slay
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
What is nuclear fusion?
Nuclear power that involves the joining of the nuclei of small atoms such as the isotopes of hydrogen
Hydrogen-2
Deuterium
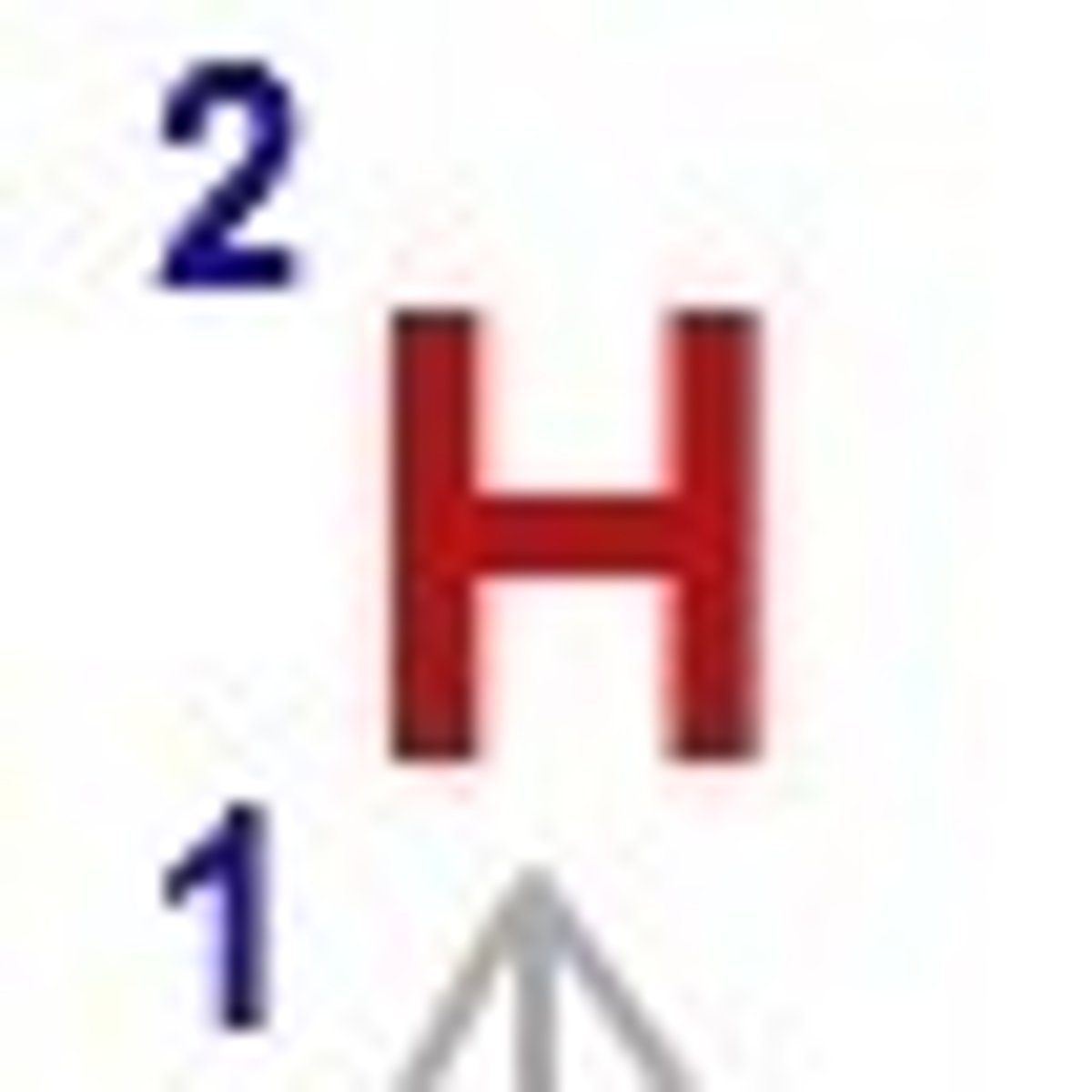
Hydrogen-3
Tritium
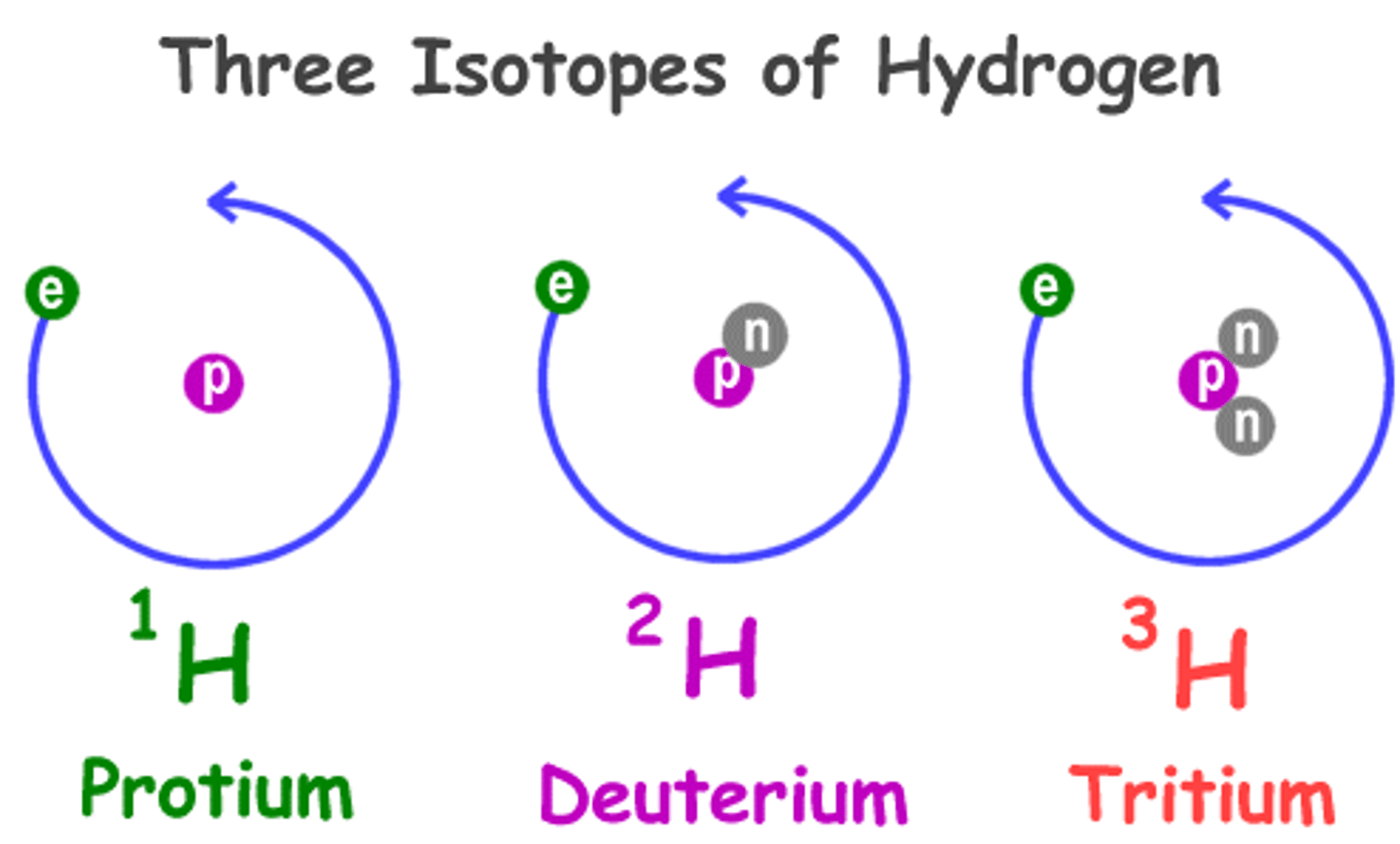
Where do you source deuterium (hydrogen-2)?
Extracted from water
Where do you source tritium (hydrogen-3)?
Produced by the neutron bombardment of lithium
Is commercial fusion possible on Earth?
No
What conditions are needed for fusion to occur on Earth?
- Hydrogen in the form of plasma
- Heavy nuclei
- Very high temps
- Vacuum
- Magnetic field
Toroidal Reactors
A doughnut-shaped device used to contain hot plasma
Magnetic fields are used to keep the plasma stable and away from the reactor walls (prevents it from touching the walls and cooling down)
Example of Toroidal Reactors
ITER
Built after JET (Join European Torus - near Oxford) and will expand off the knowledge from JET.
Plan for ITER
- Was planned to be operational in 2025
- May release more energy than it uses (500MW output from a 50MW input)
- Maintain fusion for longer periods
- Use a blanket of lithium around the reactor to breed new tritium fuel
Laser Fusion
A developmental nuclear fusion technique that uses a laser beam to cause fusion in beads of frozen hydrogen
How do you initiate laser fusion?
Small spheres of frozen deuterium and tritium would be dropped into an intense laser beam
Improved Uranium Extraction Techniques
- Polymer Adsorption
- Phosphate Mining
- Coal Ash
What's polymer adsorption?
1) Uranium dissolved in seawater adsorbs onto certain polymers that are placed in the sea
2) The uranium can be washed off using acids
3) It is then collected and concentrated
What's phosphate mining?
Uranium is actually often present in phosphate deposits, therefore they can be separated from the material extracted in the phosphate mines.
What's coal ash?
Uranium can be extracted from coal ash. This will become economic if the price of uranium rises.
What is fissile fuel?
