Body fluids Final
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
List reasons to analyze CSF
meningitis
hemorrhage
leukemia/lymphoma/tumor
multiple sclerosis
hydrocephalus/shunt
maybe when doing x-ray dye
Where is CSF created?
Choroid plexus in ventricles
What is the purpose of CSF?
-to cushion brain and spinal cord
-exchange nutirents/waste
What controls the amount of cells, protein, and glucose in the CSF?
Blood Brain Barrier
CSF normal WBC
0-5 WBC/uL
CSF normal RBC
0-10
CSF normal protein
15-45 mg/dL
CSF normal glucose
60-70% of plasma glucose
CSF Tube 1
-chemistry
-for protein, glucose
-If not analyzed within 2 hours: freeze
CSF Tube 2
-microbiology
-culture and gram stain
-if not analyzed in 2 hrs: Room temp
CSF Tube 3
-hematology
-diff and cell count
-if not analyzed in 2 hrs: fridge
CSF Tube 4
-extra tests
-serology/special tests
-if not analyzed in 2 hrs: fridge
Normal CSF appearance
Clear/colorless
Meningitis CSF appearance
cloudy
Bad tap
bloody w/ clear supernatant
Cerebral Hemorrhage
bloody and when centrifuged will be yellow (xanthochromia)
Ways to distinguish cerebral hemorrhage from bad tap
clot
In bad tap, blood will be diluted after each tube
xanthochromia: yellowish/pinkish (hemorrhage)
Basic formula for CSF cell count
[# of cells] X [dilution factor] / [Area] X [depth factor 0.1]
What is the diagnosis?
WBC: High
CSF Protein: incr
CSF Glucose: decr
CSF Lactate: incr
Bacterial Meningitis
What is the diagnosis?
WBC: incr
Diff: Lymphs/ variant
CSF Protein: norm- slight incr
CSF Glucose: norm
Viral meningitis
What is the diagnosis?
WBC: incr
Diff: erythrophages
CSF Protein: incr
CSF glucose: normal
Cerebral hemorrhage
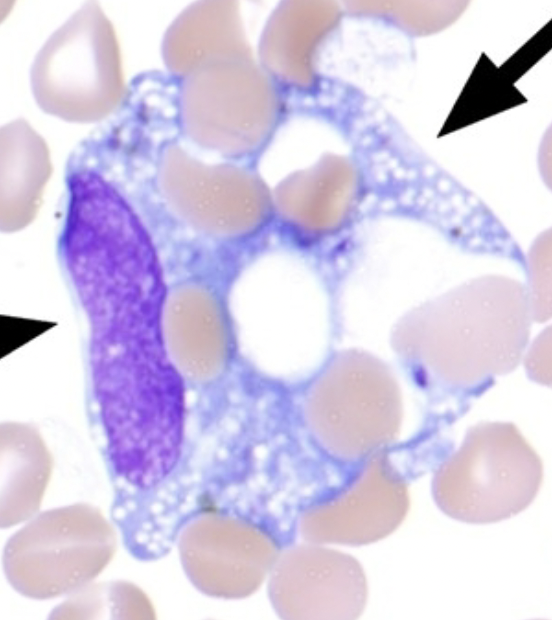
Erythrophage
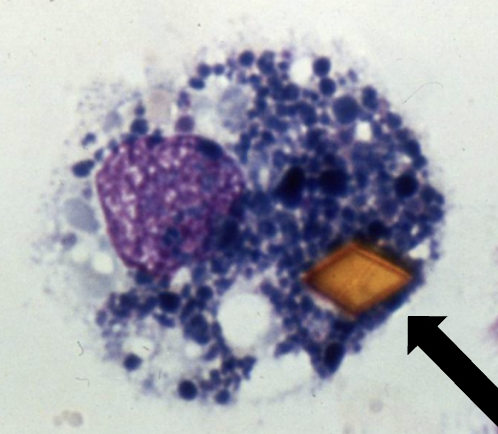
What is present in the cell and when does this usually happpen?
