Term for HP Test 1 pt 2
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
greek or latin (more specifically organs are latin, disease are greek)
most organ are ancient ____ or ____
prefix & suffix
_____ & _____ both
can be a syllable or group of syllables
vowel
root vs combining form
combining form is a root word to which a ____ has been added
melon/o poli/o
colors: ___ means black, ____ means grey
constant (ex gastr/o/enter/o/logy)
When combining two combining forms you keep the combining form vowel
When combining a combining form with a suffix that begins with a _____ you keep the combining form vowel.
vowel
When combining a combining form with a suffix that begins with a ____ you drop the combining form vowel
A prefix goes at the beginning of the word and no combining form vowel is used
suffix
When defining a medical word, start with the ____ first and then work left to right stating the word parts.
pertaining to
al means
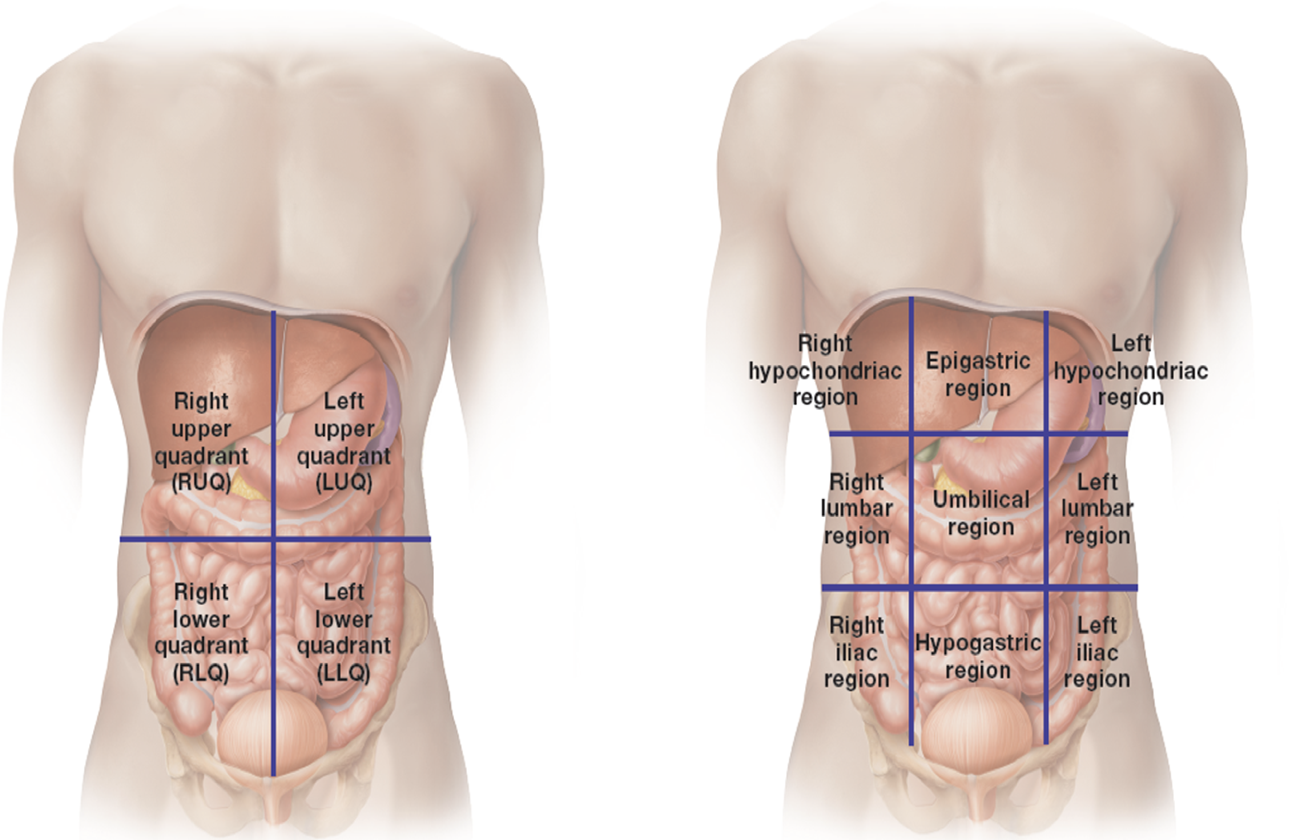
planes, directions, cavities
Anatomic(al) reference systems are used to describe the locations of the structural units of the body
These anatomical reference systems include:
Structural units
Body ____
Body ____
Body _____
anatomical position
____ _____, is that of the body standing upright, with the feet at shoulder width and parallel, toes forward. The upper limbs are held out to each side, and the palms of the hands face forward as illustrated.
