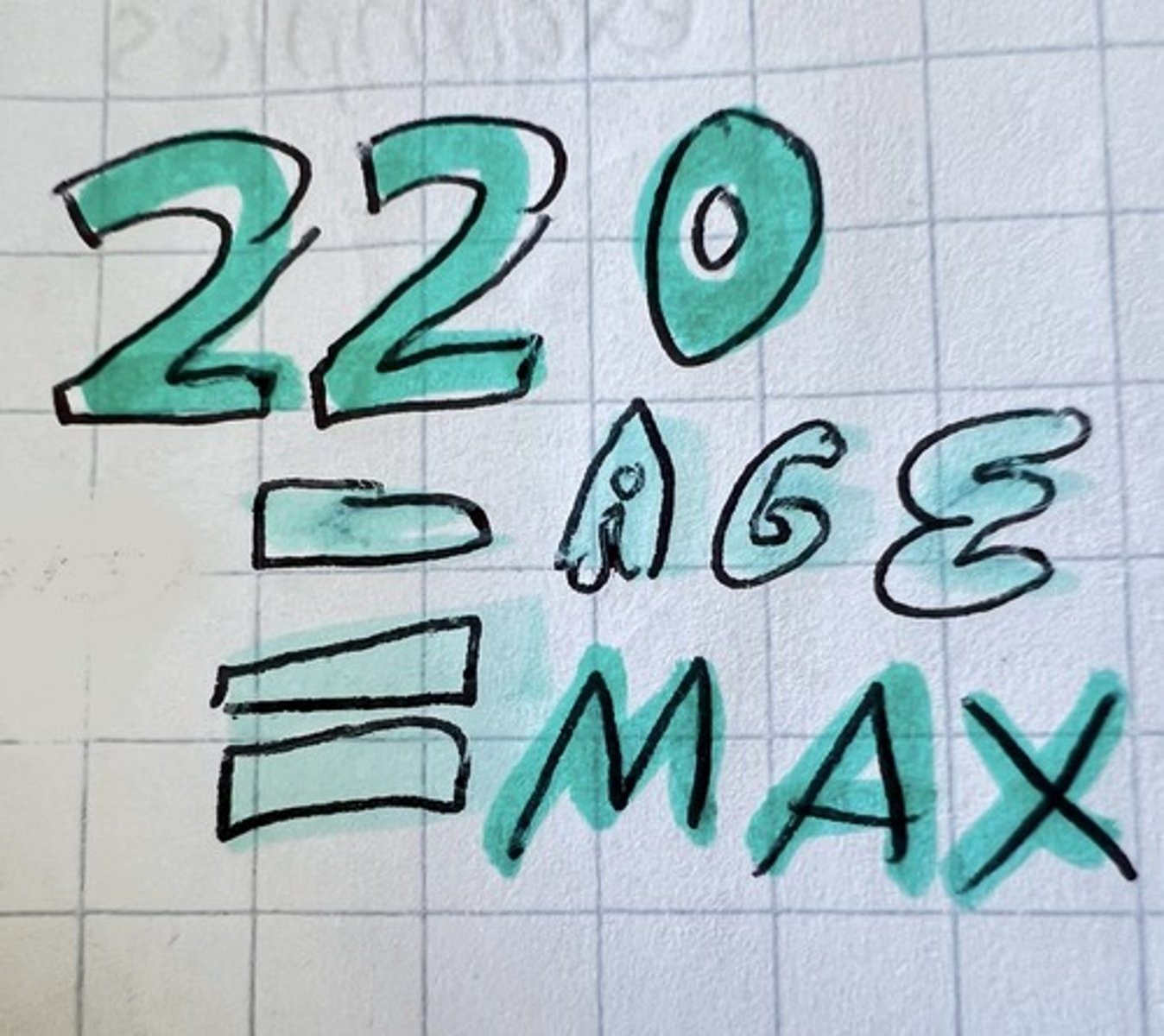Lifetime Fitness & Wellness Pursuits PISD CBE Review: Semester 1 Exam | Quizlet
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
main difference between a warm up and cool down
warm up ⬆️❤️rate, cool down ⬇️❤️
purpose of a warm up
⬆️blood flow, ⬆️ 💨oxygen delivery, ⬇️ risk of injury
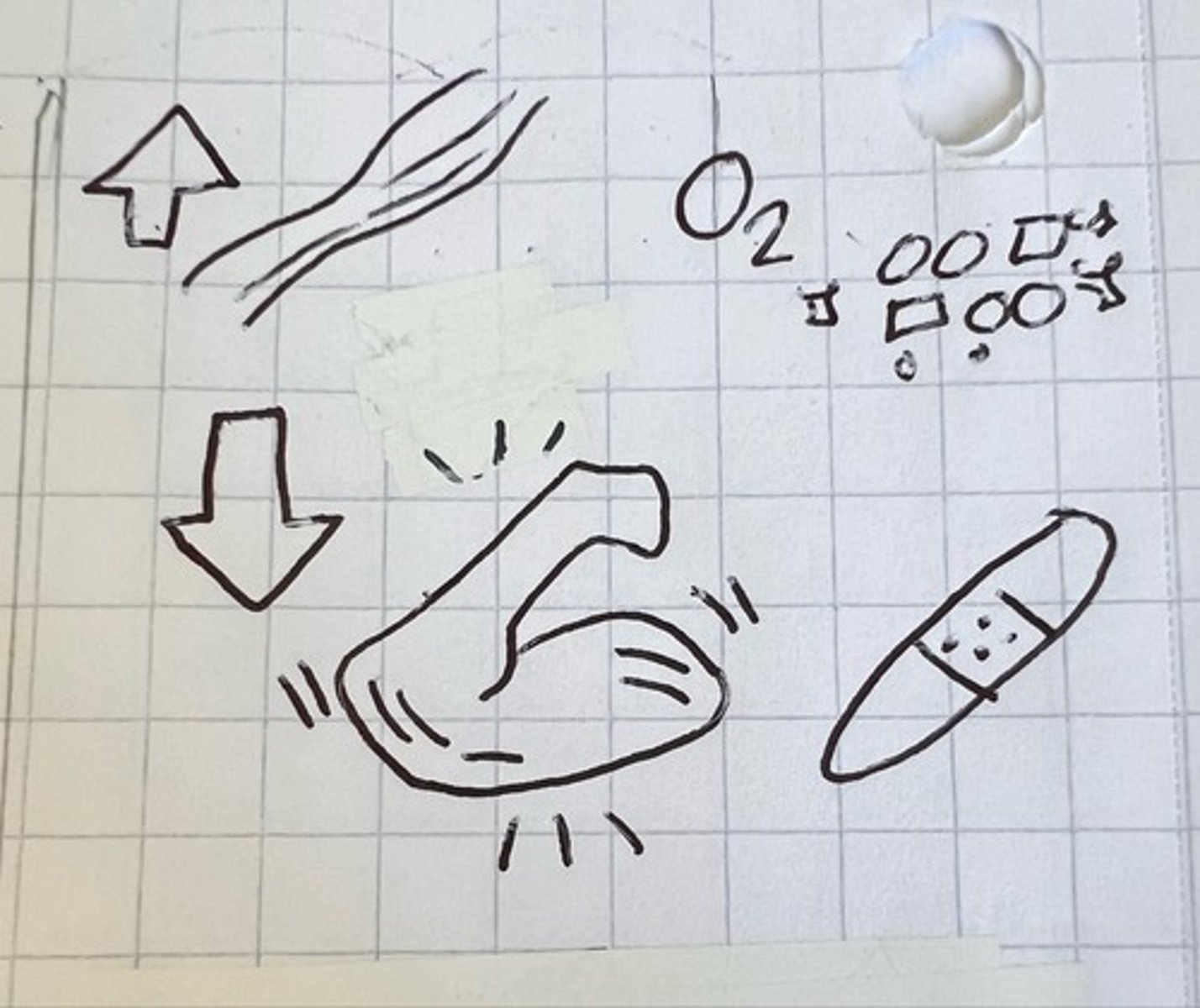
warm up benefits
⬆️ muscle 🌡️ ➡️ ⬆️ elasticity, vessels dilate, prevents overheating with sweating, ⬆️ range of motion
what should you do during a warm up?
do a milder form of your workout exercise
purpose of a cool down
returns body to pre-exercise conditions (💨, 🌡️, ❤️rate), allows muscle recovery, prevents blood pooling