-Orange: Hematin crystal
-Black: Hemosiderin
-Happens during cerebral hemorrhage
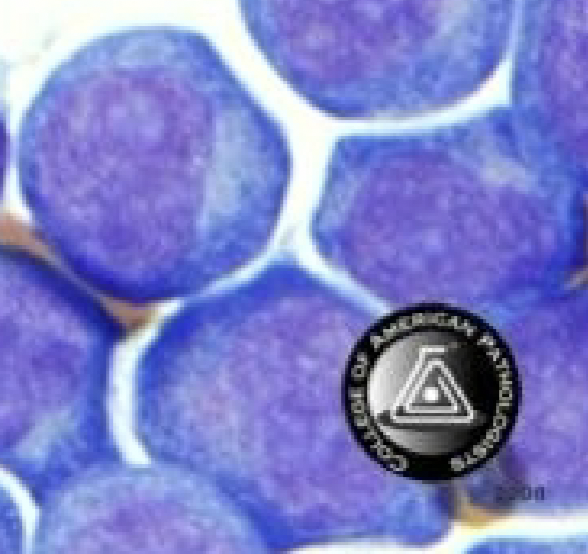
What are these cells and when would we see them?
-lympblasts
-seen in acute leukemia
If lymphoblasts are seen in the CSF, what should be done?
Chemotherapy directly to spinal to overcome BBB
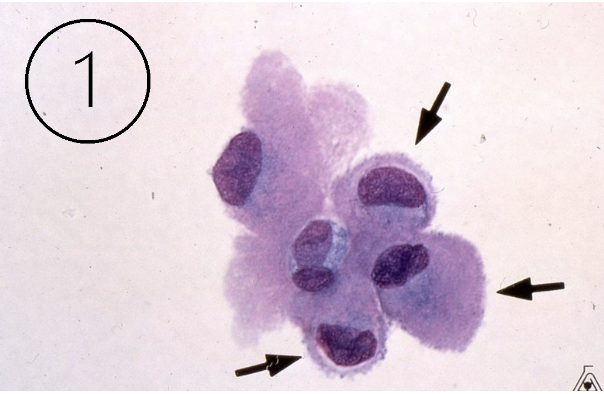
What do these cells indicate?
Lining cells
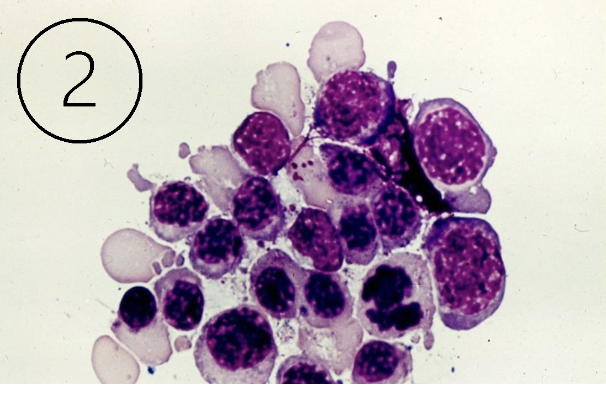
What do these cells indicate?
BM contamination
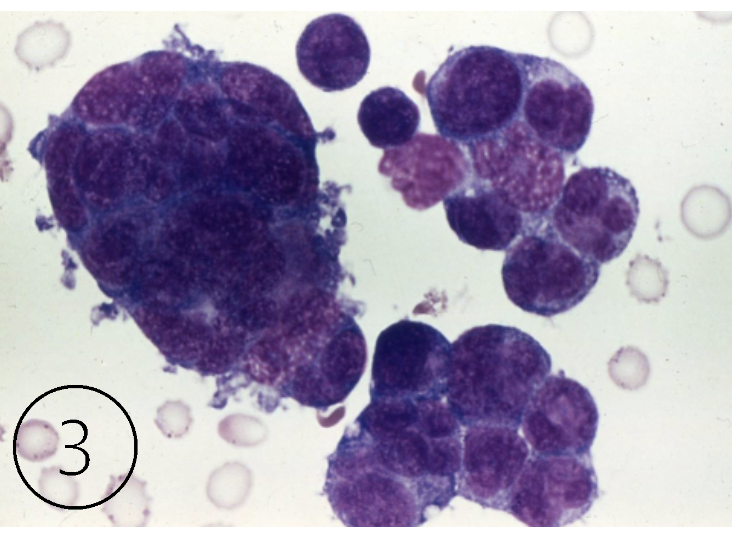
What do these cells indicate?
