Orgo Chem 1: Exam 4 - Alkene and Alkyne Reactions
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch. 8 and Ch. 9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
addition reaction
a reaction involving an increase in the number of groups attached to the alkene and a decrease in the number of elements of unsaturation
anti-addition reaction
an addition reaction in which two groups add to opposite faces of the double bond
electrophilic addition reaction
an addition in which the electrophile (electron-pair acceptor) bonds to one of the double-bonded carbons first, followed by the nucleophile
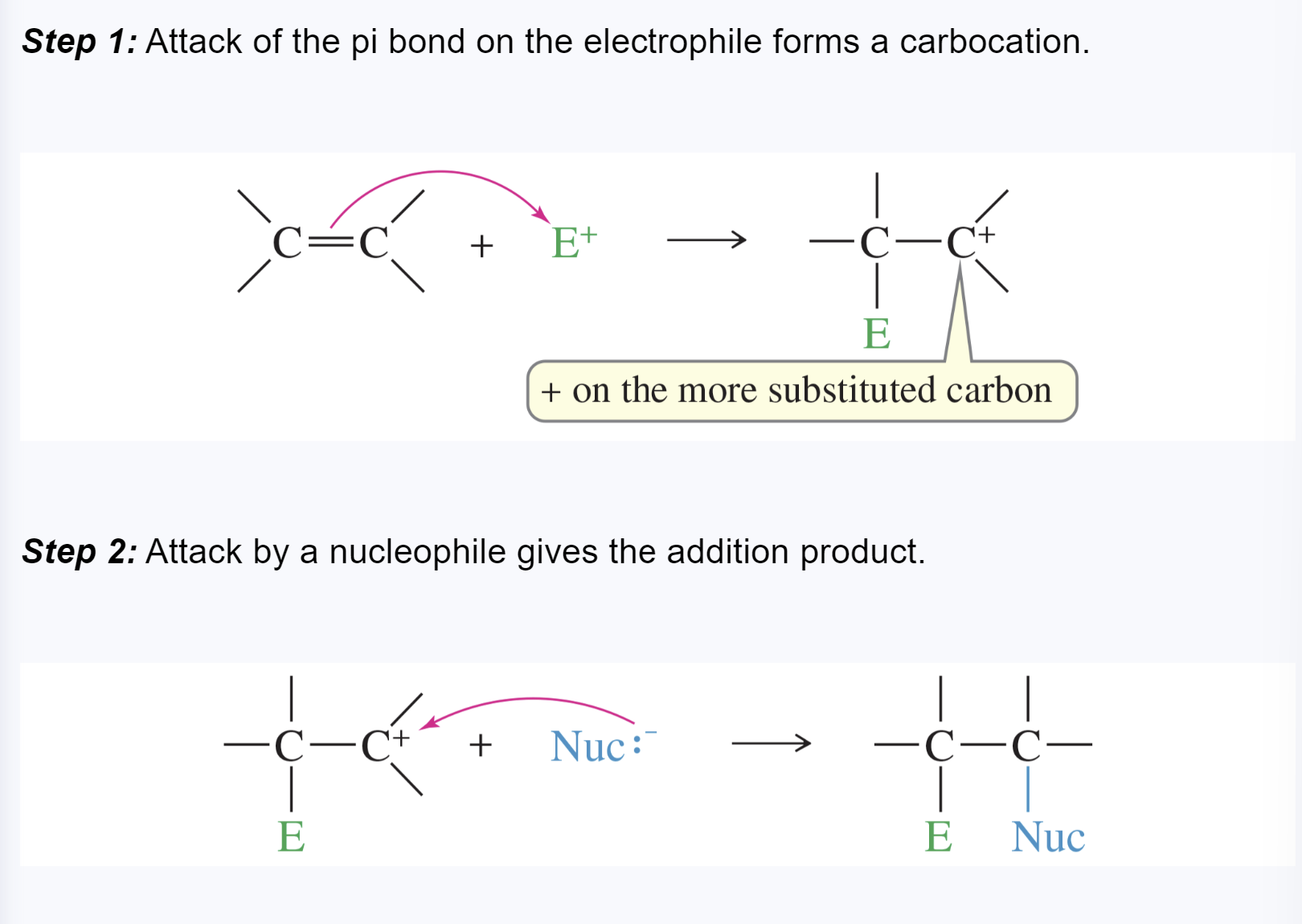
syn addition reaction
an addition in which two groups add to the same face of the double bond
addition polymer
a polymer that results from the addition reactions of alkenes, dienes, or other compounds with double and triple bonds
most addition polymers form by a chain-growth process
alkoxy group
(alkoxyl group) —> (—O—R)
an alkyl group bonded through an oxygen atom, as in an ether
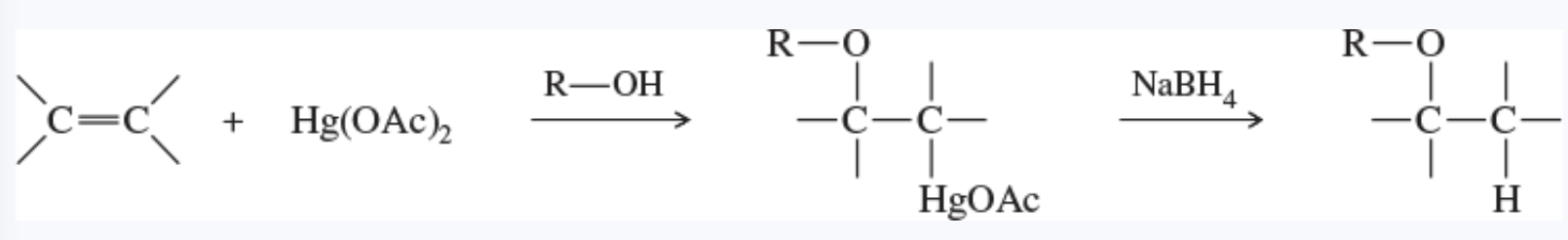
alkoxymercuration
the addition of mercuric acetate to an alkene in an alcohol solution, forming an alkoxymercurial intermediate
demercuration gives an ether
alkylidene group