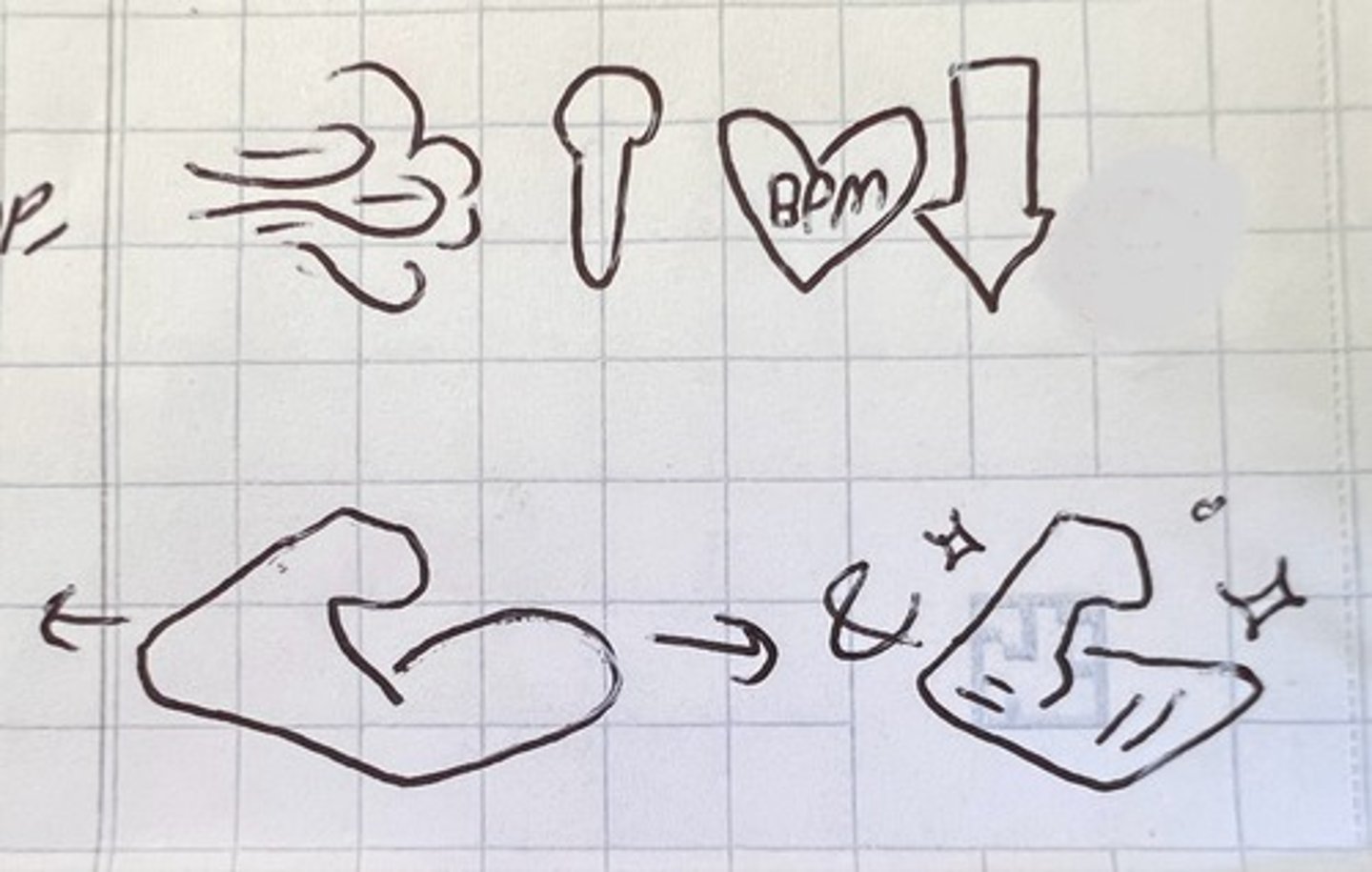
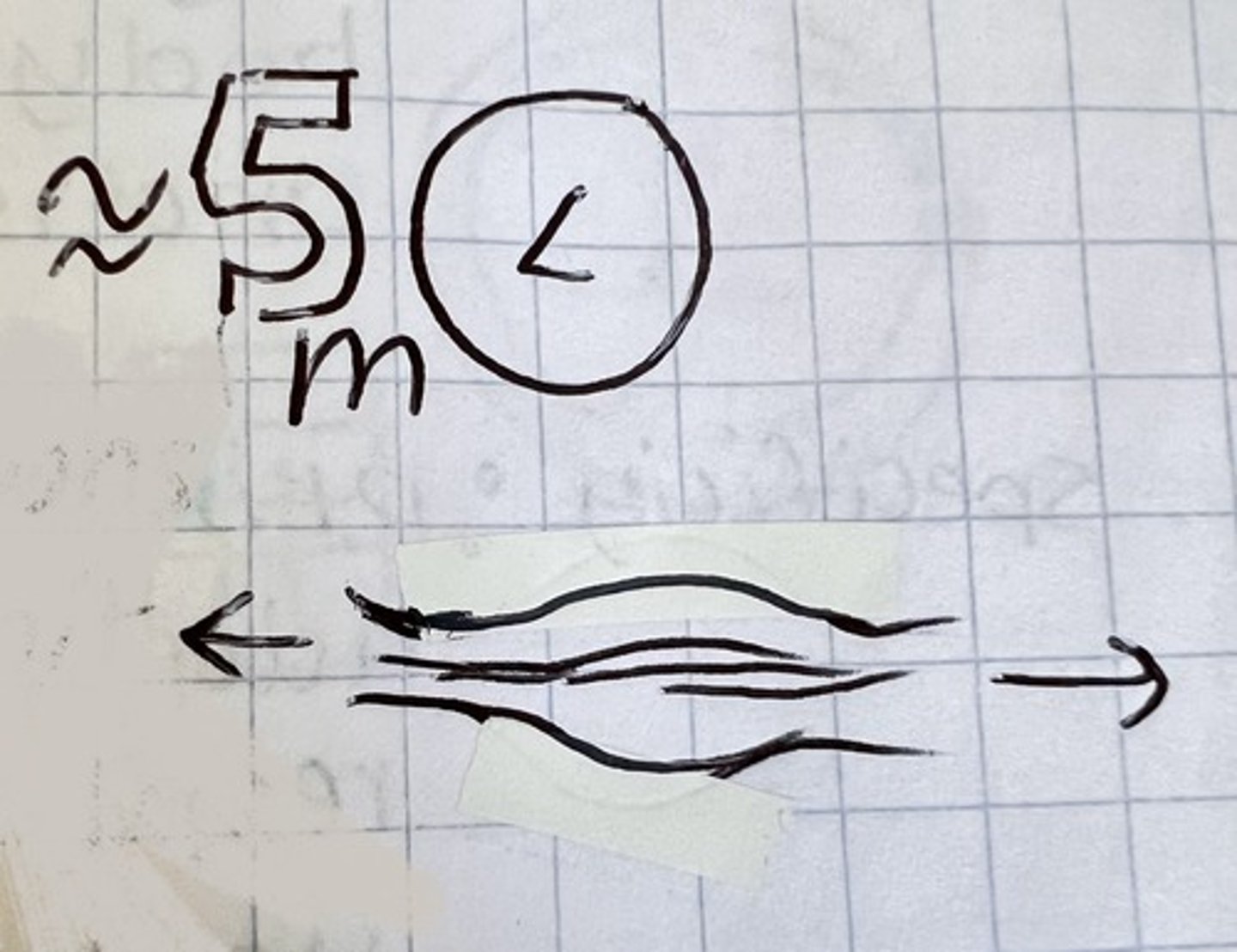
what should you do during a cool down?
do static stretching on used muscles for at least 5m
overload
working the body harder than it is normally worked
progression
increasing the amount or intensity of exercise
progressive overload
progressively working the body harder
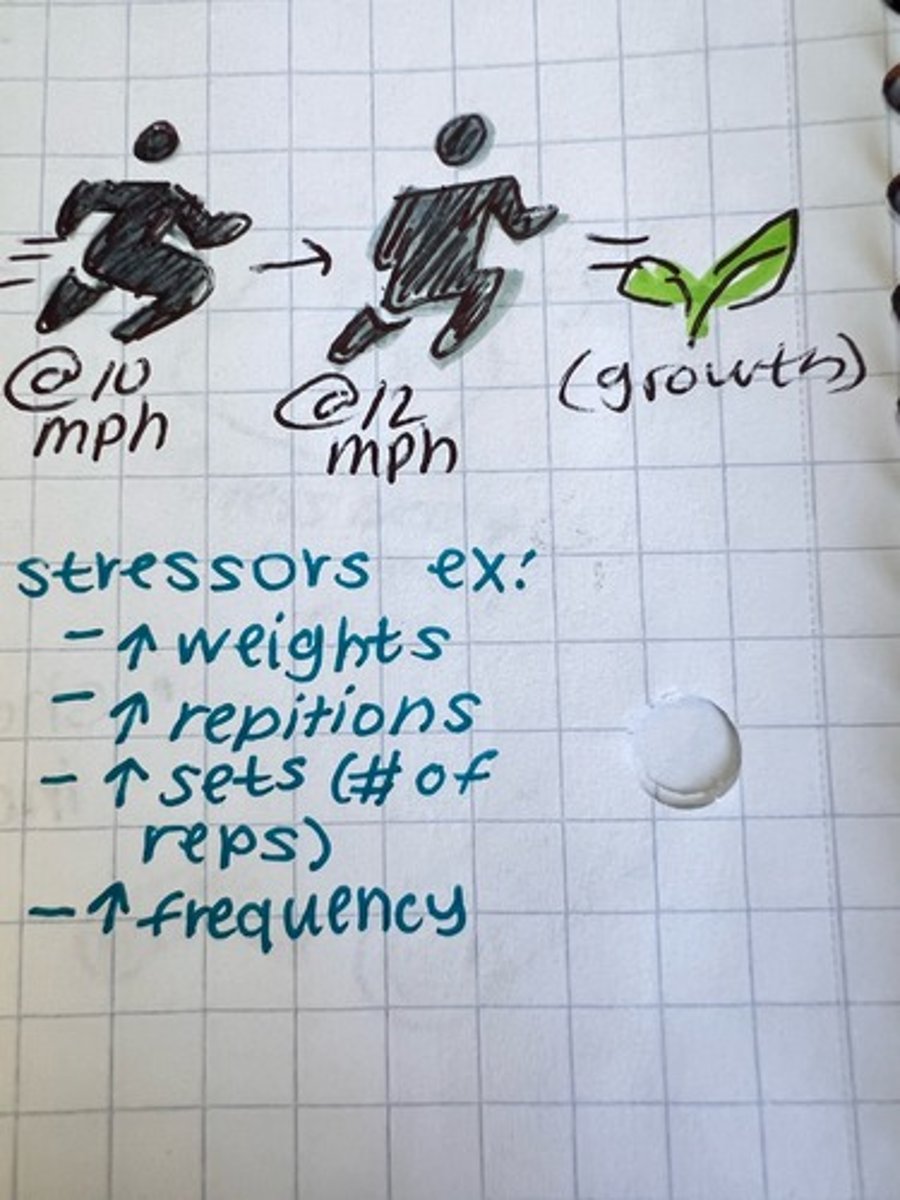
principle of specificity
rule that says growth will occur in the muscle you put stress on (ex: if you to bicep curls, your bicep will be fitter, not your legs)
FITT formula
frequency (how often), intensity (how hard), time, type (aerobic, anaerobic, strength/endurance, flexibility)

