Evolution Test 2
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is the change in focus between population genetics and qualitative genetics?
Population is a bottom-up approach (Genotype→phenotype), qualitative is a top-down approach (phenotypes→genotype)
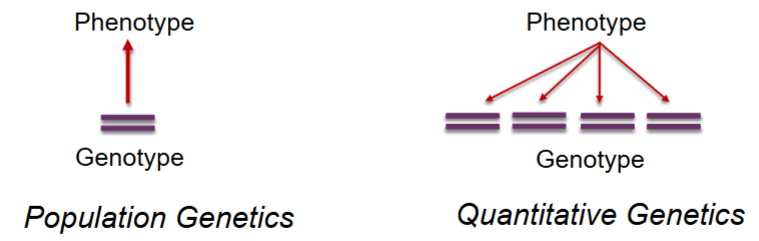
What is quantitative genetics?
The study of continuous phenotypic traits and their underlying evolutionary mechanisms
What is the genetic variance equation?
Var(P) = Var(G) + Var(E)
Continuous phenotypic variation is the result of what 2 things?
Genetic variation among individuals
Variation in the environment
What are the components of phenotypic variation?
VP = phenotypic variance
VE = environmental variance
VG = genetic variance
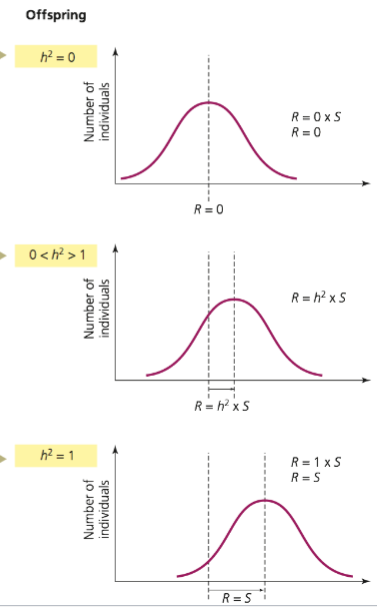
What is the Heritability (H²) equation?
he proportion of the total phenotypic variance of a trait that is attributable to genetic variance
H2 = VG / VP
= VG / (VG + VE)
What is the genetic variance equation?
VG = VA + VD + VI
VA = the additive genetic variance
VD = variance due to dominance effects of alleles
VI = variance due to epistatic interactions among alleles
What is the heritability (narrow sense h²) equation?
h²=VA/VP
the proportion of the total phenotypic variance of a trait attributable to the additive effects of alleles.
Responses to selection (R) are dependent on:
1. Heritability of the trait
2. Strength of selection (Selection differential)
What are the 3 types of selection?
Stabilizing, directional, and disruptive
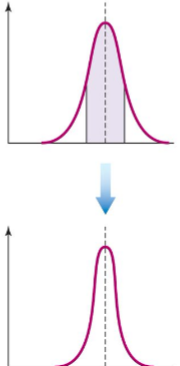
What is stabilizing selection?
preserves average phenotype
reduces variation in a population, but does not change the mean.
Example: Human birth weights
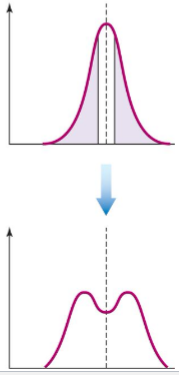
What is disruptive selection?
favors individuals that vary in opposite directions from the mean
Example: Bill size in black-bellied seedcrackers.
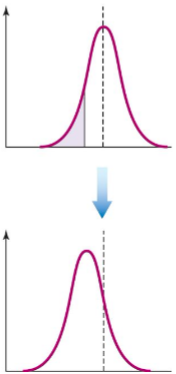
What is directional selection?
favors individuals that vary in one direction
At a single gene locus, directional selection may result in favoring a
particular genetic variant (positive selection for that variant)
What is strength of selection?
S = the difference between the mean (for a trait) of the reproducing
members of the population and the mean of all the members of a
population
High heritability results in larger or smaller change.
larger
What is linkage equilibrium?
exists if the occurrence of an allele at one locus is independent of
the presence or absence of an allele at a second locus
Loci on different chromosomes usually behave independently and
thus are in linkage equilibrium
Can loci on the same chromosome be in linkage equilibrium?
Yes if they are far apart
What is linkage disequilibrium?
It is a statistical state
Whenever a combination of alleles occur together more or less often than
expected by chance
Doesn’’t have to be a physical linkage
True or False, new alleles are always in linkage equilibrium
True, they become linkage equilibrium over time due to recombination
Predictable decay toward LE
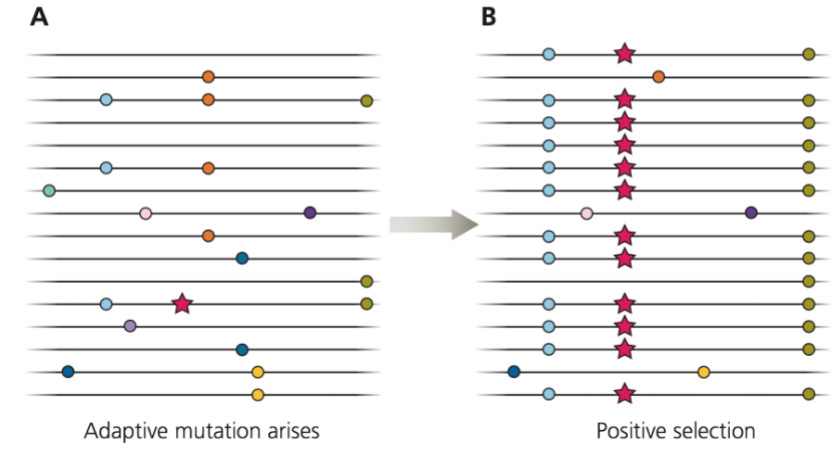
Why can linkage disequilibrium tell us?
when new alleles formed and give us a metric to estimate if under positive selection in a population
What 2 ways can you tell genetic drift from selection?
