Lecture 3: Bacterial Growth and Genetics (copy)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Bacteria replicate by ______
a) Mitosis and Meiosis
b) Binary Fission
b)
What is generation time?
time required for one cell to divide into two
Match the generation time with the correct bacteria:
Generation time= 20 mins
a) E. Coli
b) M. tuberculosis
c) M. leprae
a)
Match the generation time with the correct bacteria:
Generation time= 20 hrs
a) E. Coli
b) M. tuberculosis
c) M. leprae
b)
Match the generation time with the correct bacteria:
Generation time= 20 days
a) E. Coli
b) M. tuberculosis
c) M. leprae
c)
Place the Phases of bacterial growth in order:
a) Stationary phase —> Exponential/ Logarithmic growth phase —→ Lag phase —→ Death (decline) phase
b) Lag phase —> Exponential/ Logarithmic growth phase —> Stationary phase —→ Death (decline) phase
c) Lag phase —> Stationary phase —→ Exponential/ Logarithmic growth phase —> Death (decline) phase
d) Stationary phase —> Lag phase —> Exponential/ Logarithmic growth phase —> Death (decline) phase
b)
Which of the following phases of bacterial growth is best described:
Adjustment and preparation
a) Lag phase
b) Exponential/ Logarithmic growth phase
c) Stationary phase
d) Death (decline) phase
a)
Which of the following phases of bacterial growth is best described:
Doubling and exponential growth
Typical features seen
a) Lag phase
b) Exponential/ Logarithmic growth phase
c) Stationary phase
d) Death (decline) phase
b)
Which of the following phases of bacterial growth is best described:
Toxin build up
Depletion of nutrients
# of live cells = # of dead cells
a) Lag phase
b) Exponential/ Logarithmic growth phase
c) Stationary phase
d) Death (decline) phase
c)
Which of the following phases of bacterial growth is best described:
# of live cells < # of dead cells
a) Lag phase
b) Exponential/ Logarithmic growth phase
c) Stationary phase
d) Death (decline) phase
d)
Bacterial metabolism
sum of various chemical processes involved in obtaining the energy and nutrients for survival and reproduction
What are the Microbial requirements?
a) Source of carbon
b) Source of nitrogen
c) Phosphate, metals, ions
d) Source of energy (ATP)
e) All of the above
e)
What are the physical conditions that Microbe survival and reproduction depend on?
a) Temperature
b) Neutral pH
c) Atmosphere
d) All of the above
d)
What is neutral pH?
a) 7.0
b) 7.4
c) 6.0
d) 6.4
b)
Which of the following is best described below:
Only aerobic growth; Oxygen required
Growth only occurs where high concentrations of oxygen have diffused into the medium
Presence of enzymes catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) neutralize toxic forms of oxygen; can use oxygen
a) Obligate aerobes
b) Facultative anaerobes
c) Obligate anaerobes
a)
Which of the following is best described below:
Both aerobic and anerobic growth; Greater growth in presence of Oxygen
Growth is best where most oxygen is present but occurs throughout the tube
Presence of enzymes catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) neutralize toxic forms of oxygen; can use oxygen
a) Obligate aerobes
b) Facultative anaerobes
c) Obligate anaerobes
b)
Which of the following is best described below:
Only anaerobic growth; ceases in presence of Oxygen
Growth only occurs where there is NO oxygen
Lacks enzymes catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) to neutralize toxic forms of oxygen to be neutralized; CANNOT TOLERATE OXYGEN
a) Obligate aerobes
b) Facultative anaerobes
c) Obligate anaerobes
c)
What are the different types of media?
Simple media
Enriched media
Selective media
Differential/ indicator media
Transport media
Differential/ Indicator Media:
Which of the following is true about MacConkey (MAC) and lactose fermentation
a) Pink color= Acid production (fermentation)
b) No color change= No fermentation
c) Differentiates between Lactose fermenters and Non Lactose fermenters
d) All of the above
d)
What does MacConkey (MAC) contain as its carbon source?
Lactose
What does MacConkey (MAC) contain for its pH indicator?
Neutral red/ toluene red
Which of the following about Bacterial Genetics is best described:
Circular double stranded DNA
Contains all necessary information for growth and replication
a) Bacterial Chromosome
b) Plasmid
a)
Which of the following about Bacterial Genetics is best described:
Extrachromosomal double stranded DNA
Not essential for growth
May carry factors for survival advantage (antimicrobial resistance genes)
a) Bacterial Chromosome
b) Plasmid
b)
Which of the following best describes what occurs during:
Bacterial Replication
a) Synthesis of single strand RNA
b) Duplication of chromosomal DNA
c) Synthesis of protein from mRNA
b)
Which of the following best describes what occurs during:
Bacterial Transcription
a) Synthesis of single strand RNA
b) Duplication of chromosomal DNA
c) Synthesis of protein from mRNA
a)
Which of the following best describes what occurs during:
Bacterial Translation
a) Synthesis of single strand RNA
b) Duplication of chromosomal DNA
c) Synthesis of protein from mRNA
c)
What are the different mechanisms for horizontal gene transfer in bacteria?