An isotope that can easily undergo nuclear fission when struck by a neutron, releasing energy.
Give me an example of a fissile fuel
Uranium-235
Plutonium-239
What is a fertile fuel?
An isotope that cannot undergo fission itself, but can be converted into a fissile fuel in a reactor through the bombardment with neutrons
Give me an example of a fertile fuel
Uranium-238 (which can become Plutonium-239)
Thorium-232 (which can become Uranium-233)
New Reactor Designs
- Plutonium reactors
- Thorium reactors
Plutonium Reactors
Nuclear reactors that use plutonium-239 as a fissile fuel, often derived from reprocessed spent nuclear fuel.
What type of reactor are plutonium reactors?
A type of 'breeder' reactor
How do plutonium reactors work?
Uranium-238 fuel is bombarded by neutrons, undergoing beta decay to form the fissile fuel plutonium-239.
Plutonium-239 is very unstable and releases energy in the form of heat.
The heat is used to heat water and produce steam to turn the turbines.
Are plutonium reactors good?
They are fuel efficient but complex and expensive.
Thorium Reactors
Nuclear reactors that convert the fertile fuel thorium-232 into the fissile fuel, uranium-233
Thorium Reactor designs
They have rods of thorium-232 in the reactor core
These rods get bombarded with neutrons and breed uranium-233
Uranium-233 can then be extracted to make new fuel rods
Two types of Nuclear Power
Nuclear fission
Nuclear fusion
What is nuclear fission?
The splitting of nuclei of large atoms
Large atoms examples:
The isotopes of uranium-235 or plutonium-239
What is fissile fuel?
An isotope that can easily undergo nuclear fission when struck by a neutron, releasing energy.
Give me an example of a fissile fuel
Uranium-235
Plutonium-239
1)
A big atom (like U-235) absorbs a neutron
2)
This makes the atom unstable, causing it to split into 2 smaller atoms
3)
When the atom splits, it releases energy in the form of heat
4)
The split also releases more neutrons, which can hit other large atoms, causing them to split and lead to a chain reaction
Why has nuclear power not expanded?
