Anatomic Sciences- NBDHE
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
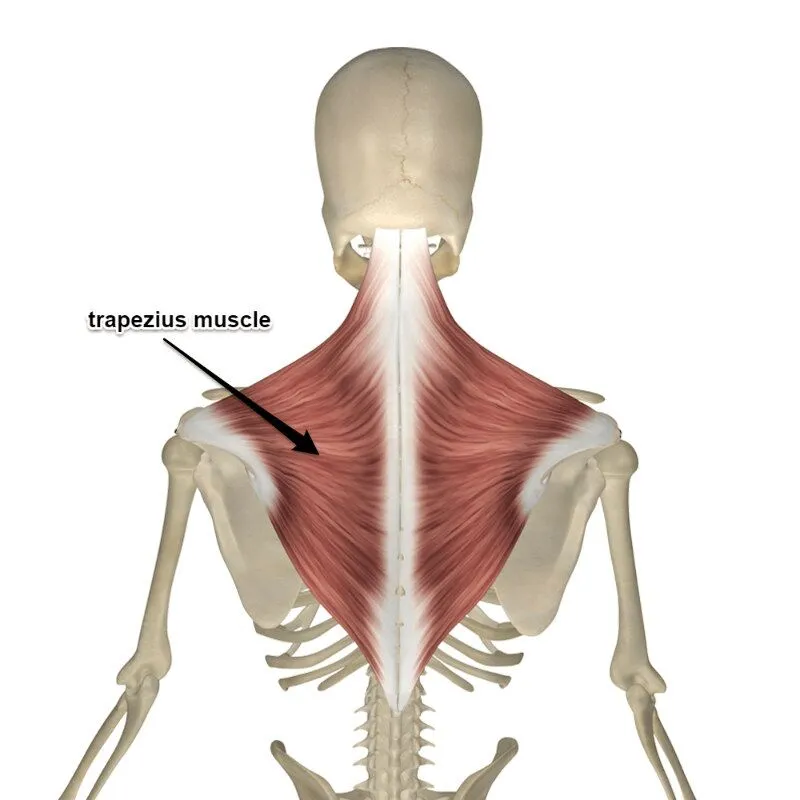
What’s the origin and insertion of the Trapezius muscle?
Occipital Bone
Posterior midline of thoracic and cervical regions
Which cranial bone makes up the socket of the eye and forms a pocket?
Sphenoid bone (1)

Which bone makes up the bridge of the nose?
Nasal Bones (2)
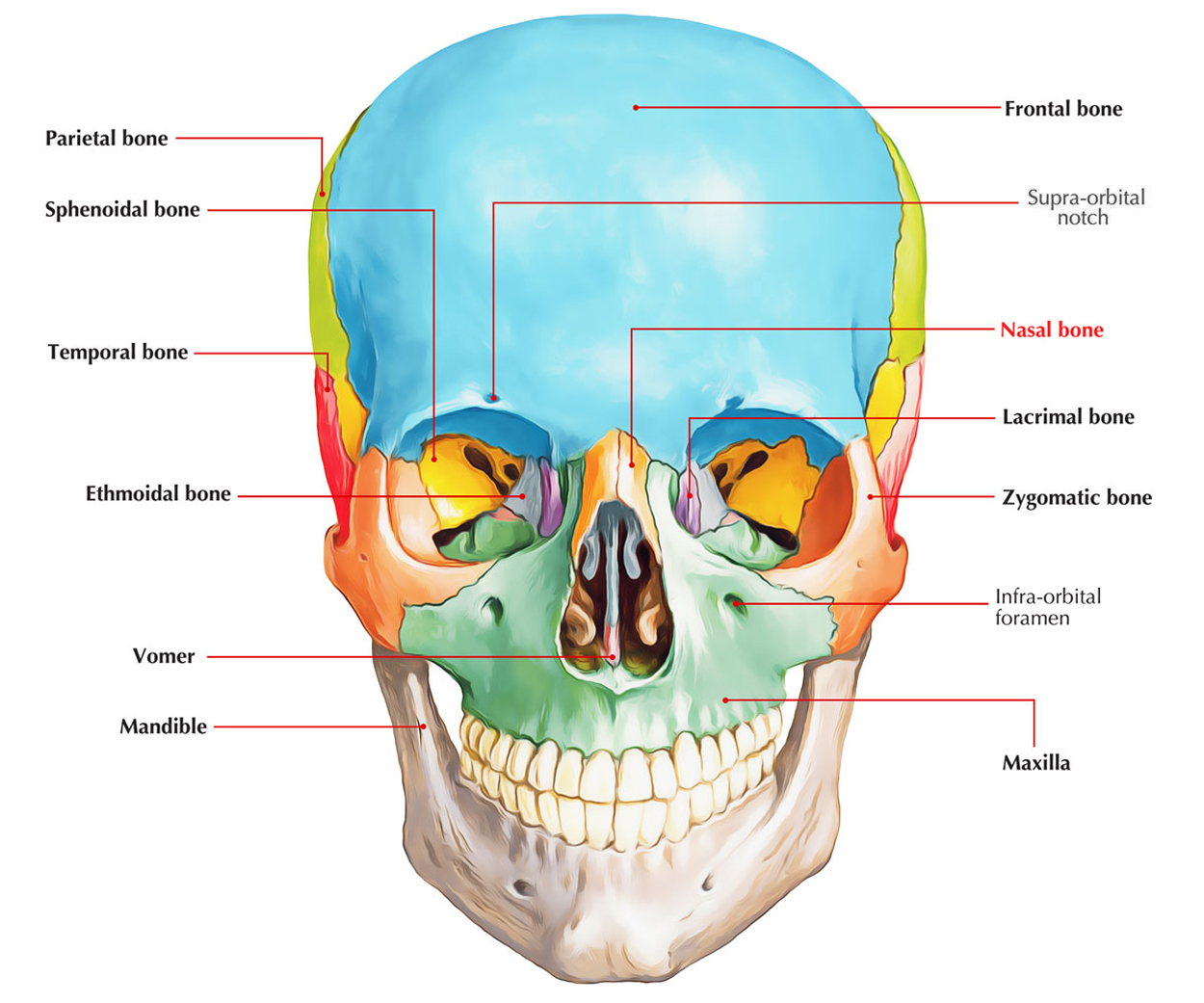
Which cranial bone makes up the cavity of the nose?
