last one best one bruh
1/274
Earn XP
Description and Tags
best way to study: "learn" mode + type out every answer (if you were close enough to the correct answer you can override and mark it as correct)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
275 Terms
carl linneaus
“father of taxonomy”
systema naturae - 1735
peter duesberg
hiv denier
charles darwin
origin of species - 1859
carl woese
3 domain system - 1970s
what group of bacteria is salmonella in
proteobacteria
symptoms/diseases of salmonella
diarrhea
nausea
4 characteristics of salmonella
bacillus
gram negative
facultative anaerobe
endotoxin
what group of bacteria is e. coli in
proteobacteria
symptoms/diseases of e. coli
diarrhea
4 characteristics of e. coli
bacillus
gram negative
facultative anaerobe
exotoxin
what group is clostridium in
gram positive
diseases from clostridium
gangrene
botulism
4 characteristics of clostridium
bacillus
gram positive
obligate anaerobe
exotoxin
what group is bacillus anthracis in?
gram positive
diseases/symptoms from bacillus anthracis
skin pustules
pnemonia
4 characteristics of bacillus anthracis
bacillus
gram positive
obligate aerobe
endospores
what group is streptococcus in?
gram positive
diseases/symptoms from streptococcus
necrotizing faciitis
strep throat
scarlet fever
3 characteristics of streptococcus
coccus shape
gram positive
aerotolerant anaerobe
what group is treponema pallidum in
spirochetes
symptoms/diseases of treponema pallidum
syphilis
2 characteristics of treponema pallidum