- Very expensive
- Strong public opposition due to concerns over safety following Chernobyl (1986, Ukraine) and Fukushima (2011, Japan)
- Uncertainty over the permanent disposal of radioactive waste
- Uncertainty over the total costs of nuclear power since no commercial reactor has been fully decommissioned
Energy Density
A small amount of fuel is needed to release a large amount of energy.
1kg of uranium fuel can release as much energy as....
13,000kg of coal
Embodied Energy
Uranium needs to be purified & concentrated & chemically processed to produce fuel, whereas coal does not
Finite Resource
Fissile materials like uranium and thorium are non-renewable resources, so quantity declines as they are used.
However, a huge amount of uranium exists, but most is found in low purity deposits and they cannot be exploited economically
Environmental Impacts
- Mining and processing uranium (and mining thorium ore to make nuclear fuel) leads to habitat loss, noise, dust, turbid drainage water, hazardous wastes
- The high embodied energy of materials used contributes to global climate change
Economic Issues
Only a few old reactors have been fully decommissioned, and costs were much higher than anticipated
Nuclear fission VS Coal
A reactor only needs around 18,000-80,00kg of fuel replaced each year
Whereas 9,000,000kg of coal would be needed to burnt everyday to have a similar energy output
Where is natural gas recovered from?
Underground rock structures of porous, permeable rock, using the natural pressure of gas
What is the typical recovery rate of gas present?
80-90%
What are methane hydrates?
A solid, ice like crystalline solid found in locations at low temperatures (polar regions) or under high pressure (marine sediments)

How are methane hydrates extracted?
Hot water is pumped into the sediments, which melts the hydrate crystals, releasing the methane gas
Drilling into the sediments to melt the hydrate crystals, releasing the methane gas
How can carbon dioxide extract methane hydrates?
At high pressures, carbon dioxide can also form bonds with ice crystals, but it bonds more strongly than methane.
Therefore injecting carbon dioxide could displace methane which could then be collected
Why aren't methane hydrates from ocean sediments being exploited?