Ethmoid bone
Which structure supplies the muscles of the facial expression?
Facial artery (branch of the external carotid artery)
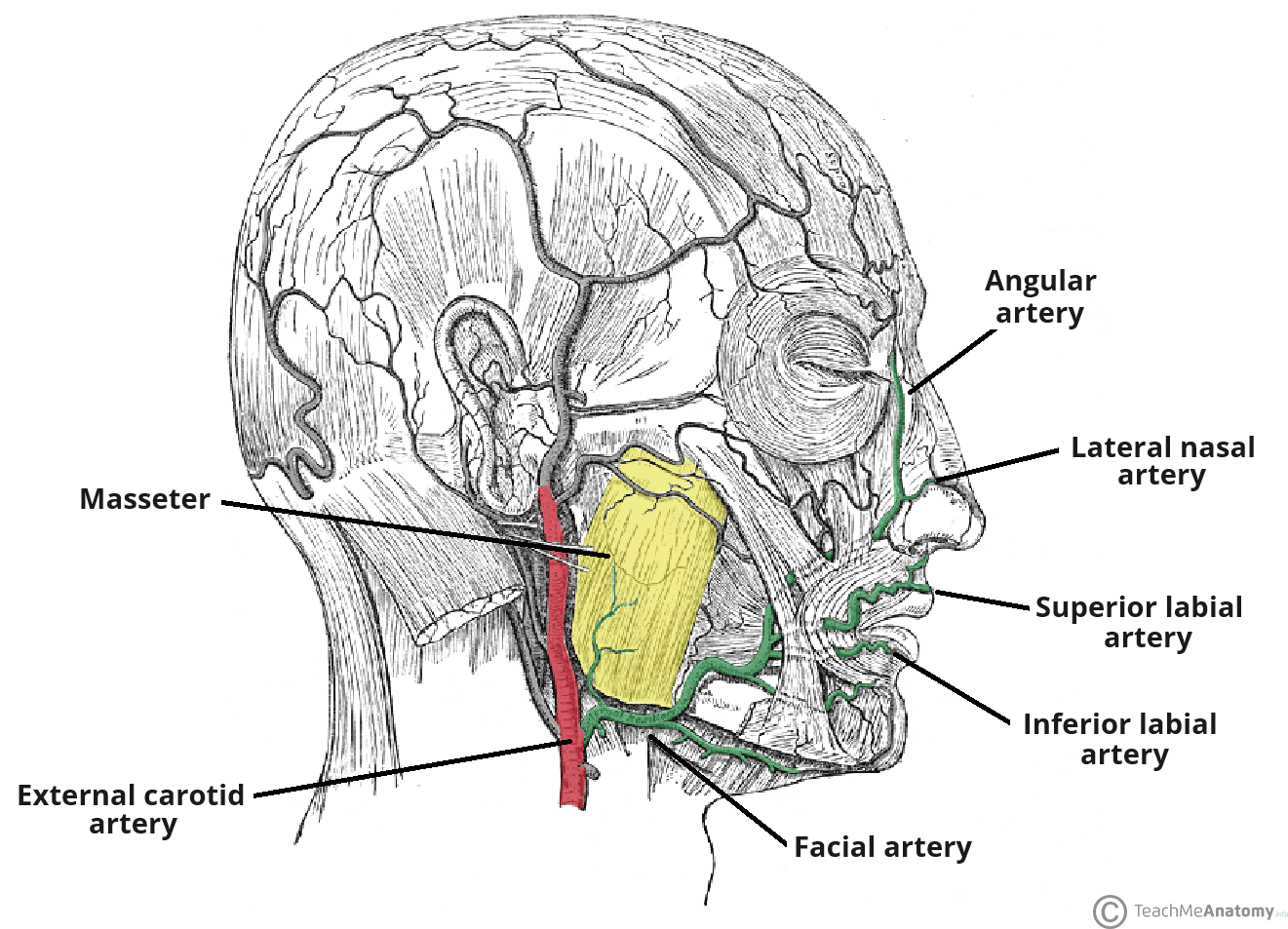
Which artery supplies the masticatory muscles?