obligate anaerobe
painless chancre sore
what group is borrelia burgdoferi in
spirochetes
symptoms/diseases of borrelia burgdoferi
lyme disease
3 characteristics of borrelia burgdoferi
microaerophile
transmitted by tick
bullseye rash
what is rabies classified as
virus
3 characteristics of rabies
long incubation period
ssrna with bullet shaped envelope
100% fatality rate with no vaccine
what is the flu classified as
virus
3 characteristics of flu
ssrna with envelope
spanish flu - 1918-1919
20-100 million deaths
what is mad cow disease classified as
prion
prion
infectious protein particle
what supergroup and clade is giardia under
supergroup: excavata
clade: diplomonad
disease from giardia
giardiasis
2 characteristics of giardia
transmitted by drinking contaminated water
2 haploid nuclei
what supergroup and clade is trypanosoma brucei in
supergroup: excavata
clade: kinetoplastid
disease from trypanosoma brucei
african sleeping sickness
1 characteristic of trypanosoma brucei
transmitted by bite of tsetse fly
what supergroup and clade is trypanosoma cruzi in
supergroup: excavata
clade: kinetoplastid
disease from trypanosoma cruzi
chagas disease
1 characteristic of trypanosoma cruzi
transmitted by bite of kissing bug (feeds on eyelids/lips when asleep)
what supergroup and clade is plasmodium in?
supergroup: sar
clade: apicomplexa
disease from plasmodium
malaria
what is the supergroup and clade of diatoms?
supergroup: sar
clade: diatoms
3 characteristics of diatoms
form diatomaceous earth
