oxidative phosphorylation
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what are the five oligomeric complexes called
I NADH-ubiquinone (Q) oxidoreductase
II succinate-ubiquinone (Q) oxidoreductase
III ubiquinol- cytochrome c reductase
IV cytochrome c oxidase
V atp synthase
how many protons are pumped per NADH that enters the cycle
4 from NADH ubiquinone oxidoreductase
4 from cytochrome c
2 from ATP synthase
10 OVERALL
where does complex v accumulate
tips of the cristae
ubiquinone (coenzyme q) reduction
reduced one electron at a time
intermediate is semiquinone
then ubiquinol
where does ubiquinone accept electrons from
oxidation of NADH at complex I and FADH2 at complex II
what happens at NADH-ubiquinone reductase
NADH is oxidised to NAD+
with flavin mononucleotide FMN to FMN2
4 protons are pumped into the inter membrane space
what binds to which module in NADH-ubiquinone reductase
nadh binds to dehydrogenase n module
ubiquinone found in q module
H+ move across the membrane arm P module
which enzyme is common to both citric acid cycle and electron transfer chain
succinate Q reductase/ succinate dehydrogenase
what happens at succinate q reductase
succinate → fumarate
allows FAD to be reduced to FADH2
then reduces ubiquinone to ubiquinol
ubiquniol-cytochrome c oxidoreductase
captures electrons from ubiqunol to cytochrome c
4H+ are translocated
electrons are transferred from ubiquinol to two molecules of cytochrome c
cytochrome is an electron carrier between which complexes
iii and iv
structure of cytochrome c
alpha helical haem protein
iron atom in centre which changes oxidative states
small
highly soluble
associated to inner mitochondrial membrane
complex iv cytochrome c oxidase
receives electrons from cytochrome C carrier, one at a time
iron atoms and copper atoms are both reduced and oxidised as electrons flow to oxygen
catalyses the reduction of oxygen and water
two more hydrogen ions are translocated using free energy
complex v atp synthase
use the proton gradient energy for the synthesis of ATP
protons flow back into the matrix via ATP synthase
3H+ needed for each ATP
knob and stalk structure of atp synthase
F1 - catalytic subunits (faces the matrix) KNOB
F0 - proton channel (embedded in the inner membrane) STALK
what is the main component that allows rotation of atp synthase
gamma of central axle
arrangement of subunits of F1
alpha and beta alternate like orange segments - rigid
gamma in central axle - moves
delta in peripheral stalk
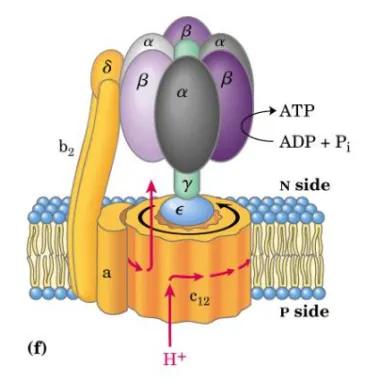
which subunit of F1 has active site for ATP synthesis
beta
beta subunit conformations
open state - binds ADP and Pi
loose state - active site closes loosely on ADP and Pi
tight state - converts ADP and Pi to ATP
what drives the rotational catalysis
flow of protons
drives F0/ gamma rotation
forced cyclic conformational changes into each beta subunit
how many protons per ATP
3H+/ATP in oxidative phosphorylation
1ATP for transport of Pi across inner mitochondrial membrane