Maxillary artery (branch of the external carotid artery)
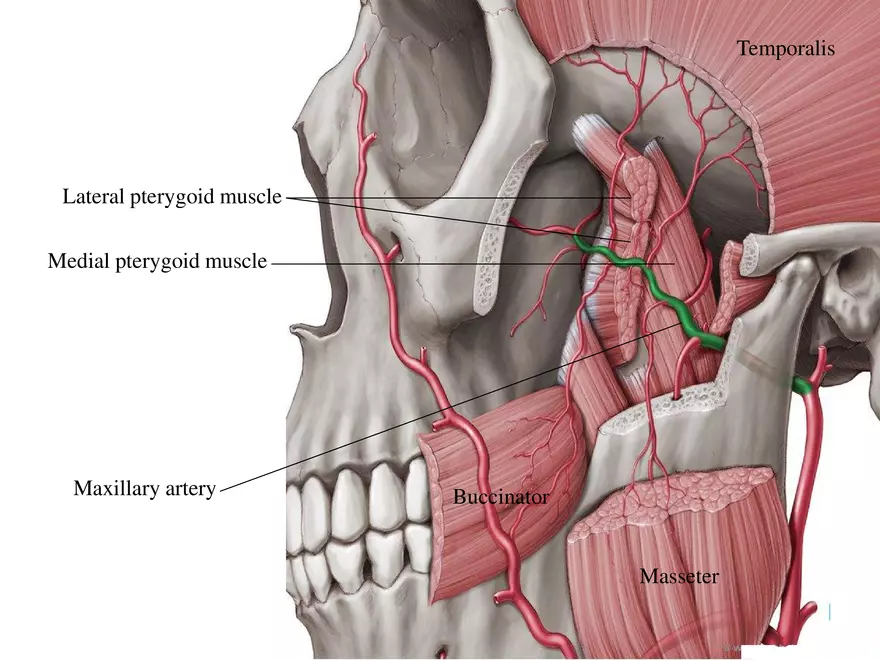
Embryonic origin of the facial expression muscle is within the
2nd branchial arch
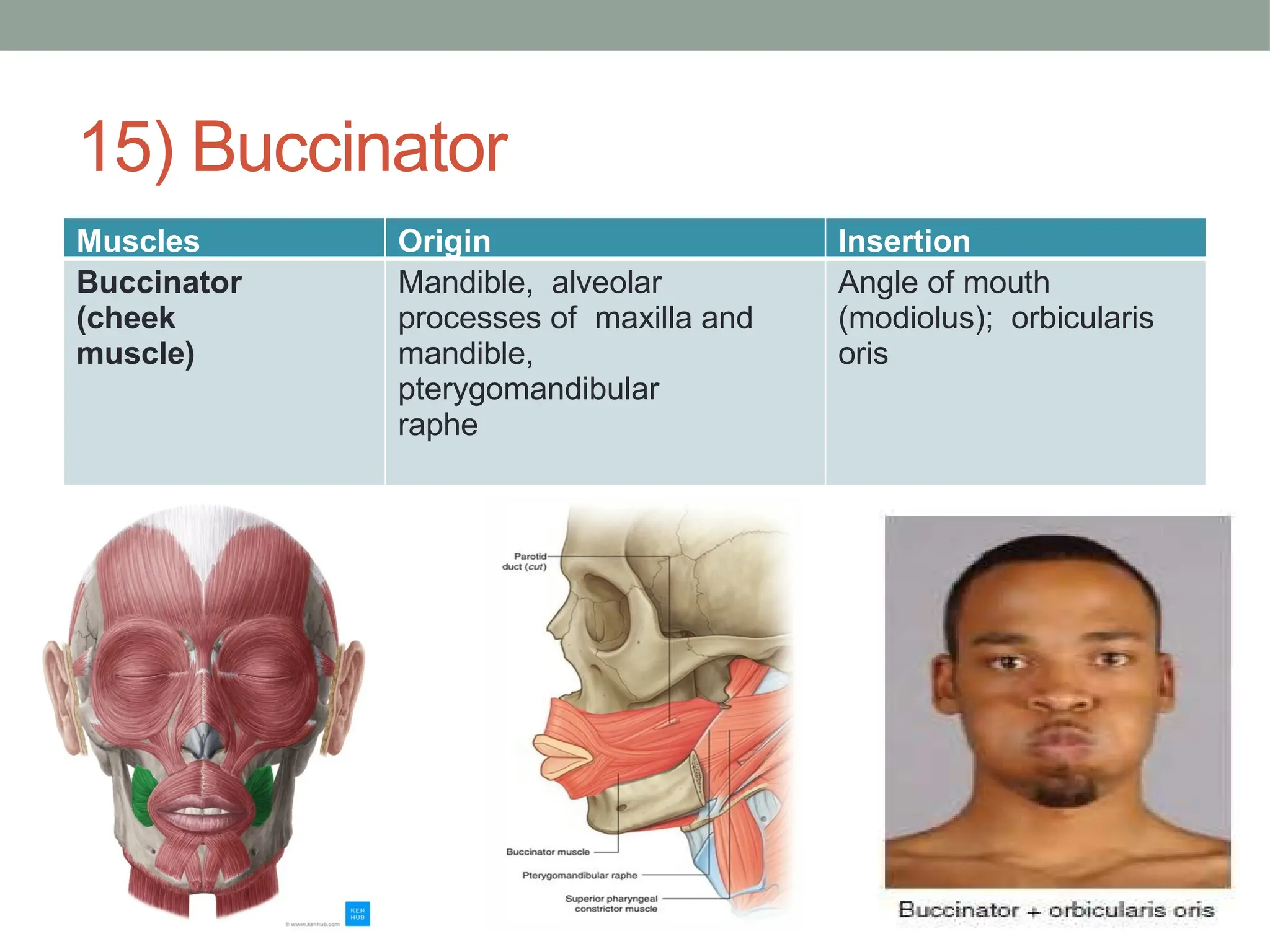
What is the origin and the insertion of the buccinator muscle?
origin: maxilla, mandible and pterygoid raphe
Insertion: angle of the mouth (medilus)
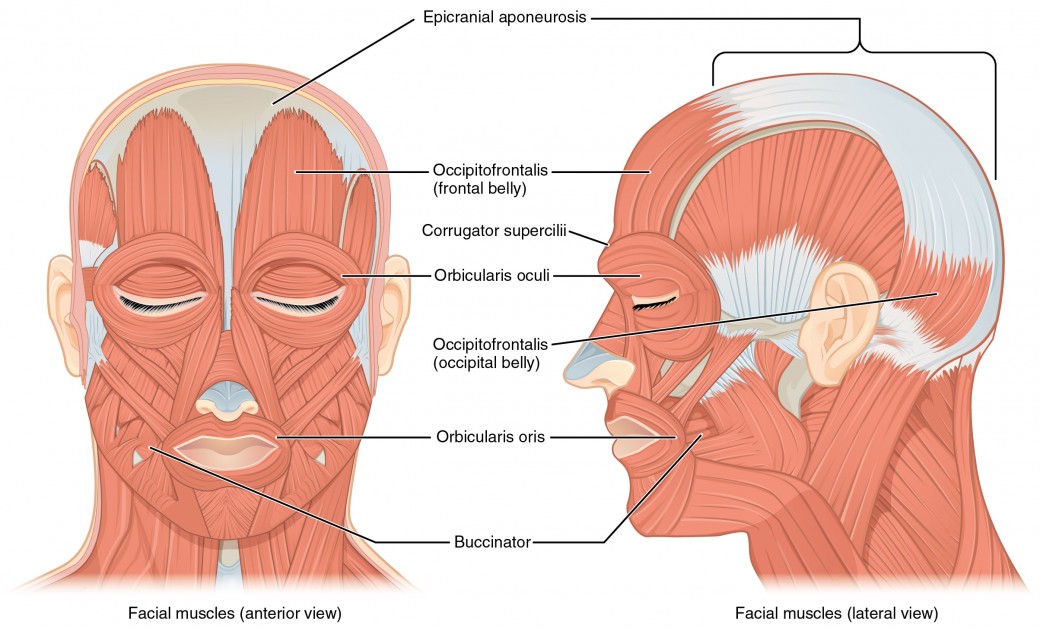
T or F: The majority of processes articulate with the same named structure
True
Which muscle(s) permit/s you to whistle?
