6.3 Complex Genetics
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is the difference between continuous and discrete variation?
Continuous variation shows a range of phenotypes with no clear categories (e.g., height); discrete variation shows distinct categories (e.g., blood type).
What type of inheritance often results in a normal distribution of variation?
Polygenic inheritance.
What are examples of human characteristics associated with polygenic inheritance?
Skin color, height, eye color, and body weight.
What are two environmental factors that can influence phenotypes?
Nutrition (affecting height and weight) and sunlight exposure (affecting skin pigmentation).
What allele combinations in gametes result from independent assortment of two unlinked genes?
Since the genes are on different chromosomes, the inheritance of one gene does not affect the other. The possible gamete combinations are AB, Ab, aB, and ab, each in equal proportions (25%).
How do you depict a dihybrid cross between two unlinked heterozygous genes using correct notation?
The easiest way to work out potential gamete combinations in a dihybrid cross is to use the FOIL method:
FOIL = First / Outside / Inside / Last
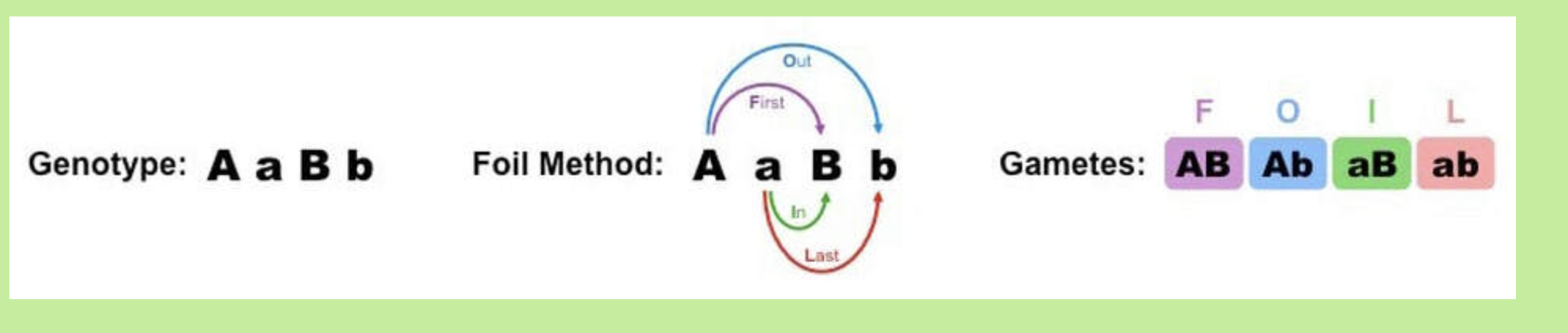
What is the expected genotype ratio for F2 offspring from a dihybrid cross of unlinked genes?
1 AABB : 2 AABb : 2 AaBB : 4 AaBb : 1 AaBB : 1 AAbb : 1 aaBB : 2 aaBb : 1 aabb (simplified to 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio).
What is the phenotypic ratio of F2 offspring from a dihybrid cross of unlinked genes?
9 dominant for both traits : 3 dominant for first, recessive for second : 3 recessive for first, dominant for second : 1 recessive for both traits.
What makes genes "linked"?
Linked genes are located close together on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together.
Why do linked genes fail to assort independently during meiosis?
Because they are physically connected on the same chromosome and usually move together into the same gamete unless separated by crossing over.
How do you represent linked genes using correct notation?
Show alleles beside vertical lines for homologous chromosomes, e.g., AB/ab (linked on one chromosome).