Little is known about the ecology of the ocean floor that the ev impacts are hard to predict.
Also, any methane released that was not collected can enter the atmosphere and contribute to global climate change.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
A technology used to capture and store carbon dioxide emissions from power plants and industrial processes to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Advantages of CCS
Theoretically makes extended use of fossil fuels possible
Disadvantages of CCS
CCS cannot be applied to small, dispersed uses, like cars
Where is CCS likely to be installed?
CCS can possibly capture CO2 at large power stations and then use the electricity can then be used to produce non carbon duels, such as hydrogen.
Primary Oil Recovery
Uses the natural pressure of water below the oil (or gas present above the oil) to force the oil up the production well to the surface
Is primary oil recovery a well established method?
Yes
How much oil is usually extracted from primary oil recovery?
20%
How do you increase the flow rate?
Fit a pump jack at ground level on the production well

Secondary Oil Recovery
Water (or natural gas) is pumped down an injection well to maintain the pressure and the flow of the oil
How much does secondary recovery increase the recovery rate to?
40%
Tertiary Oil Recovery
The viscosity of the oil is reduced for easier extraction using methods such as the injection of steam, controlled combustion, solvents or bacteria.

Steam injection
Steam may be pumped down to heat the oil
The steam can be generated by burning the fuel, or from solar heating schemes using parabolic concentrators
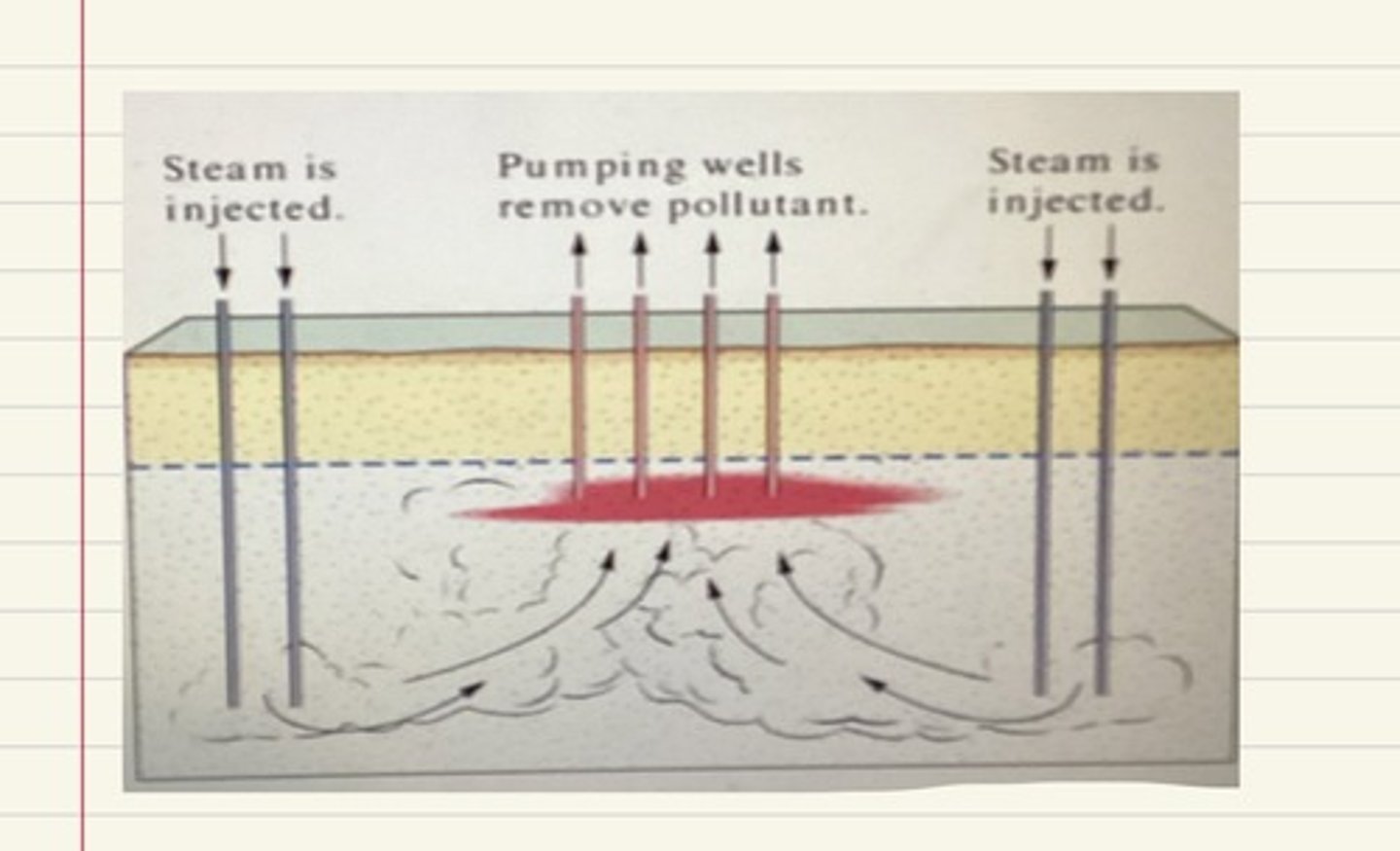
Controlled combustion
The oil viscosity may also be reduced by controlled underground combustion which heats it up
Solvents
Detergents or solvents reduce the surface tension of the oil to make it flow more easily
Bacteria
Bacteria is used to partially digest heavy oil and produce light oils that flow more easily. The bacteria also produce carbon dioxide which helps to maintain the pressure and the flow of oil
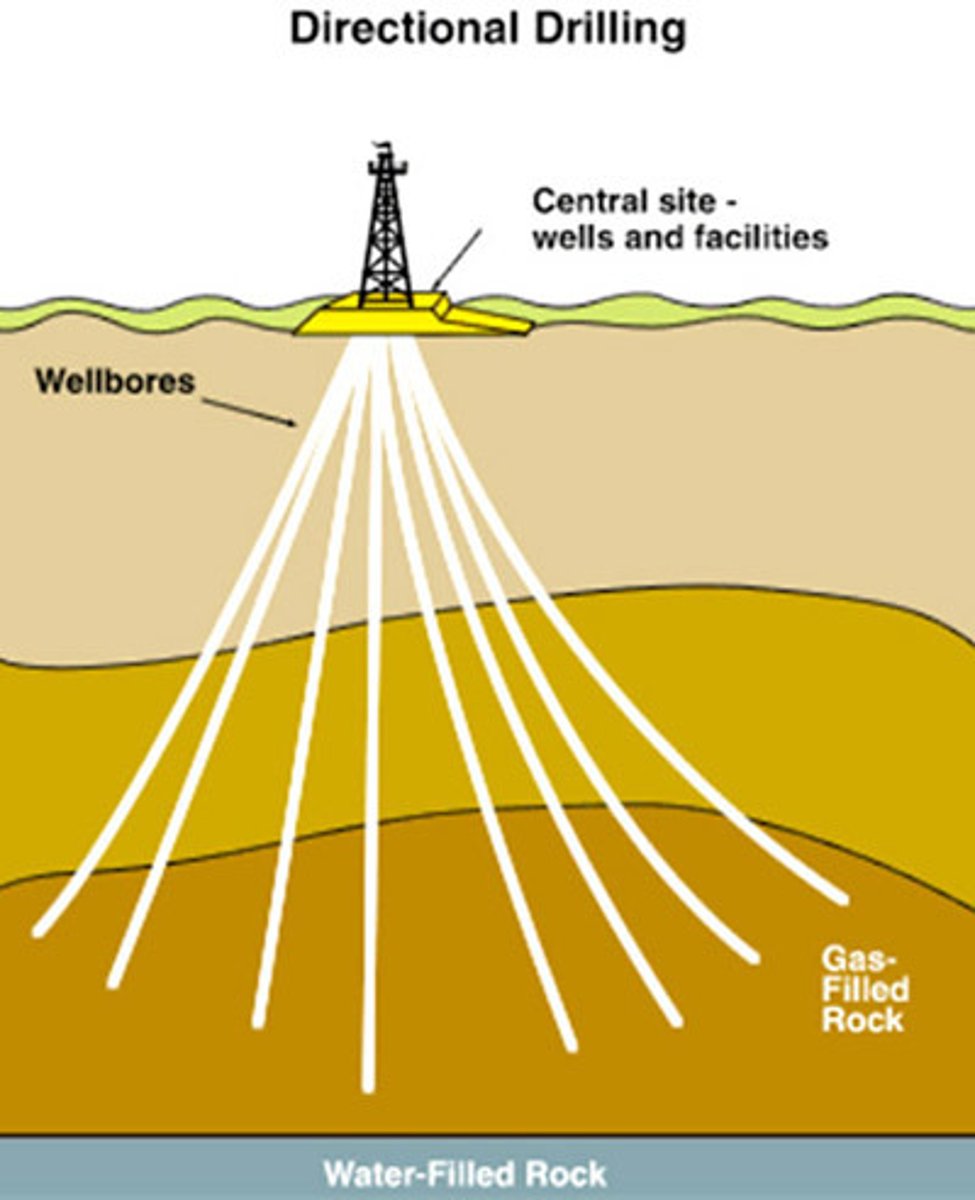
Directional Drilling
Allows for oil wells to be drilled that are not vertical
What are the advantages of directional drilling?
