BIO 290 (JMU Walker) Lab 3
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What does the thoracic cavity contain?
two pleural cavities and a mediastinum surrounded by thoracic body wall muscles and the rib cage
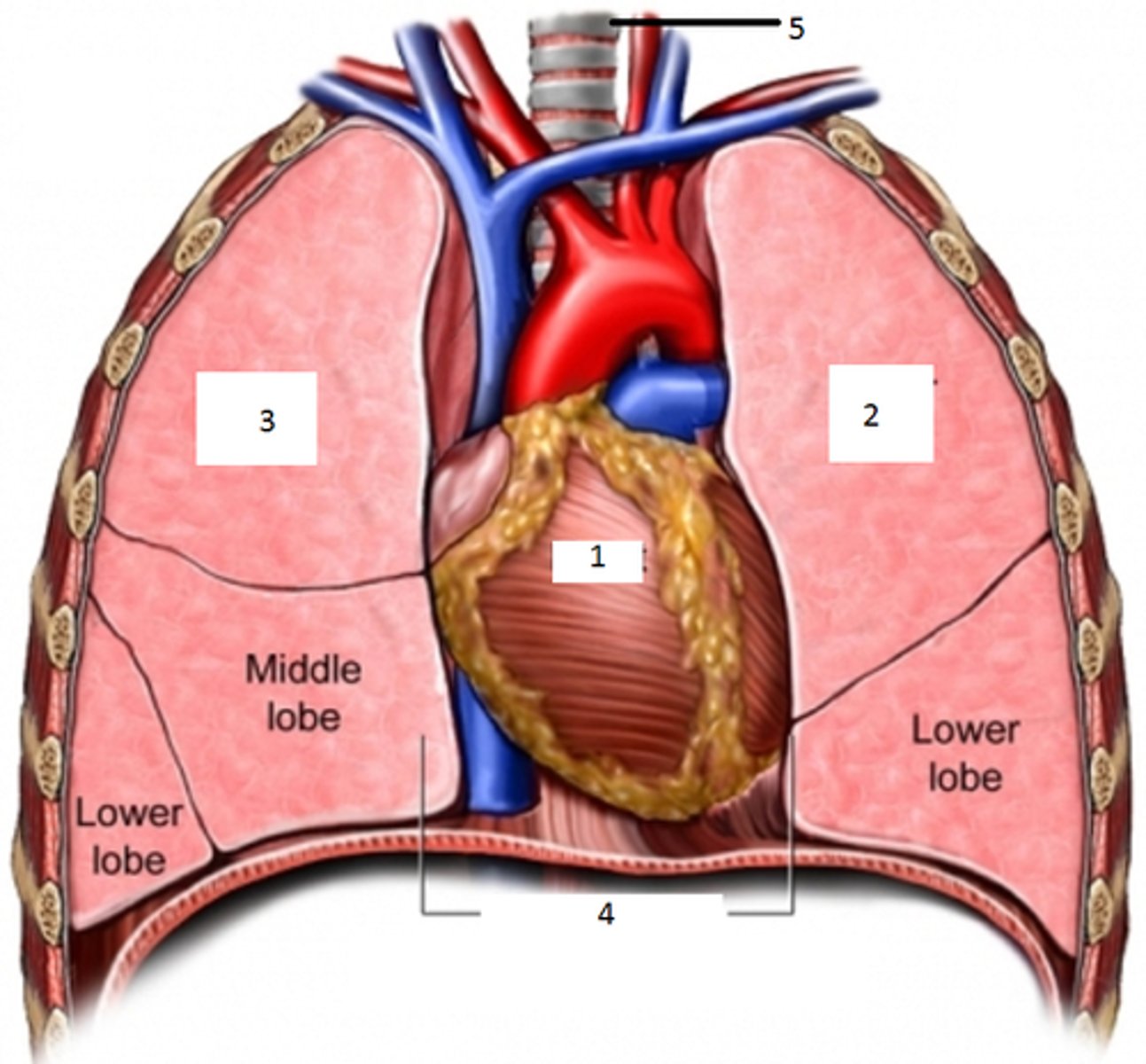
What does each pleural cavity contain?
