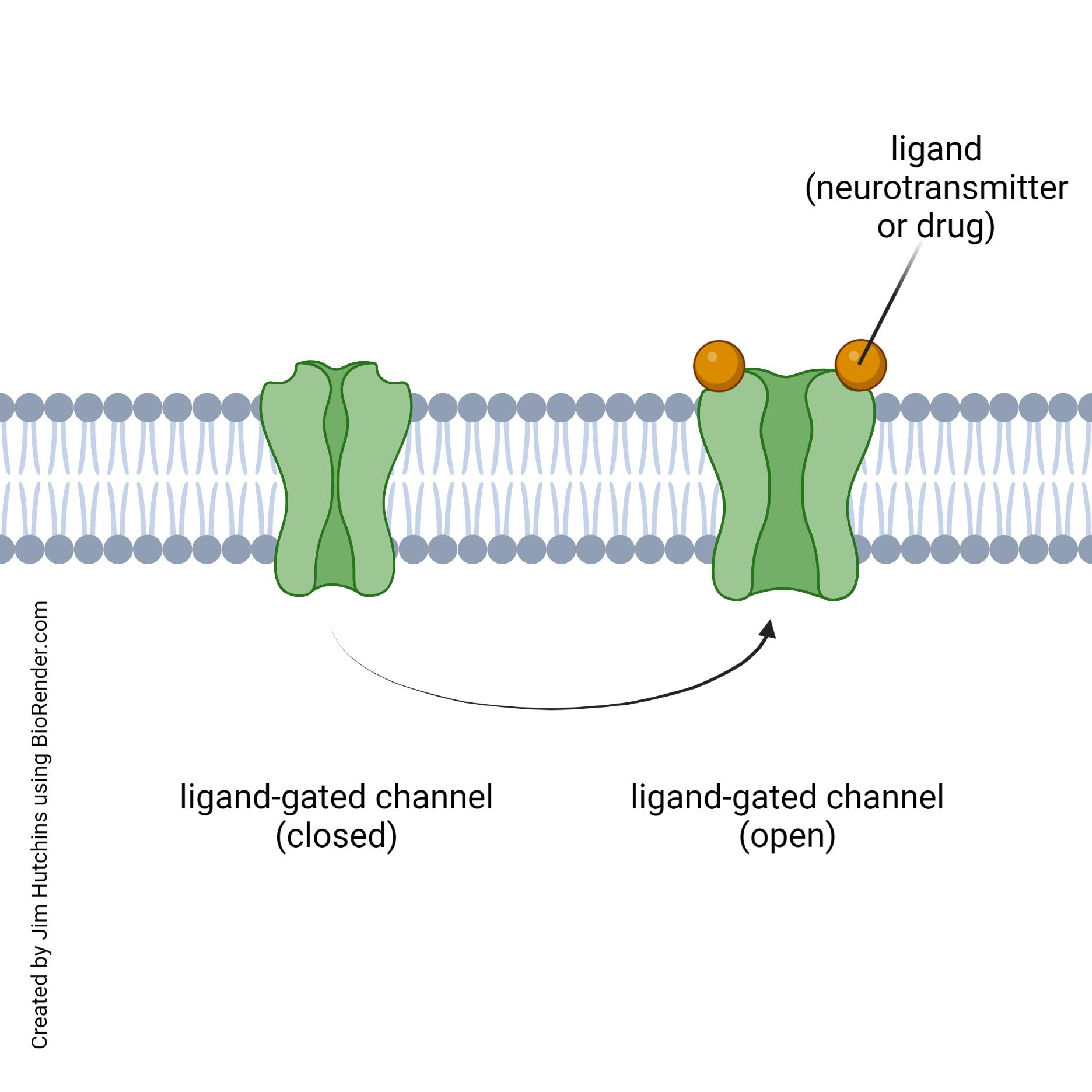
Signal transduction
he process by which a cell converts an external signal into a specific internal response.