malignancy
How to asses damage to BBB
calculate ratio of CSF albumin to serum albumin
<9 normal
>9 damage
Diagnosis of MS
oligoclonal bands
prescsnec of myelin basic protein
calculation of IgG index: ratio high
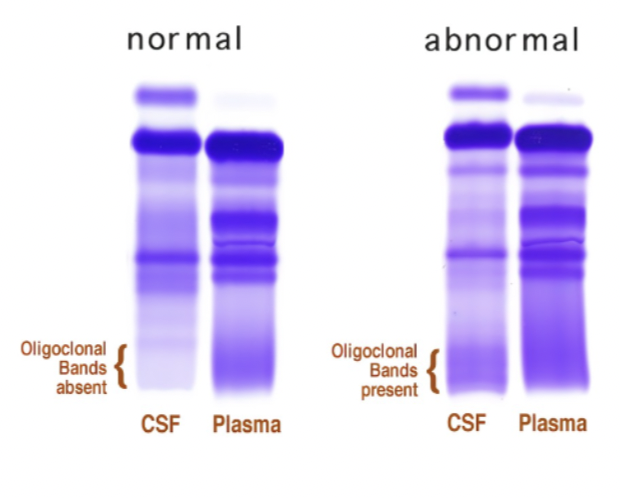
Calculate IgG index
[ CSF IgG/serum IgG]
[CSF albumin/serum albumin]
What are TAU proteins?
tubulin associated unit that help stabilize internal structures of neurons
What happens with TAU proteins in Alzheimers and Parkinsons disease?
TAU proteins become hyperphosphorylated and tangle up
-this blocks neural communication= dysfunction
Where else are high amounts of TAU proteins seen?
chronic traumatic encephalopathy
Effusion
Buildup of fluid between two serous membranes
Transudate
Buildup of fluid due to pooling between membranes
Exudate
Buildup of fluid due to disruption of membranes
