Test 5: Respiratory (histology)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
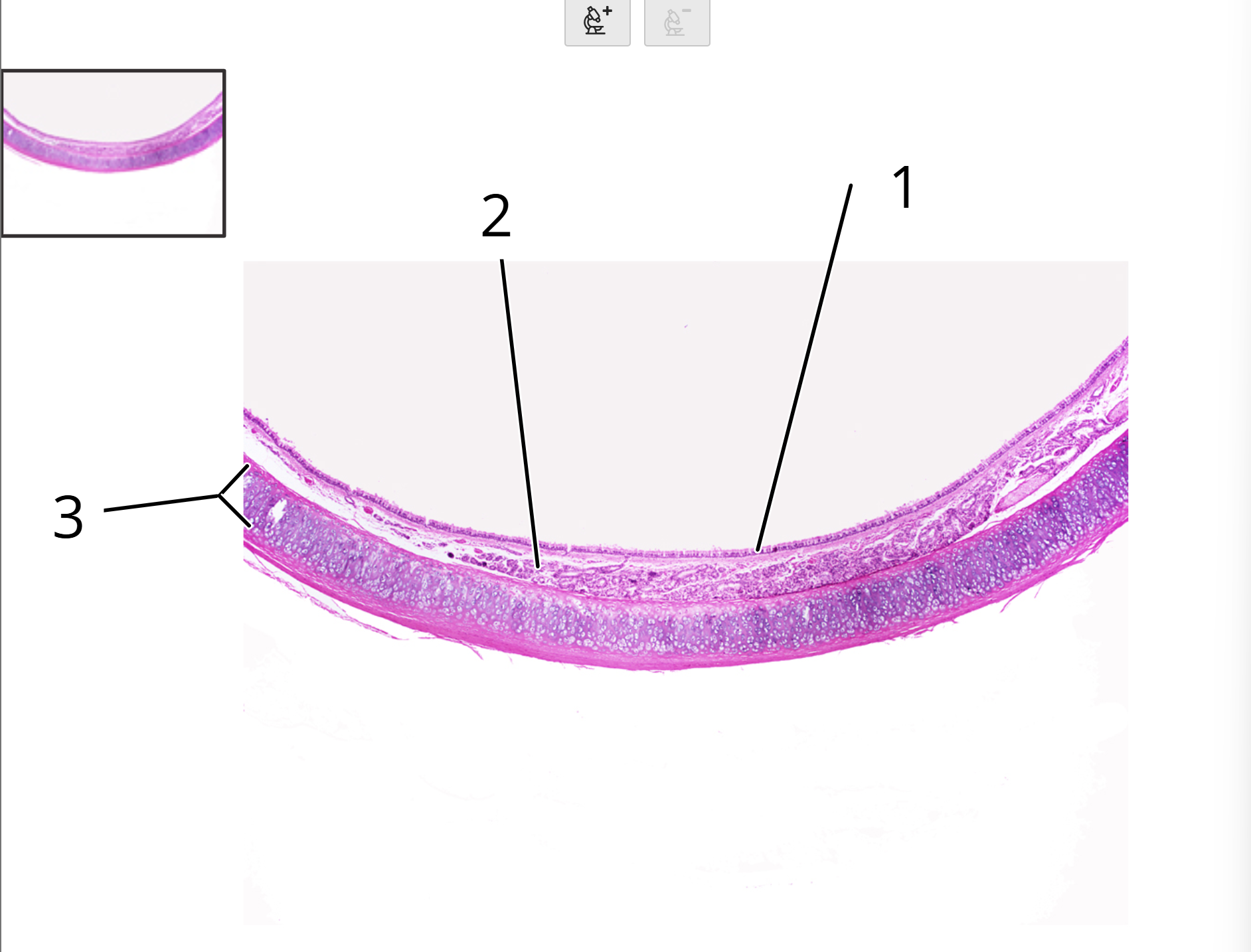
Trachea; cross section
1. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
2. Seromucous glands in submucosa
3. Hyaline cartilage
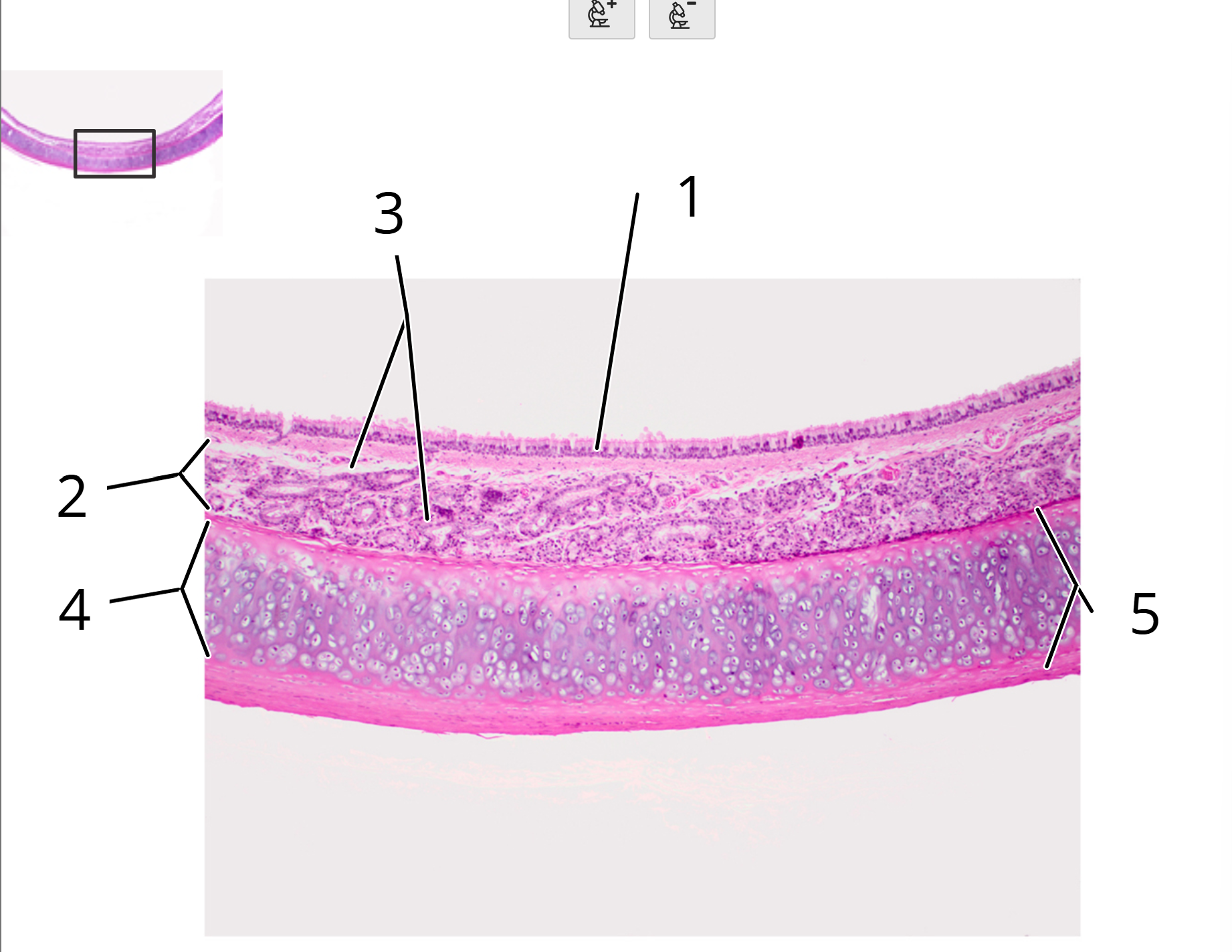
Trachea; cross section
1. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
2. Submucosa
3. Seromucous glands
4. Hyaline cartilage
5. Perichondrium
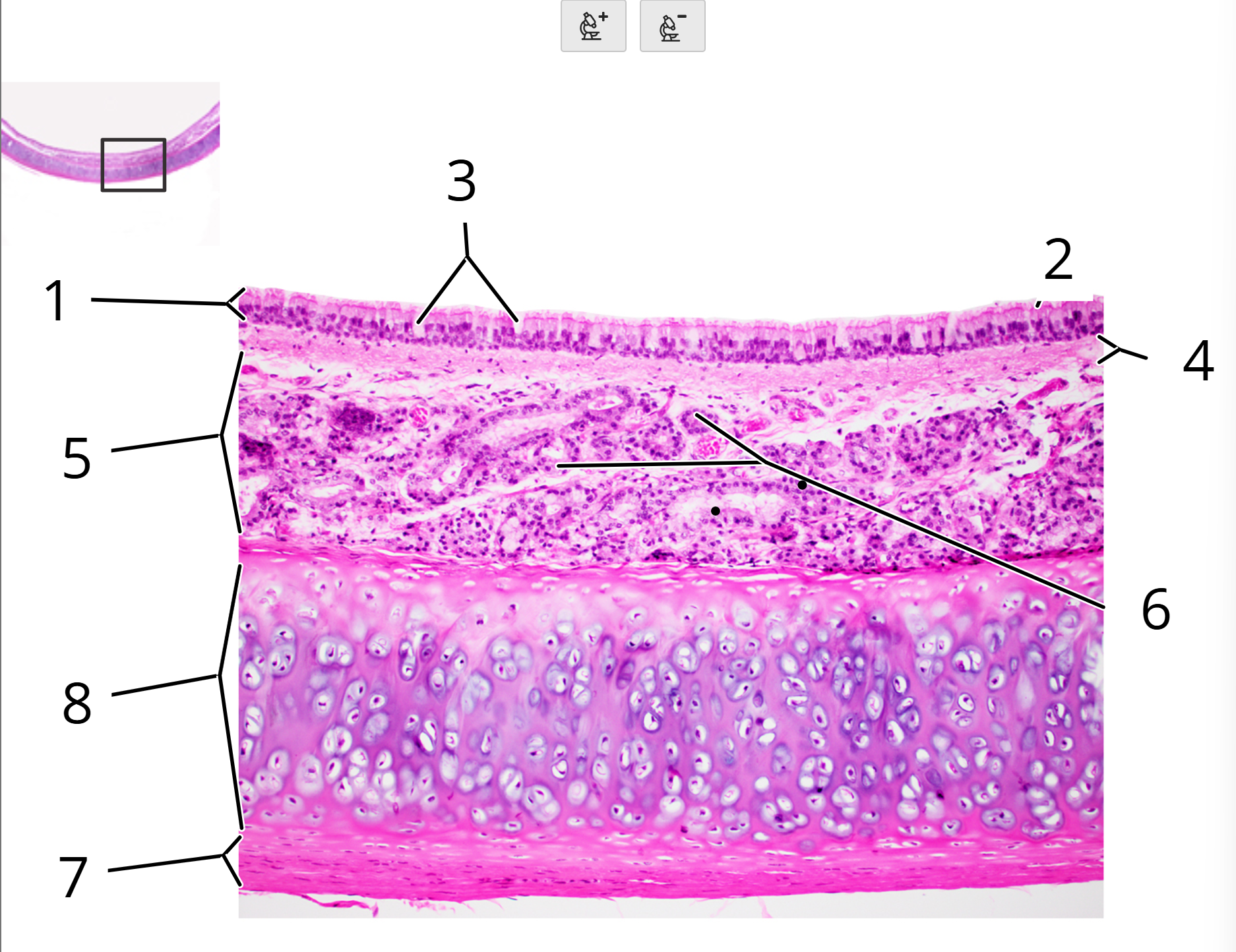
Trachea; cross section
1. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
2. Cilia
3. Goblet cells
4. Lamina propria
5. Submucosa
6. Seromucous glands
7. Perichondrium