a lung
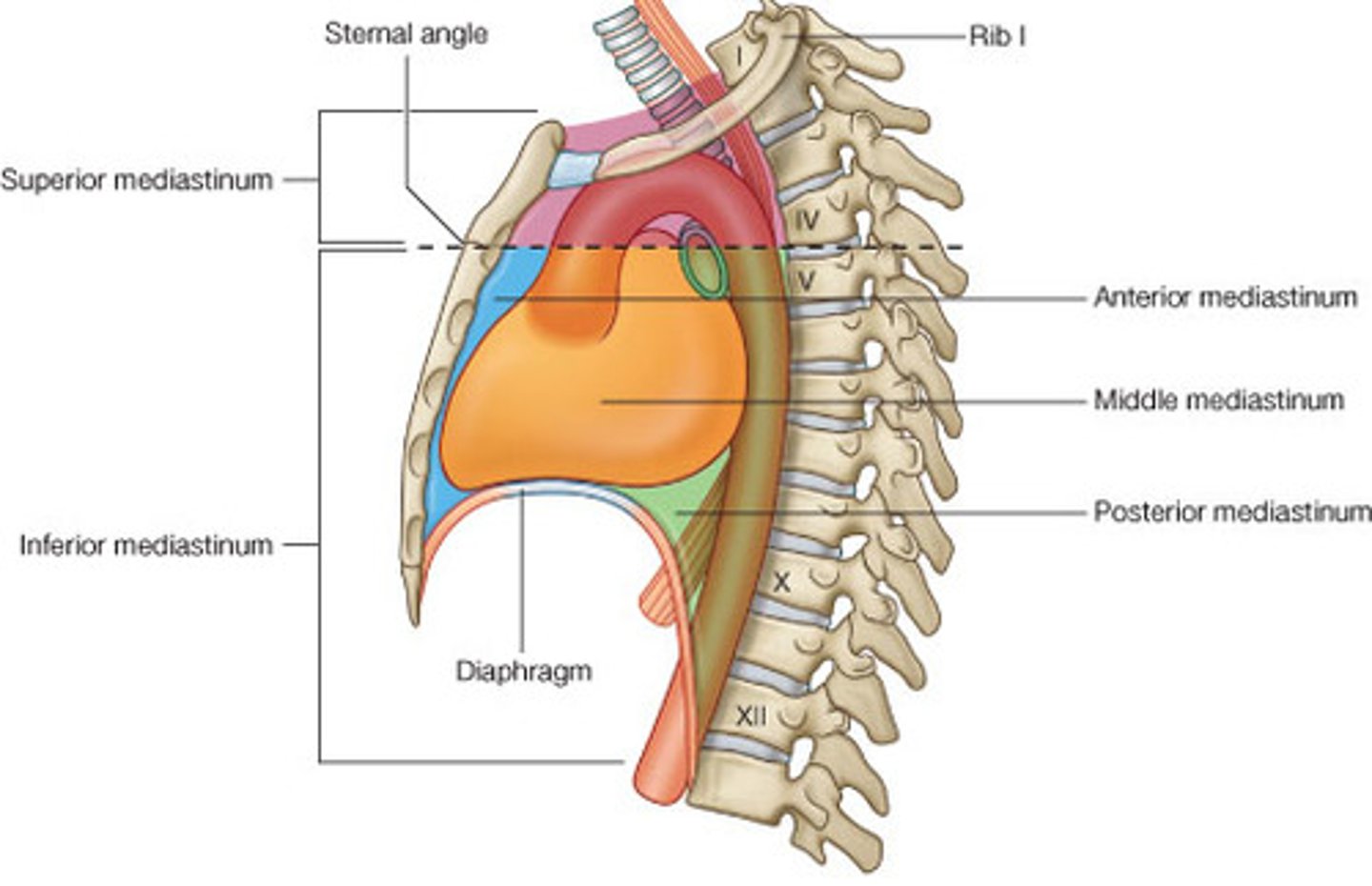
What is the mediastinum?
the subregion of the thorax located between the pleural cavities and contains the esophagus, trachea, and primary bronchi, pericardial cavity, the heart and its great vessels, phrenic and vagus nerves, and the descending thoracic aorta
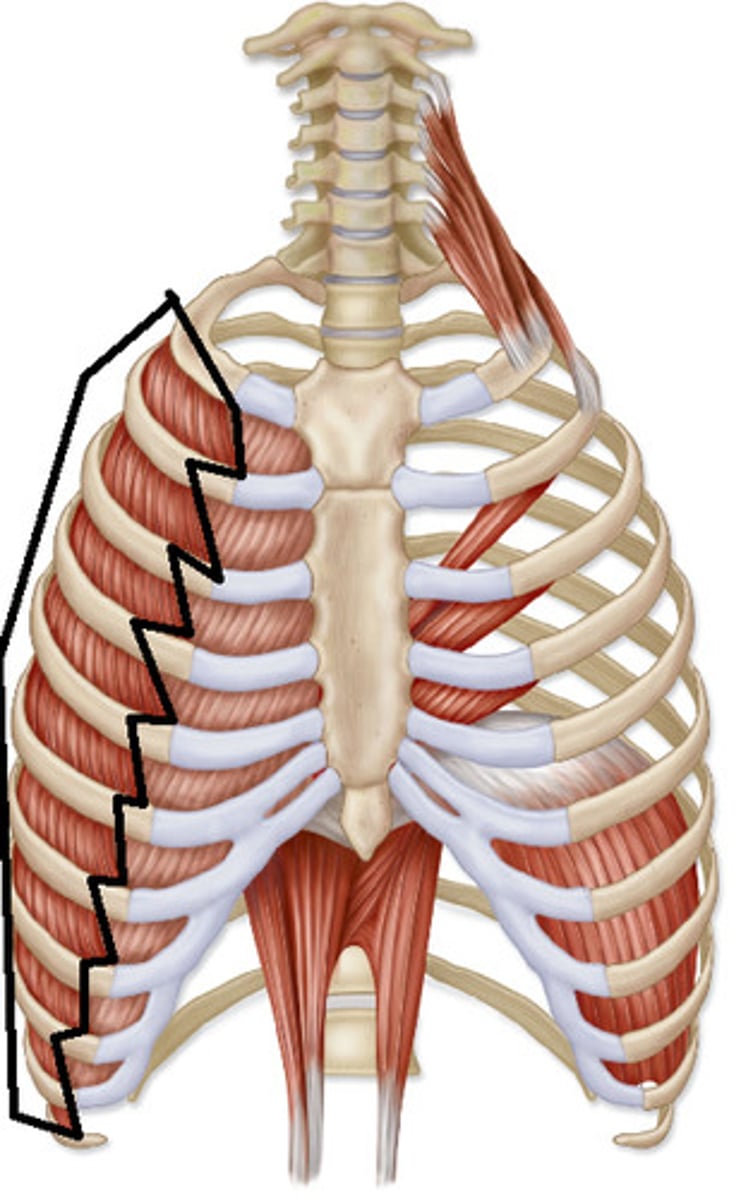
What are the muscles of the thoracic body wall?
