Pharm - CH4: Cholinergic Agonists
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Cholinergic Drugs
Act on receptors that are activated by ACH
nicotinic
muscarinic
Adrenergic Drugs
act on receptors that are activated by NE
alpha
beta
Cholinergic Agonists
Drugs that: (at cholinergic receptors = muscarinic and nicotinic)
mimic ACH
have affinity
intrinsic activity
Cholinergic Receptors
located in all areas of PNS
except the sympathetic effector organ
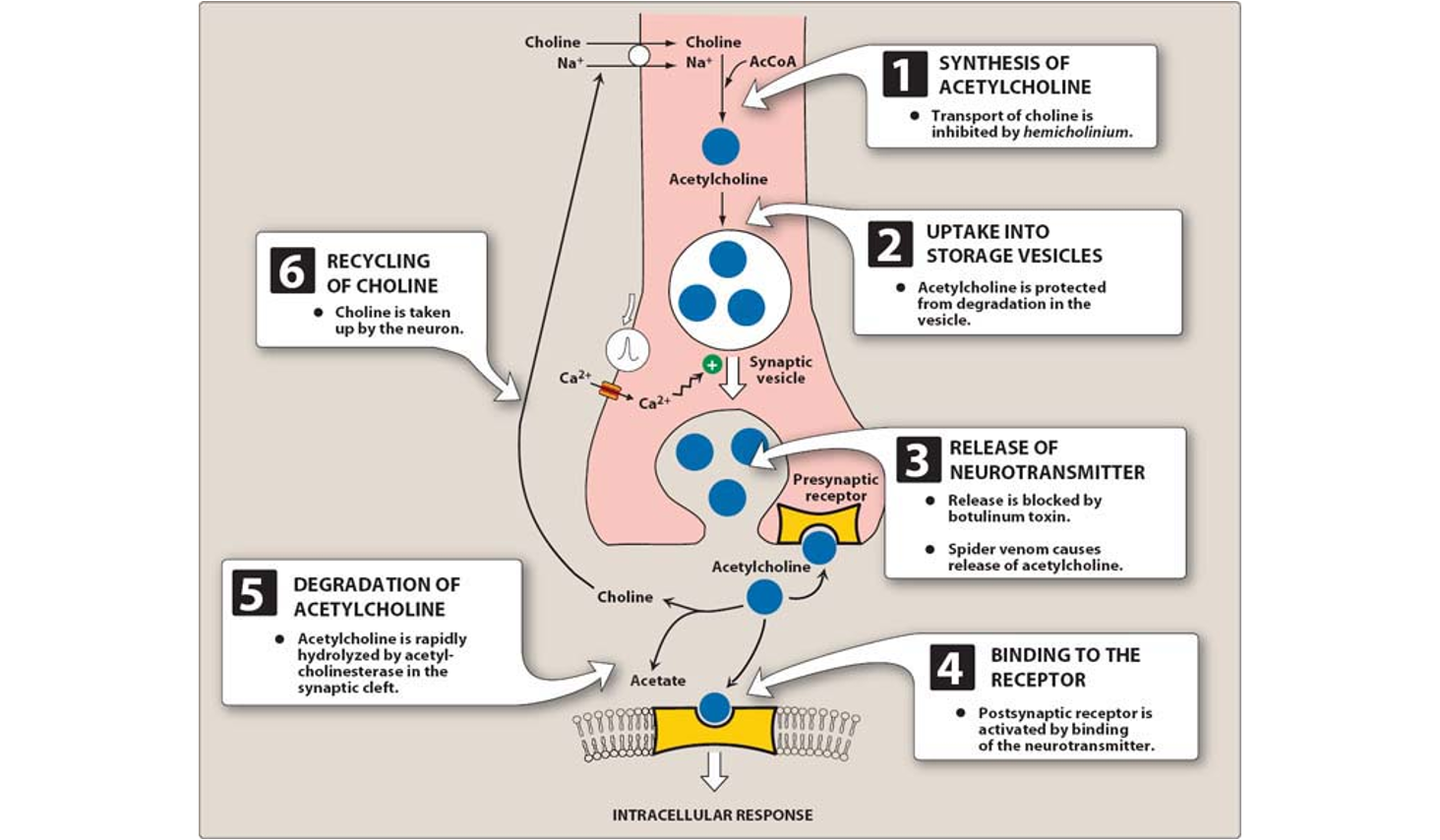
Neurotransmission of ACH
synthesis of acteylcholine in the cytoplasm from choline (cholinergic neuron)
choline ~ VitB; can be made in liver or found in some foods
used for many bodily rxns; important for NS; development of brain function
choline converted into acetylcholine
helps muscles contracts, activates pain responses, plays a role in brain functions of memory + thinking
storage of acetylcholine in storage vesicles w/n cholinergic neuron
AP propagated by voltage sensitive Na+ channels arrives at nerve ending
voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels on presynaptic membrane open
increase intracellular Ca2+ lvls
promotes docking/fusing of storage vesicle
release ACH into synaptic space
ACH released from synaptic vesicles into synaptic spaces diffuse across the synaptic space
ACH binds to cholinergic receptors (nicotinic/muscarinic)