anterior
For example, a scar in the “anterior (front) carpal (wrist) region” would be present on the palm side of the wrist. The term “_____” would be used even if the hand were palm down on a table.
prone
A body that is lying down is described as either ____ (face down)
supine
or _____ (face up).
cells
structural units of the body
-___ simplest level of org
- tissues are similar cells funtioning together
-tissues work together to form organs —> organ systems
human body levels of org
-atoms - p + n (nucleus) & e -
-elements: cannot be broken down , made of atoms
molecules
human body levels of org
-_____: chemical combination of 2 atoms that form a chem bond w/ each other
-simple or complex
-ex. water has polar covalent bonds
-most important to humans (60%)
100,000
The nucleus in the cell controls reproduction (cell division) and the overall function. The nuclear region contains rod-like genetic structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of the DNA molecules that contain the body’s genes, and each chromosome contains about _______ genes.
somatic cell
A _____ _____ is any cell in the body except the gametes (sex cells). Somatic cells contain 46 chromosomes arranged into 23 pairs. There are 22 identical pairs of chromosomes (autosomes), plus an additional pair. In a typical female, this remaining pair consists of XX chromosomes. In a typical male, this pair consists of an XY chromosome pair.
sex cell
A ___ _____ (sperm or egg), also known as a gamete, is the only type of cell that does not contain 46 chromosomes. Instead, each ovum (egg) or sperm has 23 single chromosomes. In a female, one of these will be an X chromosome. In a male, one of these will be either an X or a Y chromosome. When a sperm and ovum join, the newly formed offspring receives 23 chromosomes from each parent, for a total of 46. It is the X or Y chromosome from the father that determines the sex of the child.
planes
the body _____
-aligned to body in anatomical position
-use forum for radiology imaging
frontal
vertical planes (1) The _____ plane which divides the body into a front and back portion. Routine chest x-rays are shot from this direction
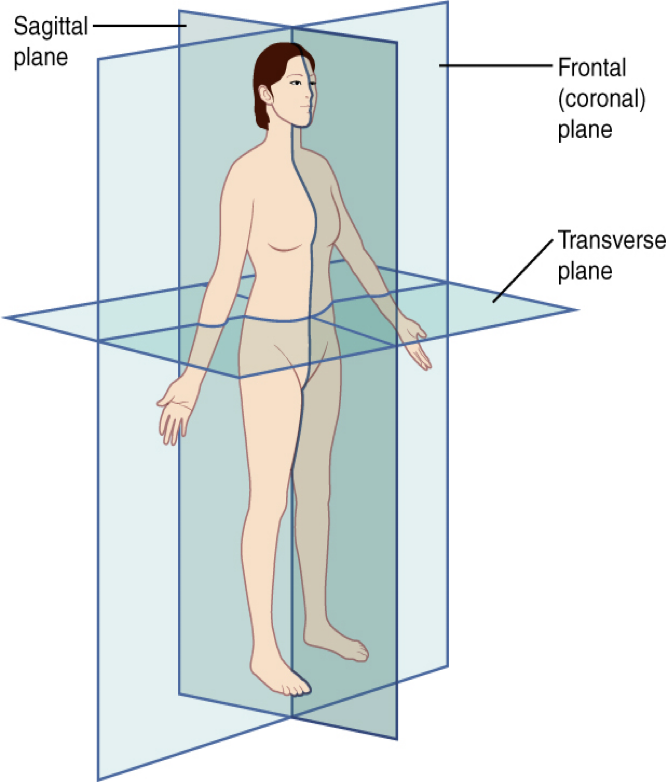
sagittal
vertical planes (2) The _____ plane divides the body lengthwise into a left and right side. Lateral chest x-rays are taken from this view
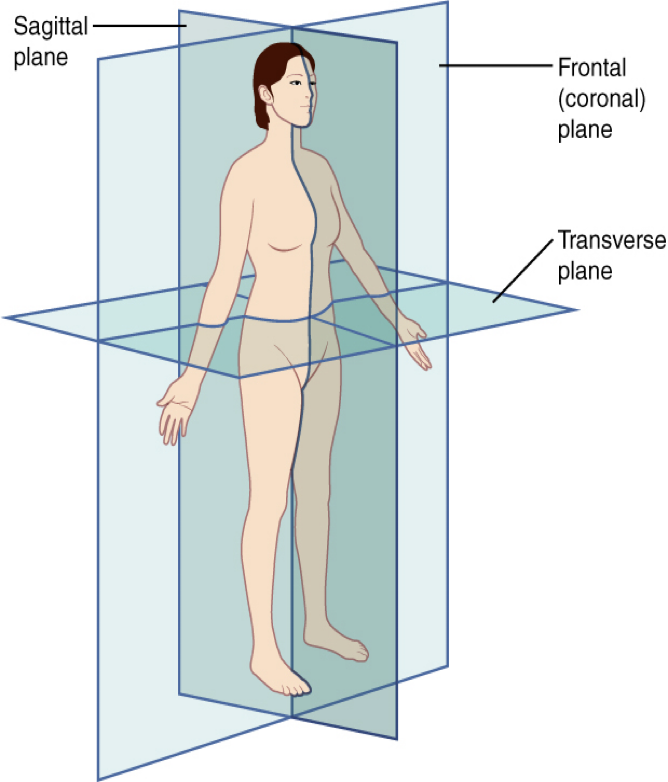
transverse
The Horizontal Plane (1)
The ______ plane is a horizontal plane that divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) portions. A transverse plane can be at the waist or at any other level across the body. This plane is utilized in computed tomography (CT scans)
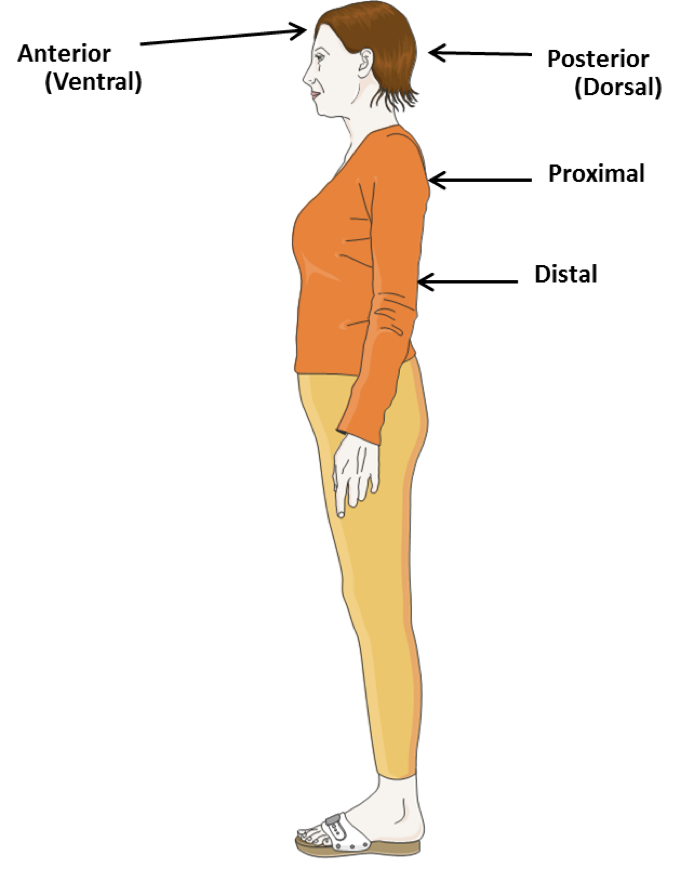
anterior
_____ means situated in the front. It also means on the front or forward part of an organ (anter means front or before, and -ior means pertaining to). For example, the stomach is located anterior to (in front of) the pancreas. Anterior is also used in reference to the ventral surface of the body.