aerobic exercise
increases ❤️ and fitness & uses oxygen 💨 (ex: briskly walking 🚶, jogging/running 🏃♀️, cycling 🚴)
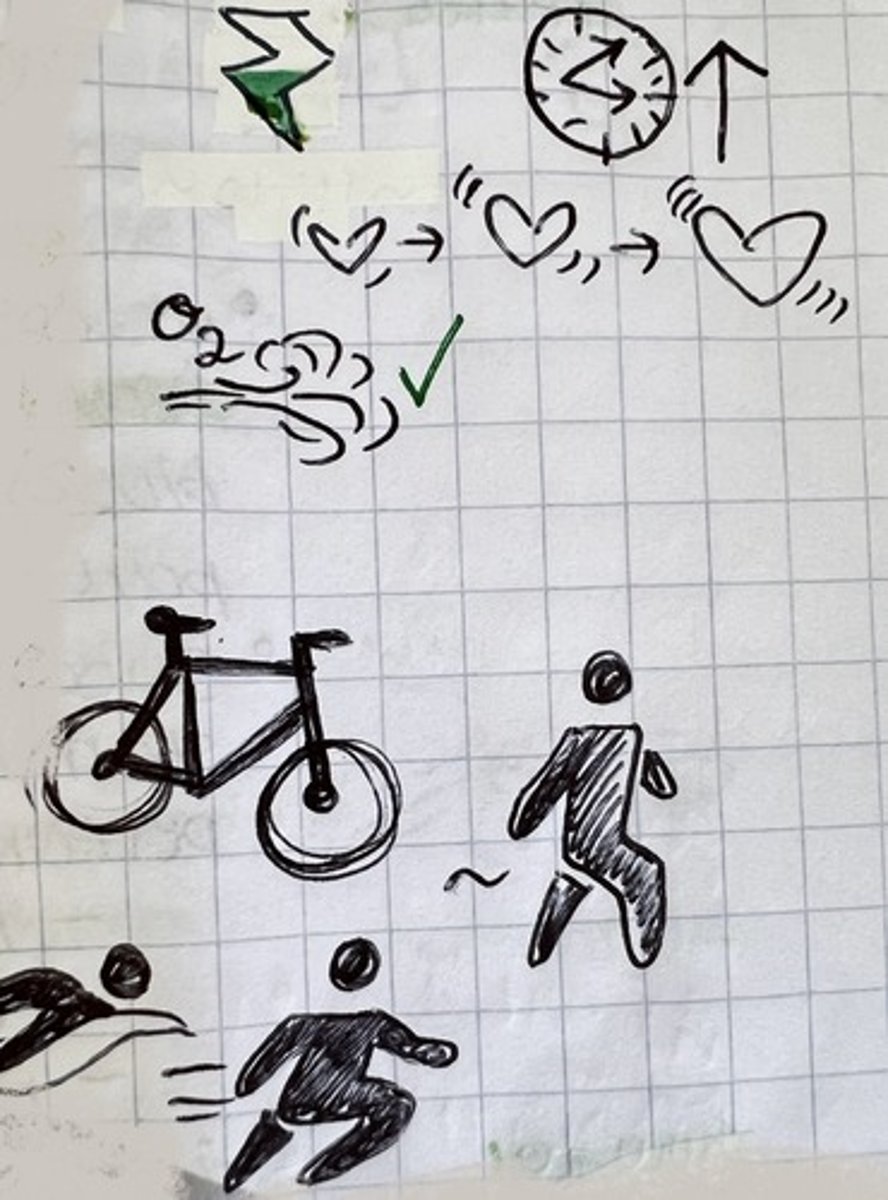
anaerobic exercise
intense short bursts ⏰, no oxygen 🚫💨 (ex: HITT training, circuit training, heavy weightlifting🏋️, sprinting 🏃♀️💨)