Orbicularis oris muscle and Buccinator muscle
Which bones hold the lacrimal ducts?
Lacrimal bone
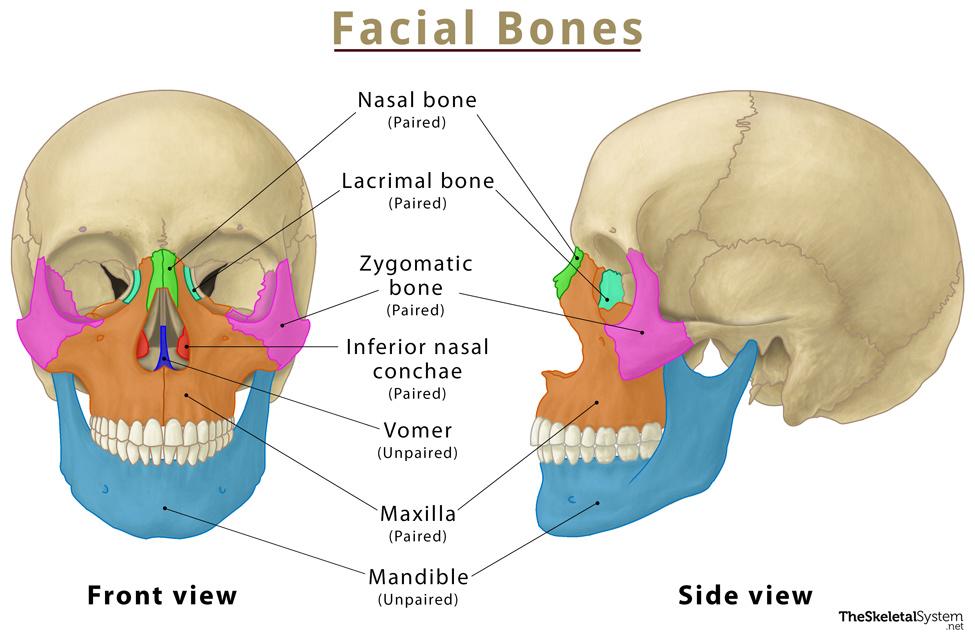
Which facial bone warms, humidifies, and filter inhaled air?
Inferior nasal concha

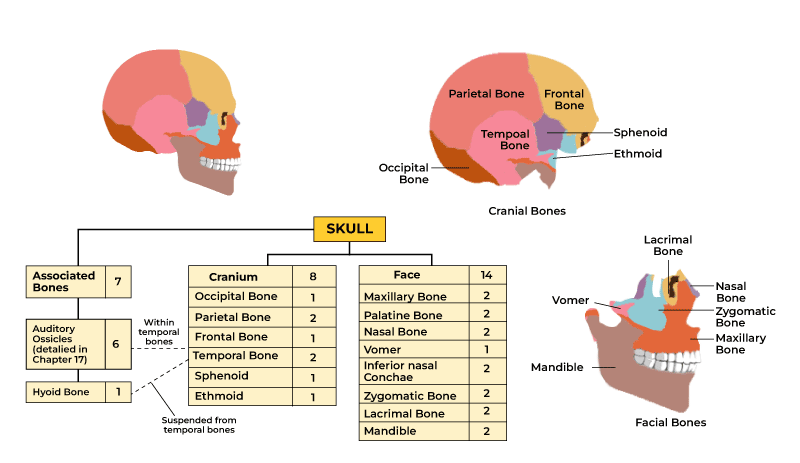
How many bones make up the human skull?
How many of them are facial bones ,and how many are cranial bones?
22 bones in total
14 facial bones
8 cranial bones
What’s the parietal eminence?
The parietal eminence (or tuber) is the most prominent, rounded bulge on the outer surface of each parietal bone, forming the high point on the side of the skull, marking its widest point, and where bone formation starts in the embryo

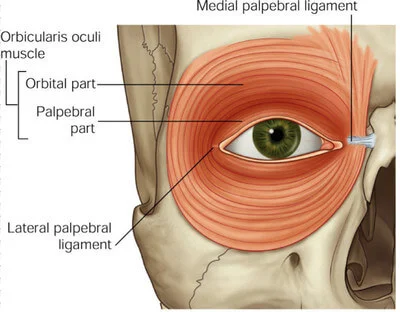
Which facial expression muscle permits the closing of the eye?