8. Hyaline cartilage
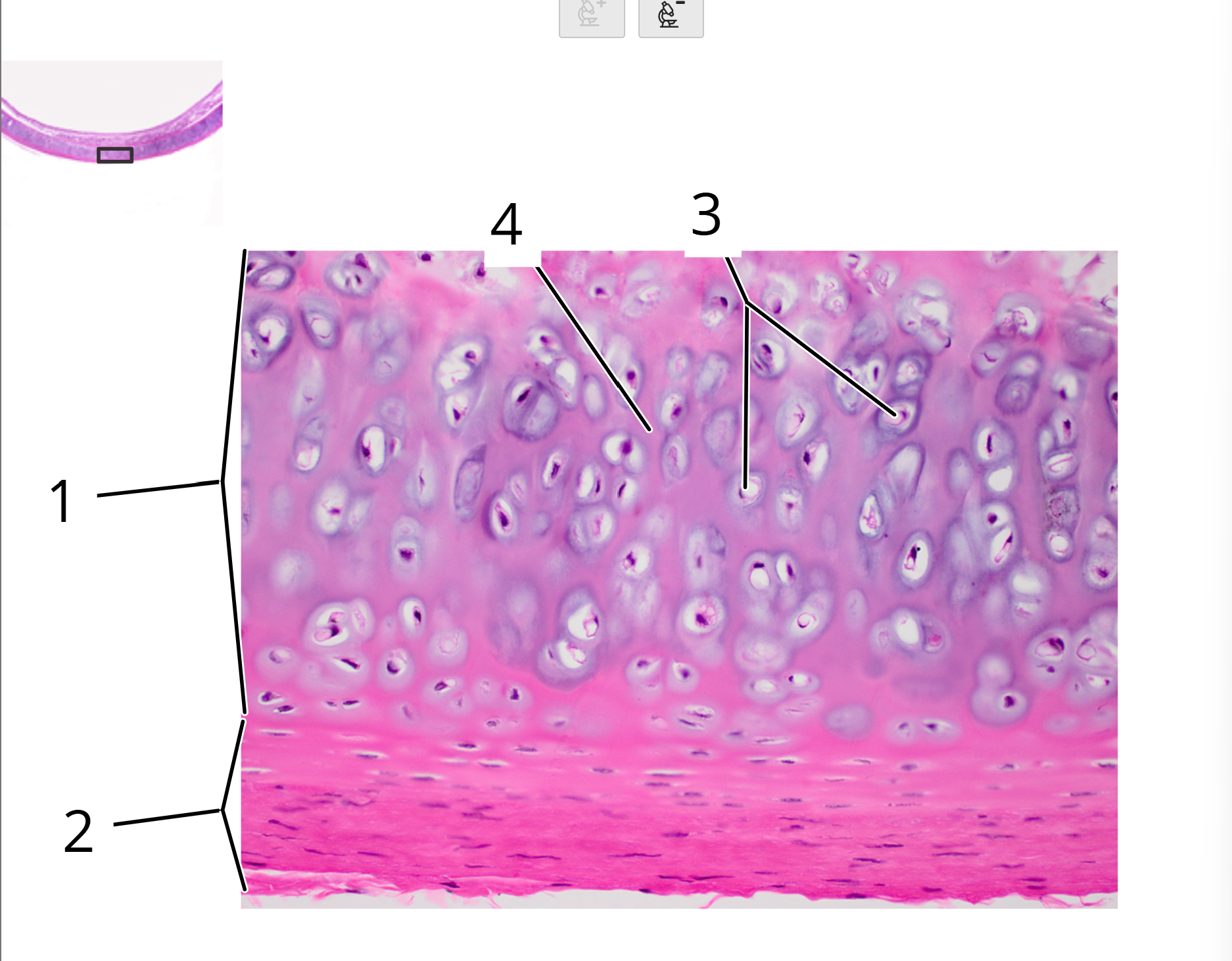
Trachea; cross section
1. Hyaline cartilage
2. Perichondrium
3. Chondrocytes in lacunae
4. Matrix
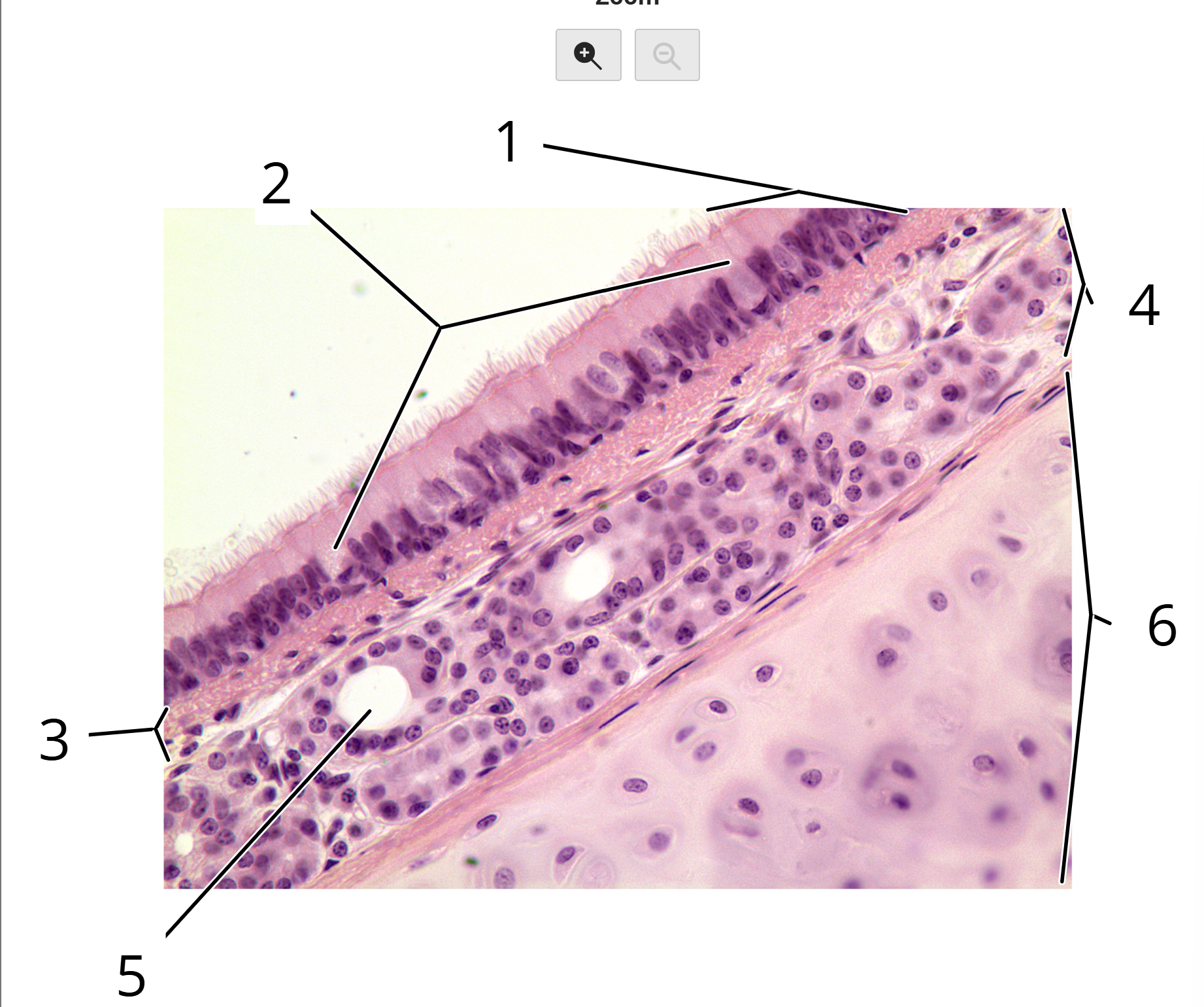
Trachea; cross section
1. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with cilia and goblet cells
2. Goblet cells
3. Lamina propria
4. Submucosa
5. Seromucous gland
6. Hyaline cartilage
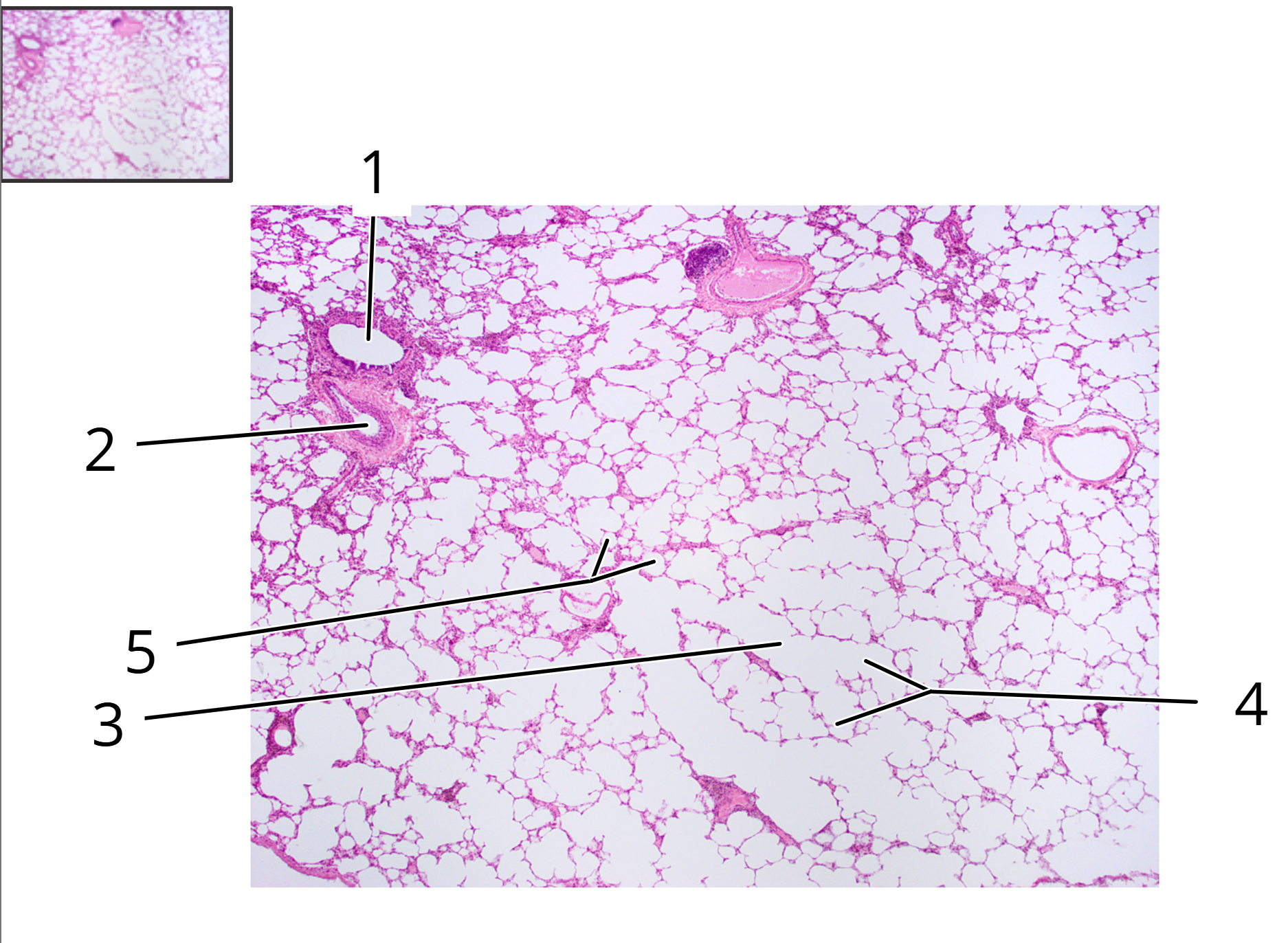
Lung; cross section
1. Bronchiole
2. Blood vessel
3. Alveolar duct
4. Alveolar sacs
5. Alveoli
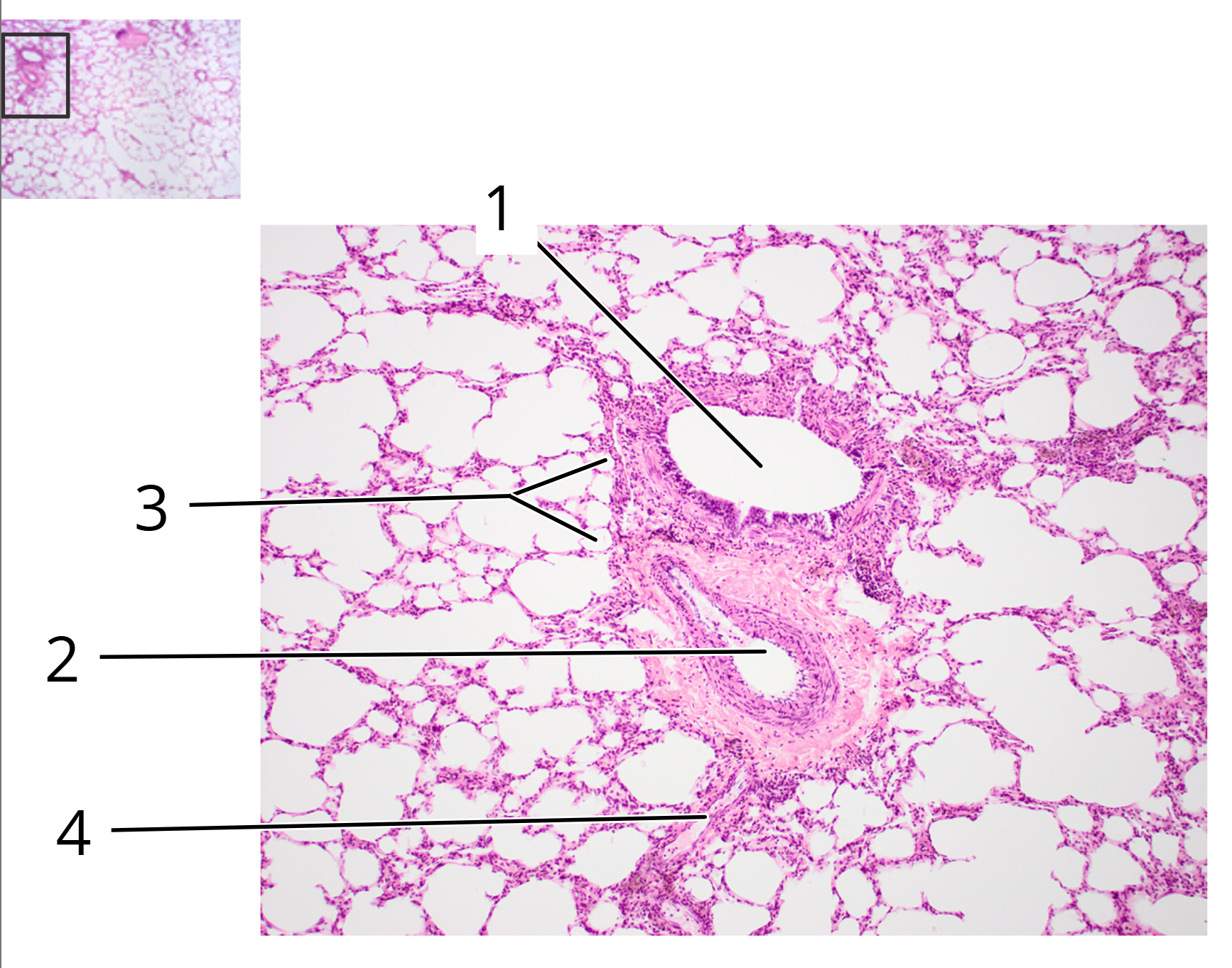
Lung; cross section
1. Bronchiole
2. Pulmonary artery
3. Alveoli
4. Pulmonary vein