Transudate vs Exudate cell counts
Transudate
pleural: <1000
Peritoneal + ascites: <500
Exudate
pleura: >1000
peritoneal: >500
Transudate vs Exudate ratio
Transudate
Fluid serum protein ratio: <0.5
Fluid serum LD ratio: <0.6
Exudate
Fluid serum protein ratio: >0.5
Fluid serum LD ratio: >0.6
Paracentesis
Procedure to remove fluid from the abdominal cavity
Thoracentesis
Procedure to remove fluid surrounding the heart and lungs
Arthrocentesis
remove joint fluid
Pericardiocentesis
withdraw fluid around the heart
Chylous
milky fluid due to increased triglyceride and chylomicrons
Pseudo-chylous
milky fluid due to incr cholesterol
Transudates caused by:
congestive heart failure
liver disease
kidney disease
Exudate caused by:
anything else: malignancy, infection, peritonitis, trauma, etc
Appearance of transudate vs exudate
-transudate is clear and yellow
-exudate is cloudy and bloody
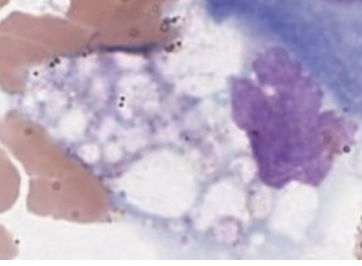
Macrophage
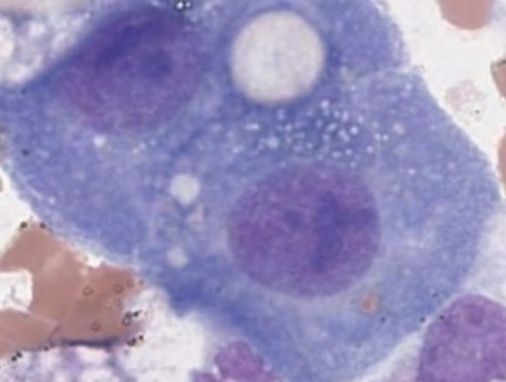
Mesothelial
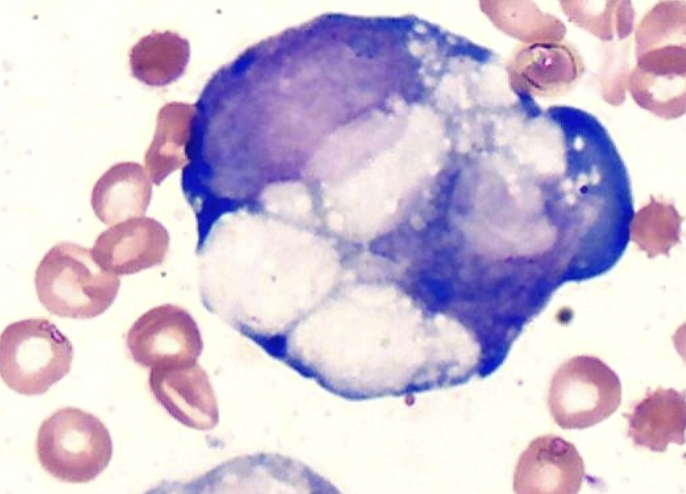
Malignant
What is synovial fluid?
clear liquid that lubricates joints
Why is snyovial fluid viscous?
Hylauronic acid
How is synovial fluid made less viscous?
pre-treatment with hylaurodinase
Mixing synovial fluid with acetic acid causes?
makes it become gel and difficult to work with
List the categories of joint disorders
hemorrhagic:RBCs
Septic: bacteria
Crystal induced: uric and calcium pyrophosphate
Autoimmune: high WBC’s
Degenerative: Low WBC
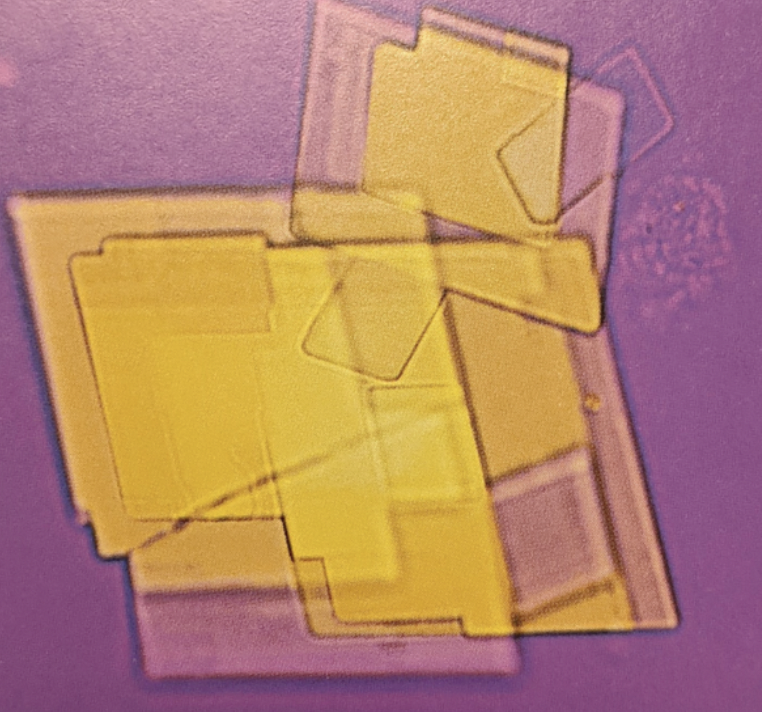
Cholesterol crystals
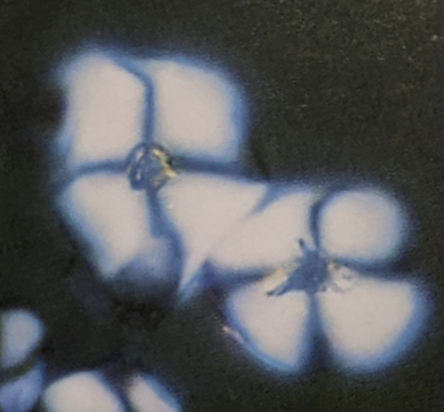
starch from gloves
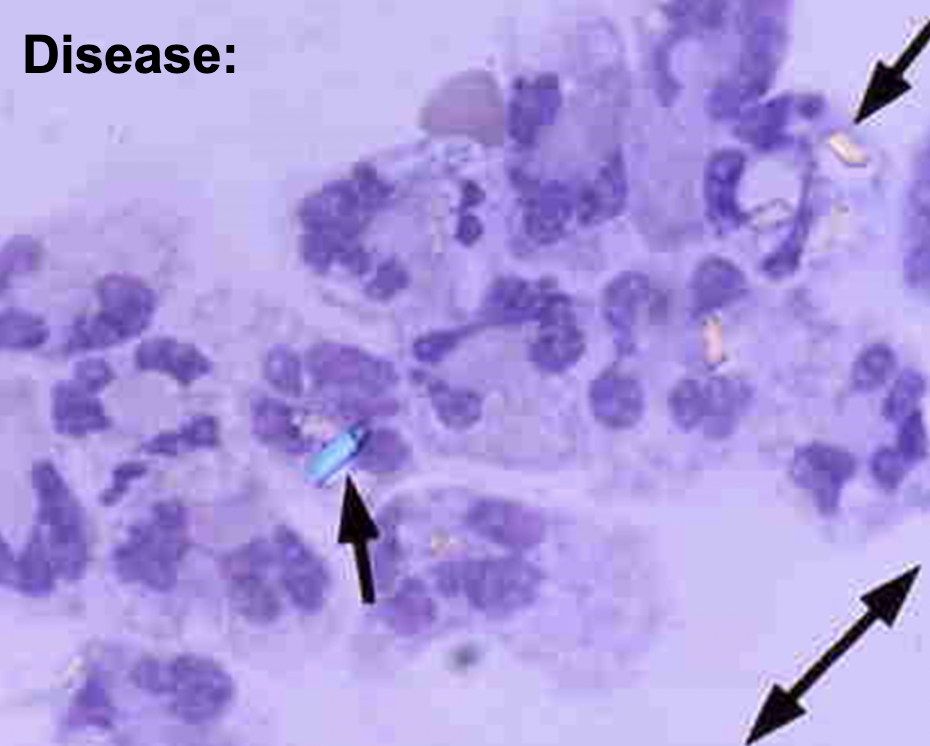
What disease and how can you tell?