a) Transduction
b) Transformation
c) Conjugation
d) All of the above
d)
What is recombination?
breakage and rejoining (rearrangement) of DNA into new combinations
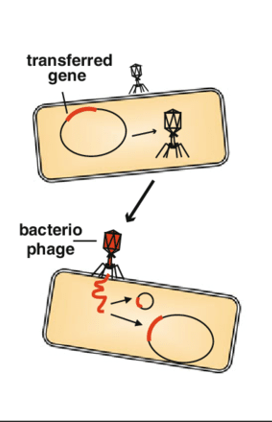
Which mechanism of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria is best described:
Via bacteriophages
Process- lysogeny
Genes acquired for toxin production some bacteria
a) Transduction
b) Conjugation
c) Transformation
d) All of the Above
e) None of the Above
a)
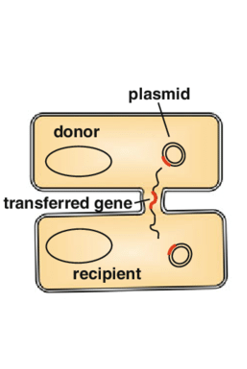
Which mechanism of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria is best described:
Via sex pili through conjugation tube formation
Usually plasmids acquired for antibiotic resistance
a) Transduction
b) Conjugation
c) Transformation
d) All of the Above
e) None of the Above
b)
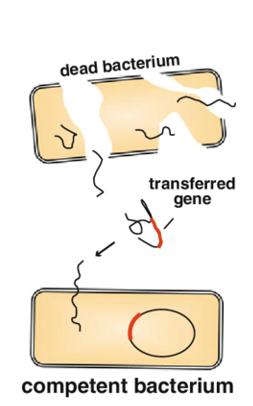
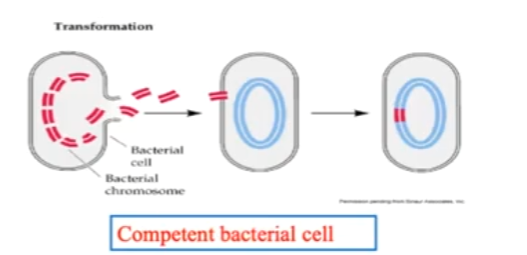
Which mechanism of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria is best described:
Uptake of naked DNA
Uncommon in nature
Possible in experimental setup
a) Transduction
b) Conjugation
c) Transformation
d) All of the Above
e) None of the Above
c)
Transduction
Bacterial virus (bacteriophage) transfers DNA from one bacterium to another
2 types of cycles
Lytic
Lysogenic
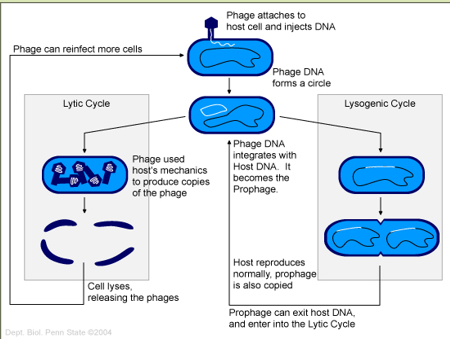
Which cycle of Transduction is best described:
Bacteriophage uses bacterial cell to synthesize phage-specific nucleic acids and proteins, destroys bacterium
a) Lytic
b) Lysogenic
a)
Which cycle of Transduction is best described:
Bacteriophage integrates its DNA (Prophage) into bacterium and replicates
a) Lytic
b) Lysogenic
b)
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Corynebacterium diphtheriae —→ diphtheria toxin
example of Lysogenic conversion
Conjugation
DNA transferred from one bacterial cell (donor/ male/ F+ cell) to another (recipient/ female/ F- cell)
F plasmid/factor is transferred via formation of a sex pilus (F pilus/ conjugation pilus)
Transfer of ss DNA from donor to recipient cell. DNA is replicated to form ds DNA in both cells
Transfer of DNA: F- cell converted to F+
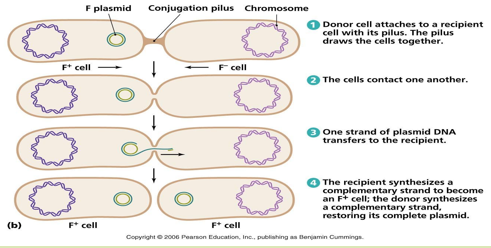
Which mechanism of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria is:
Important for transfer of genes/plasmids for drug resistance
a) Transduction
b) Transformation
c) Conjugation
c)
Transformation
uptake of small fragments of naked DNA in the environment by a recipient bacterial cell (competent)
Rare in nature-allows bacteria to take up new DNA
Technique used by scientists to introduce new genes for recombinant DNA technology