Oral Biology Exam 1
1/213
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from leah_kathryn on quizlet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
214 Terms
What is growth?
increase in size or number of cellular structures, rate of growth varies
What is development?
increase in the degree of organization and/or functional complexity
continues throughout life
What period (weeks) are critical for the formation of the oral cavity and face?
4th-14th week of intrauterine life (embryo to fetus stages)
What does the maxillary process of the 4th week embryo turn into?
maxilla
what does meckel's cartilage form?
mandible
How do meckel's cartilage and the maxillary process develop?
membranous ossification
What weeks are considered the proliferative period?
0-2 weeks --> cell division
What weeks are considered the embryonic period?
2nd to 8th weeks
What weeks are considered the fetal period?
8th week-birth
What period is the growing embryo least susceptive to environmental factors and acquired defect formation?
proliferative period (0-2 weeks)
What week do neural folds appear?
3rd week
Week the neural tube closes?
3rd week
What week do the primary brain vesicles form (forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain, cerebral hemispheres)?
3rd week
Which weeks are most critical for serious malformations and have a high susceptibility to environmental factors?
3th-8th week --> structures are developing
Which period has declining susceptibility to malformations?
8th week-birth
What are the three phases of the proliferative period?
1. fertilization
2. implantation
3. embryonic disk formation
What is present in week 1 of development?
bilaminar disc from cells of zygote, ectoderm, endoderm (2 layers)
What does the endoderm form?
GI tract epi + glands
what does the ectoderm form?
nervous system, skin, glands
tooth enamel
What are the phases of week 2 development?
gastrulation
formation of mesoderm
trilaminar disc
becomes embryo after week 2
What does the mesoderm form?
muscles, CT derivatives (bone, cartilage, blood | dentin, pulp, cementum, PDL)
What happens during the embryonic period?
development of tissues, organ systems
What week does the heart start to beat?
4th week
When does the face and oral structures form?
weeks 4-7
When does the fetal period begin
week 8
When does the face begin to appear more human?
week 8-14
What is happening during week 3?
neurolation (CNS) --> formation of neural tube --> differentiation of neural crest cells --> migrate laterally and ventrally towards area of future face
What does the neural tube become?
brain and spinal cord
When do the cranial nerves begin development and growth into tissues?
weeks 4-5
What happens in fetal alcohol syndrome?
effects stage 1 (initial organization of germ layers)
first three ventricles of brain fail to separate
olfactory placodes too close together (deficient median nasal prominence)
vary from total absence of nose to mid face deficiency
What does the foregut - upper part become?
digestive tube from throat to duodenum
What does the midgut - middle part become?
small intestine, cecum, ascending colon, most of transverse colon
what does the hindgut become?
sigmoid colon, rectum
When do the mandibular processes fuse?
by end of 4th week
What is present during the 4th week in terms of facial development?
frontal prominence (forehead), maxillary processes, stomodeum (oral cavity), mandibular processes, nasal pits
What does the stomodeum become?
oral cavity
When do the maxillary processes fuse with the intermaxillary segment?
by 10th week
When does the oral pit first appear?
4th week
What is the oral pit?
pit between brain and heart
When does the oropharyngeal membrane rupture?
5th week --> due to apoptosis
What is the oropharyngeal membrane? (what does it form)
forms therooropharynx opening from oral cavity to tubular foregut .
ectodermal lining of oral mucosa
What is the mandibular arch doing during the 5th week?
growing laterally to oral pit --> develops into maxillary process (cheeks) and mandible
What happens during weeks 5-6?
facial processes migrate
development of nose and nostrils
eyes and external ears become more evident
when does the mandible begin ossification?
late 6th week.
What do NCC’s do?
contribute to oral-facial structures, teeth, and periodontium formation
What happens when NCC’s migrate to areas with high homeobox genes? low homeobox genes? (in terms of teeth)
high: supernumerary teeth
low: missing teeth
Where do NCC’s migrate to?
epithelial areas with specific homeobox genes in high concentration
What happens during the fetal period?
tissues enlarge, differentiate, function
What does the face look like during weeks 4-8?
add picture
What does the face look like during weeks 10-14?
add picture
What happens during weeks 10-14 in terms of the face?
it is getting narrower
When do most major malformations of the craniofacial complex originate? (when what is growing?)
during transformation of the brachial apparatus into its adult derivative (pharyngeal arches development)
Where are the pharyngeal arches located?
bars of tissue at the lateral aspect of the future neck
What does a pharyngeal arch contain?
bar of cartilage, artery, cranial nerve, and mesodermal tissue
What are pharyngeal grooves or clefts?
vertical grooves separating each arch eternally (develop in 5th week)
When do the pharyngeal grooves appear?
during 5th week
What are the pharyngeal pouches?
grooves that separate arches within pharynx, match external grooves
features of the 1st pharyngeal arch? (what is it called?, what does it form?, what is it covered by?)
mandibular arch
forms bony mandible, muscles of mastication, nerves and blood supply
covered by ectoderm externally and internally
features of the 2nd pharyngeal arch? (what is it called?, what does it form?, what is it covered by?)
"hyoid" arch
forms facial muscles and vessels, hyoid bone
covered by ectoderm externally and internal anterior area
Features of the 3rd, 4th, and 5th pharyngeal arches?
paired bilateral bars divided before they reach midline by the presence of bulging heart
form hyoid bone, thyroid, and cricoid cartilages
When do pharyngeal arches 2-5 develop?
between weeks 4-7
What cranial nerve innervates the 1st pharyngeal arch? (mandibular arch)
trigeminal (V)
What cranial nerve innervates the 2nd pharyngeal arch?
facial nerve (VII)
What cranial nerve innervates the 3rd pharyngeal arch?
glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
What cranial nerve innervates the 4th and 5th pharyngeal arch?
vagus nerve (X)
What kind of vessel do the pharyngeal arches initially contain? (for their blood supply)
right and left aortic arch vessel
which arch vessel becomes the common carotid artery?