Pseudo-gout
calcium pyrophosphate crystals-blue when parallel to axis
(+) birefringence
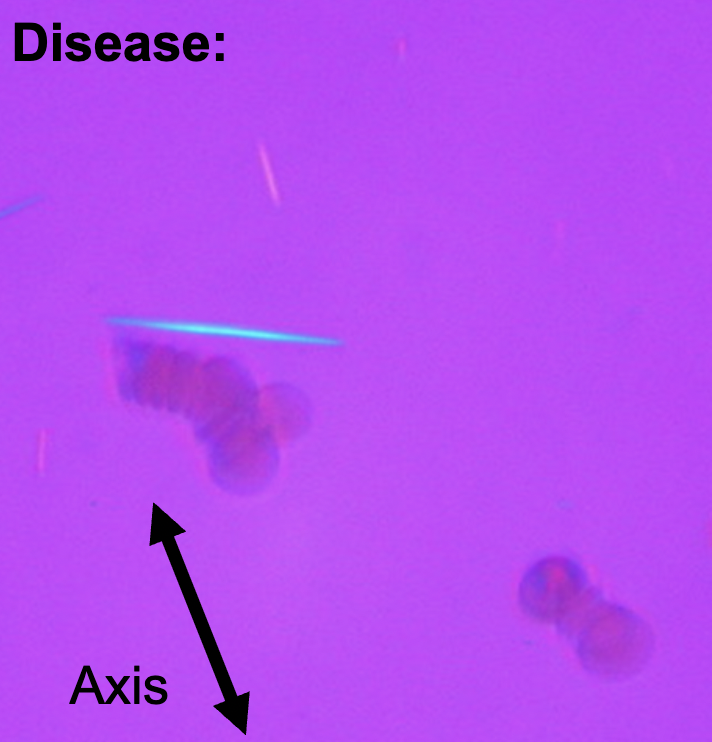
What disease and how can you tell?
Gout
uric acid crystals-yellow when parallel to axis
(-) birefringence
Semen must be analyzed within___hr
1 hr
Why can’t condoms be used for semen anaysis?
Some contain spermicides
Why must all sperm be collected?
If the first part is lost, it will mess up the count since it is highest
What temp is semen kept at?
RT or 37C
What other tests may be done on sperm sample?
-fructose to asses seminal vesicles
-sperm viability (redheads are dead)
Semen: Measure____,___, if liquefaction happens in 30-60 min.
Measure ___
volume, viscosity, pH
Semen: At 40x look for___, ____, and ____
agglutination, round cells (immature sperm), motility
Immobilize sperm in ___to count
formalin/phosphate buffer
What area should be counted for sperm?
5 RBC squares
How to calculate sperm concentration?
hemocytometer results x 1000uL/mL (needs to be in mL )
Absolute sperm count
number X volume (mL)
Post Vas sperm count
-2 months post procedure for 2 months of no sperm present
Why must centrifugation be done for post vas sperm
to concentrate and double check that there is no sperm
Amniocentesis
obtain amniotic fluid
Normal appearance and handling and storage of amniotic fluid
-colorless/hazy
-protect from light (bilirubin)
What condition is amniotic fluid tested for?
open neural tube defects
hemolytic diseases
fetal lung maturity
Spina Bifida: elevated levels of ____can be found in amniotic fluid and maternal serum
alpha fetoprotein (AFP)
How to monitor hemolytic diseases of fetus
OD 450 for bilirubin —> Liley graph(24 weeks) OR Queenan graph (17 week)
Prediction of fetal lung maturity:
L/S ratio____(lectin to sphingomyelin ;secreted by alveoli cells)
Presence of _____in amniotic fluid
____count >50
L/S ratio_>2.5_(lectin to sphingomyelin)
Presence of __phosphatidyl_in amniotic fluid
Lamellar_count >50
Fetal fibronectin (“glue-leak” )presence can signal _____ could happen
preterm labor
APT test- hemolysis mixed with NaOH, adult hgb ______/fetal hgb _____
adult: denatures and turns green
fetal: remains pink
ROM test
cartridge test to determine if vaginal fluid is amniotic or not
Fern test
bedside test to determine if vaginal fluid is amniotic or not

Materenal serum quad test
Neural defects: high AFP
Down’s: Low estriol + trisomy 18
Down’s and Edwards: High DIA
Down’s and multiple babies: HCG
Sweat chloride is used to diagnose
Cystic fibrosis
High levels of chlroide in sweat test obtained by_____
pilocarpine iontorphoresis
Pancreatic insufficiency
fecal fat measurement where pt is unable to break down fats due to pancreatic enzyme deficiency
What do eosinophils in urine indicate
drug induced instersitial nephritis
Steatorrhea
high levels of fat in stool
-normal 21g in 72 hrs
How will synovial fluid with crystals appear?
Very cloudy