used in filters
silica test
what is the supergroup and clade of water molds?
supergroup: sar
clade: oomycetes
diseases from water molds
irish potato famine
french wine crisis
what is the supergroup and clade of red algae?
supergroup: archeaplastida
clade: rhodophyta
1 characteristic of red algae
nori (sushi)
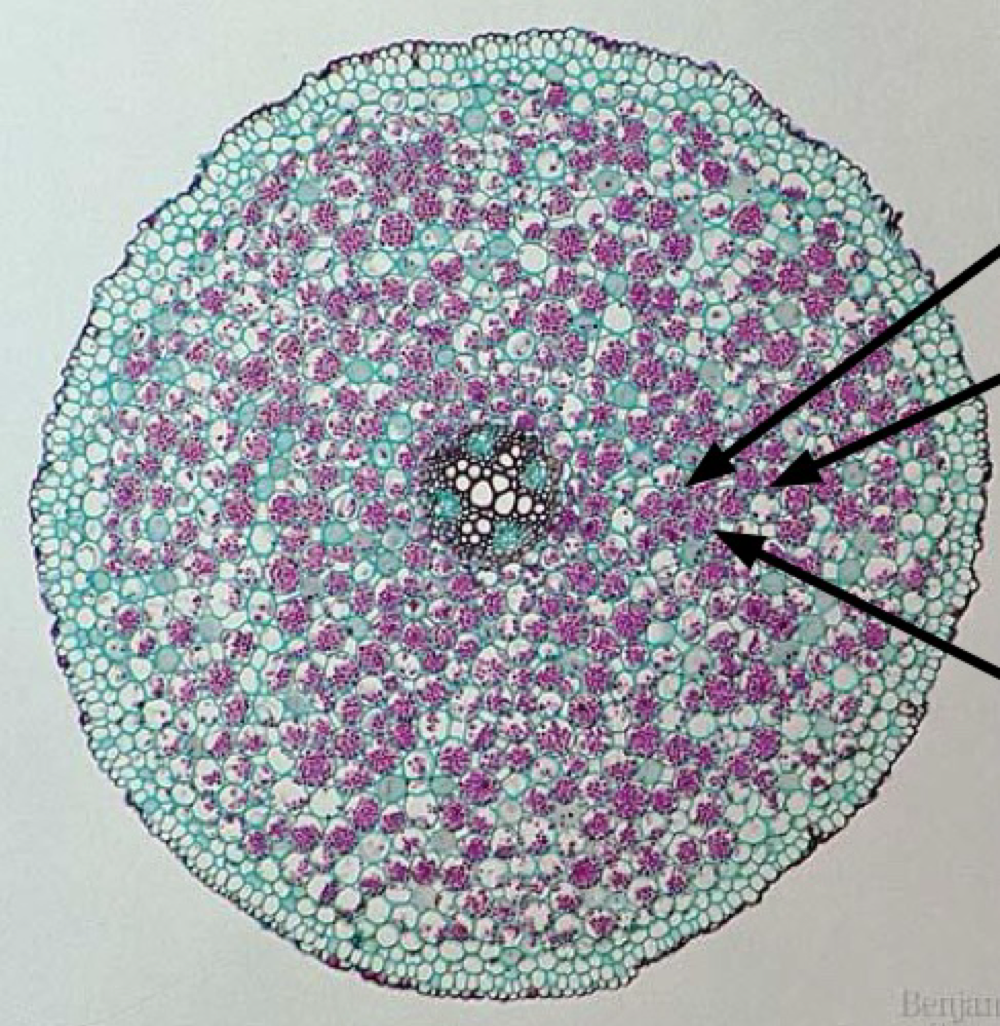
dicot root
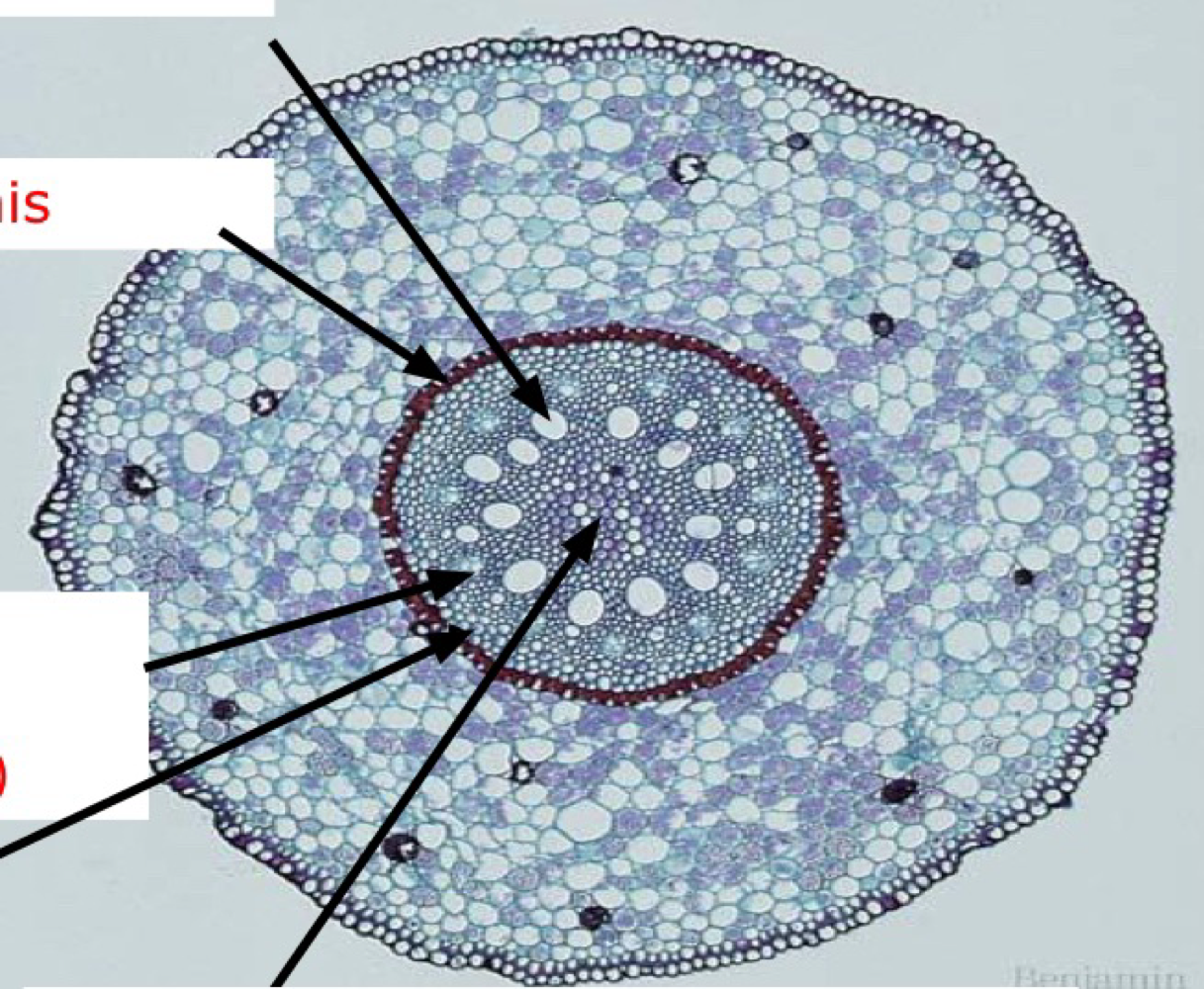
monocot root
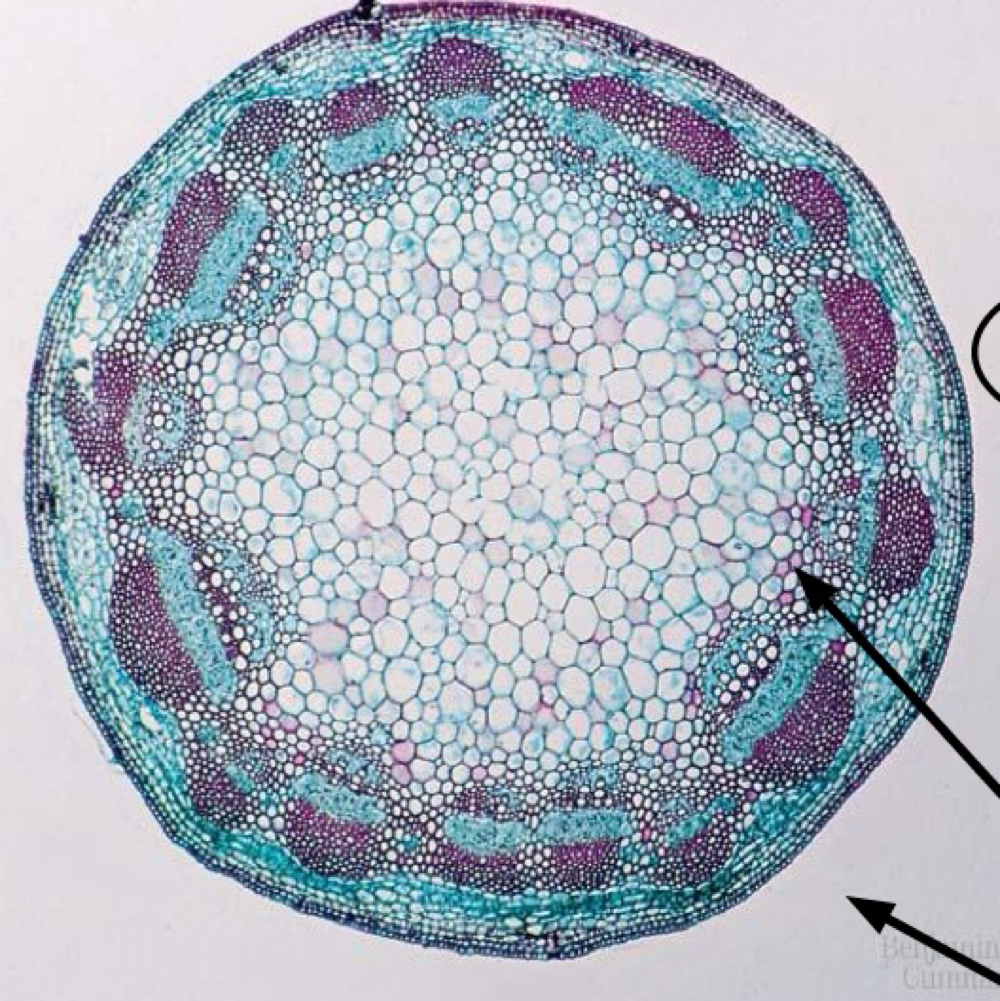
dicot stem
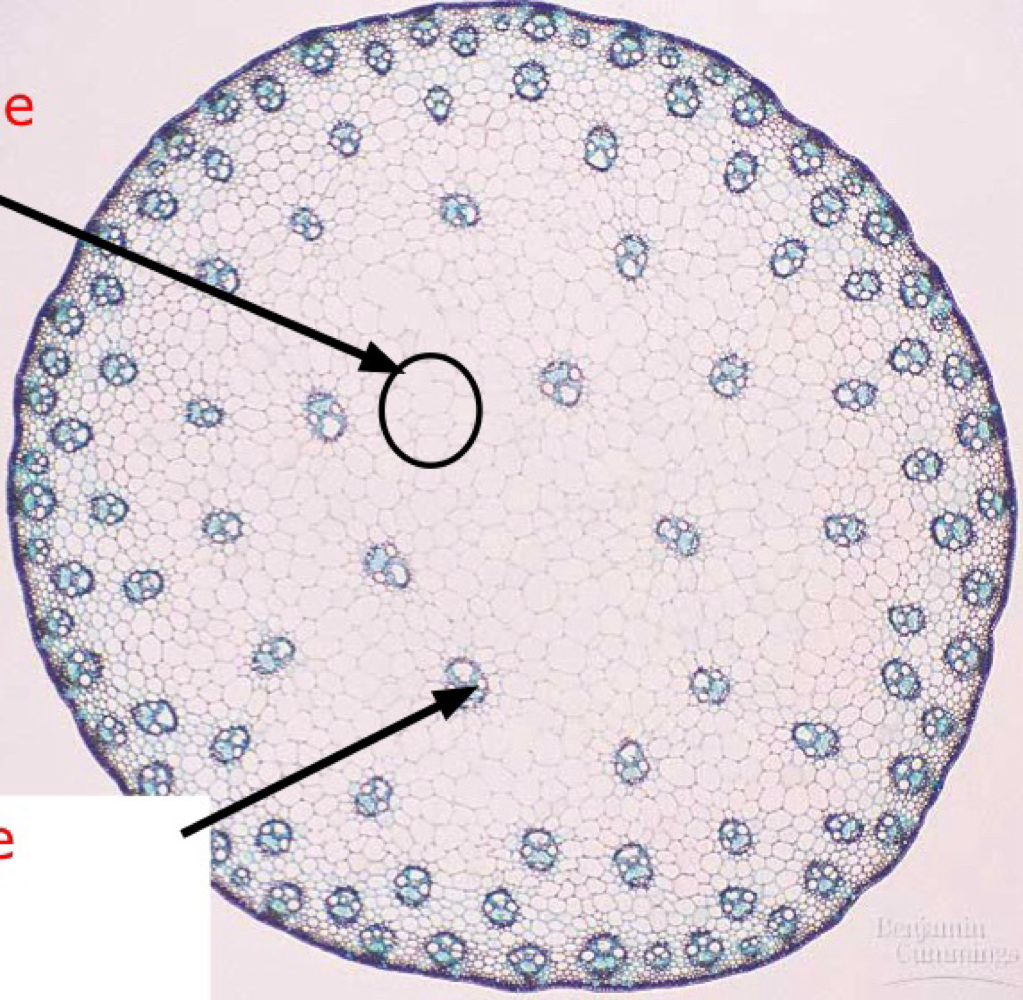
monocot stem
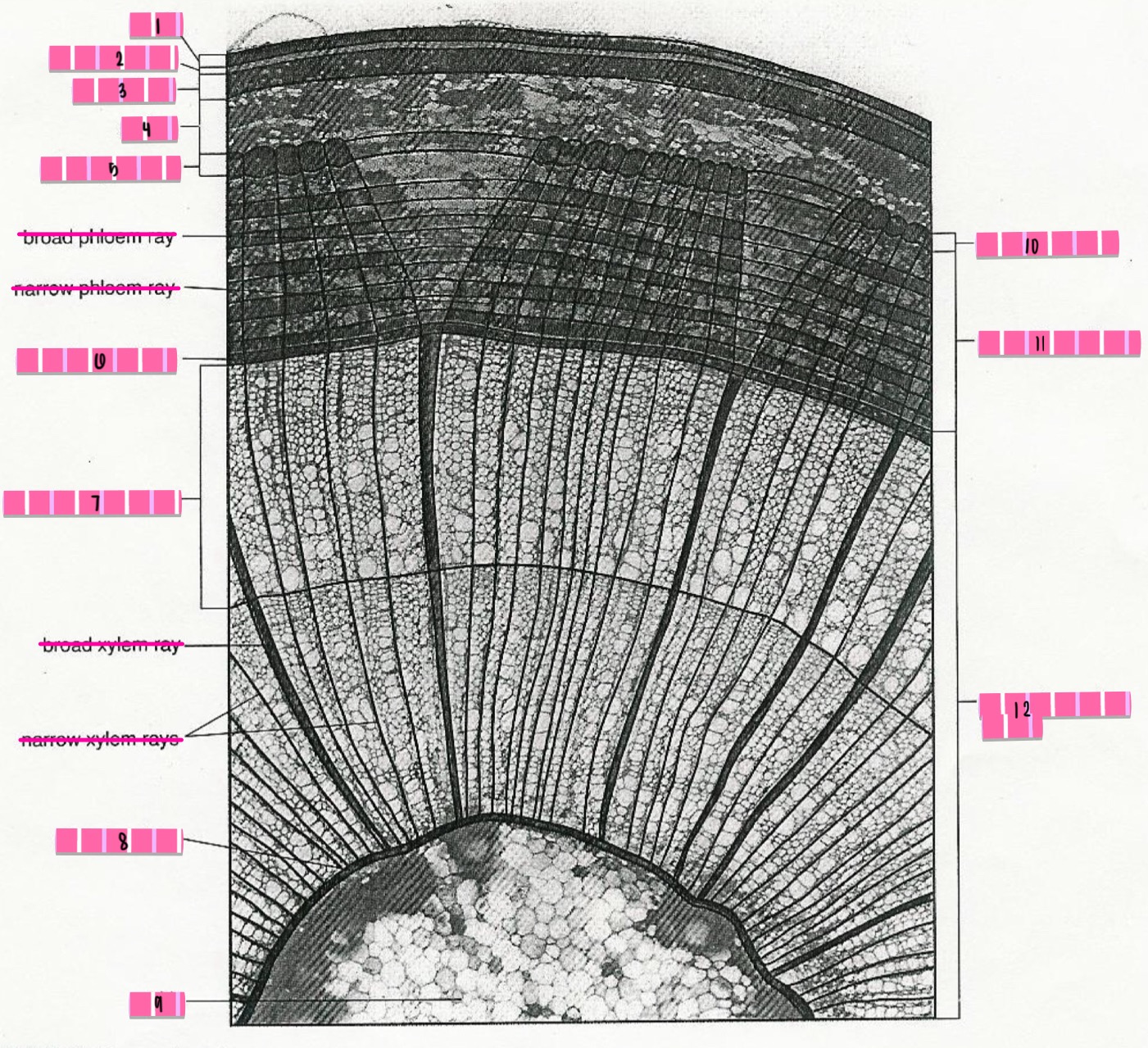
cortex
cork cambium
phelloderm
cortex
primary phloem
vascular cambium
primary xylem
pith
primary phloem
secondary phloem
secondary xylem
9 macronutrients in a plant
carbon
oxygen
hydrogen