one of the carbon atoms at either end of a double bond, together with its two substituents
most commonly: =CH2, =CHR, or =CR2
alpha elimination
the elimination of two atoms or groups from the same carbon atom
these eliminations can be used to form carbons
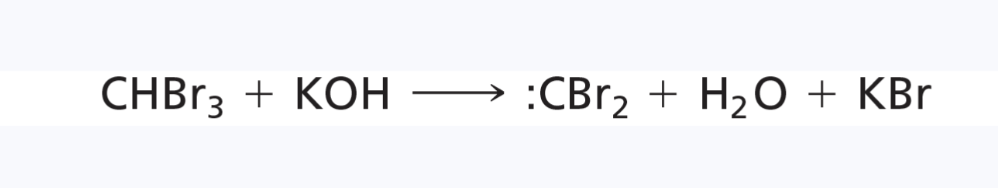
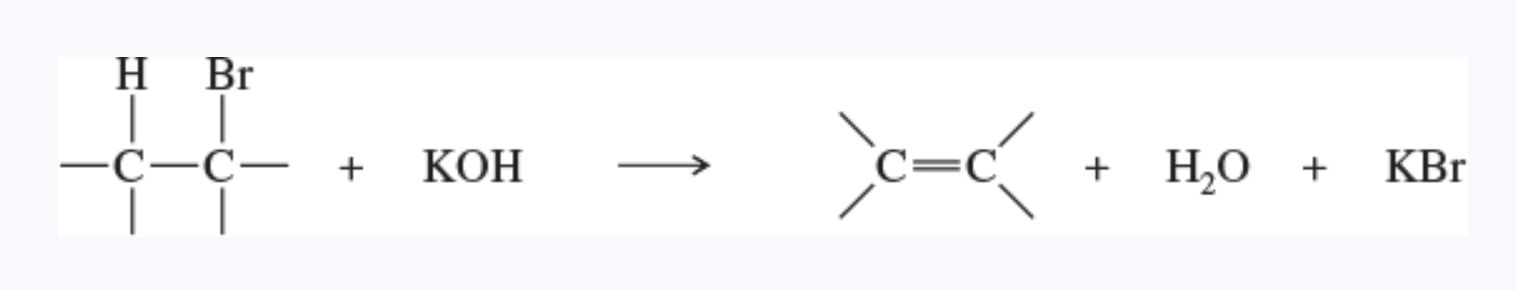
beta elimination
the elimination of two atoms or groups from adjacent carbon atoms
this is the most common type of elimination
carbene
a reactive intermediate with a neutral carbon atom having only two bonds and two nonbonding electrons
the simplest carbene is methylene (:CH2)
chain-growth polymer
a polymer that results from the rapid addition of one monomer at a time to a growing polymer chain, usually with a reactive intermediate (cation, radical, or anion) at the growing end of the chain
most of these are addition polymers of alkenes and dienes
demercuration reaction
the removal of a mercury species from a molecule
demercuration of the products of oxymercuration and alkoxymercuration is usually accomplished using sodium borohydride (NaBH4)
dihydroxylation reaction
also known as hydroxylation
the addition of two hydroxy groups, one at each carbon of the double bond
formally, an oxidation reaction
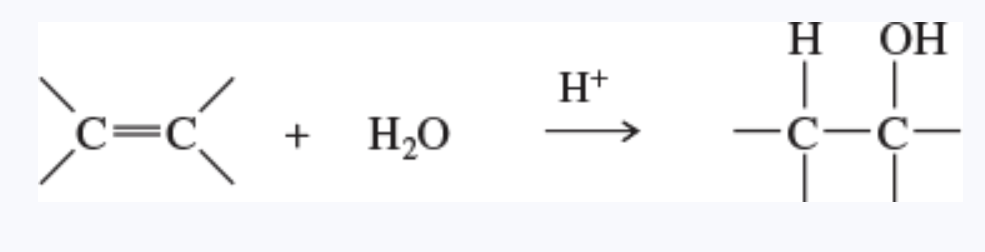
epoxide
also known as an oxirane