- Many wells can be drilled from a single platform
- It is possible to drill underneath locations where drilling rigs could not be placed like under urban areas
- Drilling can follow weaker or softer rock strata to make drilling quicker and can target multiple small reservoirs up to 10km from the well head
- Overall significantly increasing total recovery rates
Hydraulic Fracturing (a.k.a fracking)
- Large volumes of crude oil and natural gas are trapped in the pore spaces of shale rocks that have low permeability
- These are called tight oil and tight gas
- Hydraulic fracturing uses high pressure to open fissures in the surrounding shale rock along which the oil or gas can flow towards a recovery well
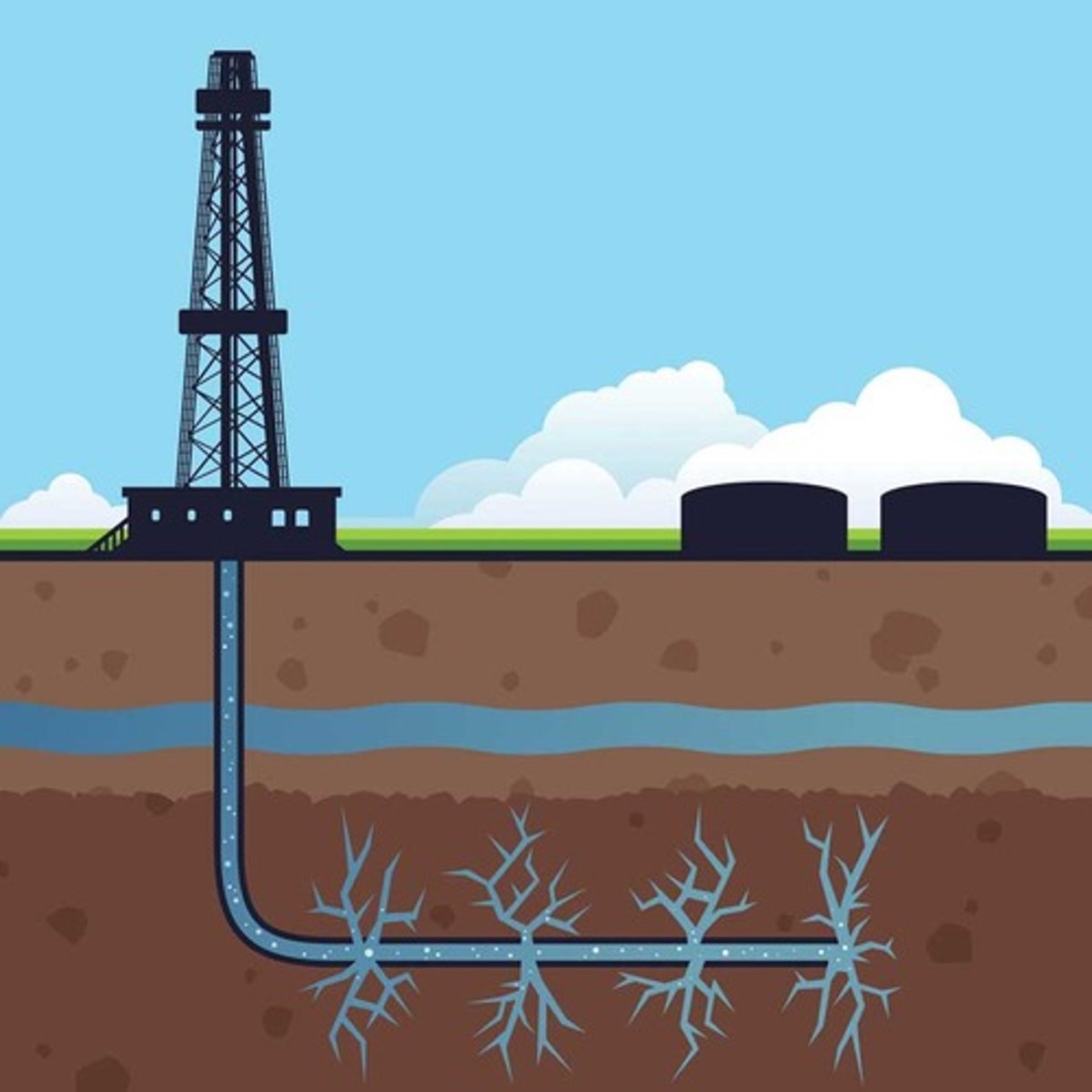

What can be pumped into these fissures?