3rd arch
(proximal part of the internal carotid)
which arch vessel becomes the dorsal aorta?
4th arch vessel
What are the 1st arch muscles? when do they appear?
MD arch (MMATT)
appear in 5th week
mastication: masseter, medial and lateral pterygoid, temporalis
mylohyoid
ant digastric
tensor veli palantini
tensor tympani
When do the 2nd arch muscles appear? what are the muscles?
by 10th week (ps, fs)
facial expression
stylohyoid
post digastric
stapedius
What are the 4th arch muscles?
pharyngeal constrictor muscles in neck enclosing pharynx
laryngeal
levator veli palantini (TENSOR veli palantini is arch 1)
What cartilage is located in the 1st arch?
meckel's cartilage
2nd arch cartilage? bones?
reichert's cartilage
stapes, styloid process, lesser horn of hyoid
3rd arch cartilage? bones?
NO cartilage
greater horn and lower part of hyoid
4th-6th arch cartilage? bones?
4: hyoid cartilage
5: no adult cartilage
6: laryngeal cartilage
What does the 1st pharyngeal groove become?
external auditory canal
What does the 1st pharyngeal groove + 1st pharyngeal pouch become?
tympanic membrane
What does the 1st pharyngeal pouch become?
middle ear and Eustachian tube
What does the 2nd pharyngeal pouch become?
palatine tonsils
What does the 3rd pharyngeal pouch become?
inferior parathyroid and thymus glands
What does the 4th pharyngeal pouch become?
superior parathyroid glands
What does the 5th pharyngeal pouch become?
ultimobranchial body → gives parafollicular cells to and fuses WITH the thyroid
What are pharyngeal grooves 2-5 covered by after the 5th week?
arches 2 and 5
(2 grows outwards, 5 grows UP)
What do accessory pouches form?
cysts
What three things lead to the tongue formation? what week?
5th week
lateral lingual swellings, tubercular impar, copula (fuse together)
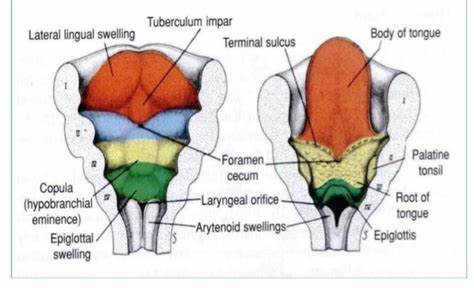
Where does the thyroid gland start and where does it end up during development?
starts at the foramen caecum and ends near the tracheal rings
What are thryoglossbal cysts or fistulas? (what are they made of)
leftover bits of thyroid gland during migration
What is endochondrial bone formation?
cartilage precursor → bone
What is intramembranous bone formation?
how is it different from endochondrial bone formation?
undifferentiated mesenchymal cells → bone
form from CT, NOT cartilage precursor.
When does the first evidence of cartilage conversion to bone occur?
week 8
When is peak cartilage development occurring?
3rd month Interutero
When does “in-growth of vascular elements” happen? what does this even mean?
4th month of pregnancy
vascular elements = blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries)
When is the first evidence of MD bone formation?
week 6
When do centers of ossification appear in calvarial and facial regions? how?
week 8 --> in areas where mild tension forces are present
calvarial = dome-shaped upper part of the skull (frontal, temporal, occipital, parietal)
Which bones are formed by intramembranous ossification?
upper cranial vault & facial bones
(CT mesenchymal stem cells, NOT cartilage)
Which bones are formed by endochondrial ossification?
cranial base & some temporal/occipital bone.
Where do the maxillary bones grow?
medially into the palate
Where does the mandible grow?
laterally to the 1st arch (MD) cartilage
How is the palate formed?
maxillary bones + medial nasal processes grow
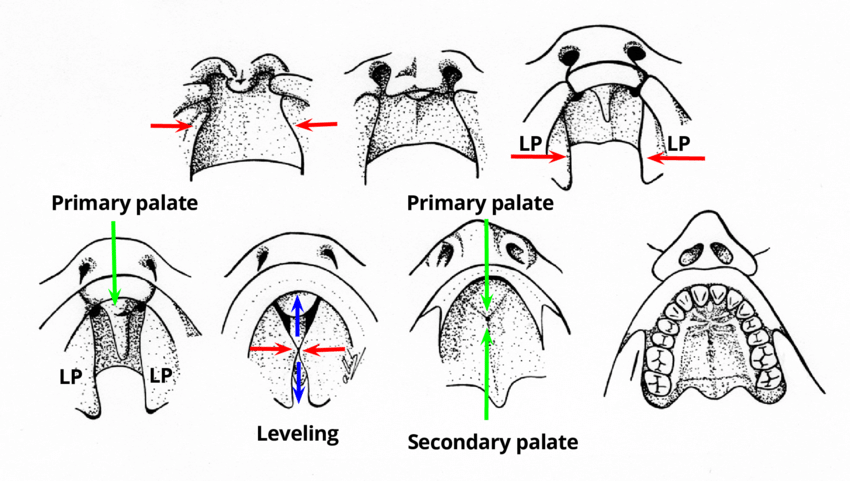
When does the palate start to fuse?
8th week