Genetic linkage: physical proximity of alleles at different loci
Selective sweeps: strong selection can “sweep” a favorable allele to fixation so fast that there is little time for recombination and the locus is therefore still in Linkage Disequilibrium
True or false: in linkage disequilibrium, selection never favors certain combos of alleles
False, it sometimes does
Selection in opposition to recombination
Supergene- A group of functionally related genes located close enough together that they segregate as a single unit
True or false: chromosomal rearrangements lead to increases in fitness
True
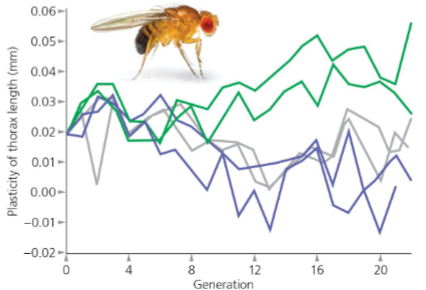
What is norm of reaction?
The variety of different phenotypic states that can be produced by a single genotype under different environmental conditions
True or False: norm of reaction is the same for every genotype
False, norm of reaction can vary from one genotype to another
Can selection shape phenotypic plasticity?
Yes, when there is genetic variation of the slopes of the reaction norms
True or False: phenotypic plasticity is always an advantage
False (ex: seasonality and shade avoidance)
True or False: selection varies across space
True (ex: kingsnake and mimic kingsnake)
If the aposematism coral snakes were only favored in one area and there is gene flow between both population, why are the aposematic coral snake still only in one area?
Aposematic favored only in areas with coral snakes. Positive selection for aposematic in one area, negative in the other
What were the two examples of similar selection pressures resulting in convergence of a specific trait?
Lactose tolerance and mice coat color
Where do you find evidence for independent origin of traits?
In the underlying genetic mechanisms (diff mutations form same phenotype)
What was the example of organisms responding to multiple selection pressures at once?
gallflies, birds, and wasps. Gall size is determined by the genotype of the gallfly (= extended phenotype), intermediate size favored
Pesticides and herbicides act as agents of selection. How can we use cost of resistance (antagonistic pleiotropy) to solve this problem?
Bt crops (GMO) select for resistance in pests, Comes at a cost when Bt is not present
Creation of Bt-free refuges favors Bt-susceptible insects, Slows evolution of resistance
Refuges are now required by law
What is incomplete lineage sorting
gene trees do not always match species trees
True or false: gene trees always match species trees
False
What are the four possible character states?
ACGT
Why are homoplasies common when building a phylogeny with genetic data?
because there are only four character states
Slowly evolving genes are useful for _ (distantly related species or closely related)
distantly
rapidly evolving genes are useful for _ (distantly related species or closely related)
closely
What is a homoplasy?
independent evolution of similar traits in different lineages (convergent evolution), can be genetic or morphological
What are the four common methods of building phylogenies with genetic data?
maximum parsimony, distance matrix, maximum likelihood, bayesian methods
What is the distance matrix method?
clusters taxa based on genetic distance
What is the maximum likelihood method?
finds most likely tree given specific model of molecular evolution
What is the bayesian method?
Looks at probability that a tree is correct given a
specific model of molecular evolution
What is introgression?
the transfer of genetic information from one species to another through hybridization and backcrossing
What happened in the Darwin finch case study?
The phylogenetic evidence supported single colonization from south america. The finches formed monophyletic group with Cocos island finches coming from the Galapagos
In the human evolution case study, what was the multiregional model and what was the out-of-africa model
Multiregional model of human origins
– Hominins across Old World were a single
species connected by gene flow
– Multiregional differences the result of local
adaptation
Out-of-Africa model of human origins
– All human populations are derived from recent
African ancestry
What was the result of the human evolution case study?
The phylogenetic data supports the out-of-Africa model
What is the neutral theory of molecular evolution
most evolution at the molecular level is neutral (due to drift)
– Neutral substitutions should accrue in a clock-
like fashion
– Different types of DNA should evolve at
different rates
we can calculate when species diverged based on mutations rates
If nonsynonymous substitutions evolve faster than synonymous sites, does this indicate positive or purifying selection
positive
If nonsynonymous substitutions evolve slower than synonymous sites, does this indicate positive or purifying selection
purifying
synonymous substitutions should evolve at a _ rate
neutral
Increased frequency of beneficial alleles and reduced diversity in linked regions indicates_
positive selection
A reduction in genetic diversity at both targeted and linked regions and elimination of deleterious mutations indicates _
purifying selection