a three-membered cyclic ether
epoxidation reaction
formation of an epoxide, usually from an alkene
a peroxyacid is generally used as a reagent
glycol
a 1,2-diol
halogenation reaction
the addition of a halogen (X2) to a molecule, or the free-radical substitution of a halogen for a hydrogen
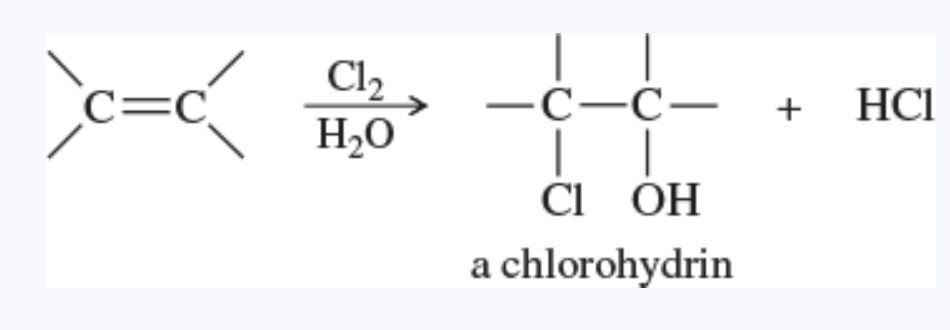
halohydrin
a beta-haloalcohol, with a halogen and a hydroxy group on adjacent carbon atoms
halonium ion
a reactive, cationic intermediate with a three-membered ring containing a halogen atom
usually, a chloronium ion, a bromonium ion, or an iodonium ion
heterogeneous catalysis
the use of a catalyst that is in a separate phase from the reactants
homogeneous catalysis
use of a catalyst that is in the same phase as the reactants
hydration reaction
the addition of water to a molecule
the hydration of an alkene forms an alcohol
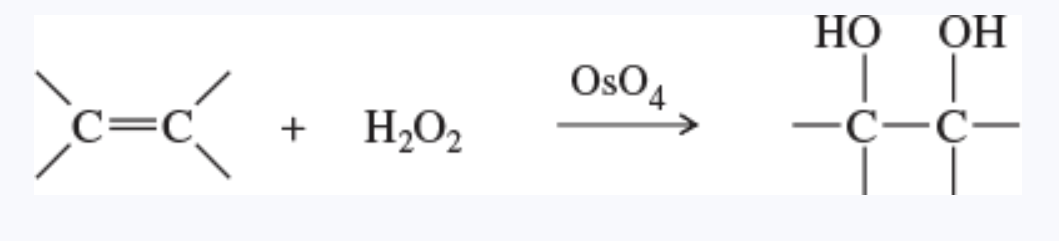
hydroboration reaction
the addition of borane (BH3) or one of its derivatives (example: BH3 / THF) to a molecule
hydrogenation reaction
the addition of a hydrogen to a molecule
the most common hydrogenation is the addition of H2 across a double bond in the presence of a catalyst
catalytic hydrogenation or catalytic reduction
Markovnikov’s rule