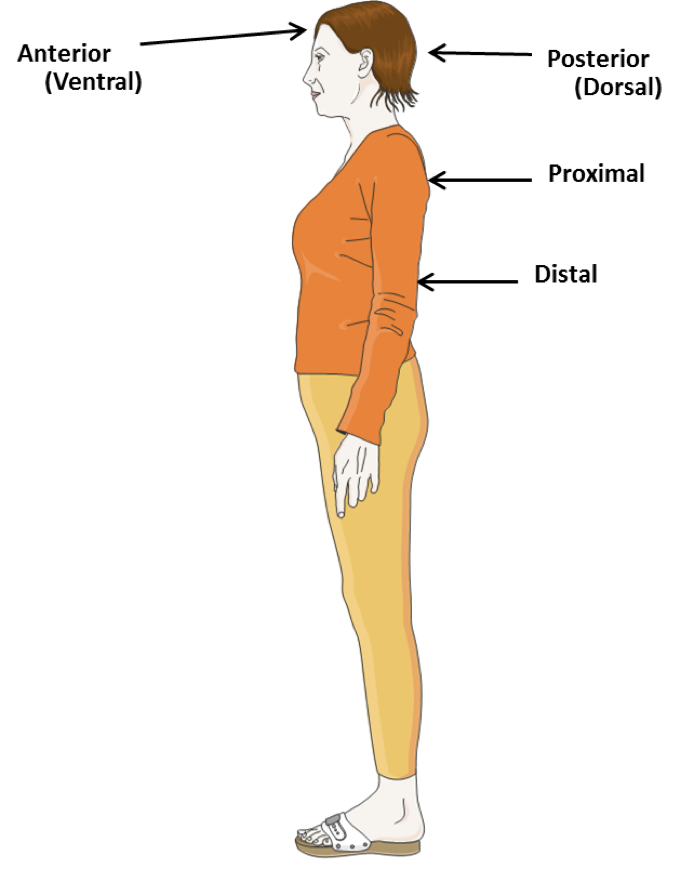
posterior
_____ means situated in the back. It also means on the back part of an organ (poster = back or toward the back, and -ior = pertaining to). For example, the pancreas is located posterior to (behind) the stomach. The term posterior is also used in reference to the dorsal surface of the body.
superior
means uppermost, above, or toward the head. For example, the lungs are located superior to (above) the diaphragm
proximal
______ means situated nearest the midline or beginning of a body structure. For example, the proximal end of the humerus (bone of the upper arm) forms part of the shoulder
medial
______ means the direction toward, or nearer, the midline. For example, the medial ligament of the knee is near the inner surface of the leg
inferior
______ means lowermost, below, or toward the feet. For example, the stomach is located inferior to (below) the diaphragm
caudal
