Topic 3.1: Genes
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
1
New cards
define genes
a gene is a portion/sequence of DNA that influences a specific characteristic of an organism
* genes can be inherited
* there exists 1000s of genes in one chromosome
* genes can be inherited
* there exists 1000s of genes in one chromosome
2
New cards
where are genes located?
in their respective loci (singular: locus)
* locus = specific place in gene
* locus = specific place in gene
3
New cards
define alleles
alleles:
* alternative forms of a gene
* codes for different variations of a specific trait
* e.g: gene for eye colour, allele for brown eyes
\
alleles occupy the same locus, only one allele can occupy a locus
* alternative forms of a gene
* codes for different variations of a specific trait
* e.g: gene for eye colour, allele for brown eyes
\
alleles occupy the same locus, only one allele can occupy a locus
4
New cards
how do alleles differ from one another
they differ by one to couple different bases:
* if they differ by one base, it is called single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)
* sickle cell anemia is caused by SNP (CTC → CAC)
* if it differs by more than one base, it is called an allelic difference
* if they differ by one base, it is called single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)
* sickle cell anemia is caused by SNP (CTC → CAC)
* if it differs by more than one base, it is called an allelic difference
5
New cards
how are alleles formed?
by mutation - random changes:
* mutation can be neutral, beneficial, or detrimental
* beneficial = new variations of a trait
* detrimental = changes the normal **function** of a trait (for the worse)
* neutral = have no effect on the function
* mutation can be neutral, beneficial, or detrimental
* beneficial = new variations of a trait
* detrimental = changes the normal **function** of a trait (for the worse)
* neutral = have no effect on the function
6
New cards
define genome
the entirety of the genetic information in an organism or organelle
* humans genome consists of 46 chromosomes + mitochondrial DNA
* in plants genome is DNA in nucleolus, mitochondria, and chloroplast
* humans genome consists of 46 chromosomes + mitochondrial DNA
* in plants genome is DNA in nucleolus, mitochondria, and chloroplast
7
New cards
What is the Human Genome Project
The human genome project is a project where the entire base sequence of humans was sequenced
8
New cards
How has the Human Genome Project contributed to knowledge?
1. Mapping
1. number, location, size and sequence of human genes has now been established
2. Screening
1. gene probes detect sufferers and carriers of genetic defects
3. Medicine
1. discovery of new proteins have lead to improved treatments
2. new and effective drugs
4. Ancestry
1. comparisons with other genomes has provided insight on the evolution, migration patterns, and origins of man
9
New cards
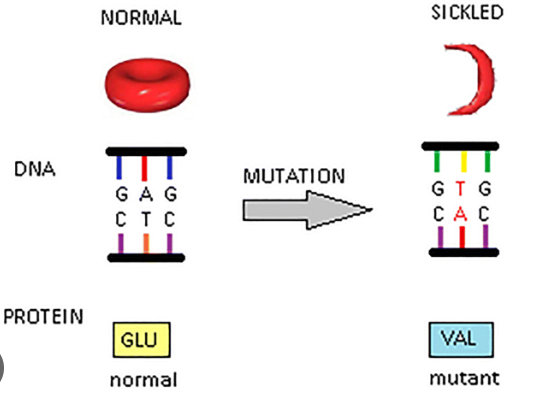
Describe how Sickle Cell Anemia is caused
1. a mutation in a single base occurs, GAG → GTG
1. this is called an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism)
2. this causes a change in mRNA sequence when the DNA is copied during transcription
3. when the normal mRNA is translated, it produces %%glutamic acid%%
4. but when the mutated mRNA is translated, it produces ==valine== instead
5. valine has a different shape and charge (compared to glutamic acid), so it causes the entire polypeptide chain’s shape and structure to change
6. therefor the shape of hemoglobin changes
7. and then the shape of the whole red blood cell changes to a half-moon shape (sickle shape)
10
New cards
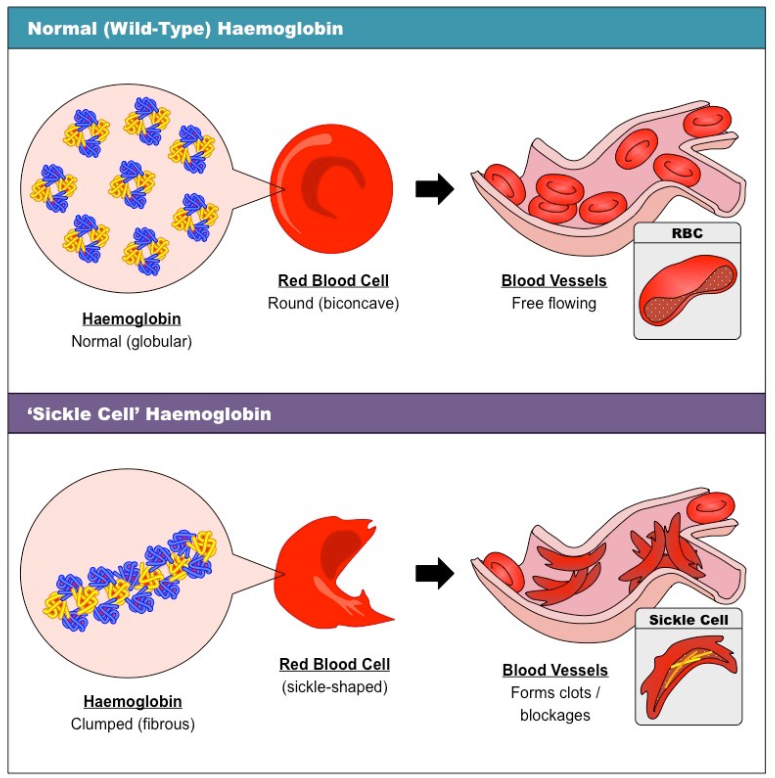
what happens when one has sickle cell anemia, problems associated with the disease?
due to the blood cells sickle shape:
* it is much smaller
* cannot carry as much oxygen
* causes clots in blood vessels
* due to abnormal shape
* + inflexibility caused by crystallization of abnormal hemoglobin
* it is much smaller
* cannot carry as much oxygen
* causes clots in blood vessels
* due to abnormal shape
* + inflexibility caused by crystallization of abnormal hemoglobin
11
New cards
state the number of genes in the human genome
approx. 21 000 genes
12
New cards
describe the relationship between number of genes in a species and complexity in structure, behavior and physiology
the more complex an organism is, the more number of genes/larger genome it will have