nitrogen
phosphorus
calcium
magnesium
phosphorus
sulfur
8 micronutrients
chlorine
iron
manganese
boron
zinc
copper
nickel
molybdenum
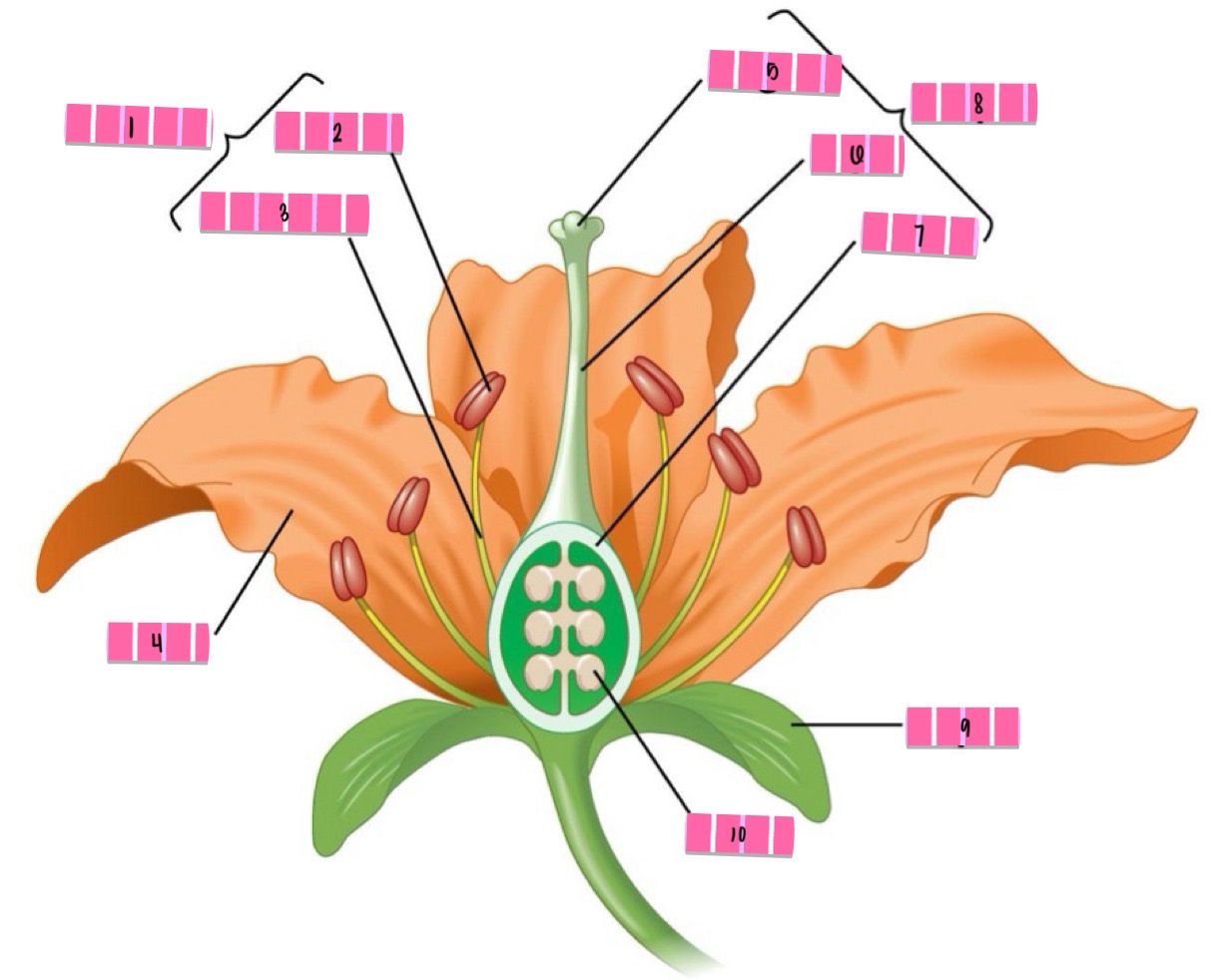
stamen
anther
filament
petal
stigma
style
ovary
carpel
sepal
ovule
characteristic of monocot embryo
one cotyledon
characteristic of dicot embryo
two cotyledons
characteristic of monocot leaf venation
parallel veins
characteristic of dicot leaf venation
netlike veins
characteristic of monocot stem
vascular bundles arranged complexly
characteristic of dicot stem
vascular bundles arranged in a ring
characteristic of monocot roots
fibrous roots
characteristic of dicot roots
taproot present
characteristic of monocot flowers
petals in multiples of 3
characteristic of dicot flowers