external intercostal mm, internal intercostal mm, innermost intercostal mm, and transverses thoracis mm
Are the muscles of the thoracic body wall epaxial or hypaxial?
hypaxial
Where do the muscles of the thoracic body wall develop?
they develop ventral to transverse processes and occur in three distinct layers
external intercostal muscles
origin/insertion: lower margin of superior rib to upper margin of inferior rib (obliquely downward, from vertebrae towards sternum)
Action: elevates ribs during inspiration; stabilizes thoracic wall
Innervation: intercostal nn. (thoracic ventral rami)
internal intercostal muscles and innermost intercostal
origin/insertion: lower margin of superior in to upper margin of inferior rib (obliquely downward from sternum towards vertebra)
Action: depresses ribs during expiration; stabilizes thoracic wall
innervation: intercostal nn. (thoracic ventral rami)
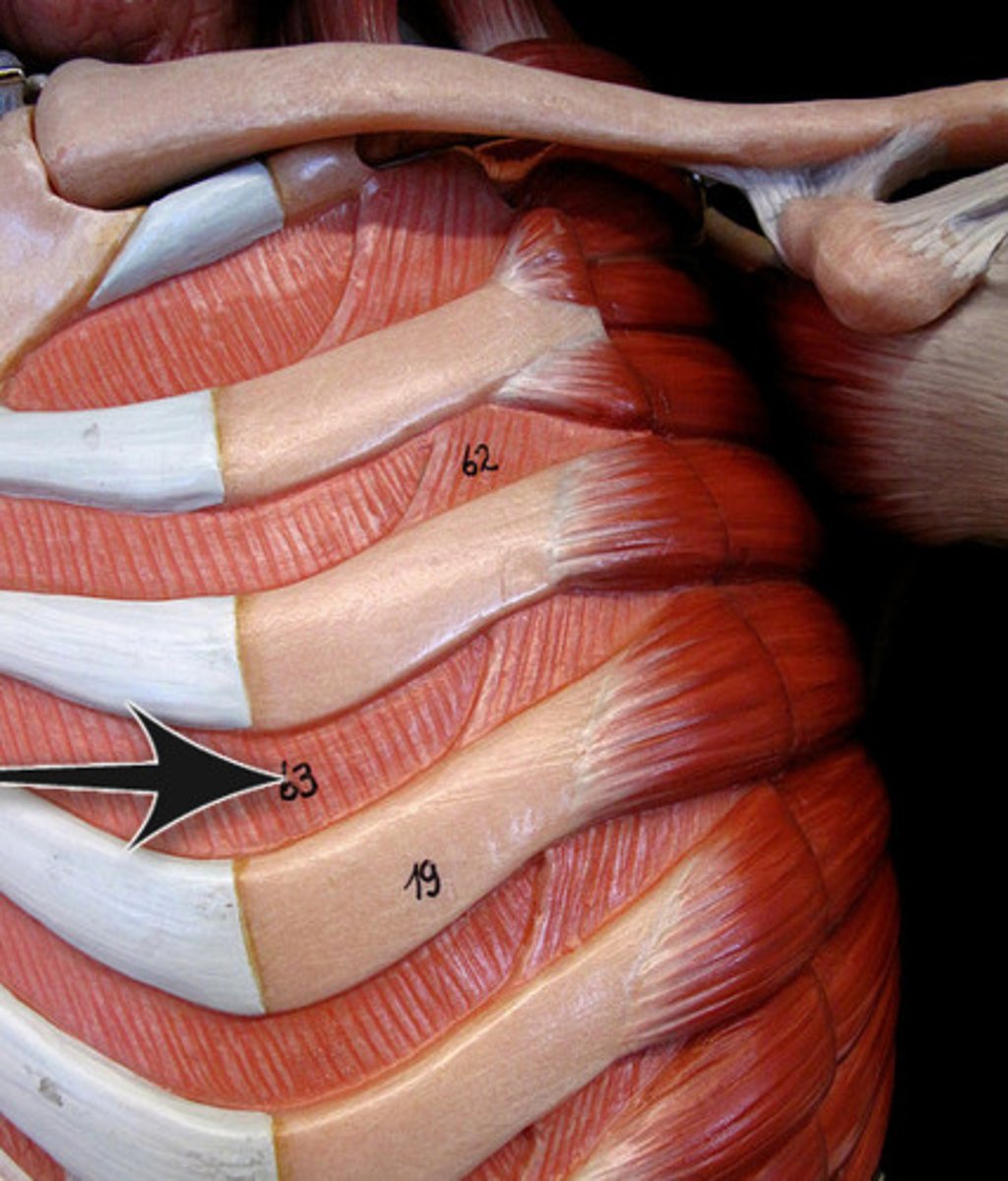
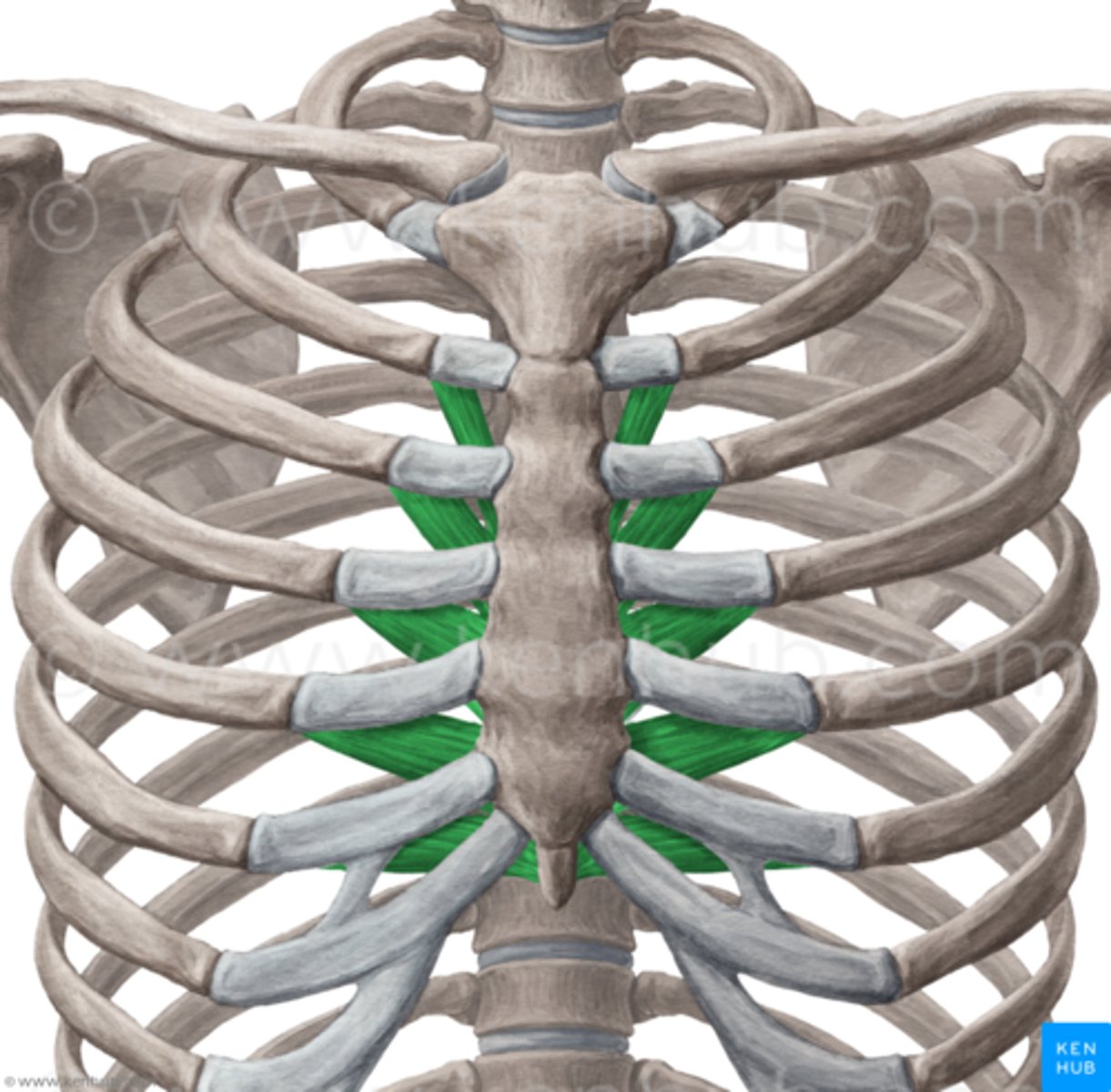
transversus thoracis muscles