when a proton acid adds to the double bond of an alkene, the proton bonds to the carbon atom that already has more hydrogen atoms
in an electrophilic addition to an alkene, the electrophile adds in such a way as to generate the most stable intermediate
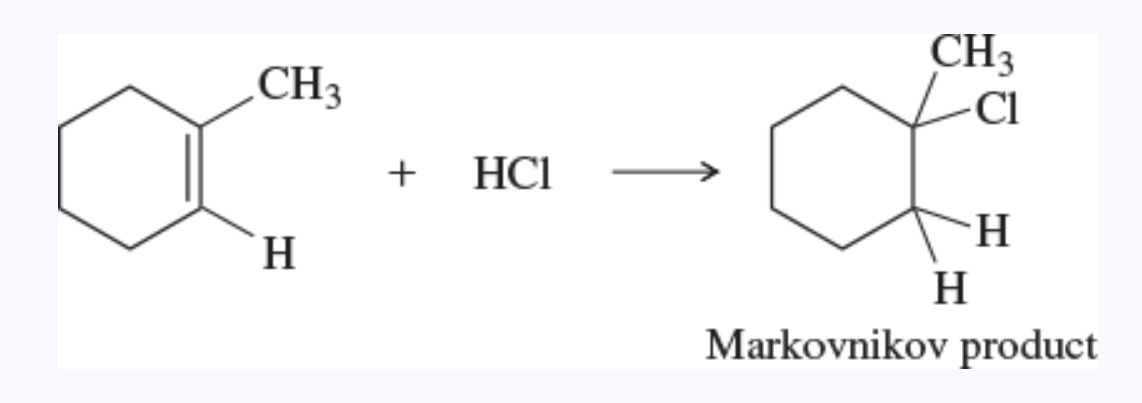
Markovnikov orientation
an orientation of addition that obeys the original statement of Markovnikov’s rule —> gives the Markovnikov product
anti-Markovnikov orientation
an orientation of addition that is the opposite of that predicted by the original statement of Markovnikov’s rule —> gives the anti-Markovnikov product
mCPBA
(meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid)
a common reagent for epoxidizing alkenes
dissolves in common solvents such as dichloromethane
as the epoxidation takes place, the m-chlorobenzoic acid by-product precipitates out of solution
metathesis
also known as olefin metathesis
any reaction that trades and interchanges the alkylidene groups of an alkene
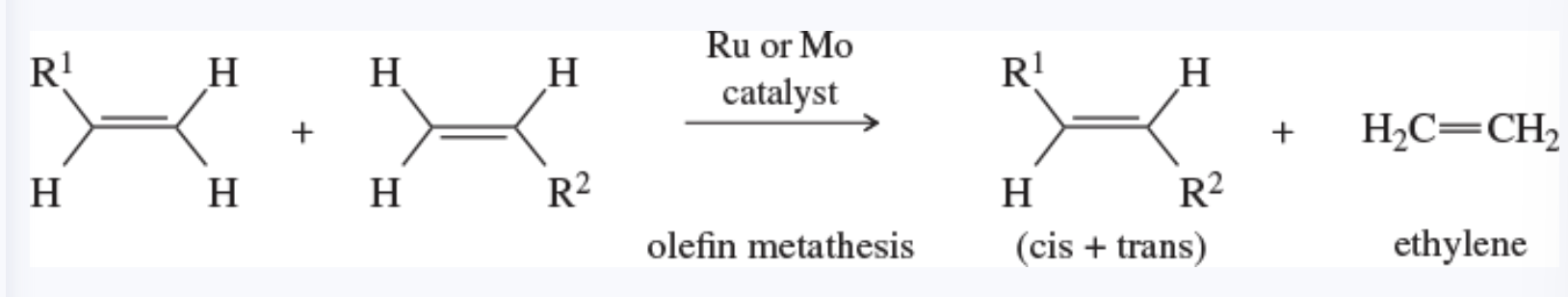
monomer
one of the small molecules that bond together to form a polymer
organic synthesis
the preparation of desired organic compounds from readily available materials
oxidative cleavage
the cleavage of a carbon—carbon bond through oxidation