Water, sand grains, solvents
These all increase the recovery rate
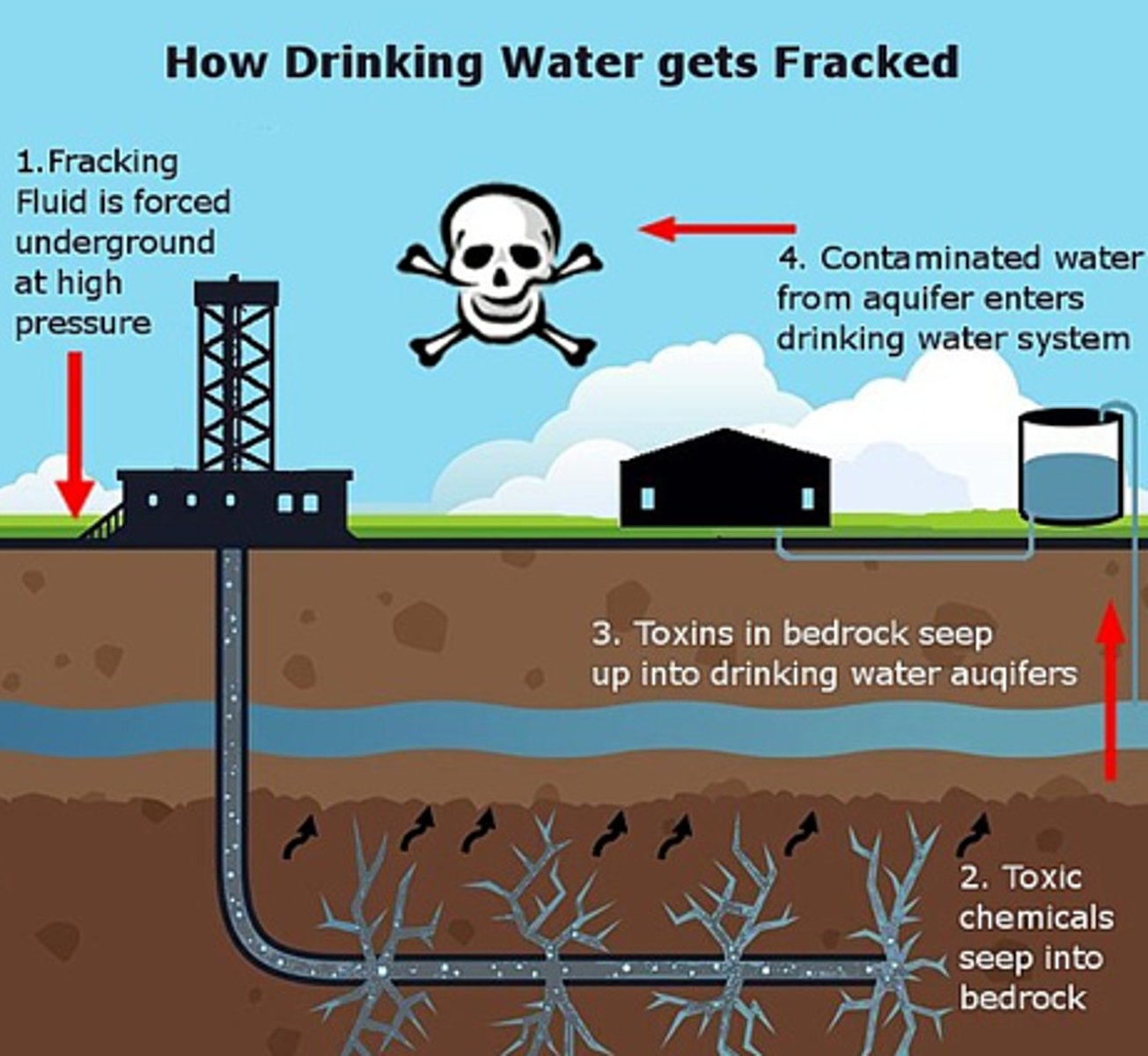
Concerns over fracking?
- Natural gas may enter the aquifer water
- Chemicals injected may enter aquifers, or reach the surface and cause pollution
- Toxic metals naturally present in the rocks may become mobile
- Large volumes of water are needed
How to reduce issues over fracking?
- Collecting and treating waste water
- Reusing waste water
- Restrictions on the location of fracking sites in sensitive areas
Tar sands
A very viscous crude oil found in sand. It includes 'heavy' oils that do not flow easily

How are tar sands used in oil extraction?
- The sands are extracted then treated with hot water to separate the oil.
- Another method is the use of steam injection, solvent or controlled combustion to produce liquid oil that can be pumped to the surface.
How much oil is produced from 2000kg of tar sands?
150 litres
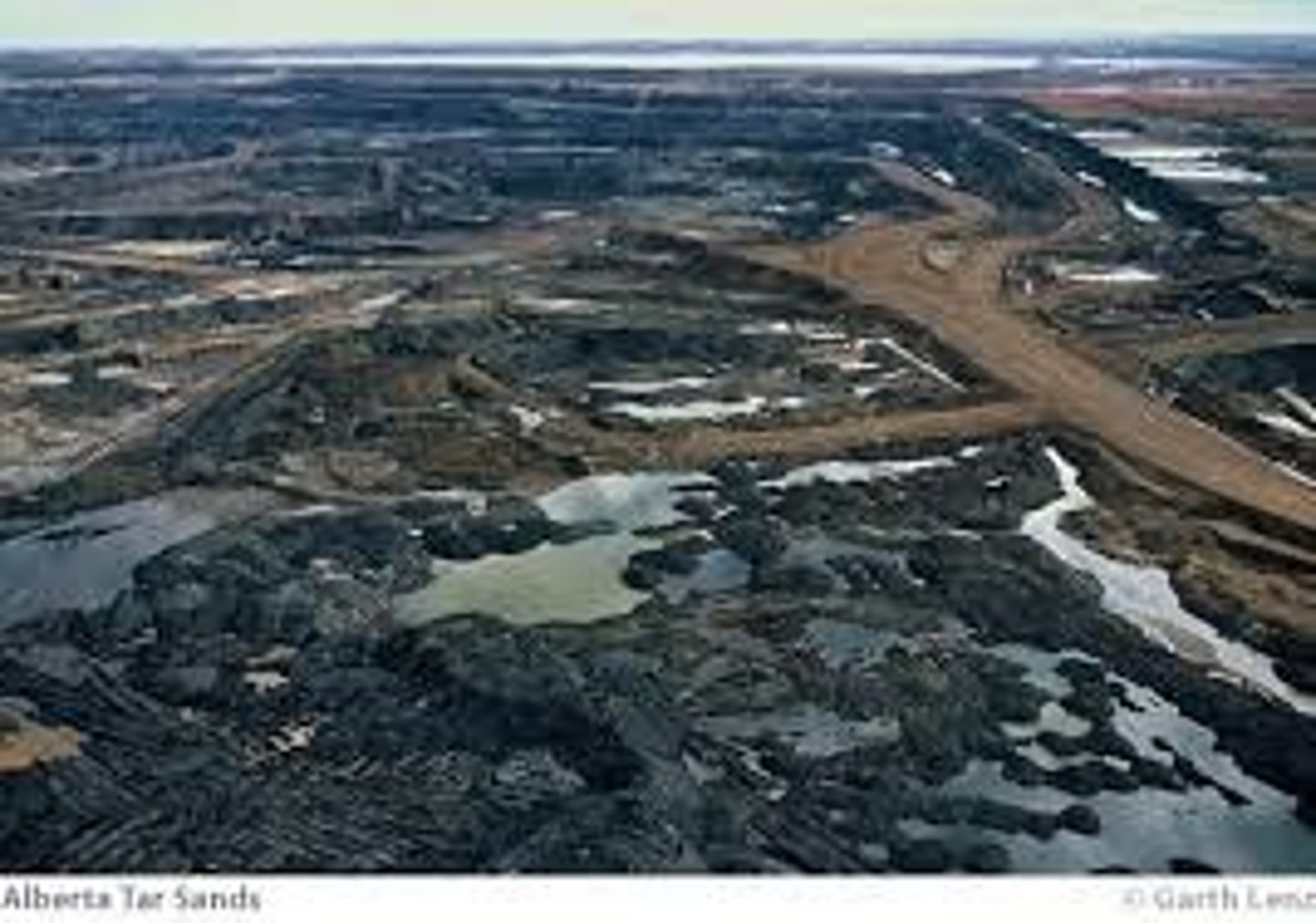

How much of the oil in tar sands recovered?