origin: body and xiphoid process of sternum (internal surface)
Insertion: costal cartilages 2-6 (internal surface)
Action: depresses ribs during expiration
Innervation: intercostal nn. (thoracic ventral rami)
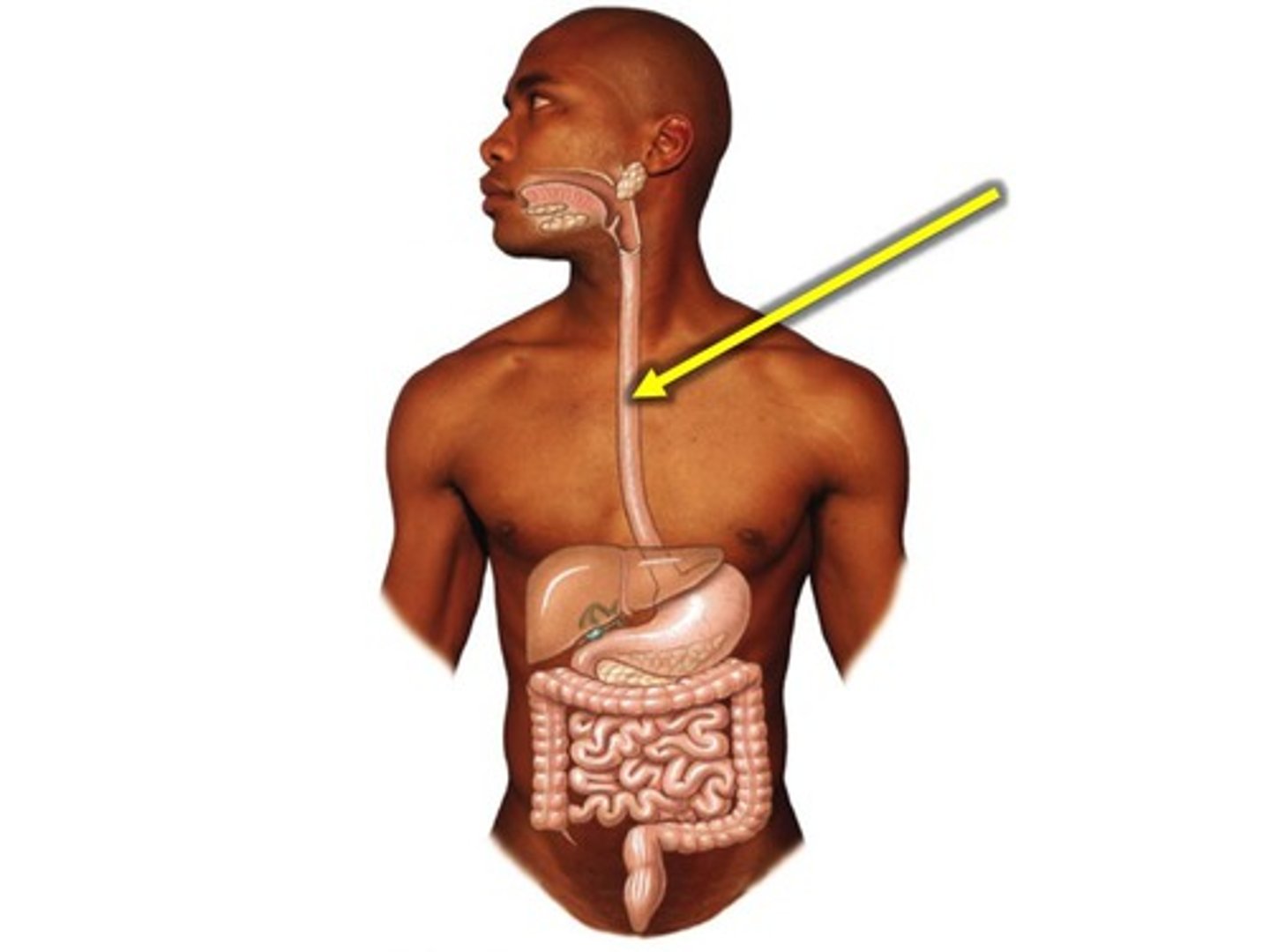
Where is the esophagus located in the mediastinum?
dorsal, lying on the anterior surface of the thoracic vertebral bodies
What is the esophagus?
a muscular tube (smooth muscle) that moves food from the pharynx to the stomach
Where does the trachea lie?