carbon—carbon double bonds are commonly cleaved by ozonolysis/reduction or by warm, concentrated permanganate (KMnO4)
oxymercuration reaction
the addition of aqueous mercuric acetate to an alkene
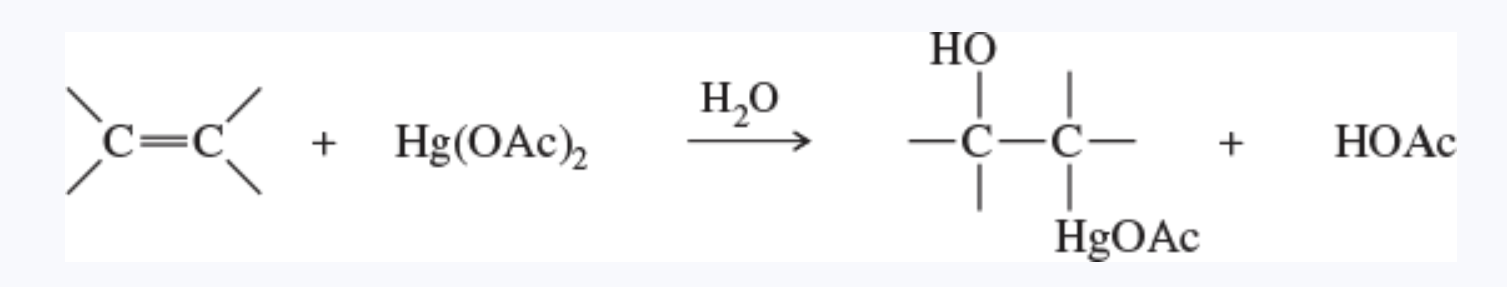
ozonolysis reaction
the use of ozone, usually followed by reduction, to cleave a double bond
peroxide effect
the reversal of orientation of HBr addition to alkenes in the presence of peroxides
a free-radical mechanism is responsible for this effect
peroxyacid
also called a peracid
a carboxylic acid with an extra oxygen atom and a peroxy linkage (—O--O—)
the general formula is RCO3H
polymer
a high-molecular-weight compound composed of many molecules of a smaller, simpler compound called the monomer
polymerization
the reaction of monomer molecules to form a polymer
regiochemistry
the orientation of a chemical reaction on an unsymmetrical substrate
in additions to alkenes, the regiochemistry of the addition involves which part of the reagent adds to which end of an unsymmetrical alkene
regioselective reaction
a reaction in which one direction of bond-making or bond-breaking occurs preferentially over all other directions
examples: Addition of HCl (predicted by Markovnikov’s rule); Hydroboration-oxidation (consistently gives anti-Markovnikov orientation
