Higher Chemistry - Unit 1 - Chemical changes and structure
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Covalent radius
a measure of the size of an atom, half the distance between nuclei of two covalently bonded atoms of an element
covalent radius along period
nuclear charge increases, number of filled shells remains same.
covalent radius down group
number of filled shells increases, nuclear charge increases.
screening / shielding meaning
"shields" outer electrons from positive nucleus so outer electrons are less strongly attracted to the nucleus
ionisation energy
energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms
first ionisation energy
energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of atoms in the gaseous state
What does an increase in nuclear charge cause?
the outer electrons to be more strongly attracted to the nucleus
what does an increase in number of electron shells cause?
outer electrons to be screened/shielded from the nucleus
Electronegativity
a measure of the attraction an atom involved in a bond has for the electrons of the bond.
what happens to the electronegativity along a period
nuclear charge increases so, increase in electronegativity
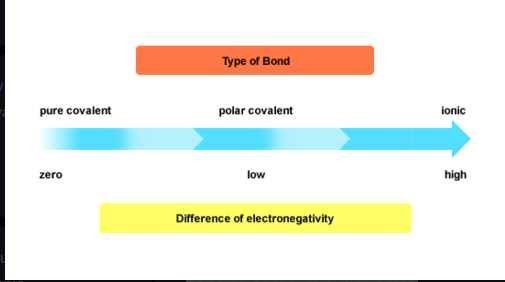
what is pure covalent bonding
occurs in compounds where both atoms have same electronegativity value, as both atoms have equal pull on shared electron
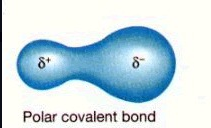
* Delta positive (δ+) and delta negative (δ-) notation used to indicate partial charges on atoms, which give rise to a dipole.
what is ionic bonding
atoms with large difference in electronegativity, inolves the transferring of electrons from one atom to another.
electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions
ionic compounds are held togther in the solid state by ______ ______
ionic bonds
covalent network compounds are held together in the solid state by _________ ______
covalent bonds
covalent molecules are held together in the solid state by forces of attraction know as ____ ___ _____ _______
van der waals' forces
Due to the stronger attractions, hydrogen bonded compounds have much _______ melting and boiling points
higher
what are van der Waals forces
Intermolecular forces between moleules \n - LDF'S \n - PDP-PDP that include hydrogen bonding
What are London Dispersion Forces
forces of attraction that can operate between all atoms and molecules
weakest bonds
formed as a result of electrostatic attraction between temporary dipoles and induced dipoles
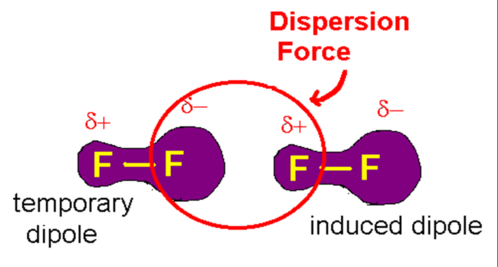
When does london dispersion forces occur?
between all molecules + atoms but only force between NON-POLAR molecules and MONATOMIC elements.
What is an induced dipole
when neighbouring atom shifts from approaching delta negative causing delta positive to appear
What causes LDF'S?
caused by uneven distribution of moving electrons. \n forms temporary dipoles with slightly positive and negative sides.
when do permanent dipole-permanent dipole interactions occur
between polar molecules
When is a molecule polar?
- If it has a permanent dipole
* stronger than LDF'S
* permanent dipole of one molecule attracted to a neighbouring one
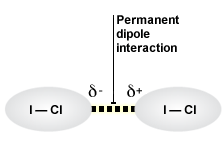
* stronger than PDP-PPD but weaker than covalent
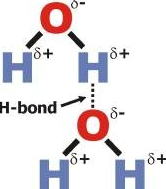
How to determine strength of intermolecular forces?
- melting points - boiling points- viscosity
What does hydrogen bonding affect?
- boiling points \n - melting points \n - viscosity/miscibility
What element's boling points are affected by hydrogen bonds?
ammonia - water - hydrogen fluoride
What is a viscous liquid
Liquid that has strong intermolecular forces between molecules.
molecules with stronger intermolecular forces will have higher melting and boiling points and a ________ ____________
higher viscosity
* (an oxidising agent is something that causes another substance to be oxidised and is reduced in the process)
* group 7 strongest oxidising agents
reducing agent meaning
substance that donates electrons
-(a reducing agent is something that causes another substance to be reduced and is oxidised in the process).
group 1 strongest reducing agents
How to tell if its an oxidising agent
elements with high electronegativities tend to gain electrons, act as oxidising agents
what are the intermolecular forces between pure covalent molecular elements?
weak London dispersion forces (LDF)
What is metallic bonding
the electrostatic attraction between the positive ions and the delocalised electrons, these delocalised electrons allow them to conduct electricity
when do successful collisions occur
- collision geometry is correct \n - particles have energy equal to or greater than the activation energy
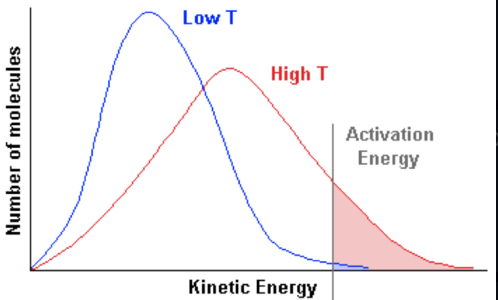
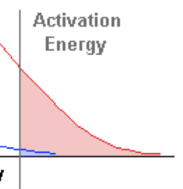
what happens in an exothermic reaction
heat energy been released to surrundings
ΔH has a negative value as energy has been lost.
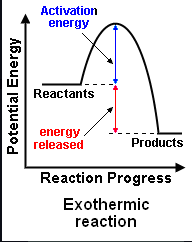
what happens in an endothermic reaction
products have more energy than reactants due to energy being taken in from surroundings
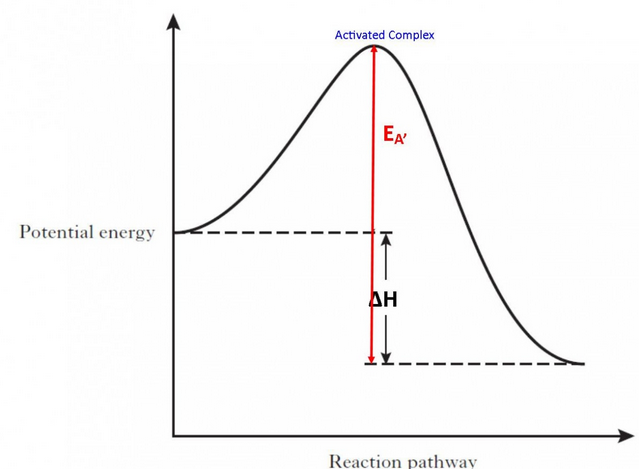
how do catalysts effect rate of reaction
speed up chemical reactions without being used up
lowers activation energy, allowing more reactions to occur
Activated complex meaning
The activated complex has the highest chemical potential energy in the reaction pathway (always higher than either the products or reactants), because it is an unstable arrangement of the atoms