Lecture 3: Biological Macromolecules
1/62
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
tetravalent
four single valence electrons
organic compounds
contain carbon bonded to C or H
carbon chains
skeletons of organic molecules
functional group
group of atoms in molecule that dictates characteristic chemical behavior and properties
hydrocarbons
consist of carbon and hydrogen and are nonpolar & uncharged, and thus are hydrophobic and insoluble in water
example of a hydrocarbon
CH4
hydroxyl group
r-OH
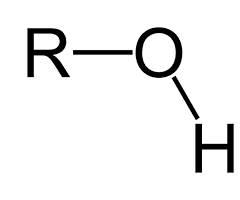
components of hydroxyl group
ex. alcohol (name ends in -hol); polar; hydrophilic; neutral (pH)
carbonyl group
CHO
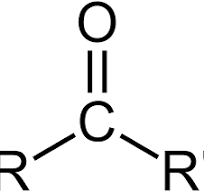
components of carbonyl group
ex. aldehyde/ketone (depend on location of C=O); polar; hydrophilic (less than OH); neutral (pH)
carboxyl group
R-COOH
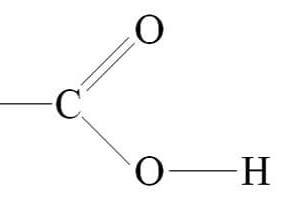
components of carboxyl group
ex. carboxylic acids (H+ easily released); polar; hydrophilic; acidic (pH)
amino group
R-NH2
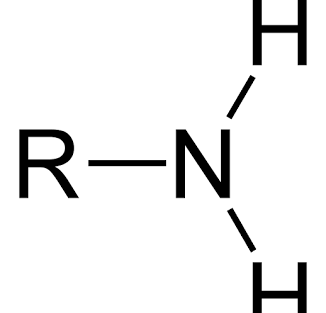
components of amino group
ex. amines (H+ easily accepted); polar; hydrophilic; basic (pH)
phosphate group
R-PO4H2
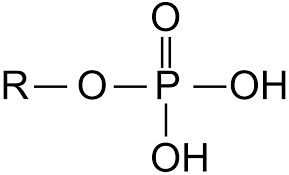
components of phosphate group
ex. organic phosphate; polar; hydrophilic; acidic (pH); often contain negative charge; phospholipids and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
methyl group
R-CH3
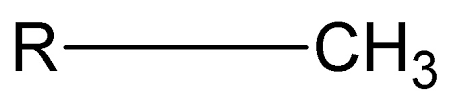
components of methyl group
ex. methyl hydrocarbon; nonpolar; hydrophobic; neutral (pH); control of gene expression, shape, and function of sex hormones
monomers
building blocks of macromolecules
polymers
monomers joined together
which biological molecules are polymers?
carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids
dehydration synthesis
remove H2O and joins enzymes; monomer→polymer
dehydrogenoses
enzymes used in dehydration synthesis
hydrolysis
add H2O and breaks enzymes; polymer→monomer
hydrolyses
enzymes used in hydrolysis
carbohydrates
CH2O; fuel and building material
monomers in carbs
sugars (monosaccharides) and glucose (C6H12O6)
polymer in carbs
polysaccharides
glucose forms
linear and ring
glucose in ring form
formed in two ways—alpha (α) or beta (β)
glycosidic linkage
covalent bond between monosaccharides
disaccharide
just two monomers (ex. glucose + fructose)
polysaccharides
more than two monomers in a chain → sugar polymers
what purpose do carbohydrates serve?
depending on the types of monomers and glycosidic linkages, it can function as energy or structural support
lipids
not polymers; hydrophobic; mostly hydrocarbonds
families of lipids
fats, phospholipids, steroids
function of fats
energy storage
what do fats consist of?
glycerol and 1-3 fatty acids
glycerol
3 carbon alcohol with three -OH
ester linkage
dehydration synthesis → covalent bond
triglyceride
storage form of fat
what does the presence of double bonds determine for fats?
if the fat is saturated, unsaturated, or trans-oleic
phospholipid
cell membrane
amphipathic
glycerol + 2 fatty acids; hydrophobic
what group are phospholipids part of?
phosphate group
steroids
three rings of 6 carbon and one ring of 5 carbon
what do z in animals lead to
communication and cell membrane structure
cortisol
stress hormone
proteins
peptide bonds between amino acids (monomers)
what type of reaction do proteins undergo?
dehydration synthesis
polypeptide
sequence of amino acids; each amino acid is bound to the next with a peptire bond BUT must be folded into the correct 3D shape to become a protein
primary structure
sequence of amino acids joined by peptide bonds in polypeptide chain; determined by DNA
secondary structure
within a single polypeptide, hydrogen bonds stick amino acids together; amino group carboxyl group; R- groups do not participate; alpha helix = coil, beta pleated sheet
tertiary structure
within a single polypeptide, R-groups interact; folds into a particular 3D shape; any/all types of bonds
quaternary structure
multiple polypeptide chains from one macromolecule (not more folding); ex. collagen
denaturation
loss of a protein’s third or fourth structure
is a denatured protein biologically active or inactive?
biologically inactive
what causes denaturation?
pH, salt concentration, and temperature; ex. frying egg
nucleotides
monomers in nucleic acids
classes of nucleotides
DNA and RNAw
what does DNA stand for?
deoxyribonucleic acidw
what does RNA stand for?
ribonucleic acid
what do nucleic acids do?
transmit hereditary information and determine protein production