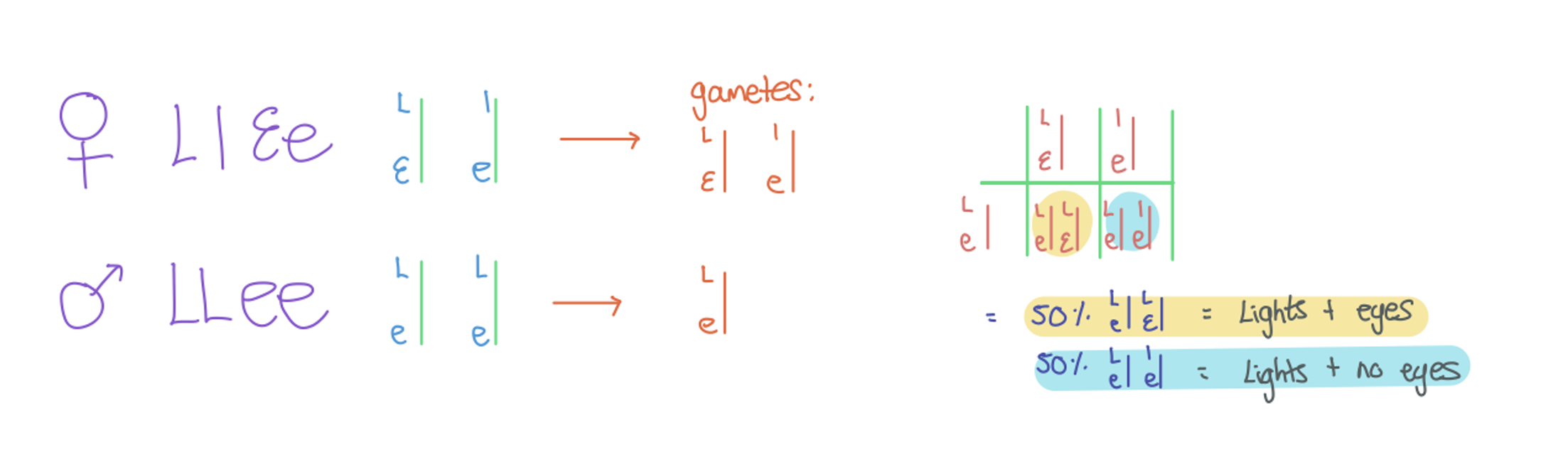
What is the effect of linkage on the outcome of a dihybrid cross?
Linkage keeps genes on the same chromosome inherited together, so most offspring show parental phenotypes, with few recombinants from crossing over. This causes the phenotypic ratio to deviate from the 9:3:3:1 expected for independent assortment.
They do not follow Mendel’s law of independent assortment, which assumes genes are on different chromosomes.
What is a recombinant?
An individual with a combination of alleles or traits different from either parent, due to new allele combinations in gametes.
How does independent assortment of unlinked genes lead to recombinants?
Unlinked genes segregate independently during meiosis I, creating new allele combinations in gametes that differ from parental combinations.
Metaphase I Random orientation of chromosome pairs
How does crossing over between linked genes lead to recombinants?
Crossing over during prophase I of meiosis can swap alleles between homologous chromosomes. This produces recombinant chromosomes and therefore gametes with new combinations of linked alleles, increasing genetic variation in offspring.
What are the recombinant offspring in a dihybrid cross of unlinked genes (AaBb x aabb)?
Ab and aB gametes create recombinant offspring: Aabb and aaBb.
What are the recombinant offspring in a dihybrid cross of linked genes (e.g., AB/ab x ab/ab)?
If crossing over occurs, recombinants will be Ab and aB; offspring genotypes will include Ab/ab and aB/ab.
How do you calculate a chi-square (χ²) value for a dihybrid cross?
Use the formula χ² = Σ[(O - E)² / E], where O = observed frequency and E = expected frequency for each phenotype.
![<p>Use the formula χ² = Σ[(O - E)² / E], where O = observed frequency and E = expected frequency for each phenotype.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/efff0f85-a5f3-420e-8c22-d8e3e475ab0f.webp)
What is the null hypothesis in a chi-square test for a genetic cross?
There is no significant difference between observed and expected results; deviations are due to chance.
What is the alternative hypothesis in a chi-square test for a genetic cross?
There is a significant difference between observed and expected results; deviations are not due to chance.
How do you use a p-value in a chi-square test?
Compare the calculated χ² value to the critical value at p = 0.05 and the appropriate degrees of freedom.
What does it mean if the p-value is greater than 0.05 in a genetic cross?
It means there is no statistically significant difference between the observed and expected results — any difference is likely due to chance. This supports the null hypothesis
What does it mean if the p-value is less than or equal to 0.05 in a genetic cross?
Reject the null hypothesis; the difference between observed and expected results is statistically significant.