75%
What happens to waste sand?
The waste sand is backfilled into the mine
Oil shales
They are fine sedimentary rocks that contains kerogen (solid form of crude oil)

How are oils extracted from oil shales?
Oil shales are mined and then are heated to drain off the fluid hydrocarbons
Are recoverable deposits of tar sands and oil shales greater than the total reserves of crude oil?
Yes
So why are tar sands and oil shales used more?
Extraction is expensive so current estimates of economically recoverable reserves are low
What is coal gasification?
Coal can be burnt underground under controlled conditions to produce useful gases (H₂, CO, CH₄)
What can the coal gases be used for?
Producing heat
Generating power
Why is coal gasification used?
Sometimes the coal is too deep to be mined
What is coal liquefaction?
The conversion of coal to liquid hydrocarbons, which have applications that solid coal cannot perform, such as liquid vehicle fuels
How is coal converted to liquid directly?
They can be converted to liquids directly using solvents
How is coal converted to liquid indirectly?
Gasification
Then chemical changes to convert gaseous hydrocarbons to liquid hydrocarbons.
What are the main uses of coal?
- Electricity generation
- Iron & steel industry
Coal Extraction
- Deep mining
- Open cast mining

Deep mining
Labour intensive and expensive
Open cast mining
Mechanised and more economically viable, but still requires clearing rock above coal
What can't either method of coal extraction access?
Deep deposits and very thin seams
Environmental Impacts of Coal Extraction
- Habitat loss
- Noise
- Dust
- Turbid drainage water
- Spoil heaps
- Surface subsidence
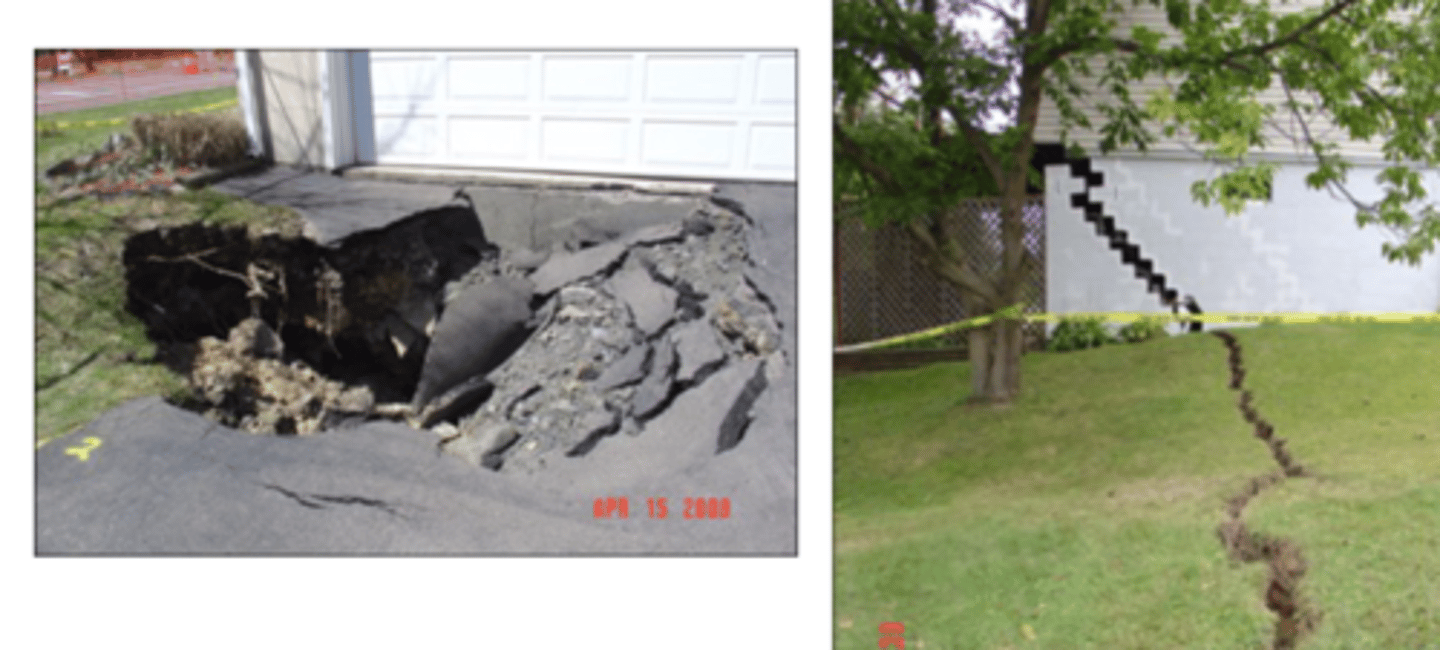

What are the main uses of oil?