Orbicularis oculi
Define articulation
It is the connection point where two or more bones meet, allowing for body movement, support, and flexibility, ranging from immovable (skull sutures) to freely movable (shoulder, hip
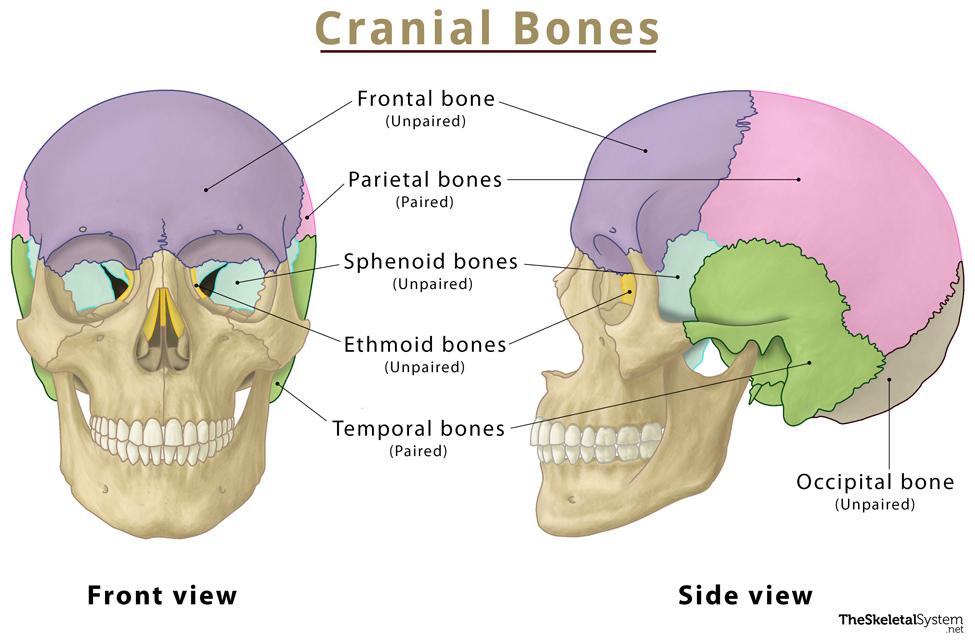
Name all paired cranial bones
Parietal (2)
Temporal (2)
T or F: If the name of a muscle is a combination, the first part is the insert while the second part it the origin?
False
Oi=Origin (PI) +Insertion (PII)
T or F: Most facial expression muscles originate on the angle of the mouth?
False
Most facial expression muscles insert into the angle of the mouth
Which muscle of the facial expression wrinkles the forehead?
Frontalis m
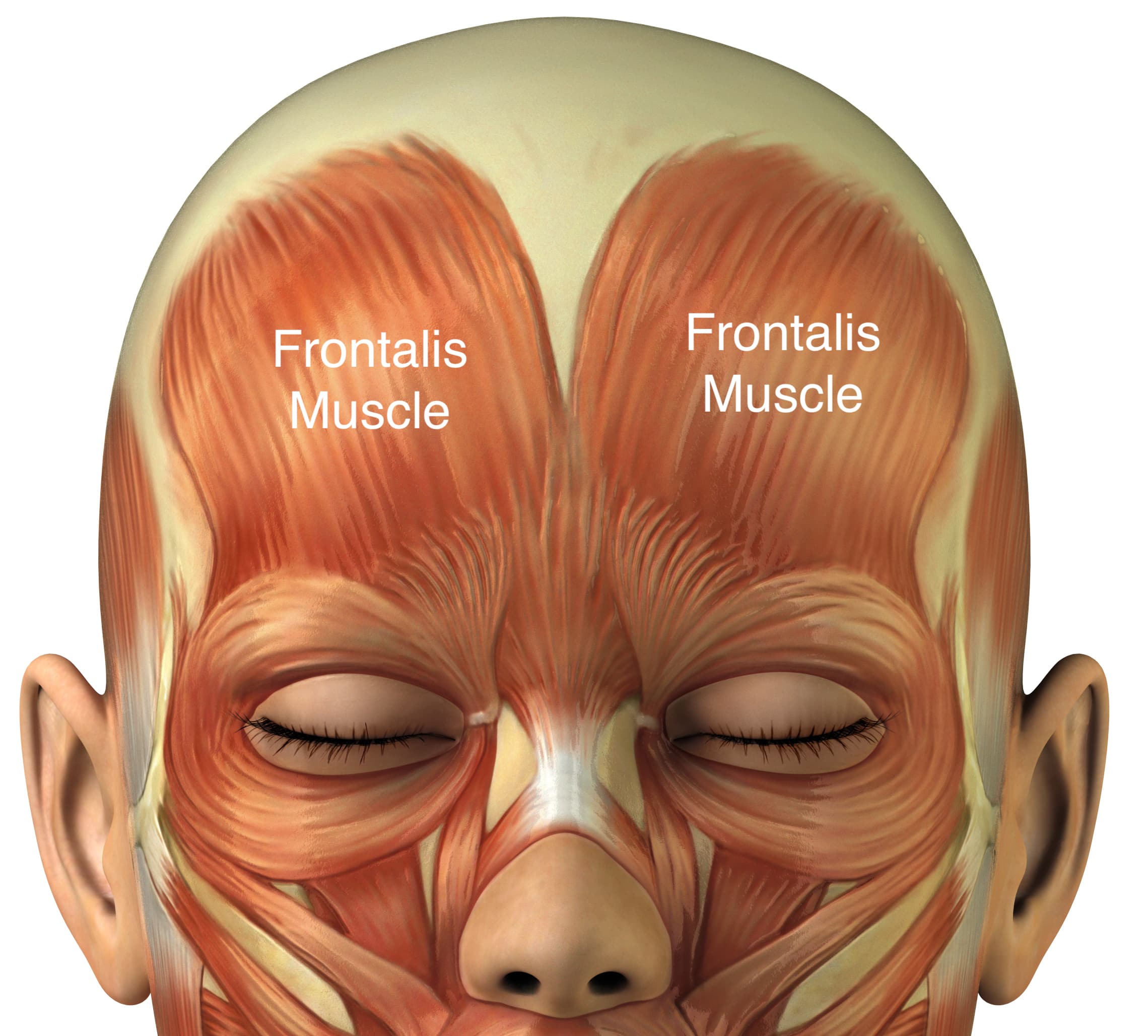
Name all cranial bones
Frontal (1)
Parietal (2)
Temporal (2)
Occipital (1)
Sphenoid (1)
Ethmoid (1)
Total: 8 cranial bones
Which facial expression muscle/s allows you to smile?