ACH signal at post-junctional effector site rapidly terminated by acetylcholinesterase (ACHE) in synaptic space
which cleaves ACH into choline + acetate
Choline is recaptured from the cytoplasm by Na+ coupled high affinity uptake system bk into the neuronal cytoplasm where it is acteyltated ag
produces ACH
Cholinergic Receptor Types
muscarinic
nicotinic
Muscarinic
Receptors are more sensitive and have a higher affinity to muscarine than both ACH and nicotine
Muscarine is a naturally occurring plant alkaloids that bind + activates muscarinic subtypes of ACH receptors
g-protein coupled receptors, bind to ACH, and recognize muscarine
located at PSN effector organ
can be either excitatory or inhibitory
Nicotinic
Receptors are more sensitive + have a higher affinity to nicotine
nicotine is a toxic colorless/yellowish oily liquid that is the chief active constituent of tobacco.
acts as a stimulant on ACHRs in small doses but in larger amts blocks the action of ACH on ACHRs in both autonomic nerve cells and skeletal muscle cells
ligand gated ion channel, binds to ACH and recognizes nicotine
located at a;; ganglia and NM junction
always excitatory
Direct Acting Cholinergic Agonist
act on cholinergic receptors, mimic ACH
“straightforward”
Indirect Acting Cholinergic Agonists
inhibits the effects of ACHE, thus maintains ACH levels in the synaptic space longer
acts on the enzyme ACHE (inhibits the degradation of ACH + increases natural levels of ACH in synaptic cleft)
