Sociology Chapter 4: Agents of Socialization
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is anticipatory socialization?
Preparing for a new social setting or a new position in life.
What is resocialization?
The process of discarding old behaviors and identity to adopt new social behaviors.
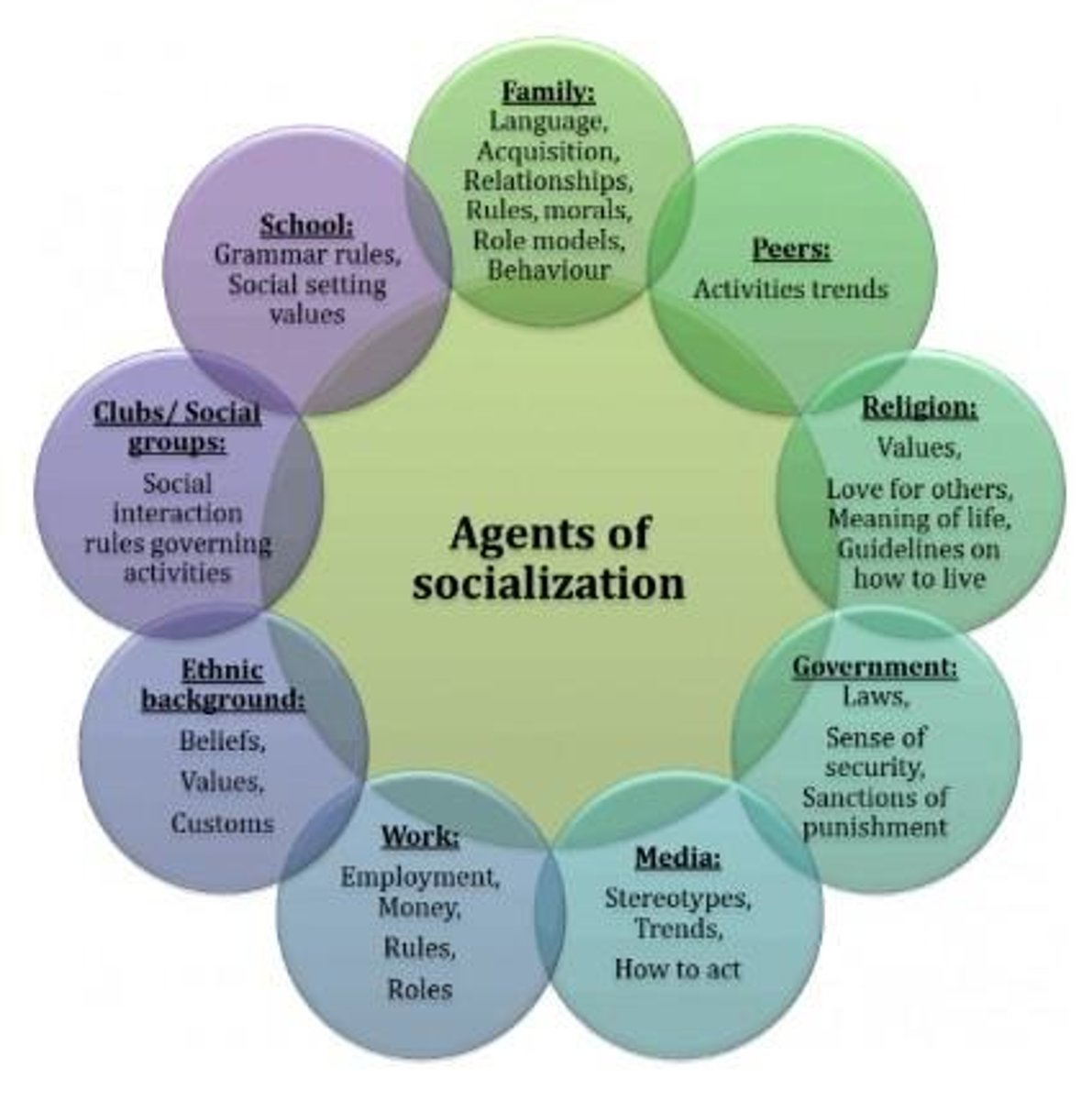
What are the primary agents of socialization?
Family, school, peers, media, neighborhood, workplace, religion, social clubs, and ethnic groups.
What concept did Goffman introduce regarding social interaction?
The Presentation of Self, which uses dramaturgical analysis to describe social interaction in terms of theater performance.
What is dramaturgical analysis?
A perspective that views social interaction as a performance where people are actors and their behavior is a performance.
What is 'face work' in social interaction?
The attempt to give the best possible performance in social situations.
What is the difference between frontstage and backstage behavior?
Frontstage refers to public performances, while backstage refers to private, relaxed, and secure behavior.
What is social structure?
The organized pattern of relationships and social arrangements that shape social interactions.
What is status in sociology?
The social position that an individual occupies, which can be ascribed or achieved.
What is the difference between ascribed and achieved status?
Ascribed status is assigned at birth or involuntarily, while achieved status is gained through individual efforts.
What is a status set?
An individual's collection of statuses, such as gender, age, race/ethnicity, and social class.
What is a master status?
A status that takes precedence over other statuses, influencing how individuals are perceived.
What are status symbols?
Cultural identifiers that visually display rank or privilege associated with a status position.
What is a role in sociology?
The expected behavior associated with a particular status.
What is role conflict?
Stress produced by competing role expectations from two or more statuses.
What is role strain?
Incompatibility among roles corresponding to a single status.
What is role exit?
The process by which individuals disengage from important social roles, such as retiring or getting divorced.
What was the Zimbardo Prison Study?
An experiment where students were assigned to the roles of 'prisoner' or 'guard' to study the effects of status on behavior.