Simmons-Smith reaction
a cyclopropanation of an alkene using the carbenoid reagent generated from diiodomethane and the zinc-copper couple
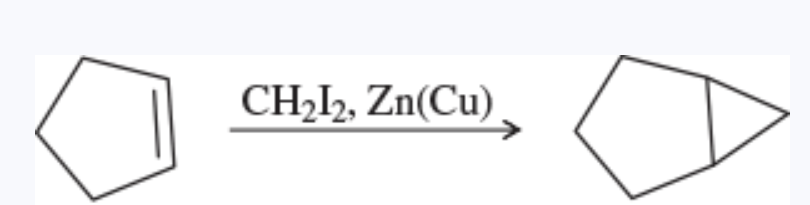
stereospecific reaction
a reaction that converts different stereoisomers of the starting material into different stereoisomers of the product
acetylene
the simplest alkyne, H-C=C-H
also used as a synonym for alkyne, a generic term for a compound containing a C=C triple bond
acetylide ion
also called an alkynide ion
the anionic salt of a terminal alkyne
metal acetylides are organometallic compounds with a metal atom in place of the weakly acidic acetylenic hydrogen of a terminal alkyne
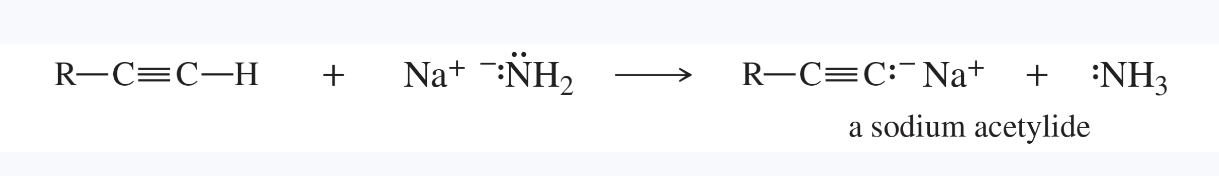
alkoxide ion
R—O(-), the conjugate base of an alcohol

alkyne
any compound containing a carbon—carbon triple bond
a terminal alkyne has a triple bond at the end of a chain, with an acetylenic hydrogen
an internal alkyne has the triple bond somewhere other than at the end of the chain
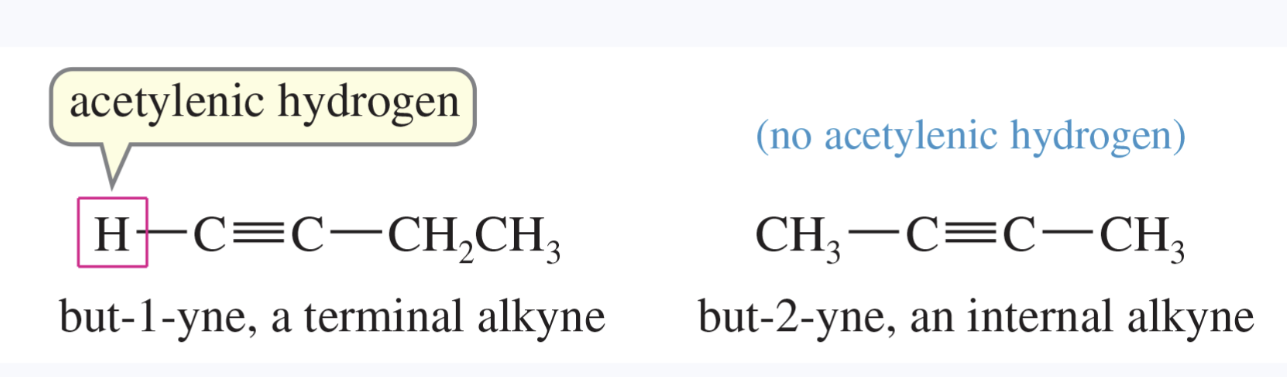
amyl
an older common name for pentyl
enol
an alcohol with the hydroxy group bonded to a carbon atom of a carbon—carbon double bond
most are unstable, spontaneously isomerizing to their carbonyl tautomers, called the keto form of the compound