_____ means toward the lower part of the body (caud means tail or lower part of the body, and -al means pertaining to)
Distal
____ means situated farthest from the midline or beginning of a body structure. For example, the distal end of the humerus forms part of the elbow
lateral
_____ means the direction toward, or nearer, the side of the body, i.e. away from the midline. For example, the lateral ligament of the knee is by the side of the leg. Bilateral means relating to, or having two sides
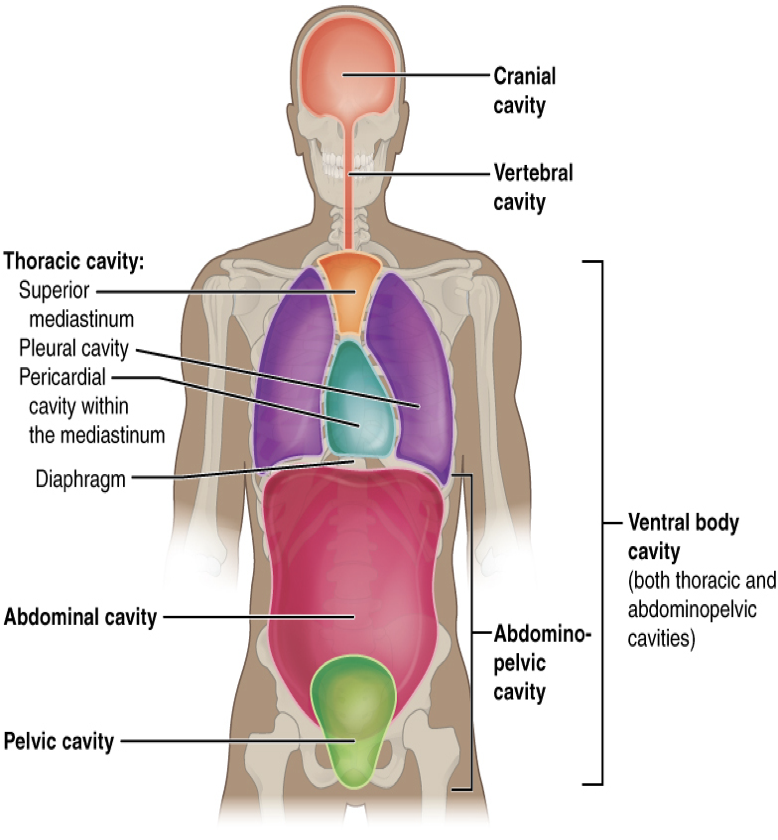
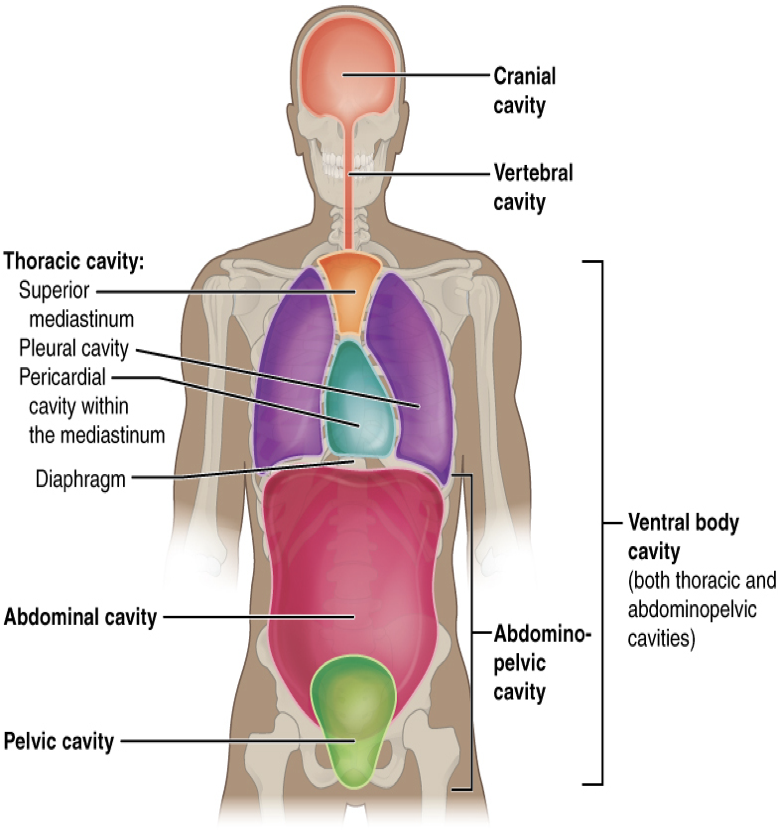
body cavities
The body maintains its internal organization by means of membranes, sheaths, and other structures that separate compartments
One way to divide the body and study the organ positions is by using the _____ ______
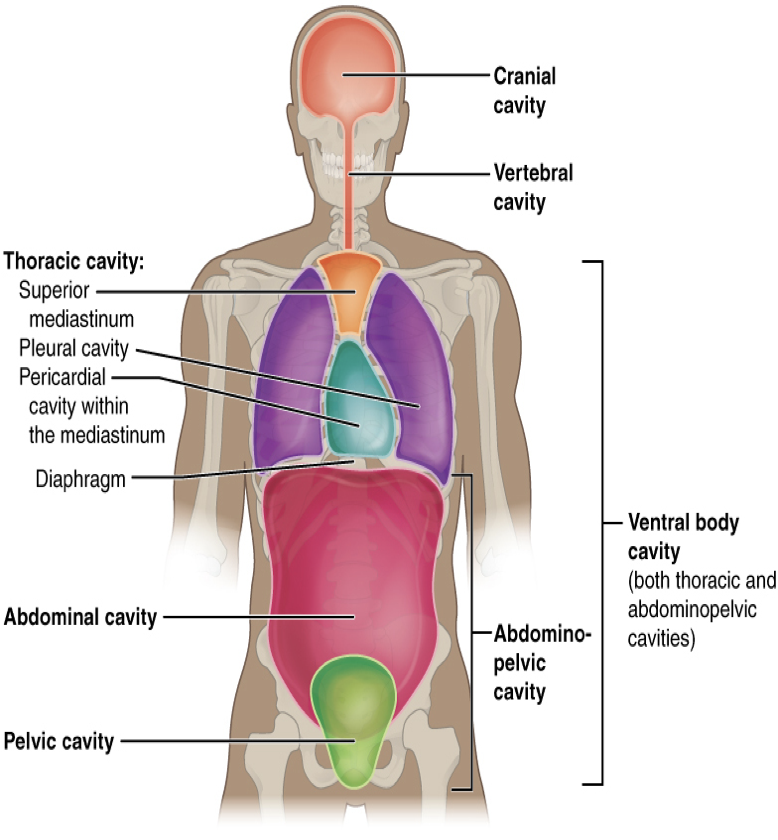
dorsal, ventral
The _____ (posterior) cavity and the ______ (anterior) cavity are the largest body compartments.
