Unit 5: Reptiles (Cram)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What class do retiles come from?
Class Reptilia
How many chambers do most reptiles have in their heart, what is a species that is an exception?
3 chambers, crocodiles have 4
True or false: Like birds, reptiles have a renal portal system in the caudal part of their body.
True
Do reptiles have a diaphragm?
No
How many lungs do most snakes have?
1 lung
Retiles are _____–thermic. Meaning they use thermal energy from an external source to maintain their body temperature
ecto
Most reptiles are also ______–thermic, meaning that their body temperature varies with their surroundings
poikilo
Term for sensing and reacting to noxious stimuli
Nociceptive
Why should you be cautious about using heat rocks with reptiles?
They are less nociceptive than mammals, meaning they are less responsive to pain. If the rock is burning them they may not move off of it
What are some names for a group of snakes?
Den, nest, pit, bed, and knot
What are some names for a group of turtles?
Bale, nest, turn, and dole
What is a name for a group of tortoises?
Creep
What is a name for a group of lizards?
Lounge
The venom of snakes is a mixture of ________ and ____________
enzymes, polypeptides
Term for shedding
Ecdysis
Term for the transparent scale that covers the eyes of snakes
Spectacle
Snakes have poor eyesight, how do they sense prey?
Can see movement, and sense heat differential between prey and the environment
What organ do snakes have at the roof of their mouth to smell?
Vomeronasal organ
True or false: In order to swallow large prey, snakes can dislocate their jaw
False. Theire jaw bones are loosely connected by a ligament and they have elascticated skin allowing them to stretch their mouths
Term that describes the way snakes can continuously replace their teeth
Polyphyodontic

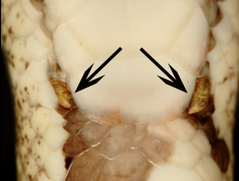
What are the structures indicated by the orange question mark?
Pits
What is the most reliable method of sexing snakes?
Cloacal probing
What is the range of scale depth the cloacal probe can be inserted on a female snake?
2–4 scales
What is the range of scale the cloacal probe can be inserted on a male snake?
6–8 scales

What are these structures on a male snake called?
Hemipenes
What are these structures on a male snake called?
Anal spurs
Are snakes omnivores, herbivores, or carnivores?
Carnivores
What should you do to your snake's prey before it is eaten, to make sure your snake is getting enough nutrition?
Gut loading
What are some warning signs that a snake is about to bite?
Curl into a "S" shape, hissing, tail flick, body enlargement, striking out
True or false: Snakes are solitary except for breeding and brumation
True
What are some preventative measures you can take to keep your snakes healthy?
Quarantine new snakes for 1–3 months, minimize stress, do not share furnishings between snakes, discard uneaten food, air out cage for 24 hours if using a bleach solution to clean, etc.
Force feeding can traumatize a snake, how can you ensure that the snake will resume eating again normally after a force feeding?
Force feed in different location to normal enclosure
Term for turtles and tortoises as a group
Chelonians

How can you tell that this is a turtle?
Flat shell, webbed front feet, aquatic

How can you tell that this is a tortoise?
Terrestrial, feet not webbed, sharp claws for digging, dome–shaped shell
Term for the top of a chelonian's shell, comprised of 10 fused thoracic, lumbar, sacral verterbrae and ribs
Carapace
Term for the bottom of a chelonian's shell, comprised of 9 bones including the clavicle
Plastron
Structures that cover the bony shell, giving chelonians their shell patterns
Scutes
Because their ribs and most vertebrae are fused into a shell, how do chelonians breath?
Muscle sling attached to shell contracts and relaxes
Not all reptiles have bladders, do chelonians?
Yes they have a bladder conneted to their cloaca by a short urethra, some lizards have this too
What urogenital problem do desert tortoises and igunanas have?
Bladder stones
Which has a longer tail? A male or female chelonian?
Male

Sex these turtles based on the concavity of their plastron
Convex (left) – Female
Concave (right) – Male
Most reptiles (like snakes) lack a penis, do male chelonians have one?
Yes
Term for the hibernation–like state some reptiles go into. They will often burrow or bury themselves in mud and slow their heartbeat to 5–10 bpm
Brumation
True or false: To prepare your reptile for brumation it is important to feed them beforehand so they don't develop post brumation anorexia
False. The food will rot in the reptile's stomach during brumation. This can kill them. Do not feed before. Instead to avoid post brumation anorexia, feed very well during recovery
What are some warning signs of chelonians?
Pulling limbs/head into shell, biting, hissing, flailing feet, excretory secretions
True or false: Unlike snakes, chelonians are more social outside of the mating season
False. Like snakes they are only social at this time
Which vitamin deficiency is common is turtles, leading to beak overgrowth?
Vitamin A
Snakes shed all in one piece, how do lizards shed?
In patches
Term for the defense mechanism some lizards possess where they can release their tail during an attack
Autotomy
True or false: Like snakes, cloacal probing is the most reliable method of sexing. Male length will be longer
True
Are lizards solitary like chelonians and snakes?
No. They are socially facultative
What are some things to ask a reptile owner when taking a history?
Enclosure size, temperature, humidity, lighting, water, diet, shelter, ventilation, substrate, furnishings, disinfection, etc.
Failure of eggs to pass through the oviduct whithin a normal time period. Often hormone related. Common problem of iguanas and chameleons
Egg binding
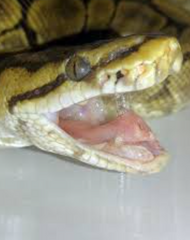
What are the clinical signs of this snake suggesting?
Open mouth gaping and bubbles from the mouth indicate a respiratory disorder

What are the clinical signs of this chameleon suggesting?
Stomatitis (mouth rot)

This snake has not left his water bowl for 8 hours, what do his clinical signs suggest?
Ectoparasites

What are the clinical signs of this gecko suggesting?
Crooked tail and deformed bone structure indicate metabolic bone disease. Other signs include muscle tremors, fractures, jaw softening, swollen limbs, shell softening, shunted growth and paralysis

What are the clinical signs of this bearded dragon suggesting?
Gout
What is a common husbandry mistake that can cause gout?
Feeding dog/cat food to reptiles. It is too high in protein


This snake is not able to right itself. What are the clinical signs suggesting?
Inclusion body disease (IBD)
What is the treatment for IBD?
None. Euthanasia recommended

What are the clinical signs of this tortoise suggesting?
Septicemic cutaneous ulcerative disease (SCUD)
Fungal infection that affects iguanas, turtles, and tortoises
Dermatophytosis
Fungal infection that can be contagious to handlers
Systemic mycosis

Jeepers creepers, where'd ya get those peepers!? What do the clinical signs of this snake suggest?
Dysecdysis (shedding abormality)
Reptiles are death resistant. What are some methods of euthanasia? Note: Applying 2 or more euthanasia methods is recommended
IV/IP (IC only if anethetized) barbituates, gas, decapitation, and pithing