Indirect and Direct Cholinergic Agonists
Have the same final effect
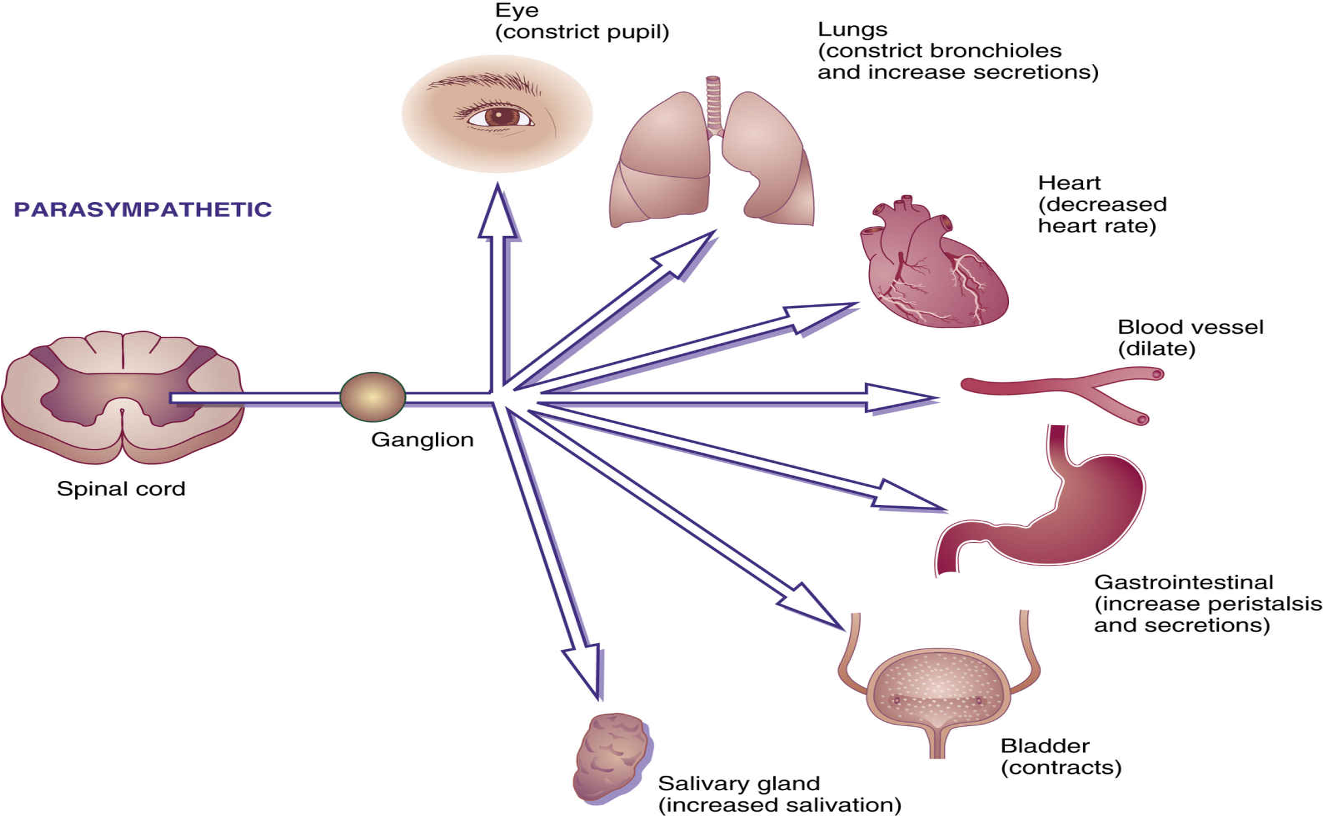
Effects of Cholinergic Agonists
rest and digest (parasympathetic)
eye - pupil constriction
heart - decrease HR and FOC
bronchiole smooth muscle - bronchoconstriction
GI - increase peristalsis + GI secretions (mucus, HCL, pepsin, pepinogen)
Bladder - increase in contraction of the detrusor muscle, bladder empties
Blood vessels - there is no parasympathetic influence on vascular smooth muscle, but receptors on the endothelium respond and release nitric oxide second messenger, which goes on to vasodilate vascular smooth muscle (more later)
Secretions - all increase, saliva, mucus
Acronym for Parasympathetic Stimulation
SLUDGE BAM
Salivation, Lacrimation, Urination, Defecation, GI Upset, Emesis
Bradycardia
Abdominal Cramps
Miosis
-chol
Cholinergic Agent
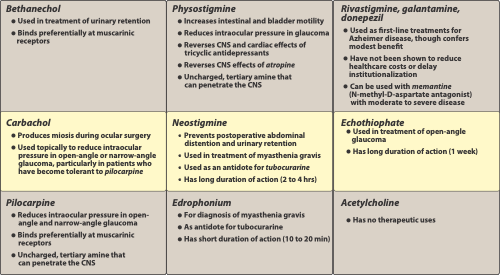
Direct Cholinergic Agonist Drugs
acts directly on the receptor
acetylcholine
bethanechol tab (urecholine)
Carbachol (Isopto-Carbachol)
Pilocarpine (Isoptocarpine)
Acetylcholine (as a drug)
by itself — not specific enough — lacks therapeutic importance
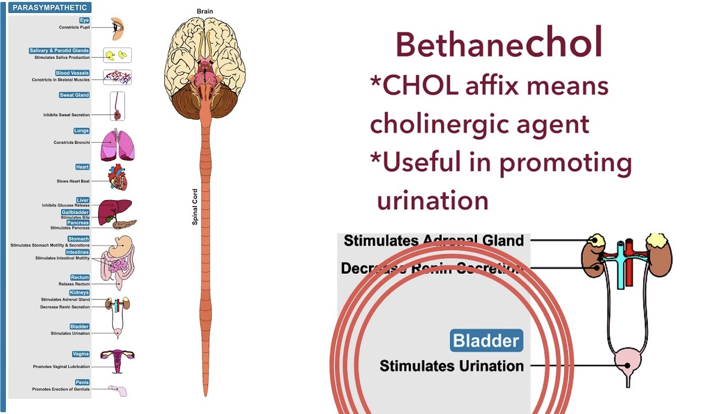
Bethanechol Tab (Urecholine)
not affected (hydrolyzed) by ACHE
effect is at muscarinic receptor, used post-op to stimulate atonic (lacking muscular tone) bladder