These cavities contain and protect delicate internal organs
ventral
The _____ cavity allows for significant changes in the size and shape of the organs as they perform their functions.
The lungs, heart, stomach, and intestines, for example, can expand and contract without distorting other tissues or disrupting the activity of nearby organs.
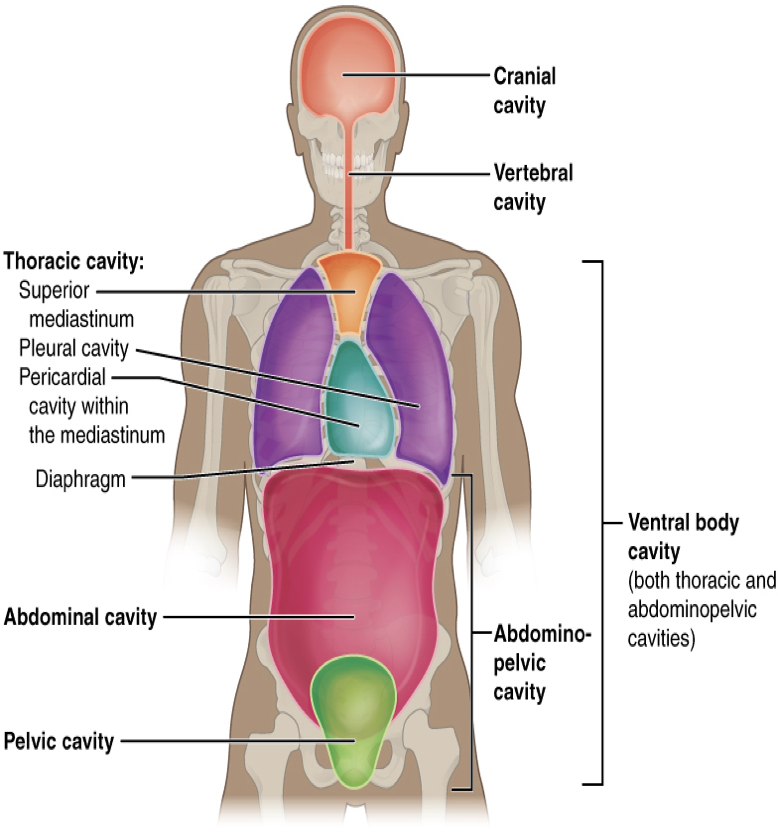
cranial
The dorsal and ventral cavities are subdivided into five spaces or cavities in which the organs are located.
Dorsal cavities
The _____ cavity is located within the skull, surrounds and protects the brain and the pituitary gland. Cranial means pertaining to the skull
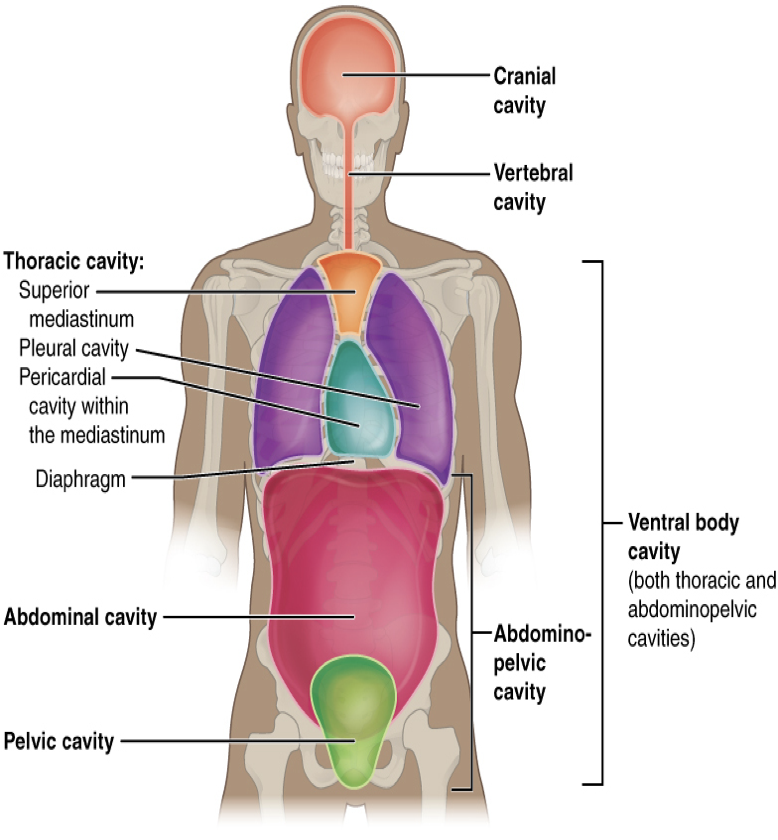
spinal
The dorsal and ventral cavities are subdivided into five spaces or cavities in which the organs are located.