strength/endurance exercises
weightlifting, calisthenics, isometric exercises
flexibility exercises
yoga , pilates, gymnastics, dance

how can you measure intensity?
heart rate (beats per minute), reps (# of repetitions of an exercise), sets (# of groups of different reps)

how do you use progressive overload with the FITT formula?
slowly overload our body by increasing or changing one aspect of FITT (ex: increase frequency, change type of exercise, etc)
what are the 5 steps to making an exercise plan?
collect info, consider activities, set goals, write down program structure, evaluate program
3 types of muscle contractions
isotonic, isometric, isokinetic
trick to remember contractions
isotonic tones muscles, isometric has no movement, isokinetic is constant movement (kinetic means movement)

isotonic contraction
change in muscle length, concentric and eccentric
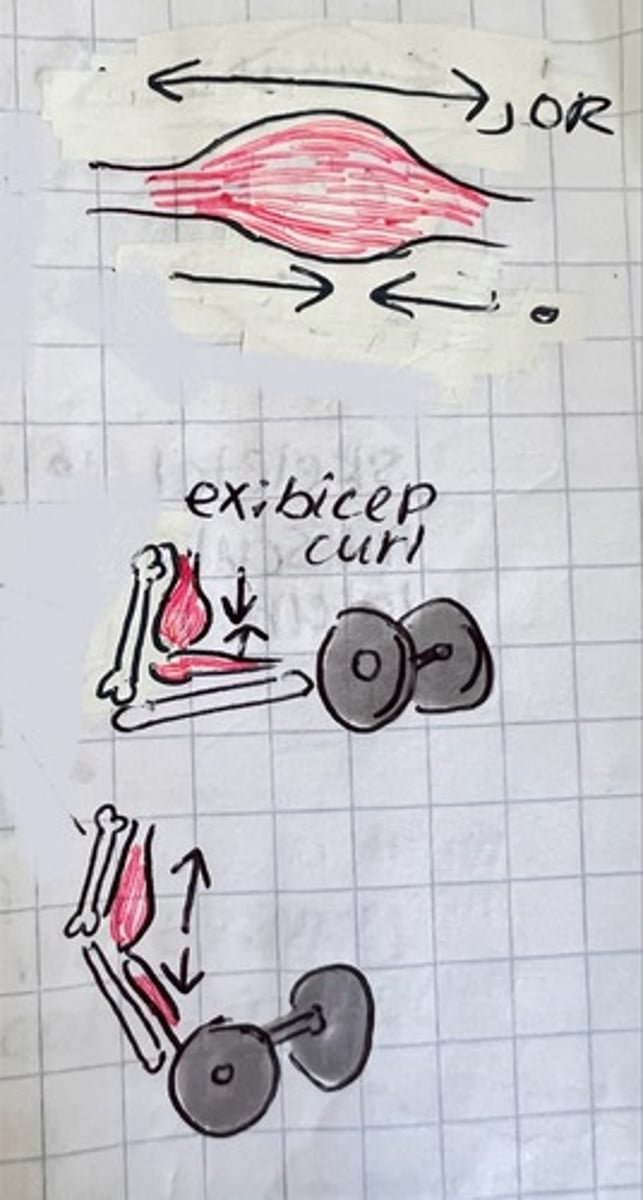
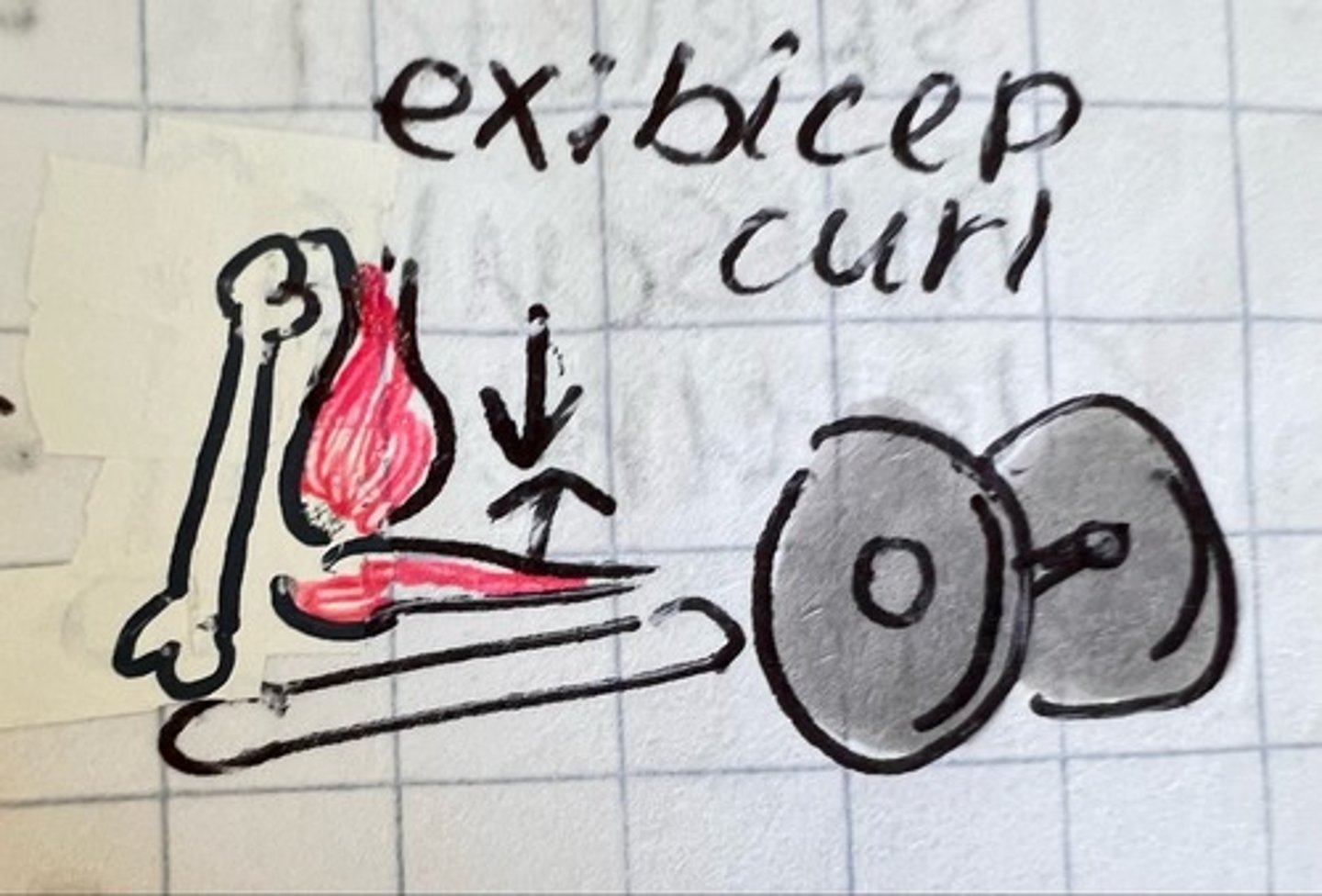
cocentric contraction
shortens (ex: quadriceps shorten during kicking a ball)
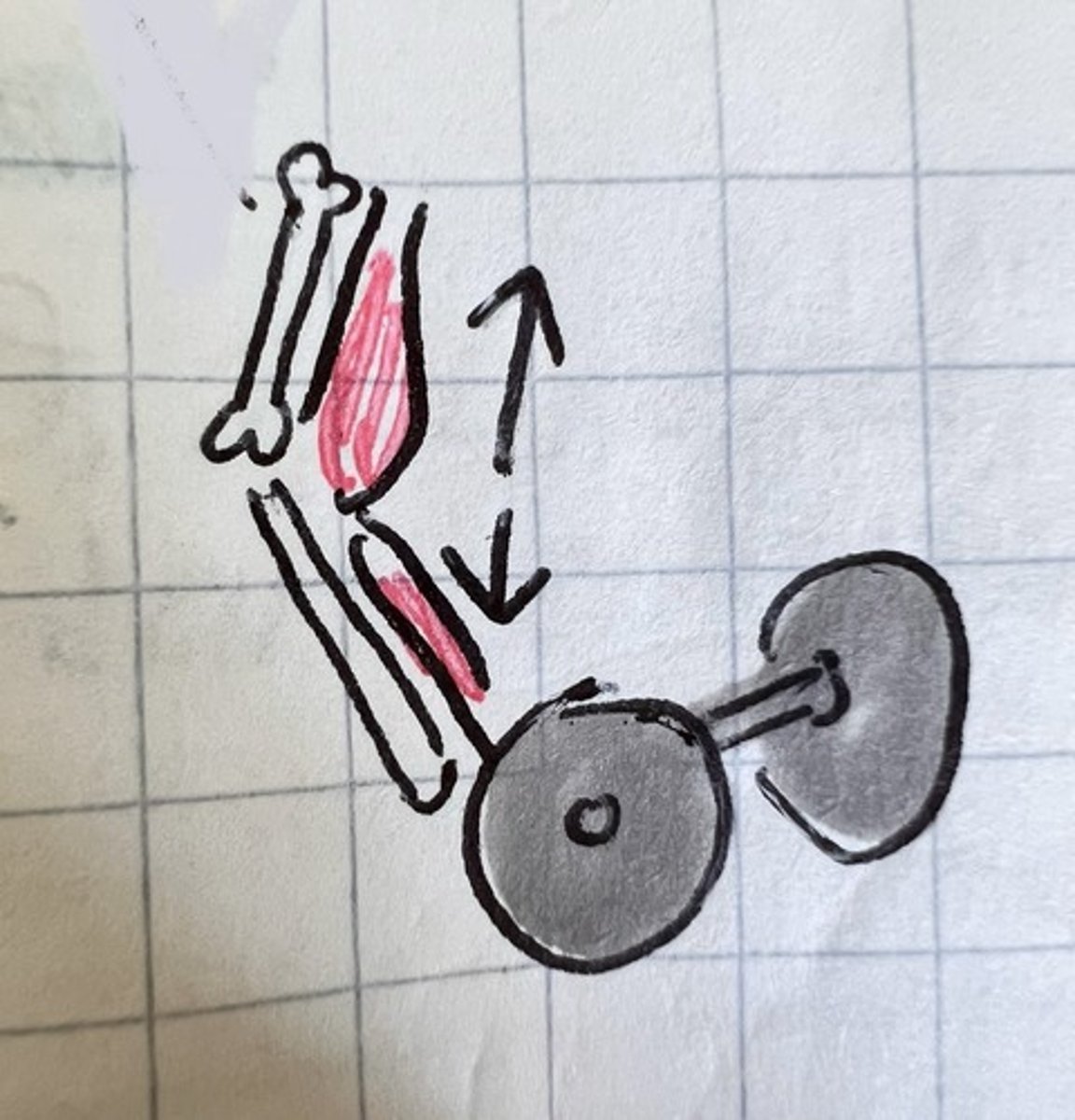
eccentric contraction
lengthens (ex: stretching)
isometric contraction
static, no movement (ex: plank)
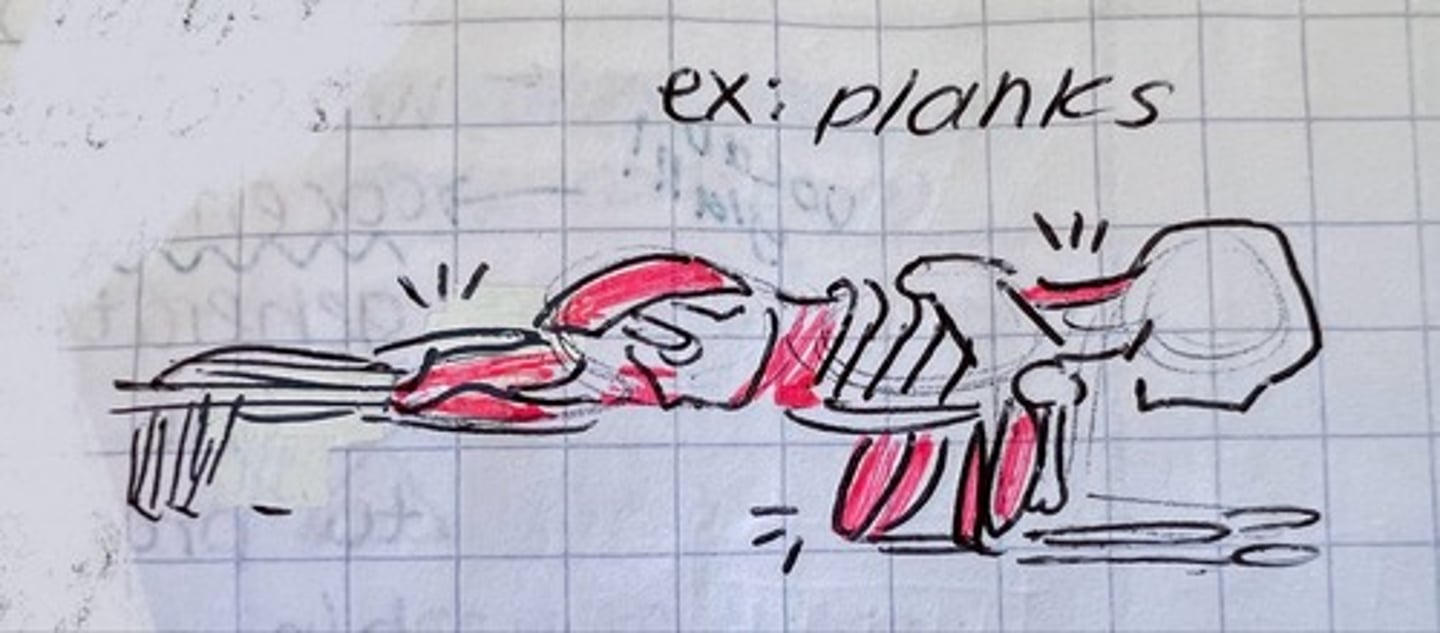
isokinetic contraction
rarest contraction, movements at a constant speed against a force (ex: breaststroke swimming)