given orally to treat urinary retention
results from gen. anesthesiac, diabetic neuropathy of bladder, side effect of antidepressants, treat GI atony (lack of muscular tone)
the muscarinic receptors on the bladder and GI tract stimulate contraction of the bladder (detrusor muscle) + expulsion of urine, _ increased GI motilit
SLUDD
Sum: increase urine output
Carbachol (Isopto-Carbachol) Drops
has both nicotinic +muscarinic actions
pupil constriction
used as an eyedrop to constrict the eye (para. pupil ciliary muscle constriction part of rest + digest) to increase drainage of aqueous humor + decrease pressure on the retinal nerve for glaucoma
Sum: used to treat glaucoma
Aqueous Humor
clear fluid filling the space in front of the eyeball b/n the lens + cornea
bathes and nourishes the lens and maintains pressure in the eye
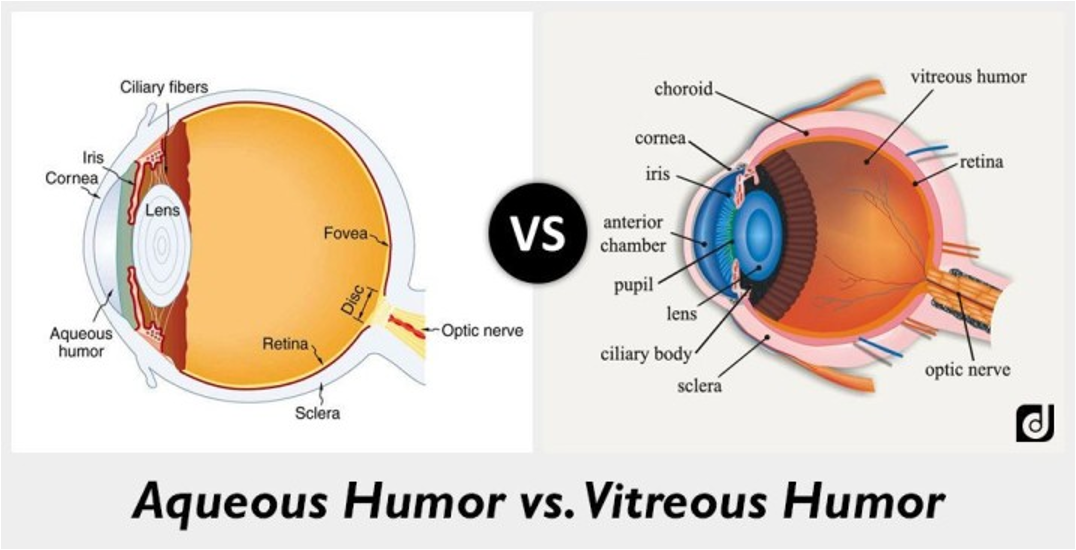
Vitreous Humor
transparent gelatinous tissue filling the eyeball behind the lens
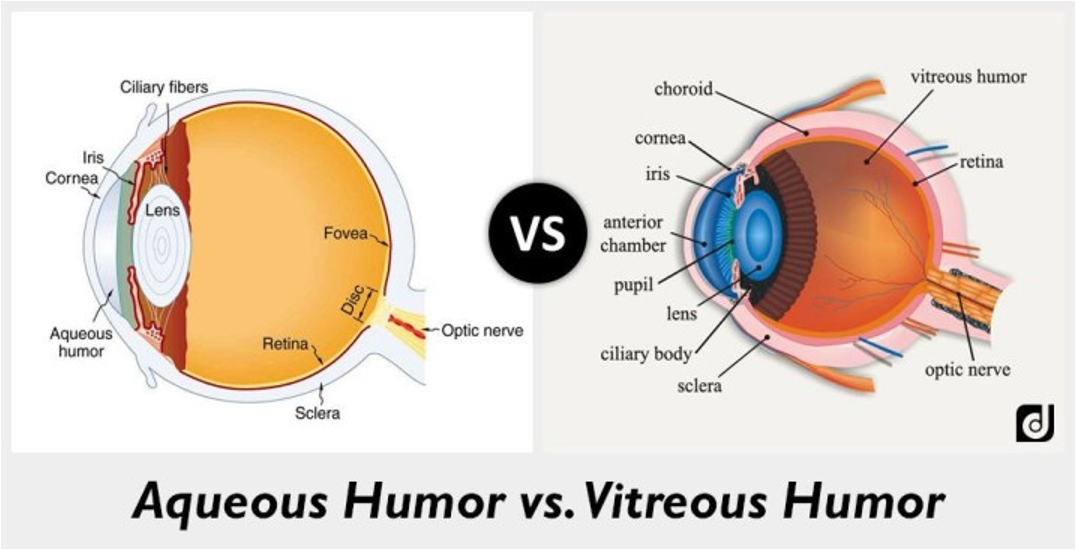
Glaucoma
abormality in the eye’s drainage system
excess aqueous flu. can buildup —> excess pressure that damages the optic nerve
damage in the optic nerve + retina
can cause vision loss
Risk Factors: increasing age, high pressure in eye, a family history of glaucoma, use of steroid medication
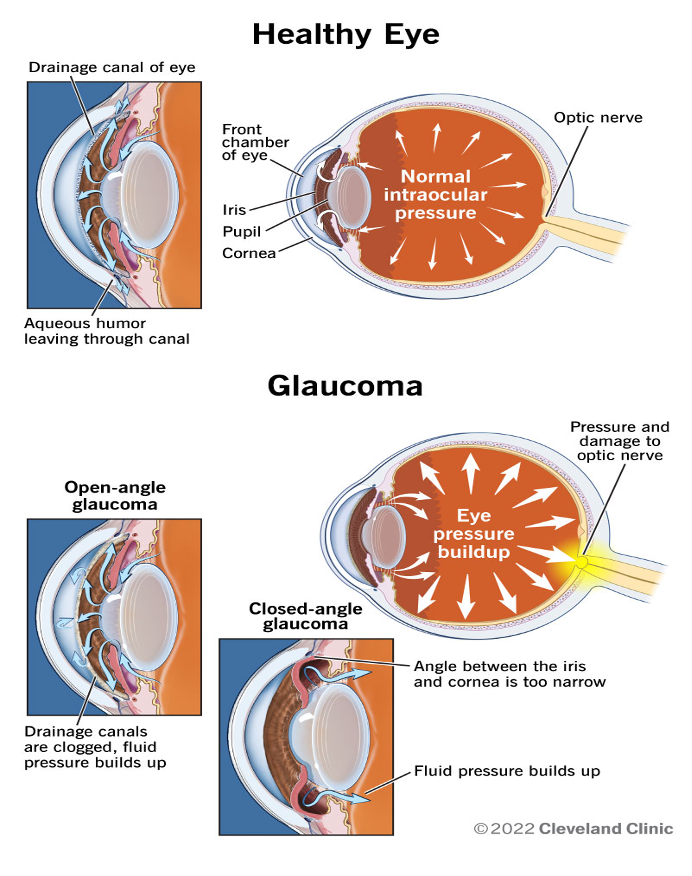
Pilocarpine (Isoptocarpine)
muscarinic activity only