petals in multiples of 4-5
stolon
strawberry
modified stem
rhizome
iris
modified stem
tuber
potato
modified stem
bulbs & corms
onion
modified stem
cladophyll
cactus
modified stem
tendrils
climbing vines
modified leaf
bracts
poinsettia
modified leaf
spines
cactus
modified leaf
storage leaves
succulents
modified leaves
food storage
carrot
sweet potato
modified root
water storage
pumpkin
modified root
propagative roots
cherries
pears
modified root
pnematophores
mangrove trees
modified roots
aerial roots
orchids
modified roots

western sycamore

freemont cottonwood
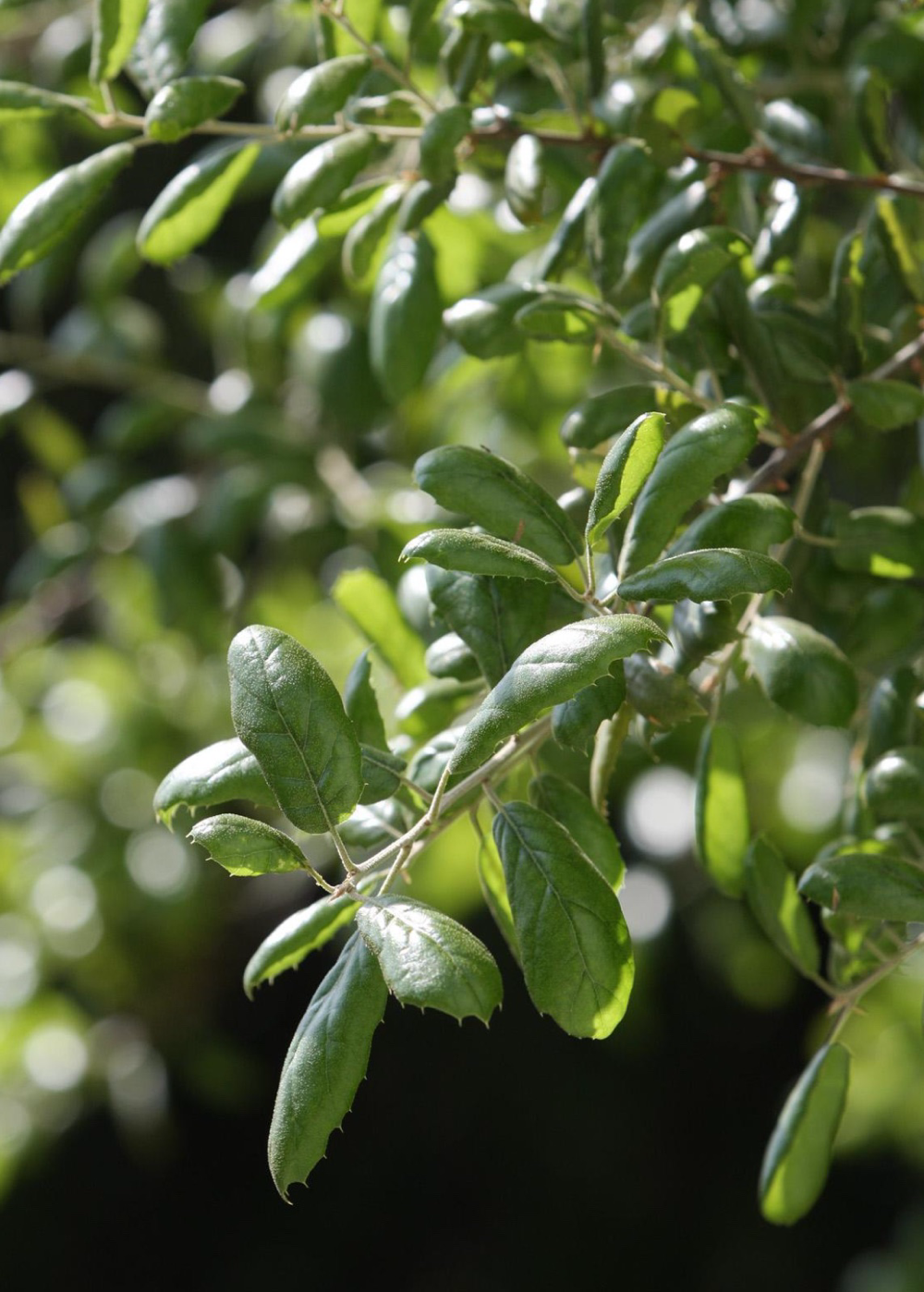

coast live oak
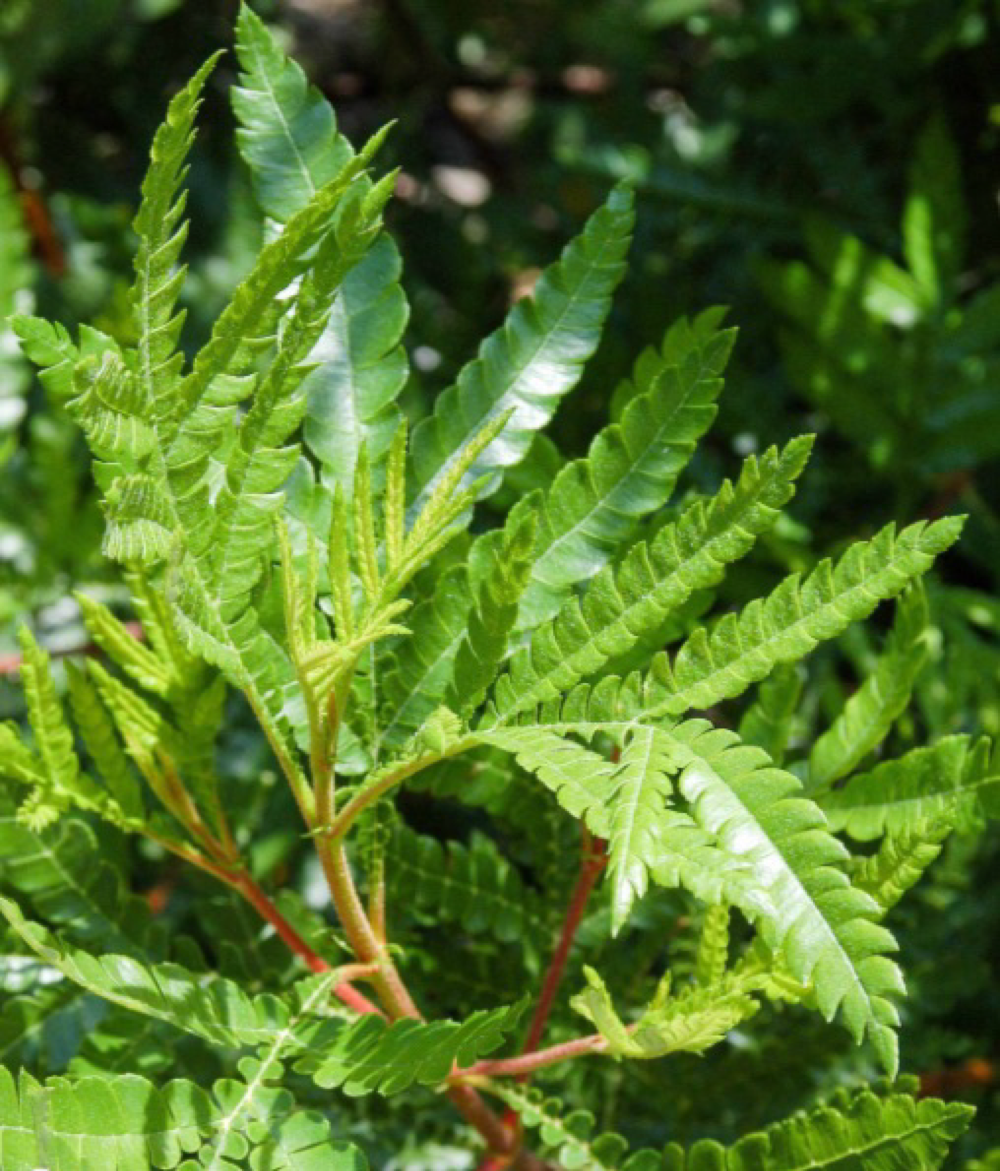

catalina ironwood
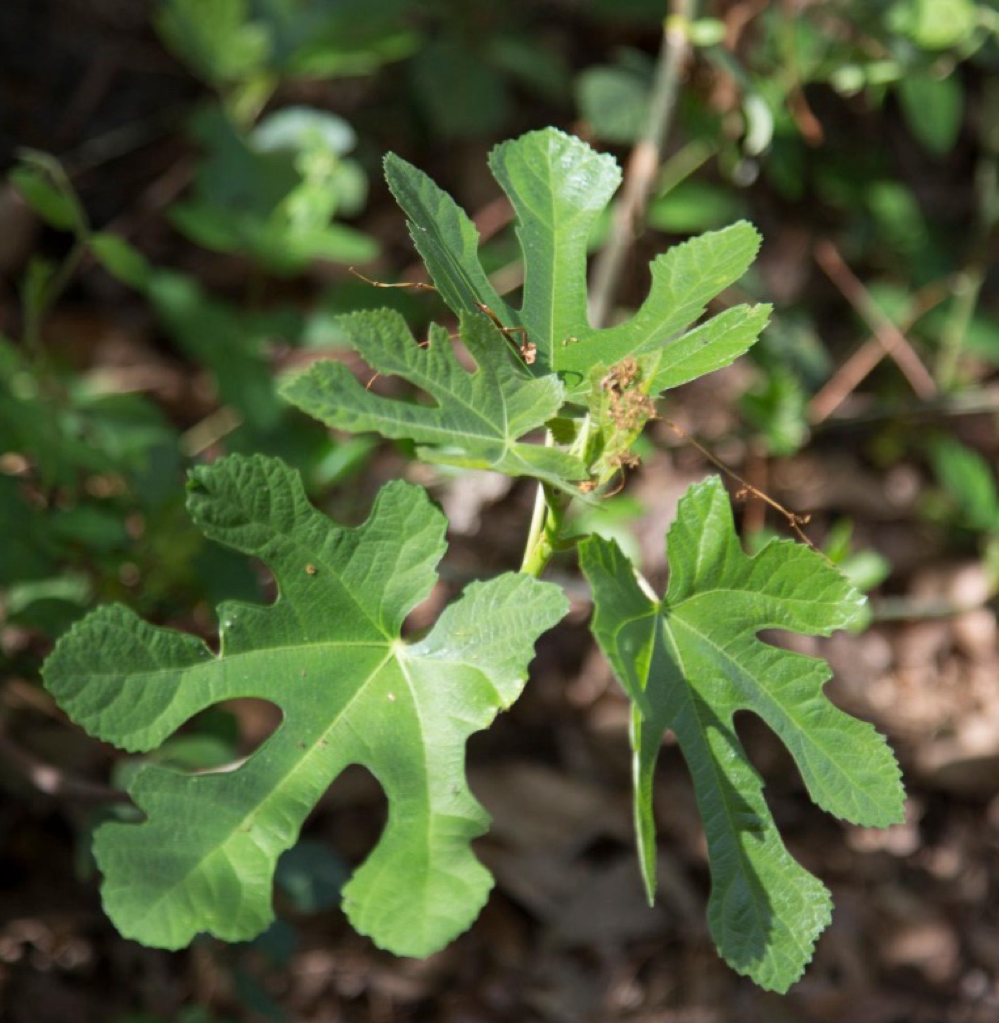

wild fig

bulrush