Dorsal cavities
The _____ cavity is located within the spinal column, surrounds and protects the spinal cord
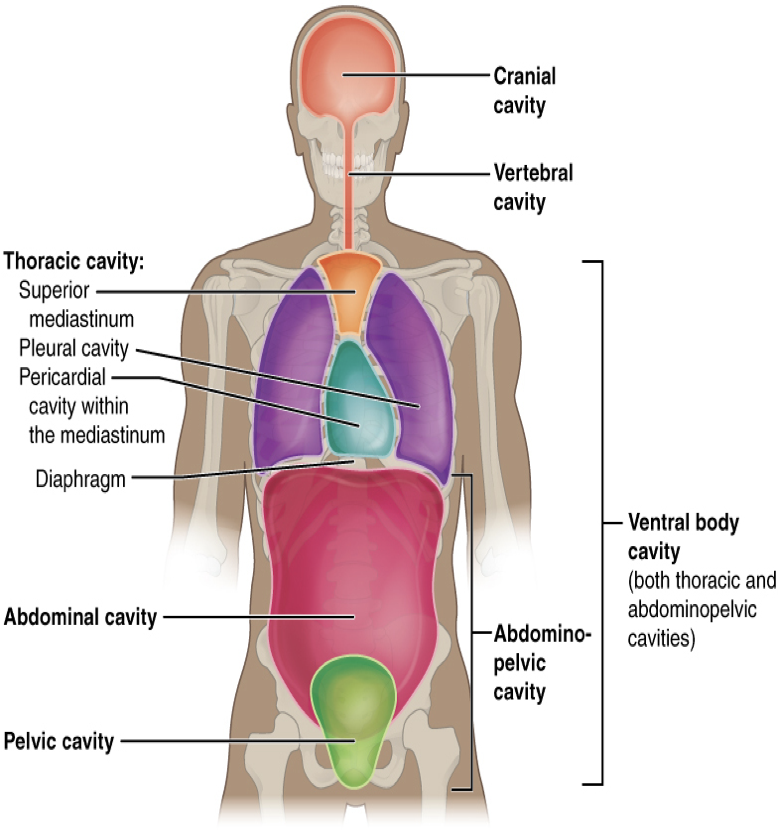
thoracic
The ventral cavity is located along the front of the body, contains the body organs that sustain homeostasis: the processes through which the body maintains a constant internal environment (home/o means constant, and -stasis means control).
The ventral cavity is divided into the following portions:
The _____ cavity- chest cavity (thorax) surrounds and protects the lungs, heart, esophagus, and trachea. The diaphragm is a muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities
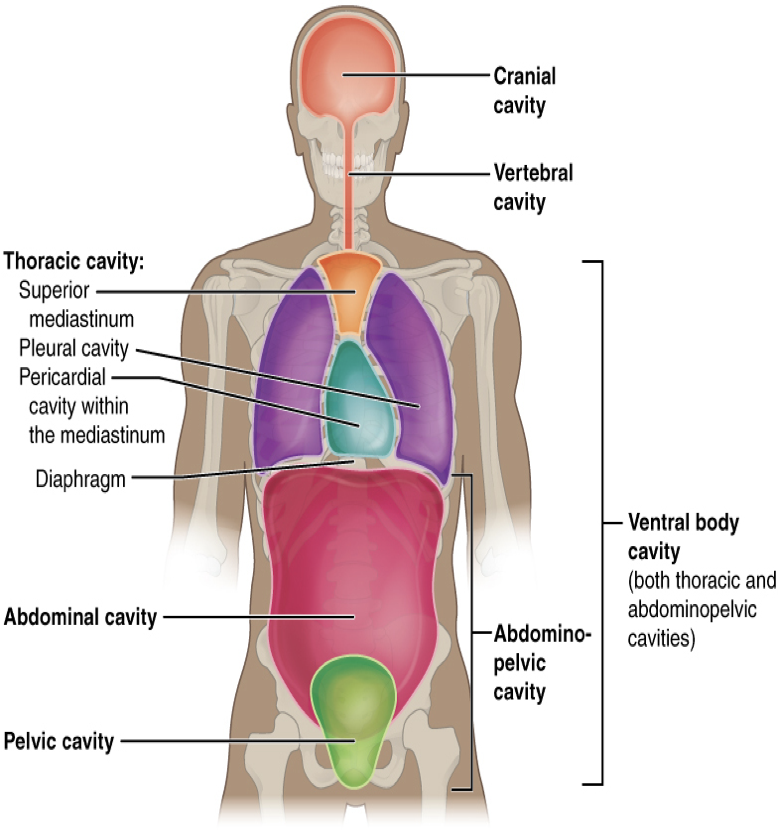
abdominal
The ventral cavity is located along the front of the body, contains the body organs that sustain homeostasis: the processes through which the body maintains a constant internal environment (home/o means constant, and -stasis means control).