acts on subtype of muscarinic receptor (M3) found at the iris sphincter muscle, causing the muscle to contract — resulting in pupil constricting (miosis)
action facilitates the rate aqueous humor leave the eye to decrease intraocular eye pressure (IOP)
stable to ACHE
DOC for emergent decrease in IOP for glaucoma
cholinergic agents increase conventional outflow by constricting longitudinal portion of ciliary muscle
cause immediate stop in IOP = increase drainage of aqueous humor (onset ~ few minutes, duration ~ 4-8 hours)
drug of choice for narrow angle/wide angle glaucoma
Reversible Indirect Acting Cholinergic Agonists
drugs bind to and block the actions of ACHE
prolongs the effect of ACH in the synaptic space to affect the receptors that remain intact
reversible; reversibly binds to ACHE + blocks its actions on ACH, providing more ACH in the synaptic cleft
Physotigmine
Nestigmine
Pyridostigmine (Mestinon)
Rivastigmine ( Exelon)
Donepezil ( Aricept )
Physostigmine
indirect acting cholinergic agent
wide range activity at muscrinic, nicotinic, and neuromuscular junction
increases intestinal + bladder motility
used to treat glaucoma + delayed gastric emptying
enhances transmission of ACH signals in brain and can cross BBB
physostigmine salicylate is used to treat anticholinergic poisoning
Neostigmine
greater effect/selectivity at the NMJ than physidtigmine
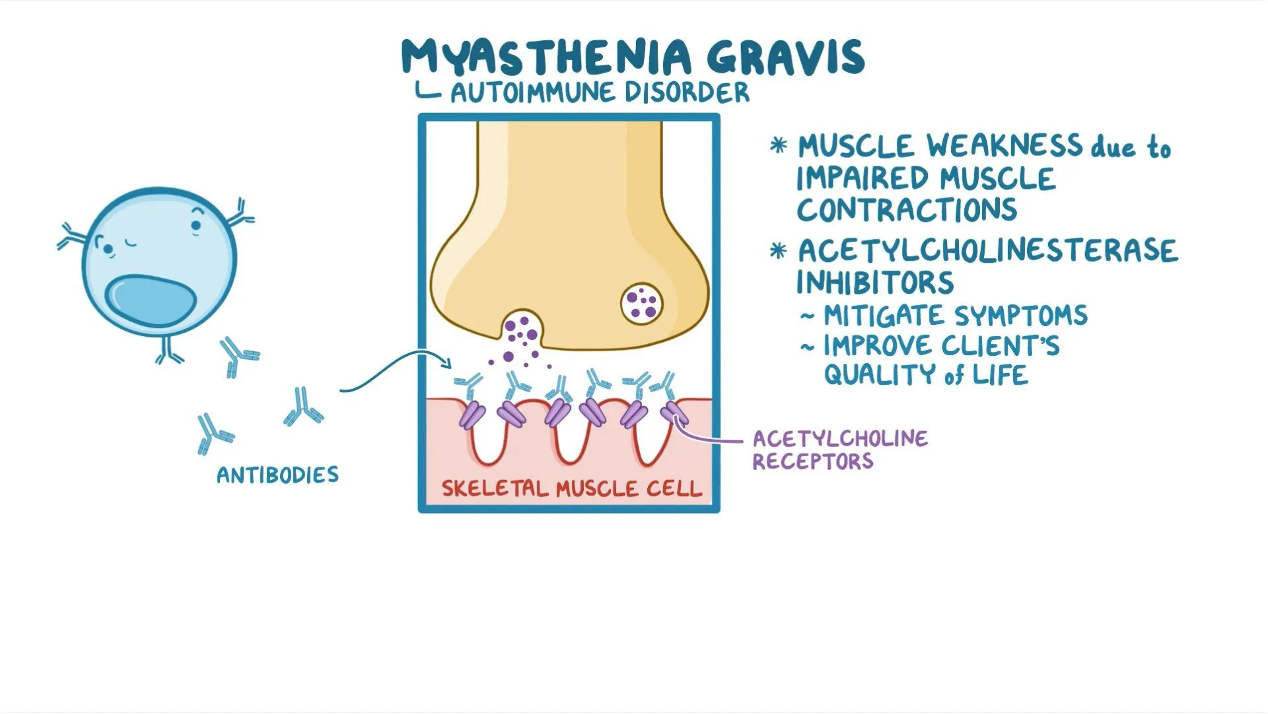