Liquid vehicle fuels (petrol, diesel)
Gas fuel for heating (propane, butane)
Petrochemicals (plastics)
Oil Extraction
Crude oil in liquid form flows through permeable rock and collects in the pores of porous rocks in between the particles.
When a pipe is drilled down to these reservoirs, oil will be forced to the surface, either by the natural pressure of gas above the oil, or by water beneath the oil

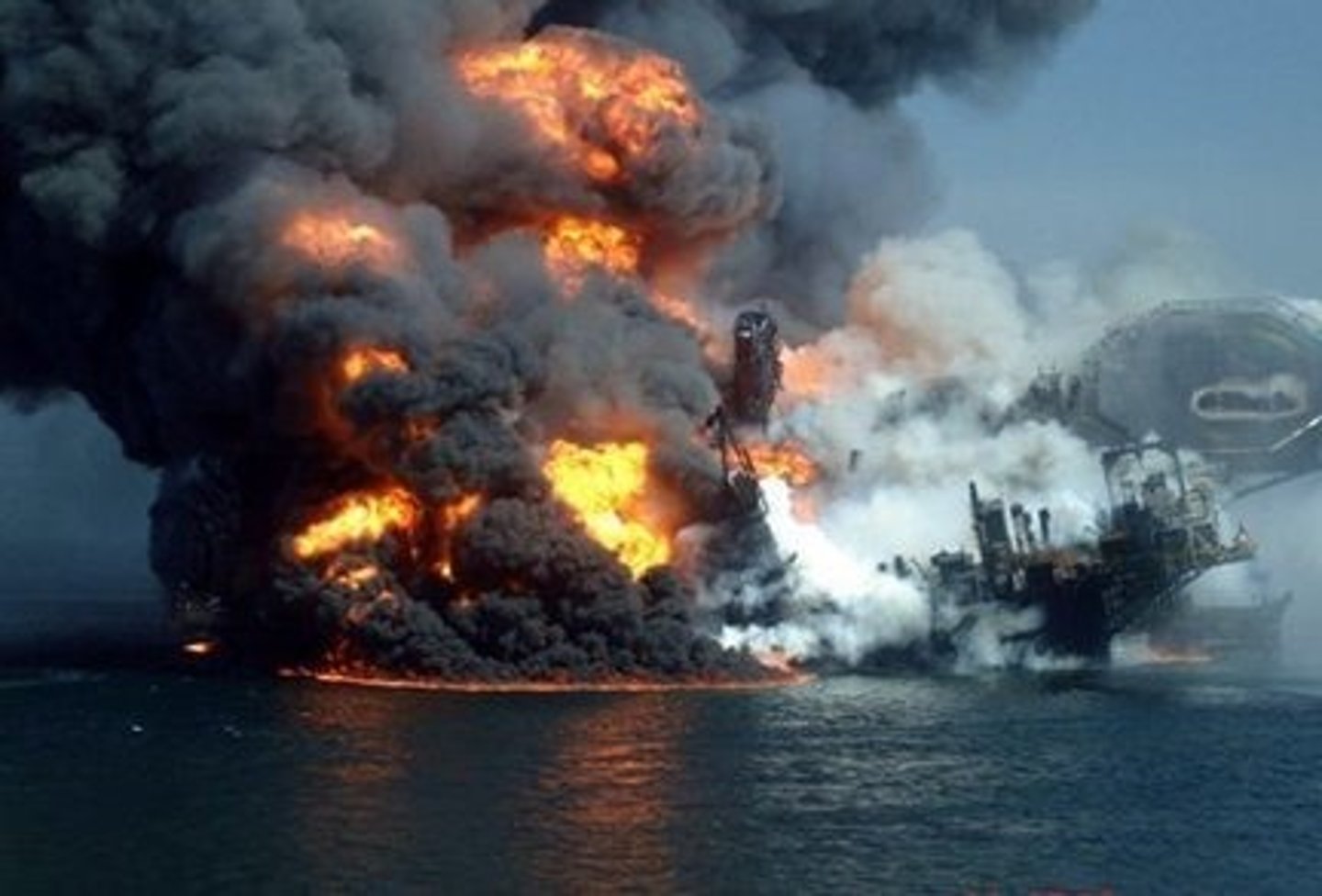
Environmental Impacts of Oil Extraction
- Oil spills
- Oil based drilling mud used to lubricate the drill pipes can cause pollution in groundwater, rivers, and the sea
- Surplus gas on oil rigs may be burnt (flared) to reduce the risk of explosions, causing atmospheric pollution through pollutants like SOx, CO2, and smoke
- Marine seismic surveys

What are the main uses of natural gas?
- Domestic & industrial heating
- Electricity generation
What are fossil fuels?
Fuels produced over millions of years from decayed animal and plant matter, like oil, gas, and coal

Why are fossil fuels popular?
- Easy to store
- Have a very high energy density, so they can power high energy intensive activities
- Found in very abundant local deposits
Why are new technologies required for fossil fuels?
The most accessible fossil fuel deposits have been depleted, so new technologies are required to exploit remaining deposits
The chemical energy of fossil fuels:
- Easy to store
- Easy to convert into heart energy that is usually required