Zygomatic m (main smiling muscle)
Risorius (allows wide smiles)
L.anguli oris (lifts the angle of the mouth as its name indicates: levator= lifts anguli= angle oris=mouth)

Name all facial bones
maxillae (2)
zygomatic bones (2)
nasal bones (2)
lacrimal bones (2)
palatine bones (2)
inferior nasal conchae (2)
Unpaired facial bones (2 total):
mandible (1)
vomer (1)
Which facial expression muscle activates when you flare your nostrils?
nasalis m
Which triangle makes up the anterior triangle of the neck?
Carotid triangle
Muscular triangle
Submental triangle
Submandibular triangle
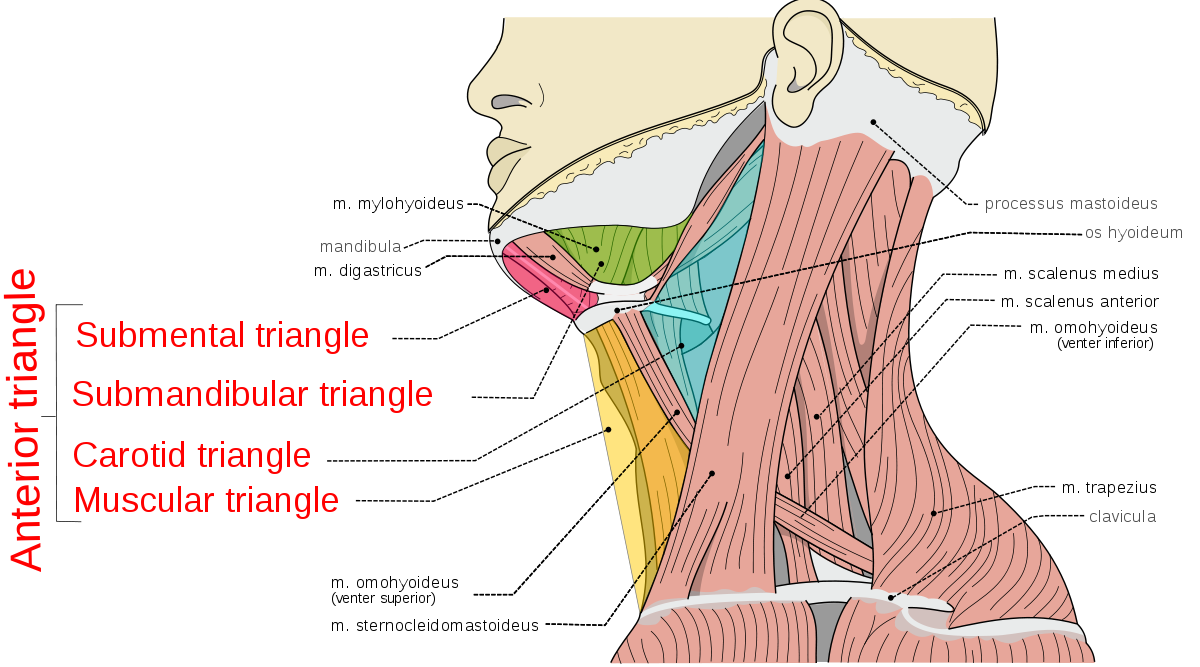
Which triangle makes up the posterior triangle of the neck?
Subclavian triangle
Occipital

Which muscle tenses the cheek to and allows to keep your food between your teeth?
Buccinator
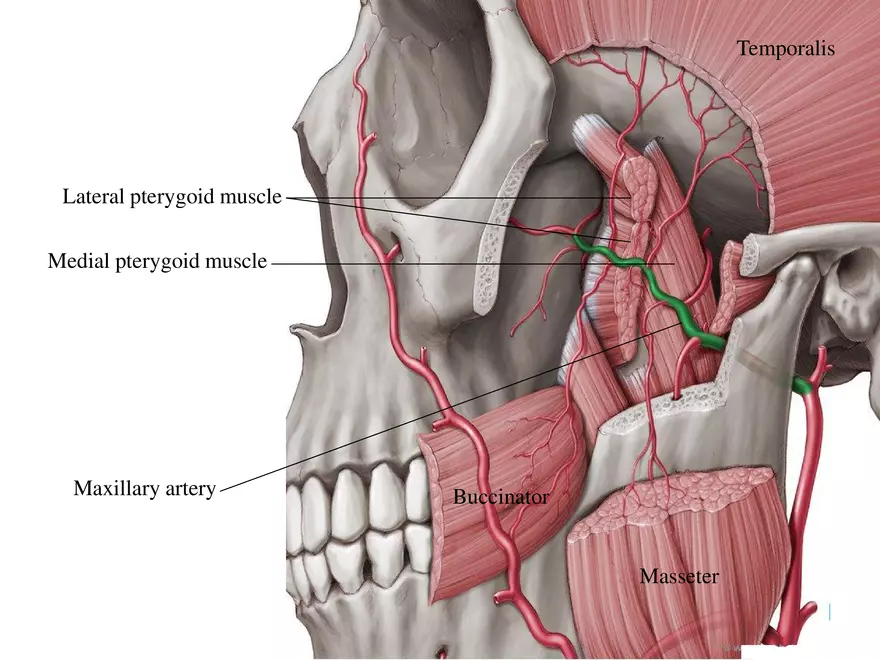
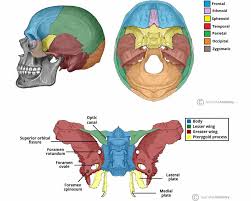
Which bone is known for acting as the bridge between cranial and facial bones, contains pterygoid processes and up to 14 articulations?