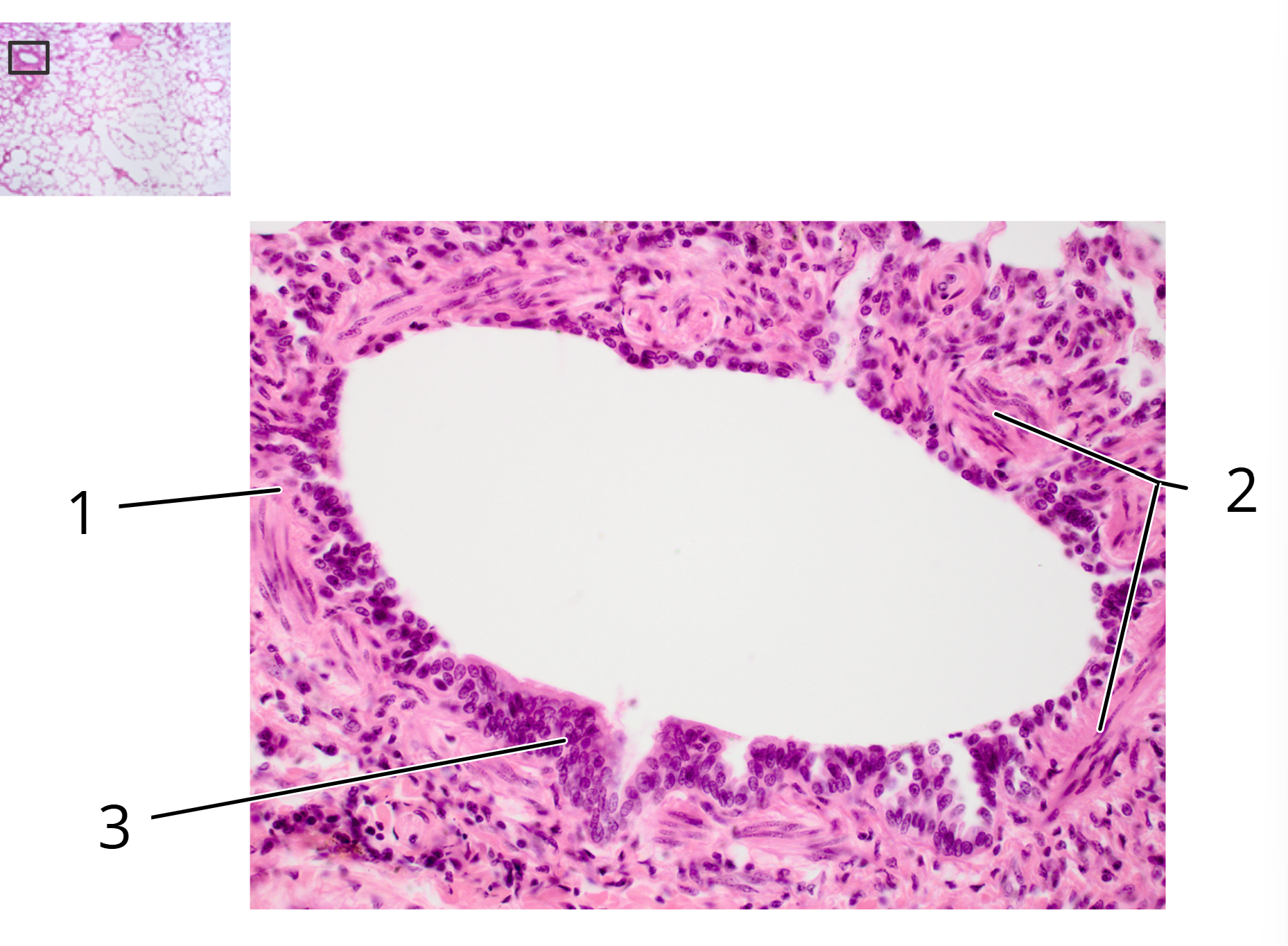
Lung, bronchiole; cross section
1. Bronchiole
2. Smooth muscle
3. Epithelium
Lung, pulmonary artery; cross section
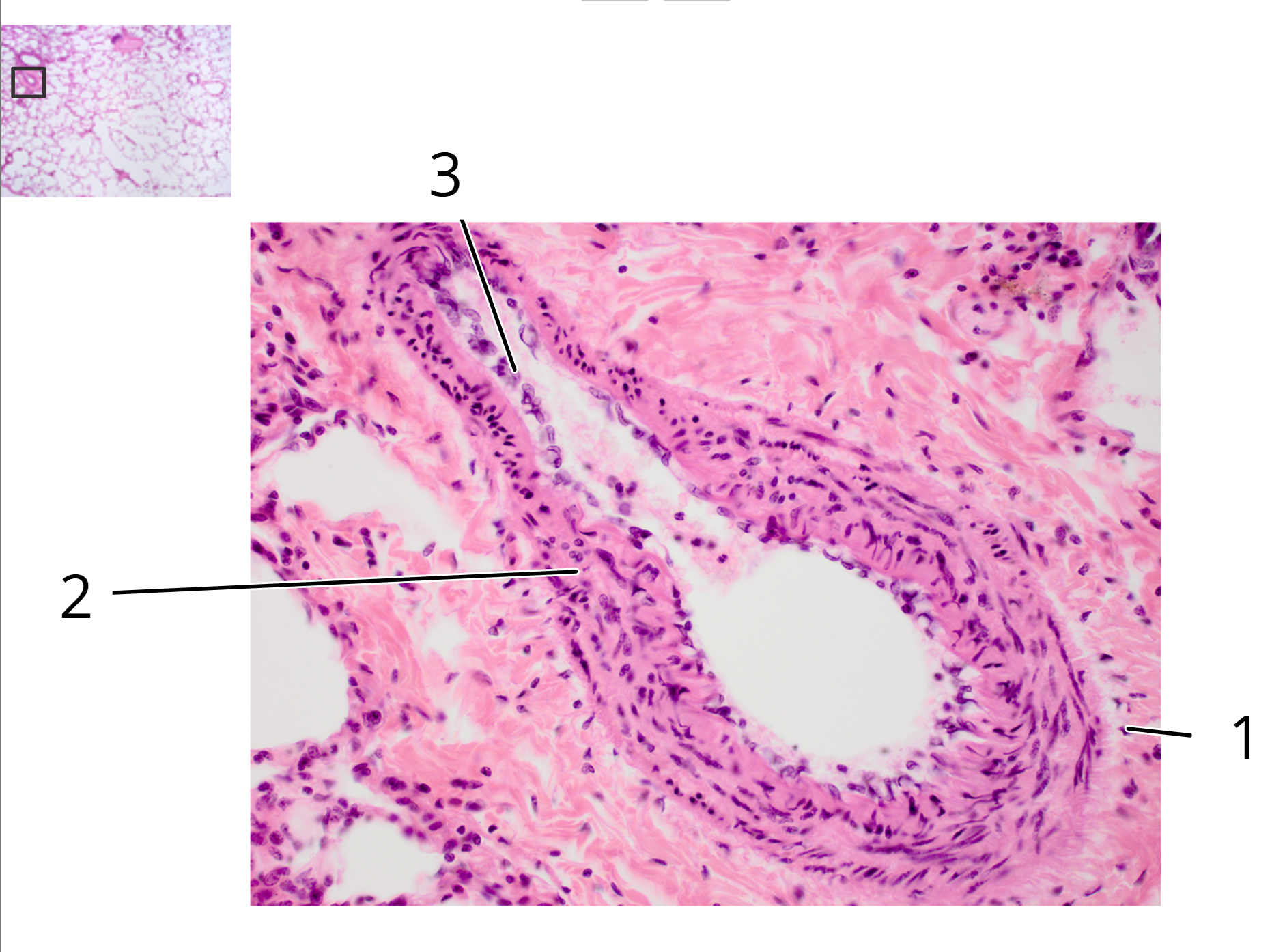
1. Tunica externa
2. Tunica media
3. Pulmonary artery
Lung; cross section
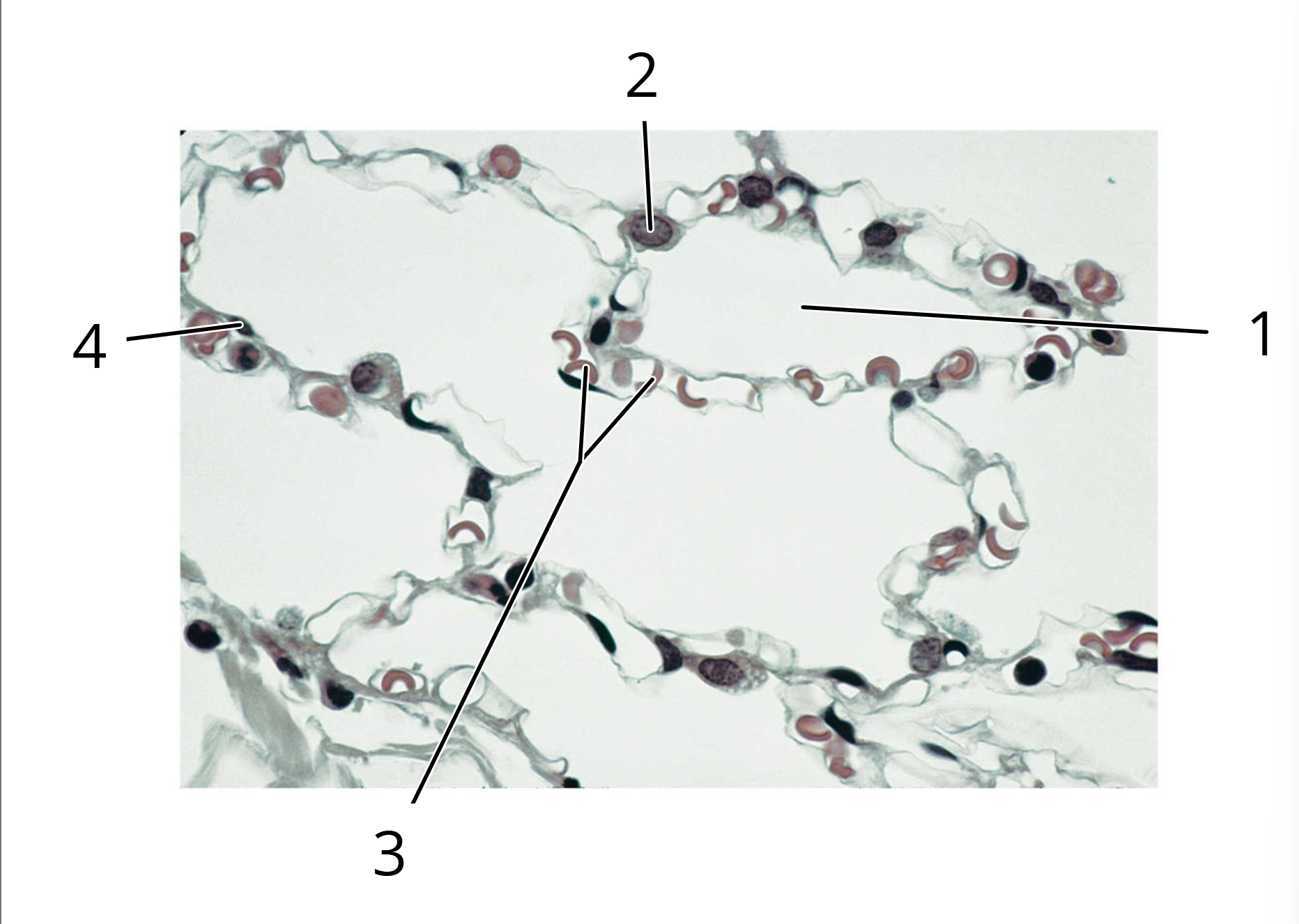
1. Alveolus
2. Type II cell
3. Red blood cells in capillary
4. Type I cell
The trachea is kept open by cartilage rings. These rings are composed of what type of cartilage?
The trachea is kept open by cartilage rings composed of hyaline cartilage. Hyaline cartilage provides structural support and maintains the trachea's open shape.