Lindlar’s catalyst
a heterogeneous catalyst for the hydrogenation of alkynes to cis alkenes
in its most common form, it consists of a thin coating a palladium on barium sulfate, with quinoline added to decrease the catalytic activity
s-character
the fraction of a hybrid orbital that corresponds to an s orbit
about ½ for sp hybrids, 1/3 for sp2 hybrids, and ¼ for sp3 hybrids
siamyl group
a contraction for secondary isoamyl, abbreviated “Sia”
this is the 1,2-dimethylpropyl group
Example: disiamylborane is used for hydroboration of terminal alkynes, since it is bulky and adds only once to the triple bond
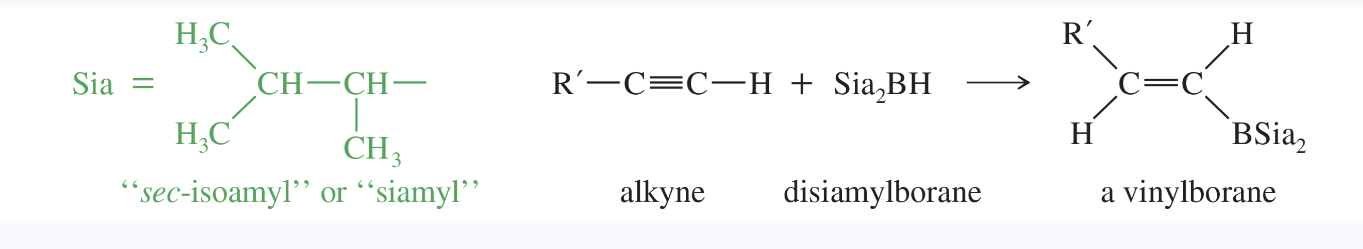
tautomers
isomers that can quickly interconvert by the movement of a proton (and a double bond) from one site to another
an equilibrium between these isomers is called a tautomerism
keto form is more stable than enol form
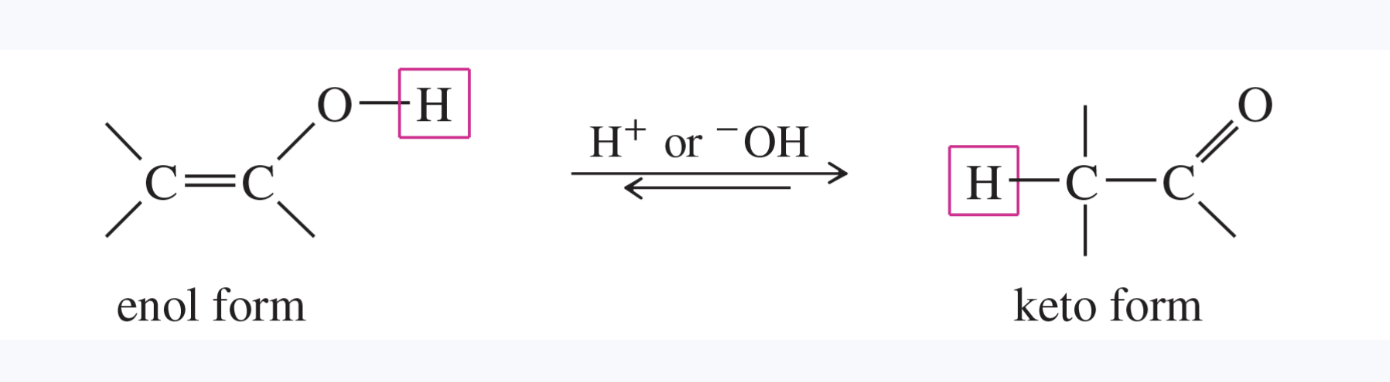
vinyl cation
a cation with a positive charge on one of the carbon atoms of a C=C double bond
the cationic carbon atom is usually sp hybridized
these types of cations are often generated by the addition of an electrophile to a carbon—carbon triple bond
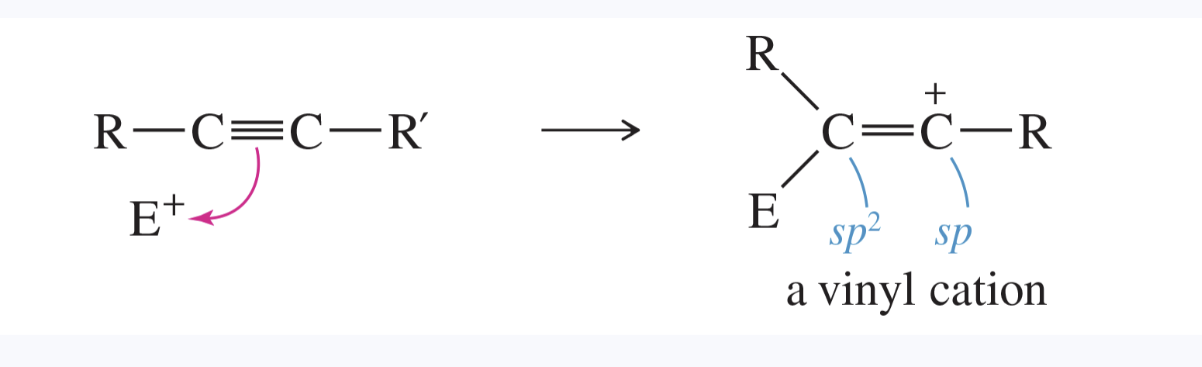
Electrons always move…
from high concentration to low concentration