trick to remember muscle levers
123, FLE
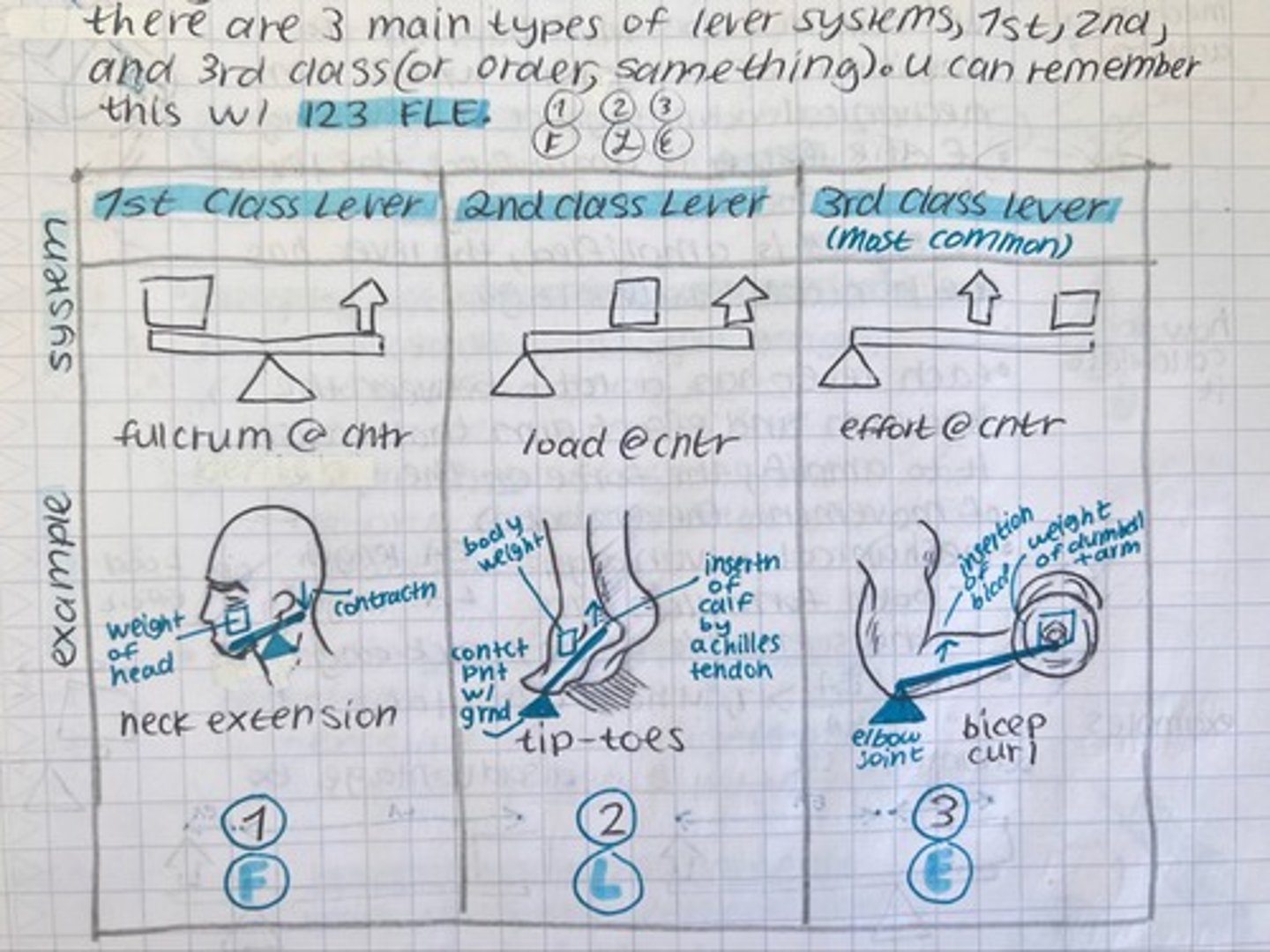
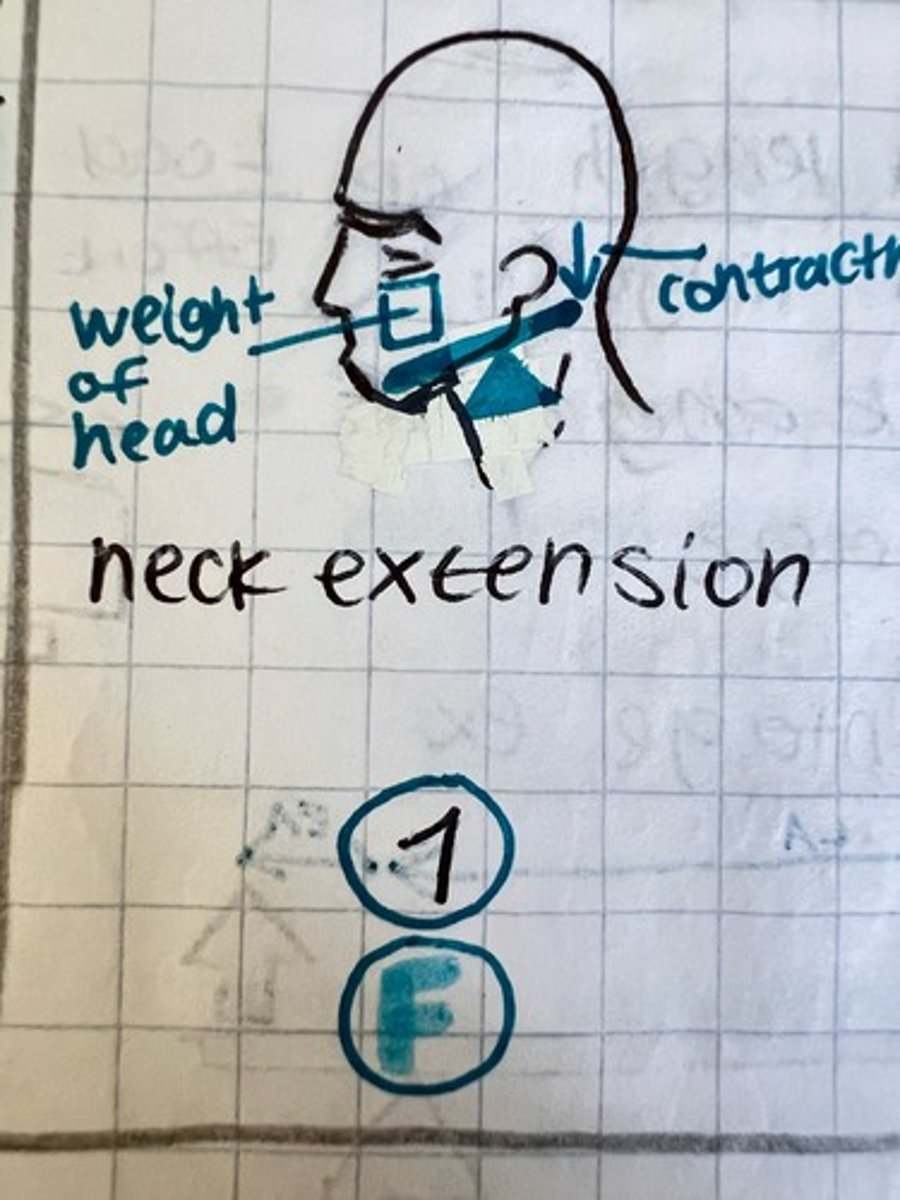
1st class lever example
neck extension
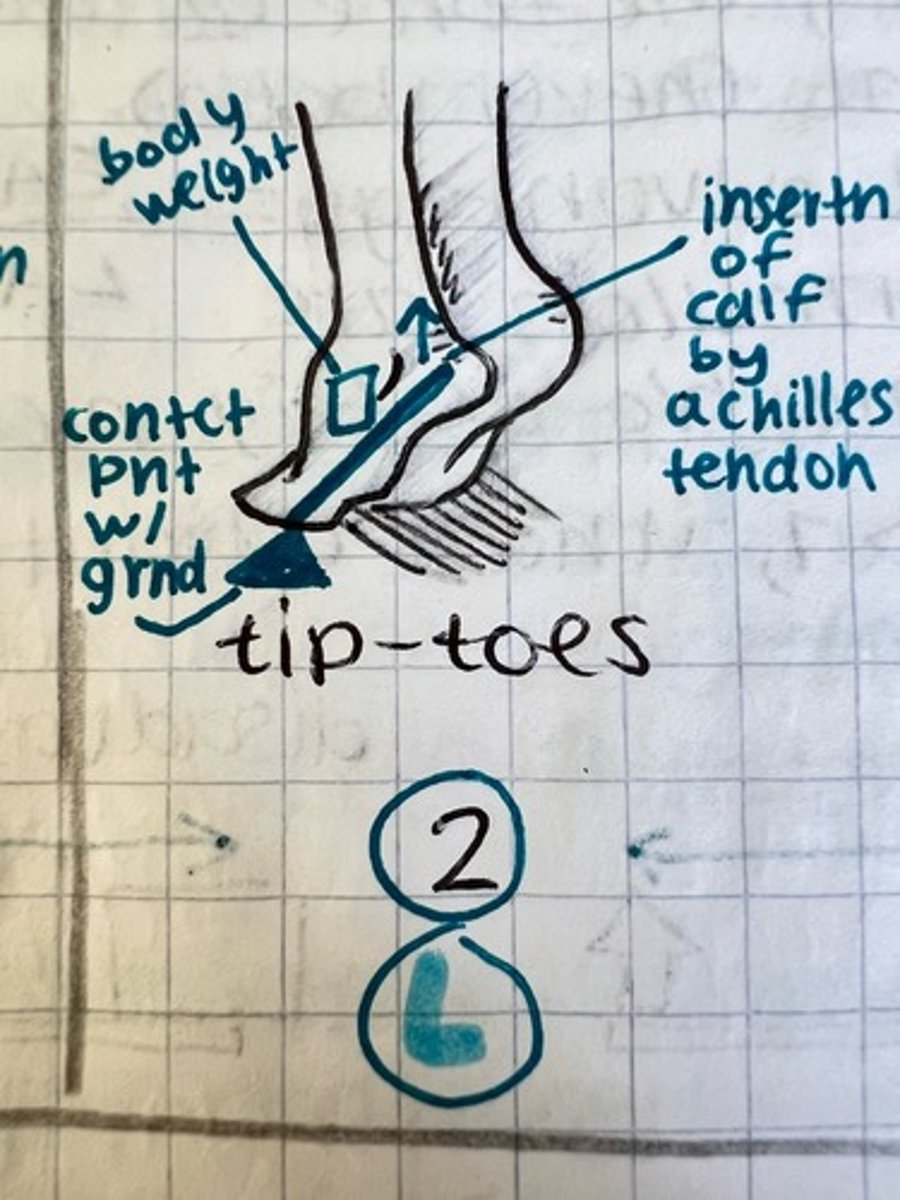
2nd class lever example
calf raise, tip-toes
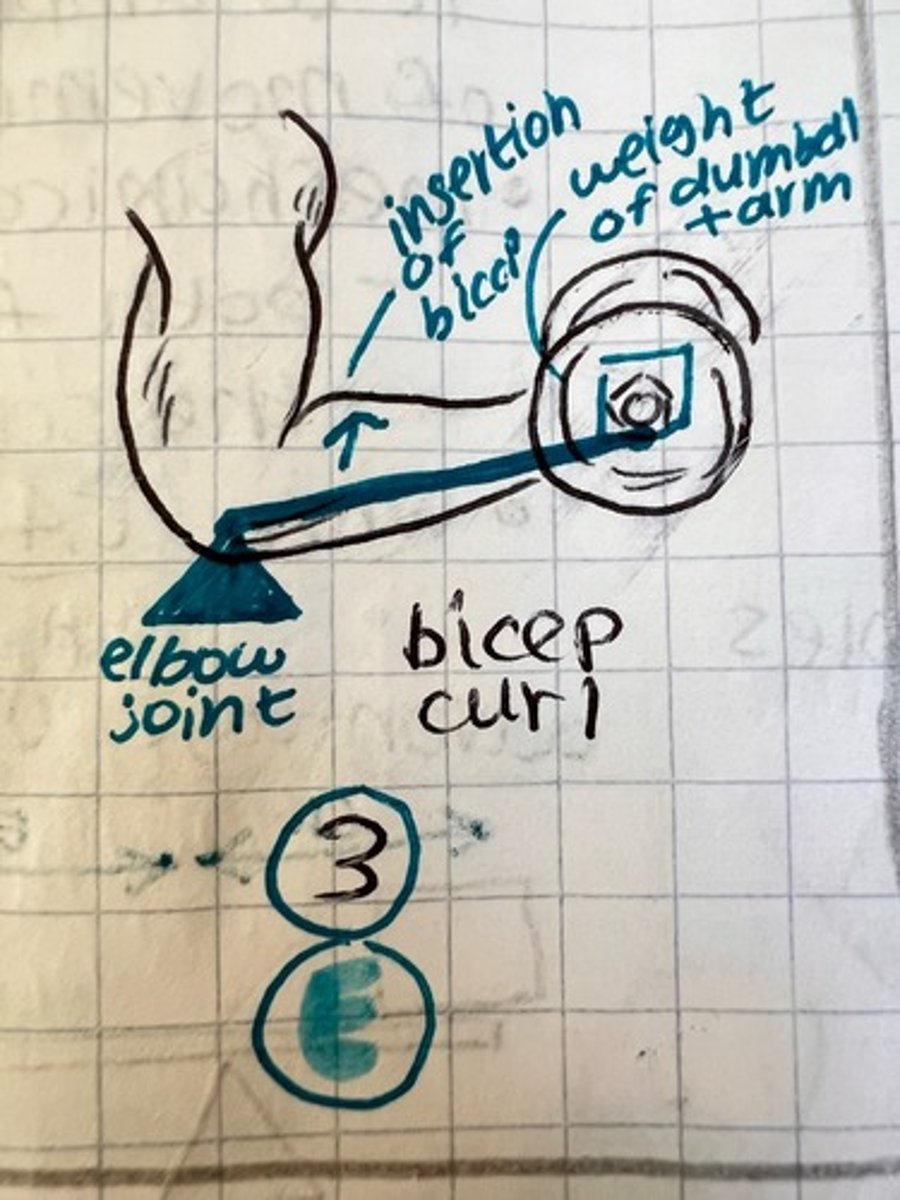
3rd class lever example
bicep curl, baseball bat, broom
what is the best way to resolve conflict?
always stay respectful and take responsibility for your. actions
what are bad ways to resolve conflict?
ignoring team members, defending teammates causing conflict, holding true to your beliefs
fitness safety procedures
warm up to prevent injury, avoid overtraining, listen to your body, stay hydrated to prevent muscle soreness, maintain proper form, wear braces or compression wear (ex: wrist wraps, knee/elbow sleeves)
3 types of injuries
overuse injury, side stitch, micro trauma
types of overuse injuries
shin splints, achilles tendinitis, strains, IT band syndrome/runner's knee, plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow, shoulder impingement/swimmer's elbow
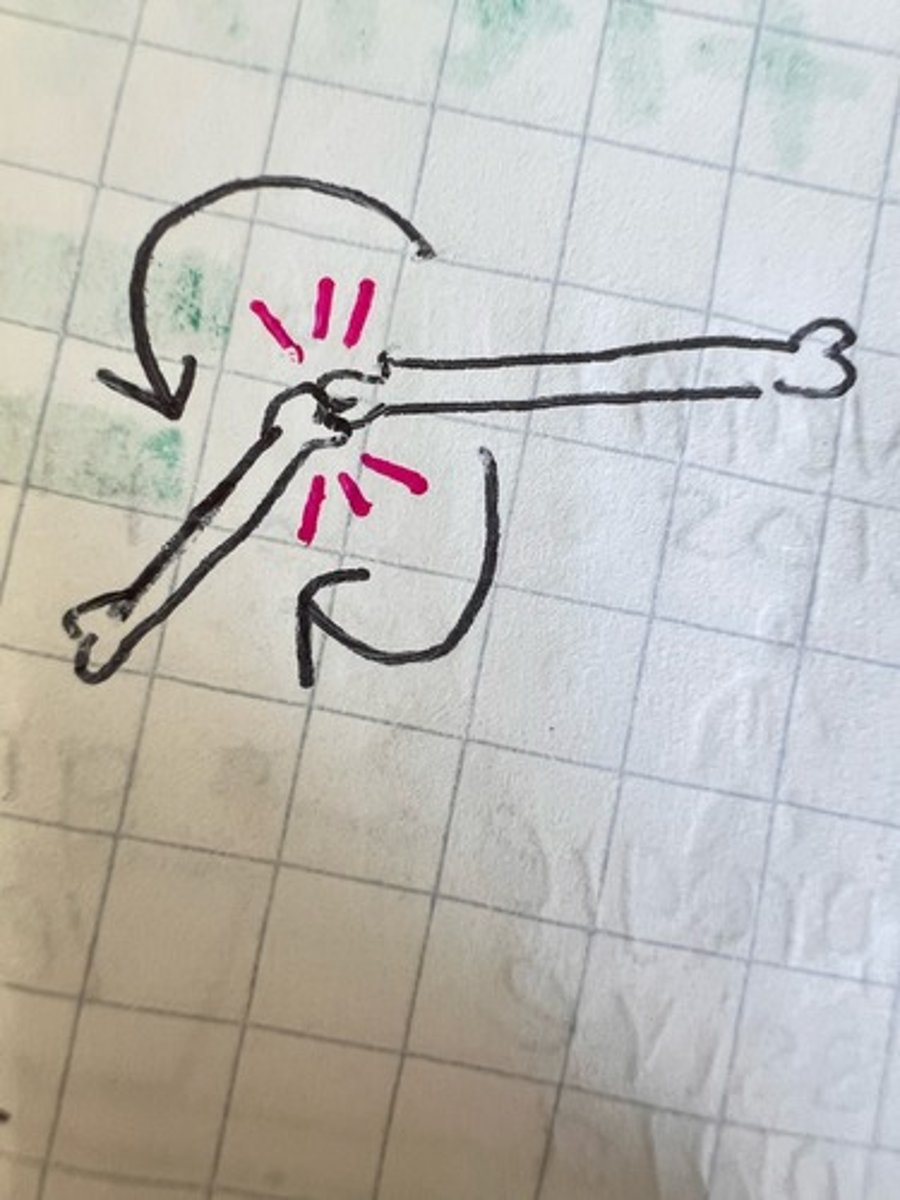
shin splint
pain caused by the muscle tearing away from the tibia (calf bone)
achilles tendinitis
painful inflammation of the achilles tendon/heel
strains
muscle tears
iliotibial band syndrome (runner's knee)
A painful condition in which connective tissue rubs against the thighbone
plantar fasciitis
inflammation of the sole of the foot
tennis elbow
inflammation of the tendon that connects the arm muscles to the elbow
shoulder impingement/swimmer's shoulder
shoulder pain caused by tendon rubbing against a shoulder blade
side stitch
temporary sharp abdomen pain from exercise
micro trauma
small unnoticed strains that build up over time, often from bad form or posture