The ventral cavity is divided into the following portions:
The _____ cavity- (the abdomen) contains the stomach, intestines, spleen, liver, pancreas, and gall bladder.
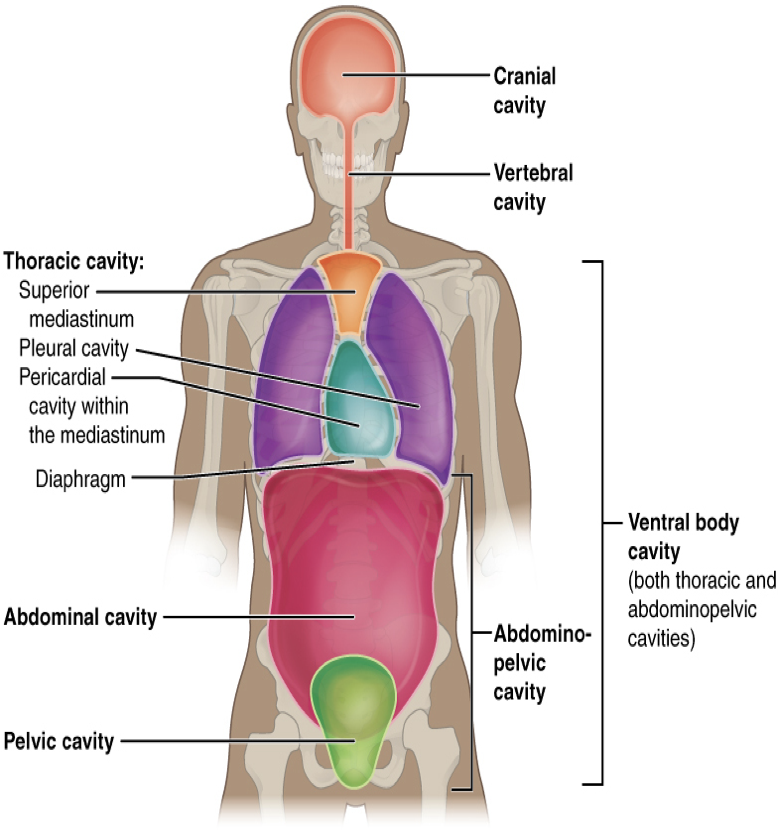
pelvic
The ventral cavity is located along the front of the body, contains the body organs that sustain homeostasis: the processes through which the body maintains a constant internal environment (home/o means constant, and -stasis means control).
The ventral cavity is divided into the following portions:
The _____ cavity- contains the urinary bladder, female reproductive structures, and lower parts of intestines
can they let Santa cook ?
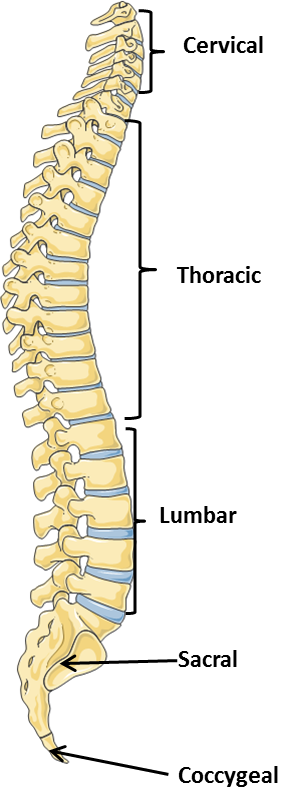
division of the spine
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
Coccygeal
how to remember?
disc
The last two divisions are fused segments of bone. In between the other vertebrae is a pad of cartilage called a _____. prevents rubbing!
do we need to know this?