Topic 1 - Structure of Atoms
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what was the dalton model

what was the plum pudding model

what was the nuclear model

what was the planetary model

what was erwins model

what is the structure of an atom
a nucleus containing protons and neutons surrounded by electrons in shells
what is the relative charge and relative mass of a proton
RC: 1+ RM: 1
what is the relative charge and relative mass of a neutron
RC: 0 RM: 1
what is the relative charge and relative mass of a electron
RC: -1 RM: almost 0
why do atoms contain equal numbers of protons and electrons
so that the atom has no charge and is neutral as the charge of protons and electrons cancel each other out
how big is the nucleus
the nucleus is very small comapred to the overall size of the atom
Where is most of the mass concentrated in an atom
the nucleus
what is the meaning of ‘mass number' of an atom
The mass number of an element tells us the number of protons and neutrons
in an atom
how would you describe atoms of a given element
having the same number of protons in the nucleus and that the number is unique to that element
What are isotopes
isotopes are different atoms of the same element containing the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nuclei.
how do you calculate the number of protons,neutrons and electrons in an atom
number of protons = atomic number
number of electrons = atomic number
number of neutrons = mass number - atomic number
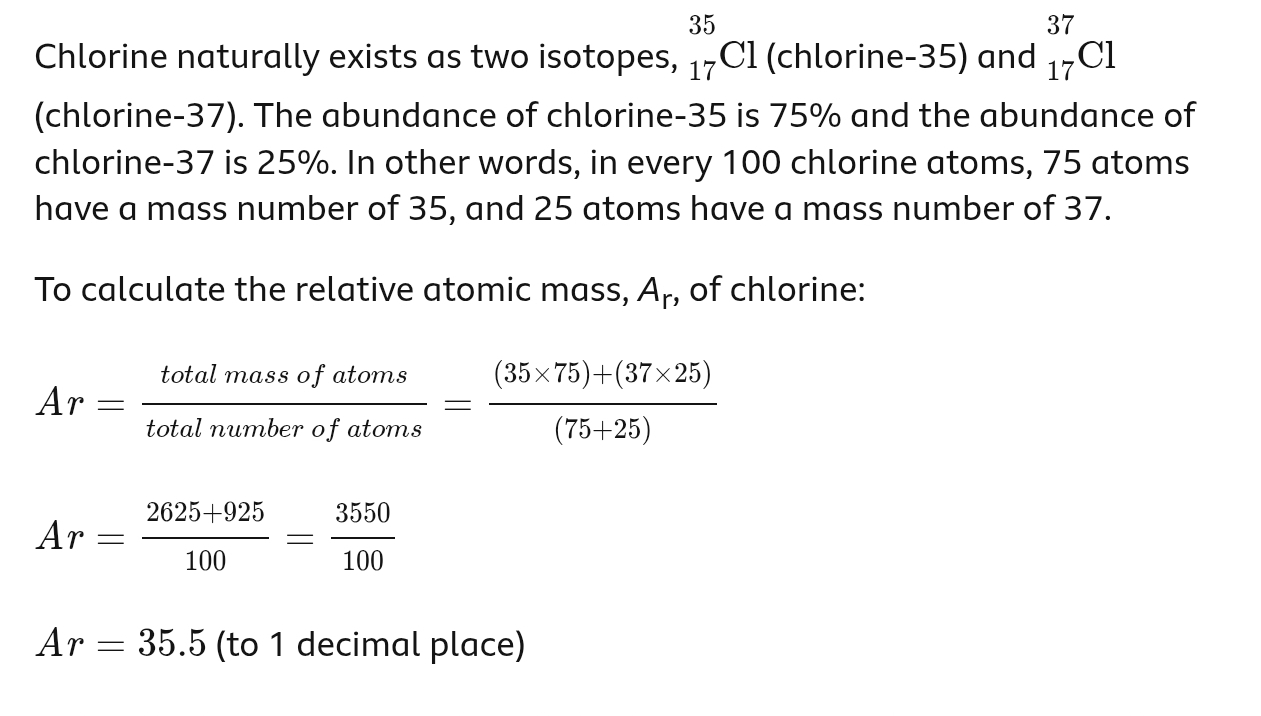
Explain how the existence of isotopes results in relative atomic masses of some elements not being whole numbers
The relative atomic masses of elements are often not whole numbers because they represent the weighted average of the masses of all the isotopes of that element, taking into account their natural abundance
how to calculate relative atomic mass - example given in answer