how to heal injuries
RICE (rest, compress, ice, elevate)
types of training
interval, HITT, circuit, functional fitness, strength, cardio
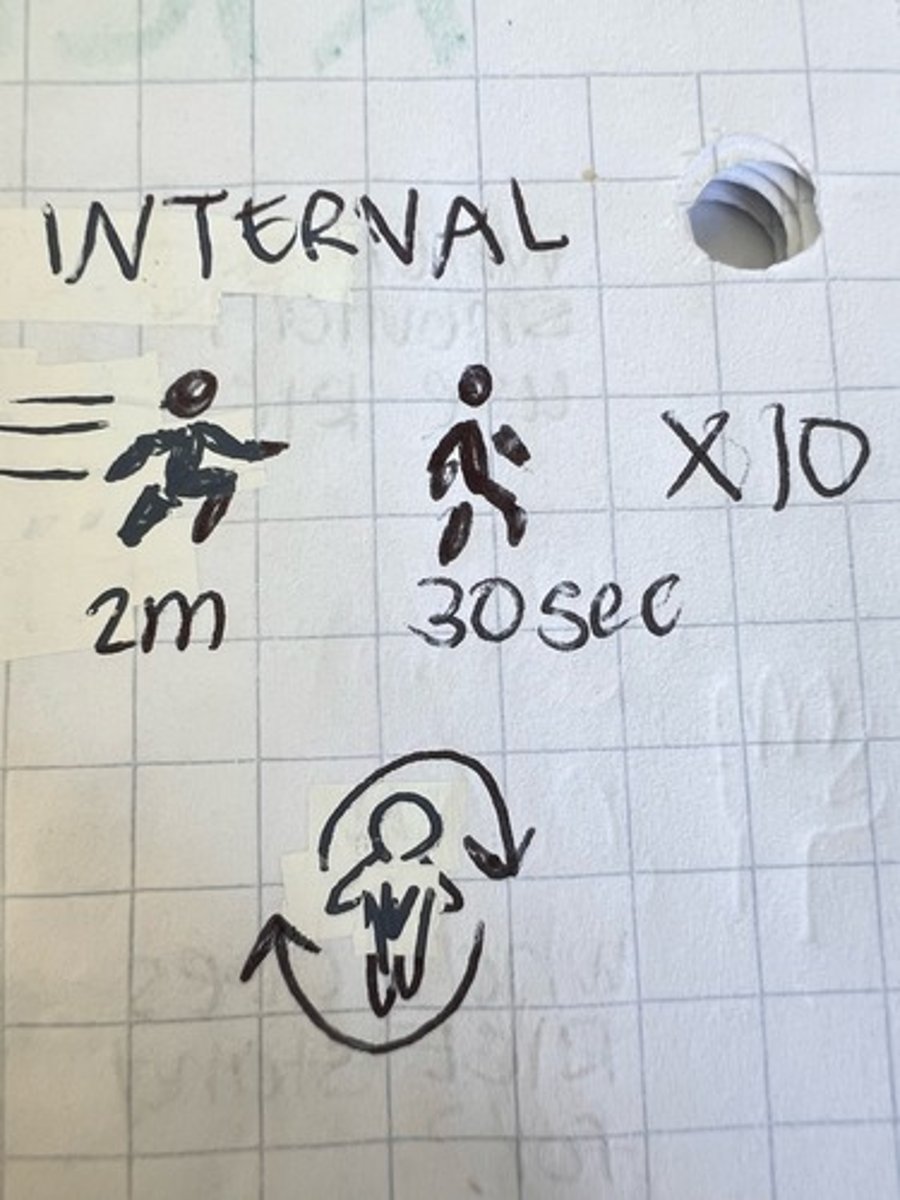
interval training
alternating intensity, good for calorie burning 🔥 and athletic performance🏃♀️
HITT
high-intensity interval training, burns more calories 🔥🔥 and is good for cardiovascular system