Sphenoid bone
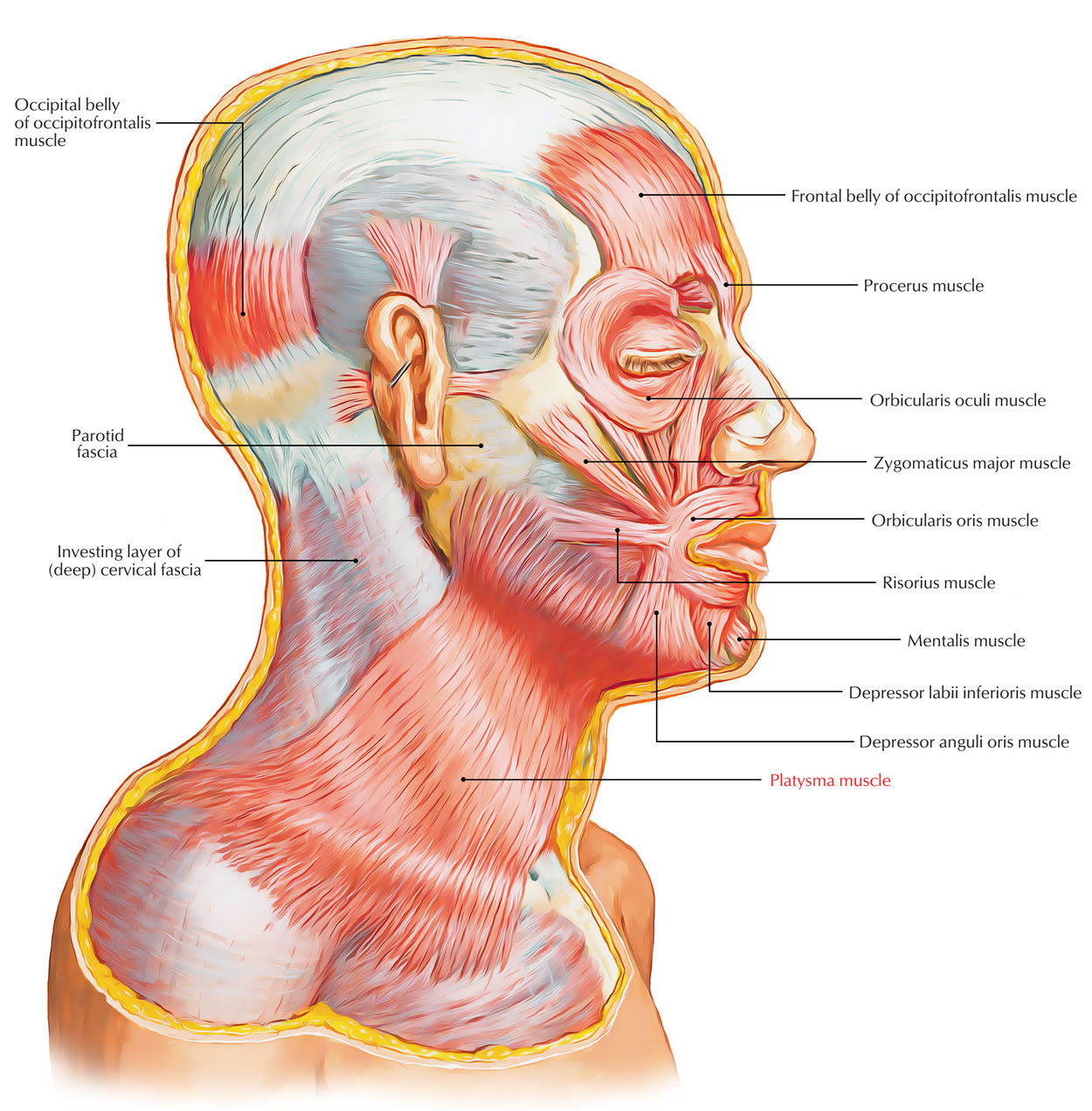
Which muscle tenses the skin of the neck when men shave their beard?
Platysma m
This muscle is known as the smiling muscle
Zygomaticus m
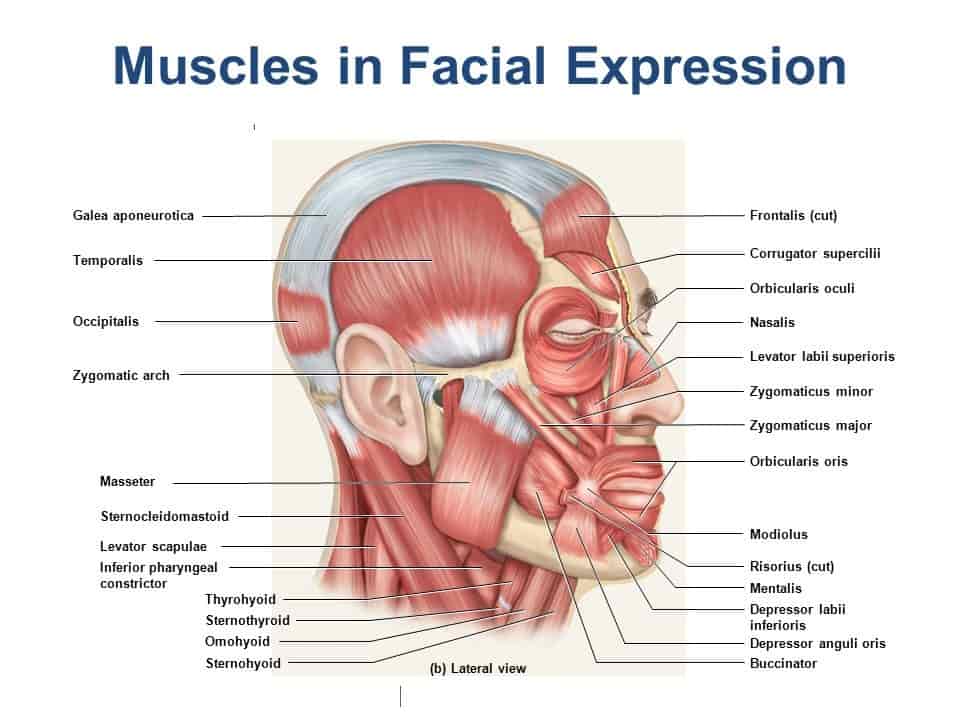
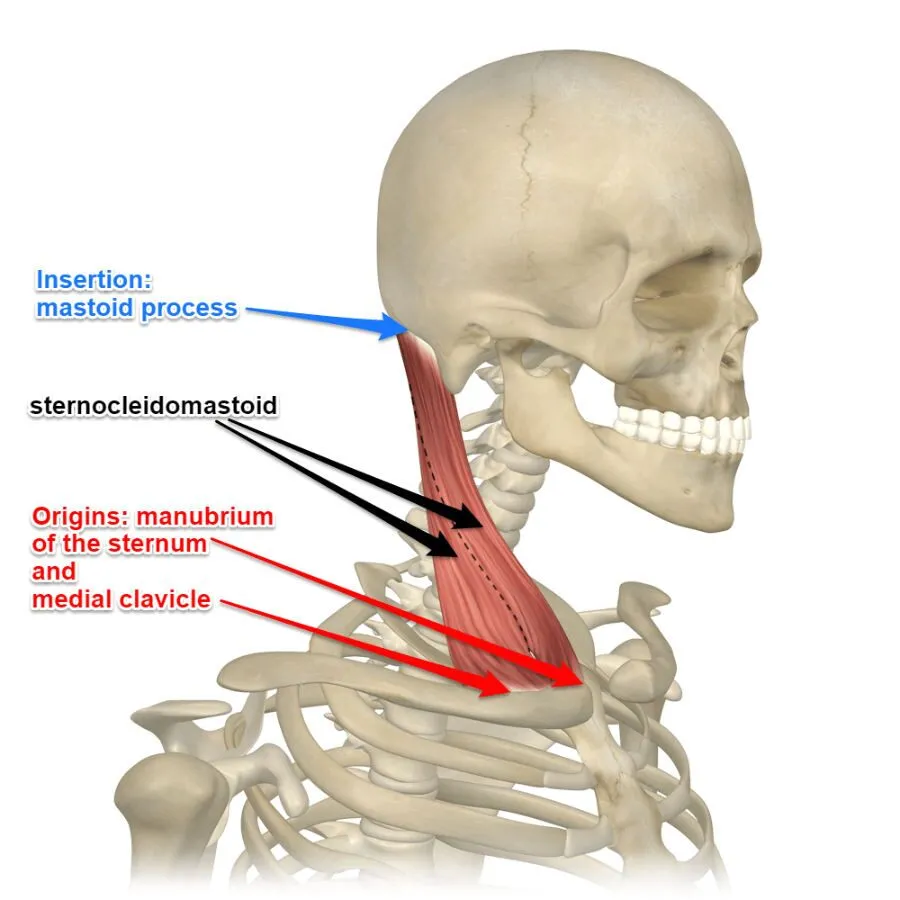
What are the origin and the insertion of the Sternocleidomastoid muscle?
Origin
• sternal head: anterior surface of the manubrium of the sternum
• clavicular head: medial third of the clavicle