ventral to the esophagus
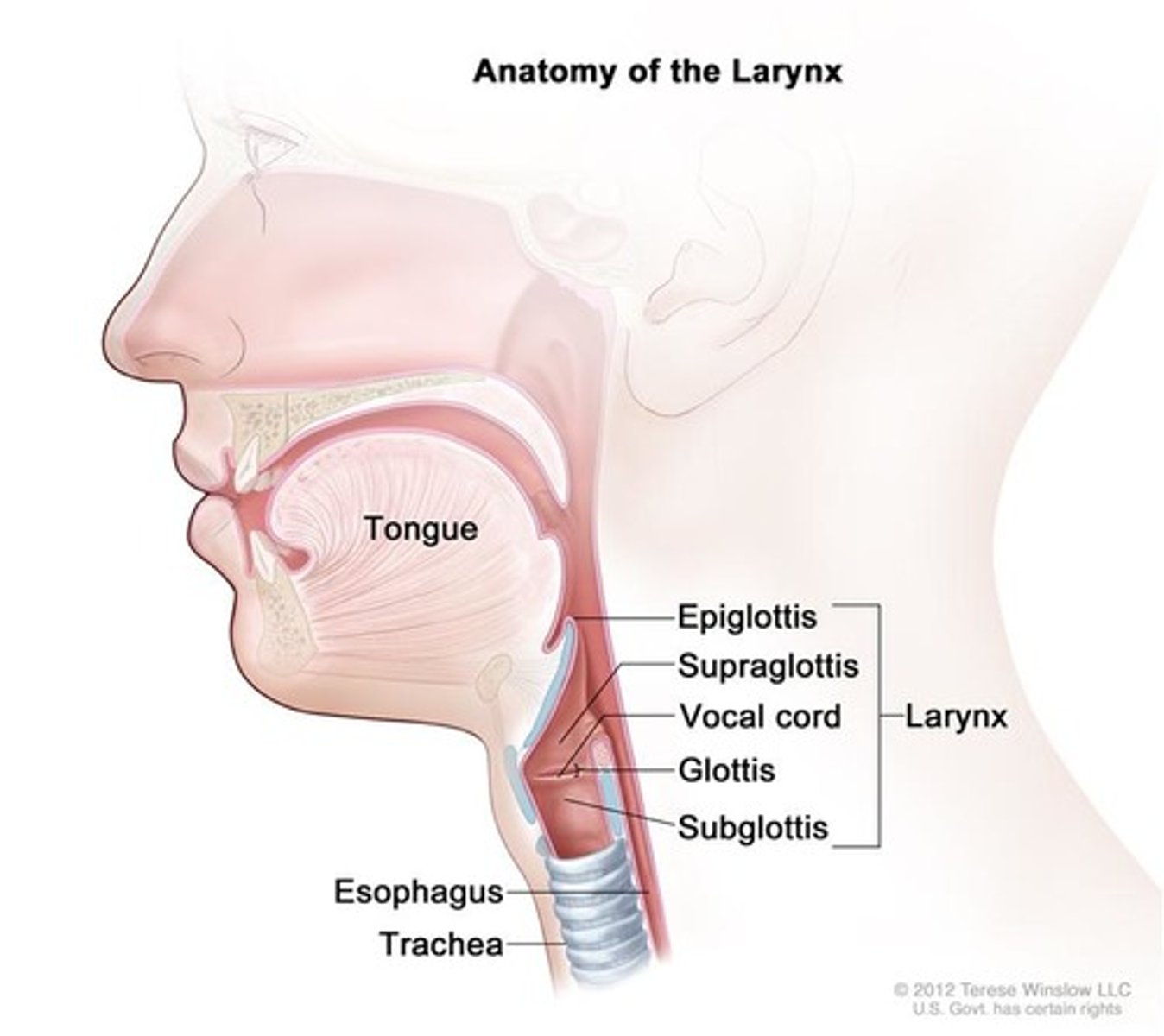
What is the trachea composed of?
C-shaped rings of cartilage joined one to another by intervening membranes of connective tissues, it is flexible but not collapsible
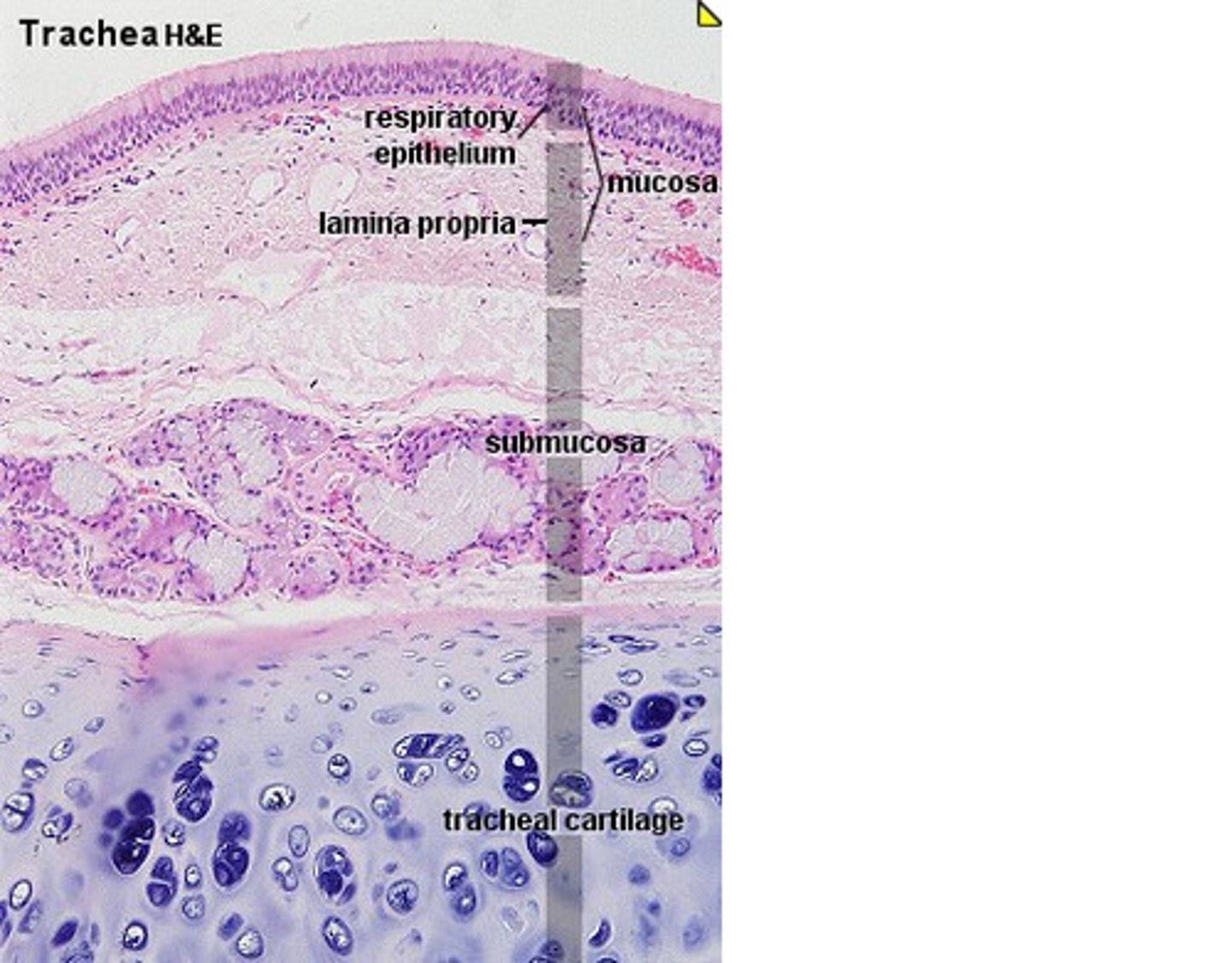