Which type of alveolar cell secretes surfactant? What is the purpose of surfactant?
Type II alveolar cells (also known as pneumocytes) secrete surfactant. Surfactant reduces surface tension within the alveoli, preventing their collapse and ensuring efficient gas exchange.
Which cells located within the epithelium contribute mucus to the secretions lining most of the structures of the respiratory system?
Goblet cells, located within the epithelium, contribute mucus to the secretions lining most of the structures of the respiratory system. This mucus traps particles and pathogens, aiding in their removal.
What structure is formed by the fusion of simple squamous epithelium of an alveolus and simple squamous epithelium of a capillary via a basement membrane?
The structure formed by the fusion of the simple squamous epithelium of an alveolus and the simple squamous epithelium of a capillary via a basement membrane is called the respiratory membrane. This thin barrier facilitates gas exchange between the air in the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries.
What type of tissue composes the lamina propria?
The lamina propria is composed of loose connective tissue. It supports the epithelium and contains blood vessels, nerves, and immune cells.
Do the pulmonary arteries contain oxygenated or deoxygenated blood?
The pulmonary arteries contain deoxygenated blood. They transport blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
Bronchial asthma is a reaction to inhaled allergens such as pollen, mold, or dust. In individuals who are hypersensitive to those allergens, the body experiences an inflammatory response in the bronchial tubes, and muscle surrounding the larger bronchi constrict.
1. Which type of muscle is found within the bronchi? Is the muscle relaxed or constricted when under sympathetic control?
Bronchi contain smooth muscle. Under sympathetic control, this muscle is typically relaxed, allowing for bronchodilation and increased airflow.
Bronchial asthma is a reaction to inhaled allergens such as pollen, mold, or dust. In individuals who are hypersensitive to those allergens, the body experiences an inflammatory response in the bronchial tubes, and muscle surrounding the larger bronchi constrict.
2. Part of the inflammatory response is an increase in mucosal secretions into the bronchi due to the release of histamine from mast cells. Which bronchial cells or structures increase their mucosal secretions in response to histamine?
In response to histamine, goblet cells and submucosal glands increase their mucosal secretions in the bronchi, contributing to the inflammatory response.
Bronchial asthma is a reaction to inhaled allergens such as pollen, mold, or dust. In individuals who are hypersensitive to those allergens, the body experiences an inflammatory response in the bronchial tubes, and muscle surrounding the larger bronchi constrict.
3. Which do you think would be the best initial treatment for chronic bronchial asthma: a bronchodilator to relax the smooth muscle OR an inflammatory such as glucocorticoids? Why?
The best initial treatment for chronic bronchial asthma is typically a bronchodilator to relax the smooth muscle. This provides immediate relief by opening the airways and improving airflow. Glucocorticoids, which address inflammation, are often used as a long-term management strategy.