describe high intensity interval training
a combination of brief but intense bursts of cardio and equal periods of rest
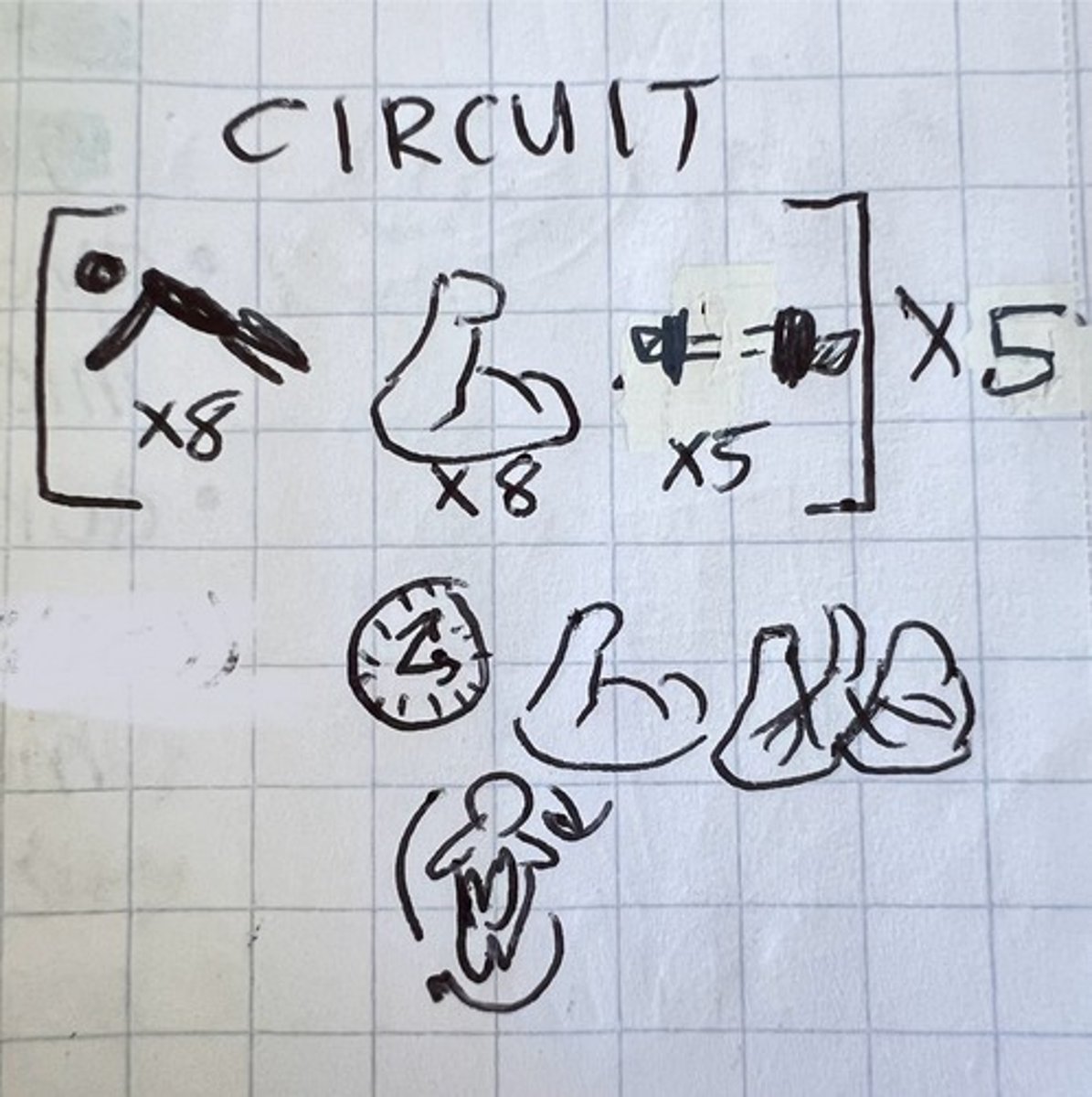
circuit training
series of exercise with minimal rest 🔄
functional fitness training
designed to work all muscles used in daily life like carrying supplies or walking up stairs (ex: squat, lunge, push ups)