What happens to the trachea during inhalation?
the trachea stretches and descends
What happens to the trachea during exhalation?
it recoils to its original position
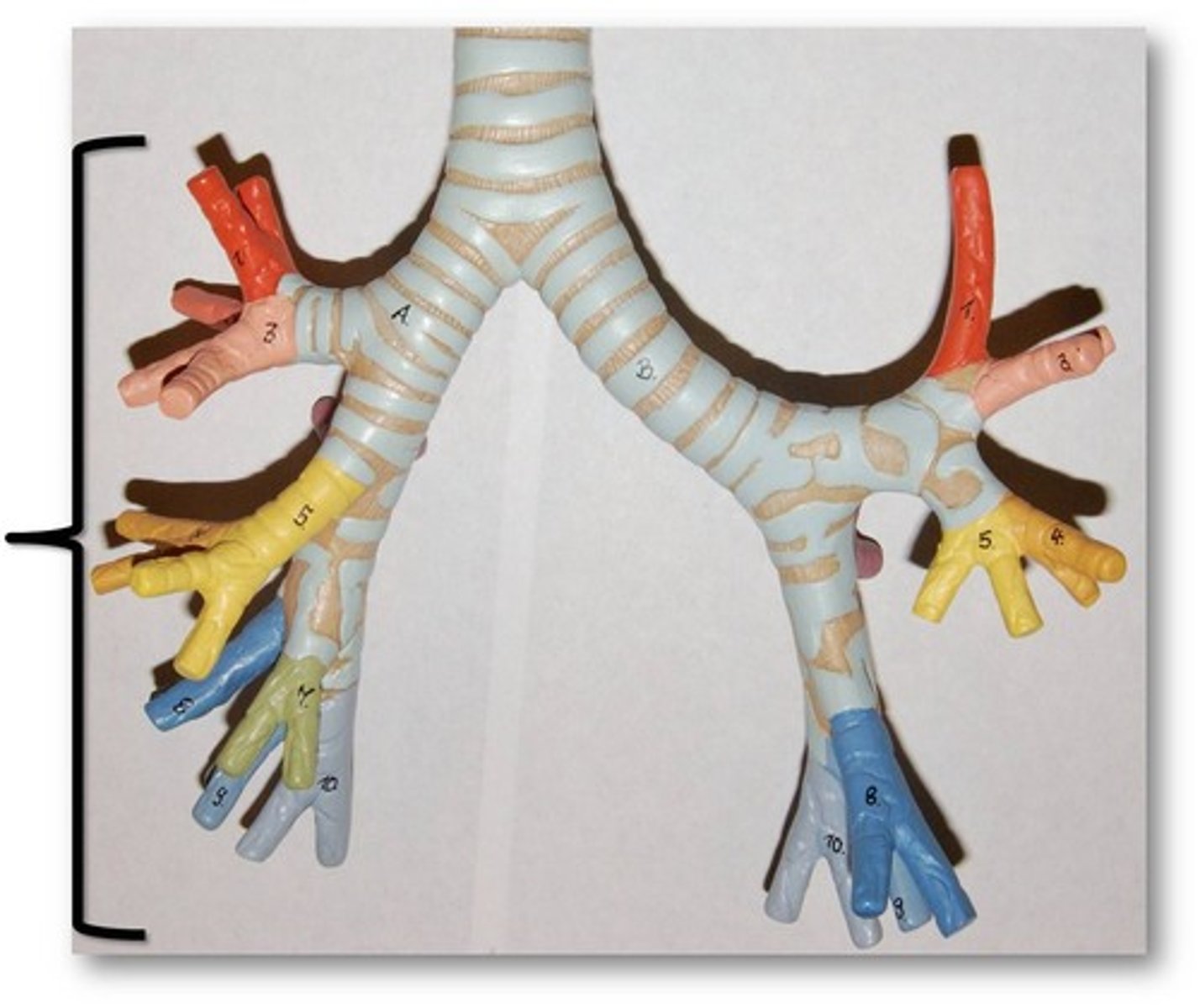
Where does the trachea divide into left and right bronchi?
