NATF320 L9 Tropical deserts
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
defining deserts - challenging, many defintions exists
different criterai have been used
climate, vegetation phsuiognomy, vegetation cover, soil properties
border with grassland/savanna biomes is often blurry
central aspects → water scarcity (i.e. drought)
how do we quantify aridity
aridity index
aridity index = precipitation / potential evapotranspiration
potential evaportranspiration
wind, solar radiation, air temperature, relative humidity
desert substrates
desert pavemetn and exposed rock make up most desert
what creates deserts
atmospheric circulation → subtropical belt of high pressure, with stable and dry conditions
continentality → humid sea air tends to become drier as it moves further inland
rain shadows → orographic lift causes the air to dray as it goes over mountains
cold coastal currents → associated with upwelling systems, cause cooling and drying of the air
desert biota - the abiotic stressors
drougth → minimize water loss/maximize water acquisition
high solar radiation → protect from excess sunlight and avoid overheating
soil → physiological adaptatons
salinity, poor soil structure, scarce nutrients, special soil types
strong winds
sand abrasion
desert biota - plants
abiotic constraints
minimize water loss through transipiration
minimize damage from excessive solar radiation and overheating
some genral xeromorphic adaptions → low surface area:volume ratio, small leaves, sunken stomata, thick waxy cuticle, hairs
desert biota - plants
different ecophysiological strategies
different ecophysiologicla strategies
drought escape → complete life cycle in favourable season → ephemeral plants
drought avoidance → store water in tissues → succulent plants
drought tolerance → tolerate water loss → true xerophytes
succulents
water storage
renders the plant temporrily independent of external water supply
desert biota - xerophytes
(often evergreen shrubs/subshrubs), some lose their leaves during the driest season (drought deciduous), sometimes aphyllous, shrubs
hidden precipitation
importance of hidden precipitatoin → fog and dew
water uptake through hydathodes in crassula (crassulaceac) from the succulent karro and the namib
desert biota - animasl
abiotic constraints
minimize water loss
minimize damage from excessive solar radiation and overheating
desert biota - ecological strategies
heat evaders → shady microhabitats, hiding during hotter hours, being active during cooler hours
heat endures → limited activity during hotter hours, heterothermy, physiological adaptations to cope with water loss, increasing surface area
desert biota - animals
general adaptations
high surface area:volume ratio for heat dissipation (homeotherms/heterotherms)
waxy cover (arthropods) or hairs/feathers (vertebrates) → insulation form heat and cold
some adaptations to use hidden precipitation (fog, dew)
aridity could be driving cooperative breeding in mammals
desert biota - insects
fog basking behaviour → headstand position
ecology of deserts
in terms of plant diversity, most deserts are rather poor at regional scale
high geological, edaphic and topographic diversity → highly heterogeneous landscape with diverse microhabitats
differences between quartz islands and matrix habitats in terms of
soil physicochemical parameters and land cover
plant community regarding distribution ranges and life forms
interesting aspects of deserts ecohydrology
different root distribution among plant funcitonal groups
hydraulix redistribution or lift -
. passive process when transpiration decreases
vegetatoin structure in deserts
islands of fertility → shrubs accumulate moisture and nutrients, thus increasing icrobial activity in the soil → creates resource heterogeneity in the landscape
islands of fertility → some promote establishemt of seedlings of other species → nurse plant
self-organized vegetatoin patterns → often observed in ecosystems with limited resources → positive feedback between vegetation growth and distribution of moisture and nutrients
threats to deserts
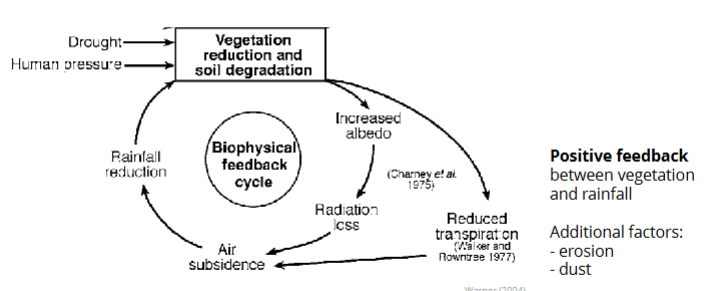
desertification → biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities → climate change (increasing aridity and/or changes in rainfall regimes)+ land use
vegetation changes
shifts between ecosystem stable states
thresholds of aridity, leading to abrupt ecological shifts
more than 20% of land surface, and almost 30% of dryland surface, will cross at least one of the thresholds by 2100 (sceanrio of sustained increase in CO2 emissions)
additonal factors beside changes in climate → e.g. CO2 fertilizaton and landuse/degradation
CITES
Convention on international trade in Endangered speceis of wild fauana dn flora
all parts and derivatives, live or dead, regulated