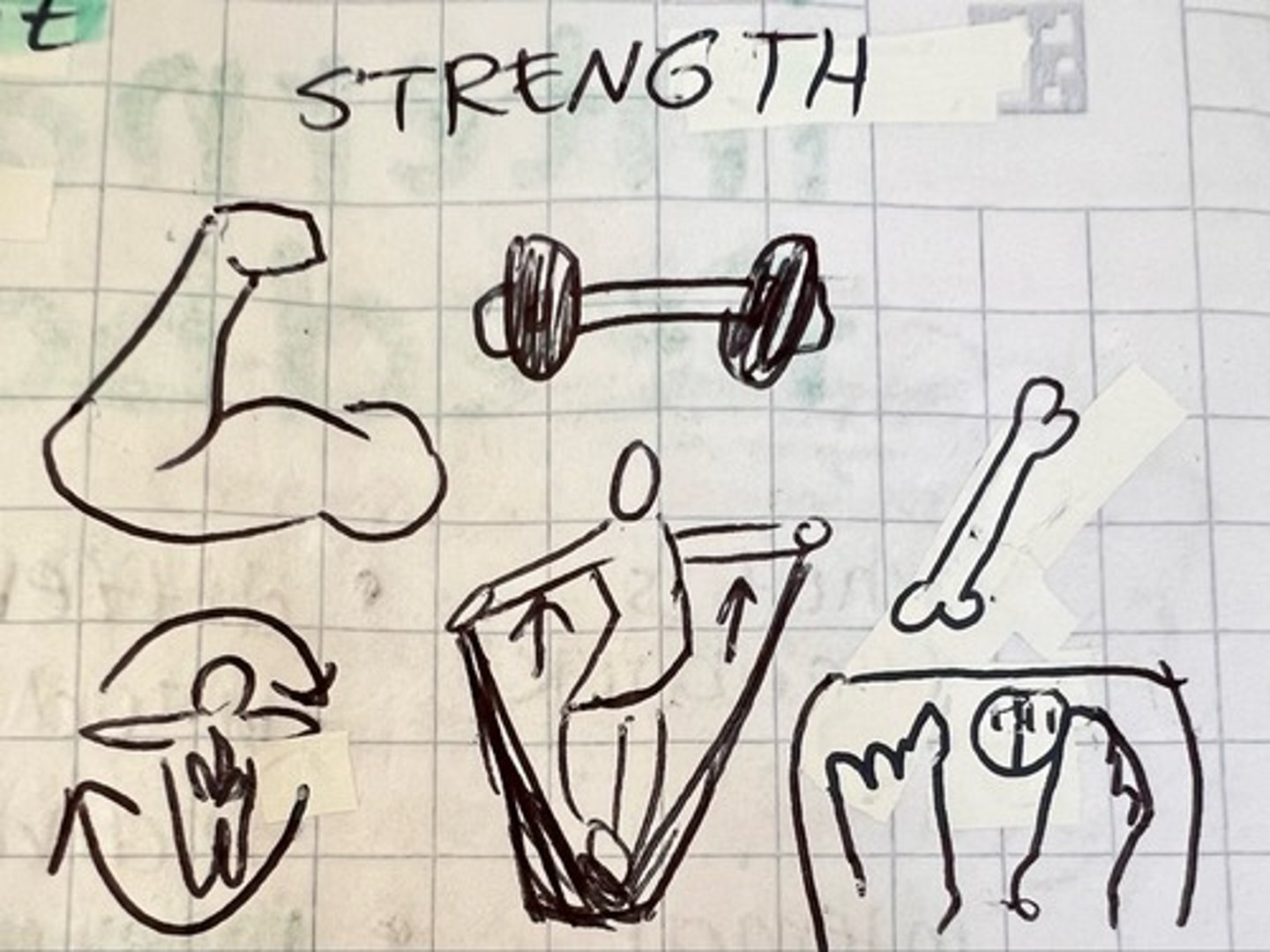
strength training
uses resistance to strengthen muscles (ex: weights, resistance bands, calisthenics) 🏋️💪, ⬆️ metabolism
cardio training
repetitive movements to elevate heart rate. for a prolonged period of time (ex: running, cycling, swimming), strengthens ❤️

internal feedback
naturally received and processed through the senses (ex: splash after a dive)

external feedback
feedback from outside sources (ex: coach, applause, watching a video of performance)

proprioception (kinesthetic sense)
our sense of body position and understanding of our bodies' extremities

contraindicated exercises
deep squat, unsupported forward flexing, the plow, hurdler's stretch, back bend, full or straight-leg sit up
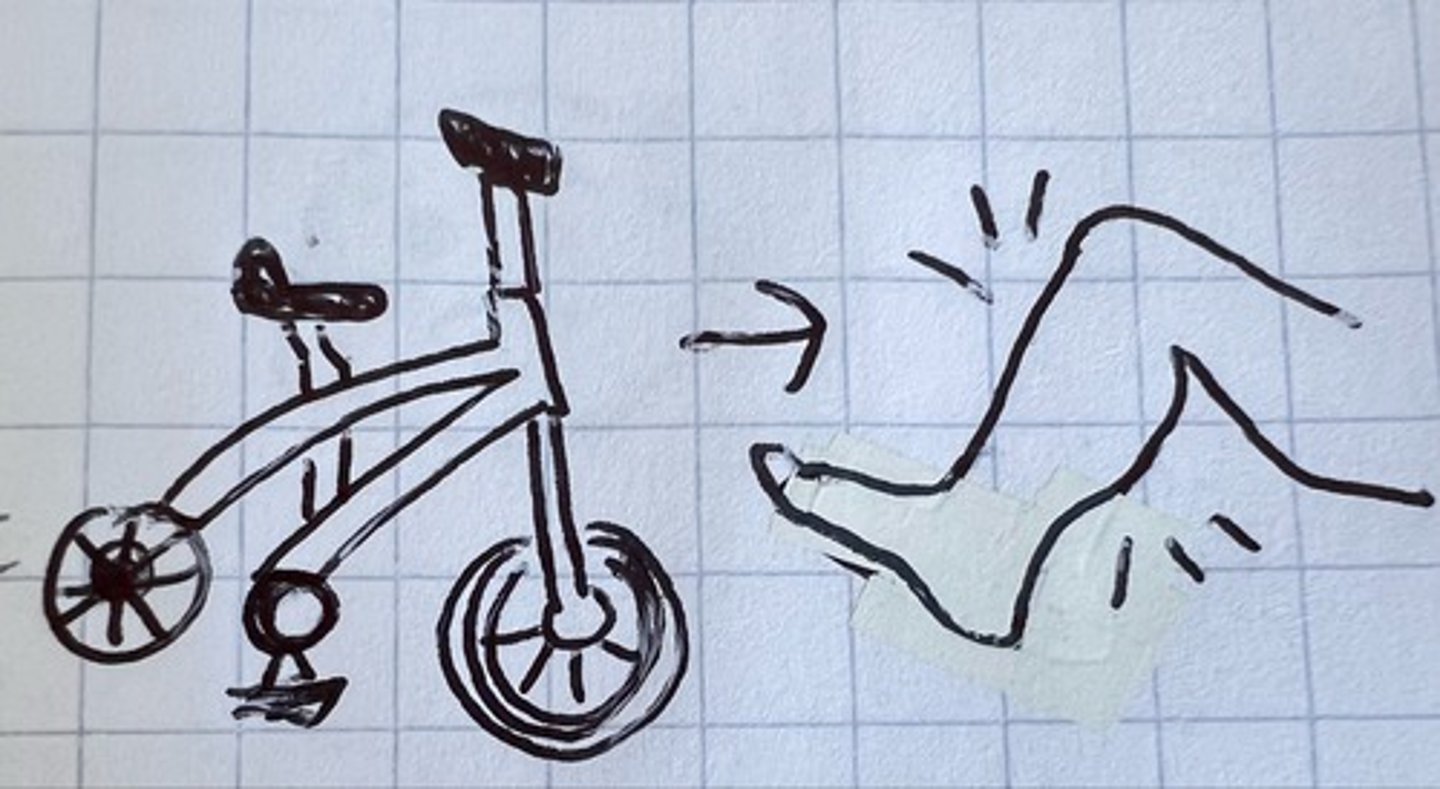
3 points of contact rule
when mounting or dismounting exercise equipment, always gold on to two places and put your foot on a third
why should you stay hydrated while exercising?
to decrease muscle soreness
pulse
beat of the ❤️ as felt through the walls of the arteries

❤️ rate
The number of times the ❤️ beats per minute

how to calculate ❤️ rate
feel pulse on wrist's radical or windpipe's carotid artery, count beat for 15 seconds, multiply that number of beats by 4

target 🎯❤️ rate
number of beats per minute you should aim for during exercise, 50-70% of your maximum ❤️🔥 rate
maximum ❤️🔥 rate
220-age