At about T4 vertebral level
What are characteristics of the bronchi?
-run obliquely and then plunge into the hilus (medial depression) of each lung
-the right bronchus is wider, shorter and more vertical than the left bronchus
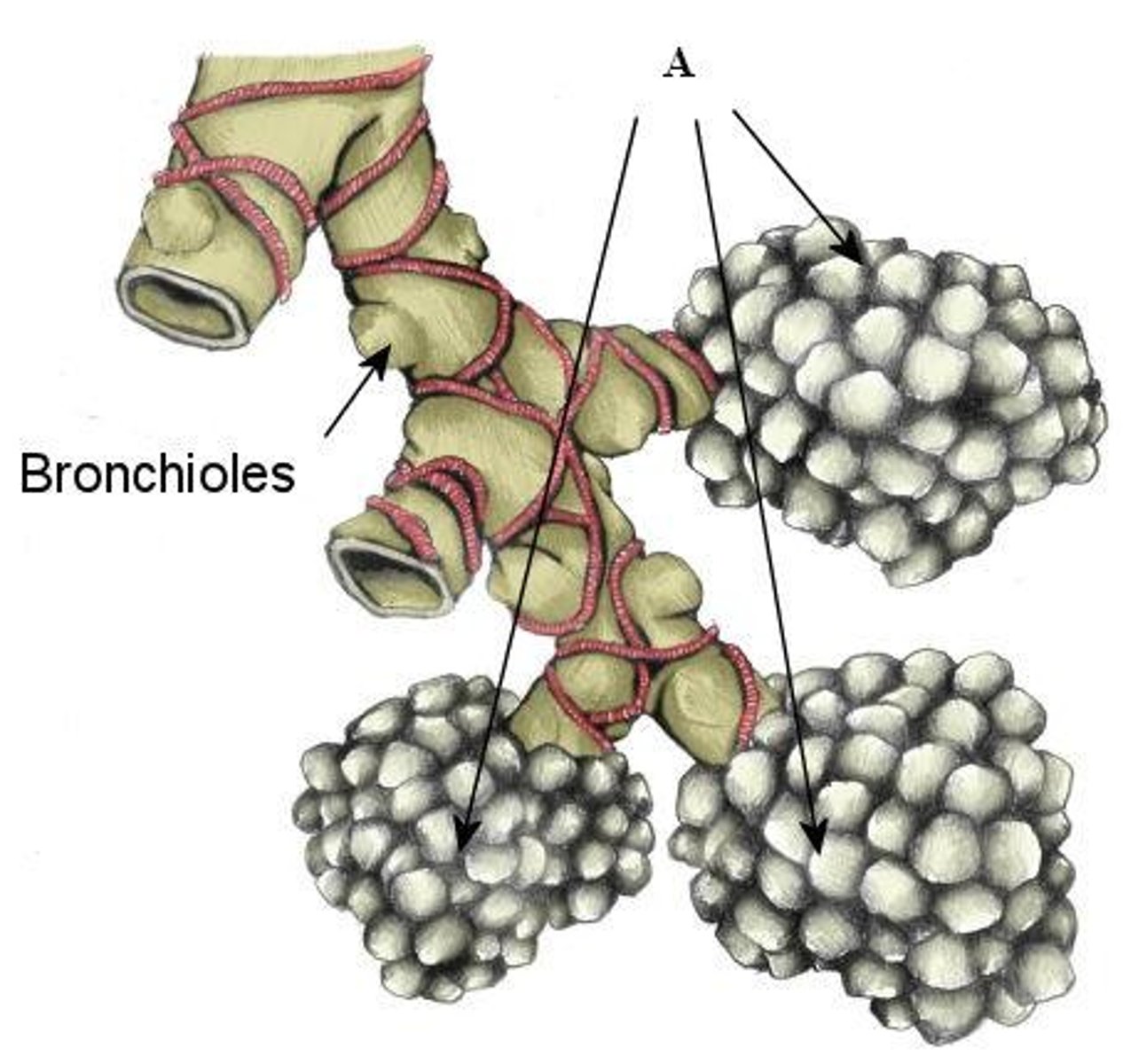
What are bronchial trees?
the bronchi branch profusely in the lungs
What are the blind sacs at the ends of the bronchial trees called?
alveoli