used in treating muscle weakness associated w/ myasthenia gavis
antibodies block, alter, destroy, ACH receptors at N/M juction
Pyridostigmine ( Mestinon)
has greater effect at NMJ
used for myasthenia gravis at NMJ
preferred for treatment of myasthenia gravis b/c has longer duration of action + less likely to cause unwanted effects
Myasthenia Gravis
chronic autoimmune disorder —> antibodies target + destroy ACH at NMJ (somatic NS)
decrease comm. b/n nerves + muscle, resulting in diverse weakness of skeletal muscles
less ACH receptors
affects voluntary muscles of the body, esp. control of eyes, mouth, throat, limbs
Symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis
weakness of eye muscles
difficulty swallowing
drooping of one or both eyes (ptosis)
change in facial expressino
Irreversible Indirect Cholinergic Agonists
permanently inactivates ACHE
restoration of ACHE requires the synthesis of new enzyme
Echothiophate (Phospholine Iodide)
Echothiophate (Phospholine Iodide)
Organophosphate
used as an eyedrop to decrease IOP in the treatment of chronic glaucoma
Indirect Cholinergic Agonists also used Centrally for Alzheimer's Dx
bind to central ACHE
pts w/ alzheimer’s dx have deficiency of cholinergic (ACH producing) neurons in CNS
despite the ability to delay the progression of alzheimer’s disease, none can stop progression
Rivastigmine (Exelon)
Donepezil (Aricept)
Summary Drugs
Pyridostigmine ( Mestinon)