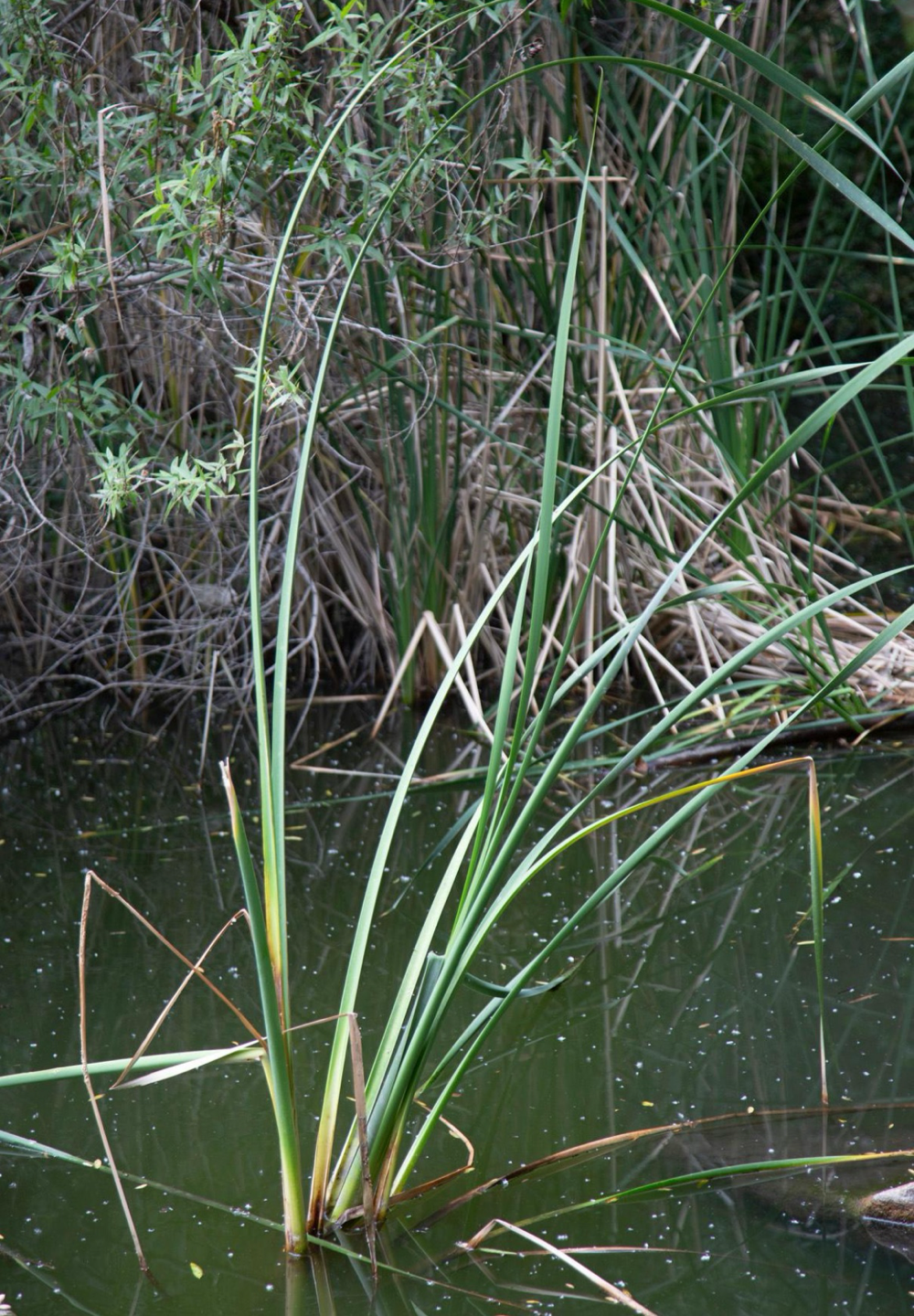

cattail
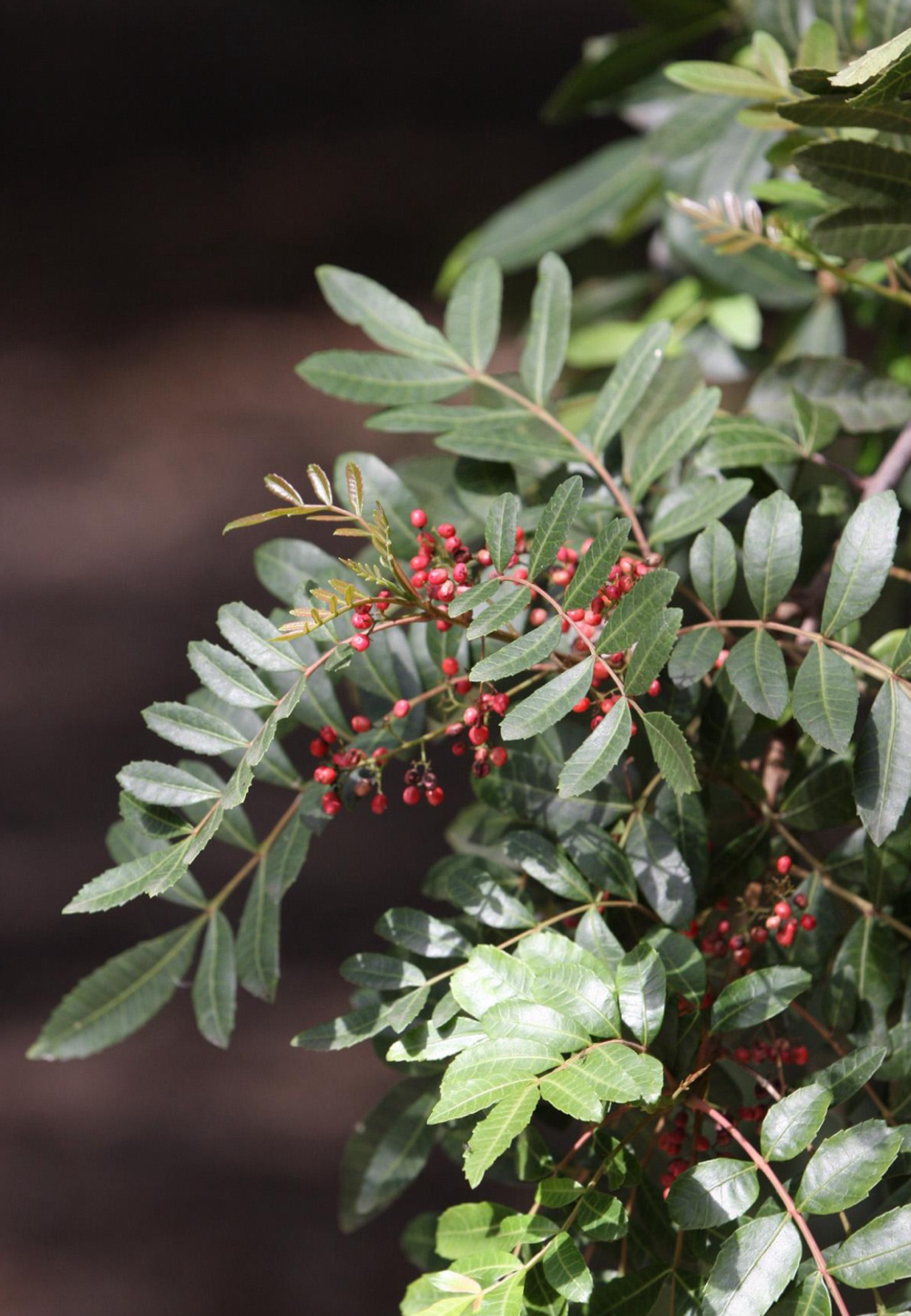

toyon
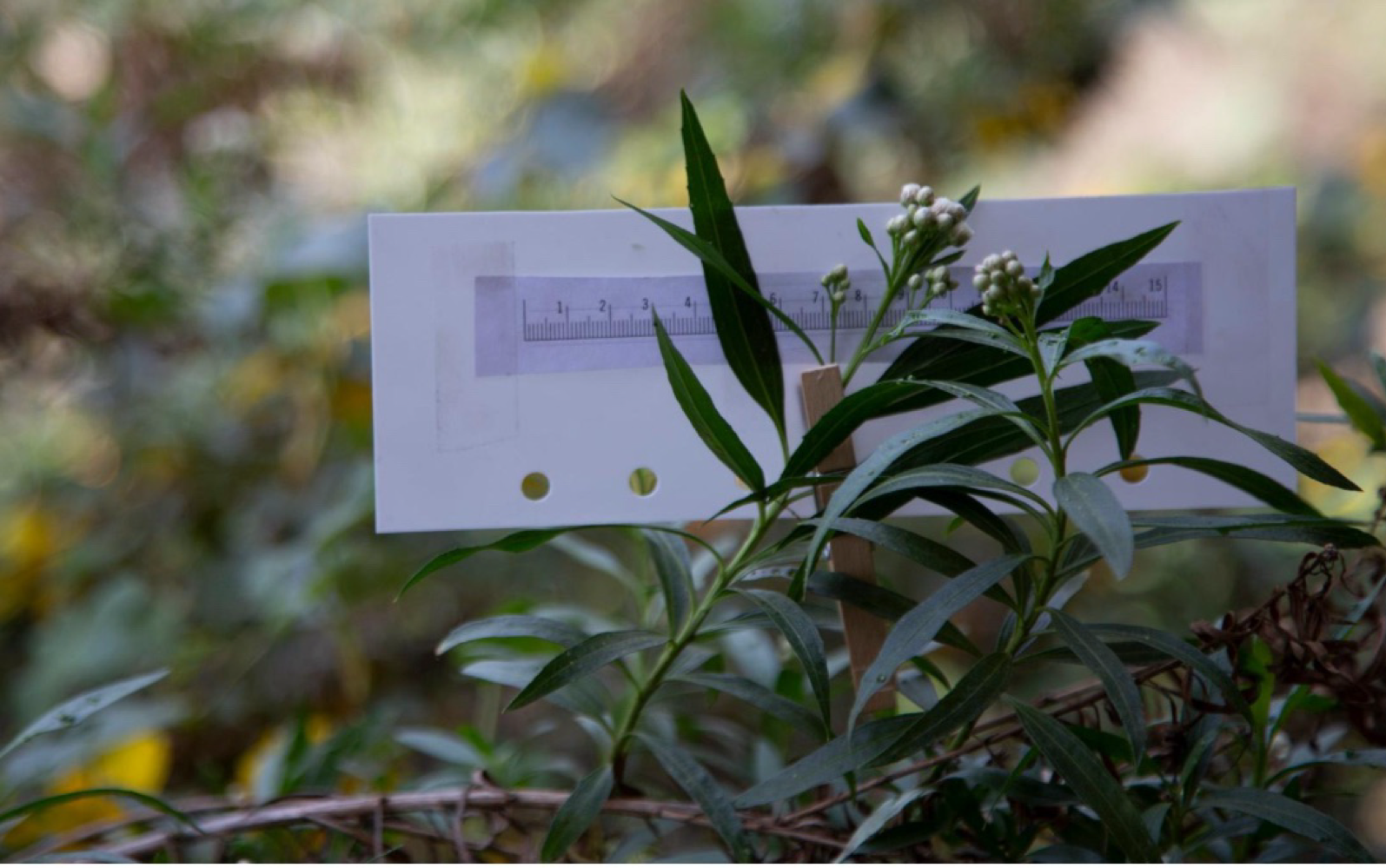

mulefat
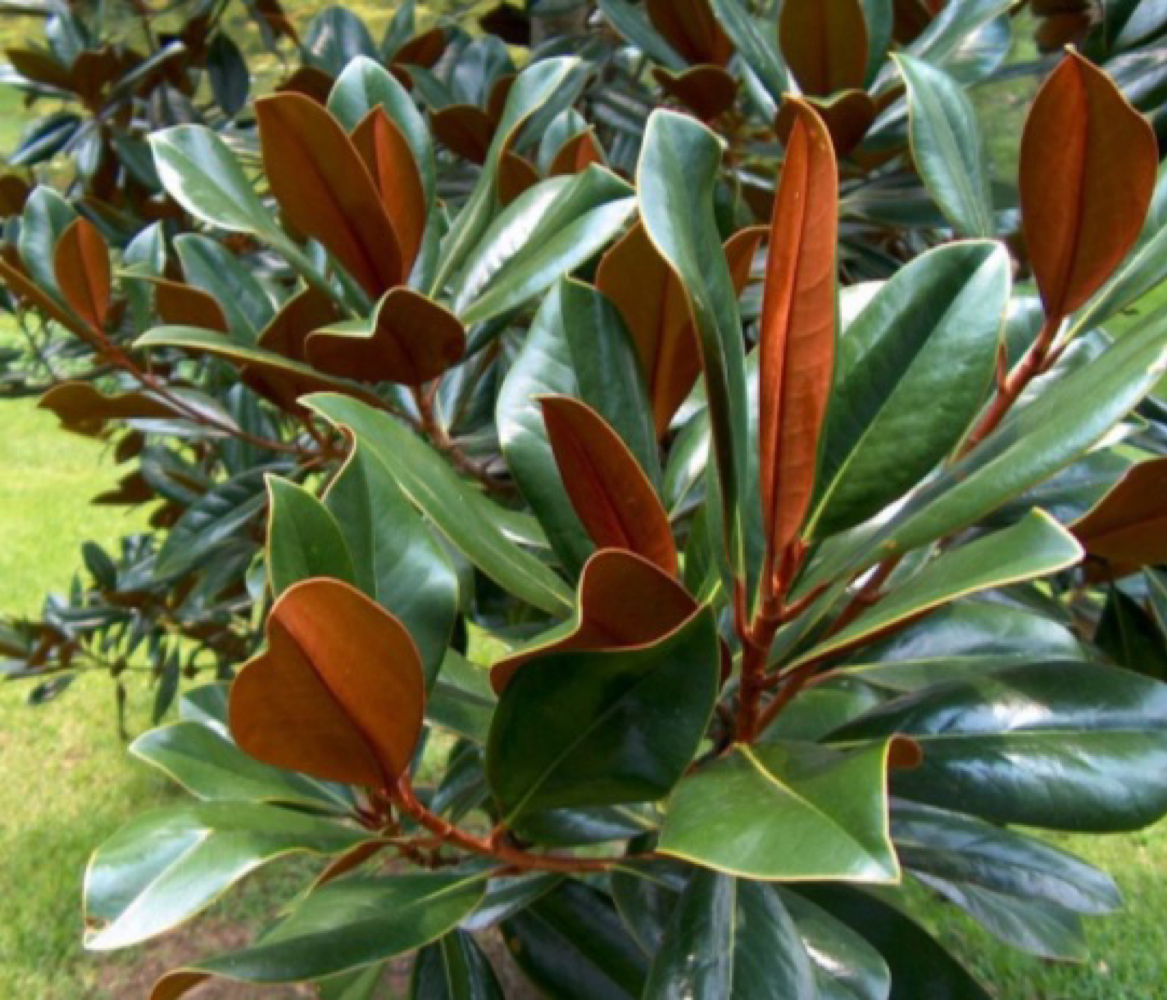

southern magnolia
what is porifera
sponges
cnidaria
hydras
jellies
sea anemones
coral
polyp + medusa
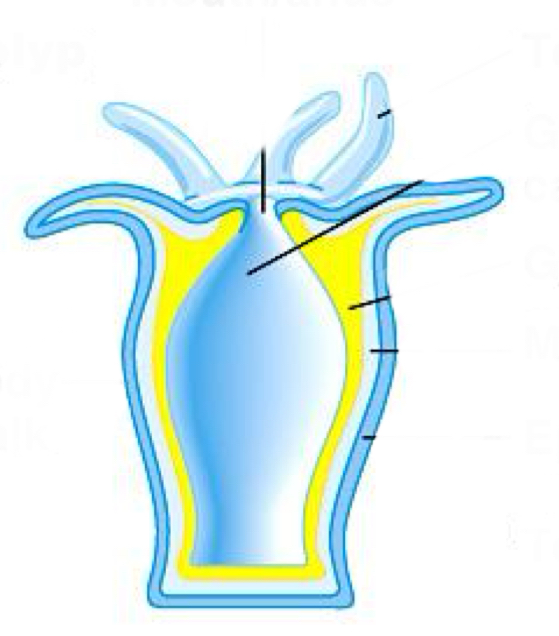
polyp
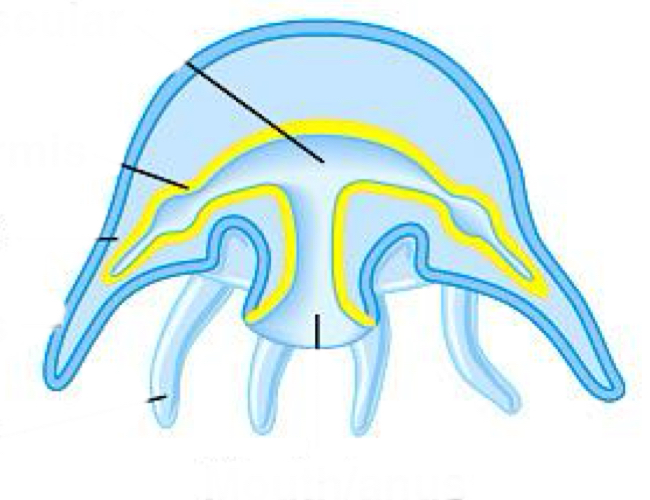
medusa
nematocyst
stinging capsules with barbs on cnidarians
ctenophora
comb jellies
colloblasts
adhesive cells on tentacles of ctenophora
mode of infection: schistosoma
enters through skin + moves to intestines
host: snail
mode of infection: clonorchis
enters by eating raw fish + moves to bile ducts
host: snail
mode of infection: taenia
tapeworm
eating undercooked beef/pork