Insertion
• mastoid process of the temporal bone
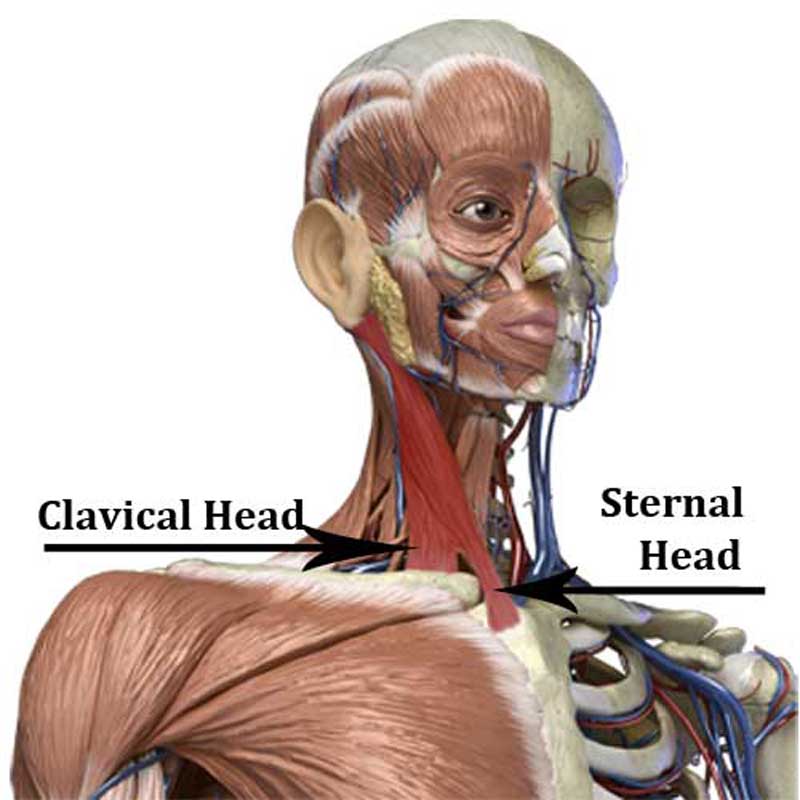
Which structure innervates the Sternocleidomastoid muscle?
Accessory nerve (911) Cranial nerve XI
spinal accessory nerve (cranial nerve XI) — motor innervation
cervical spinal nerves C2–C3 — sensory/proprioceptive fibers

Which muscles are innervated by V3 or the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve?
Masticatory muscles
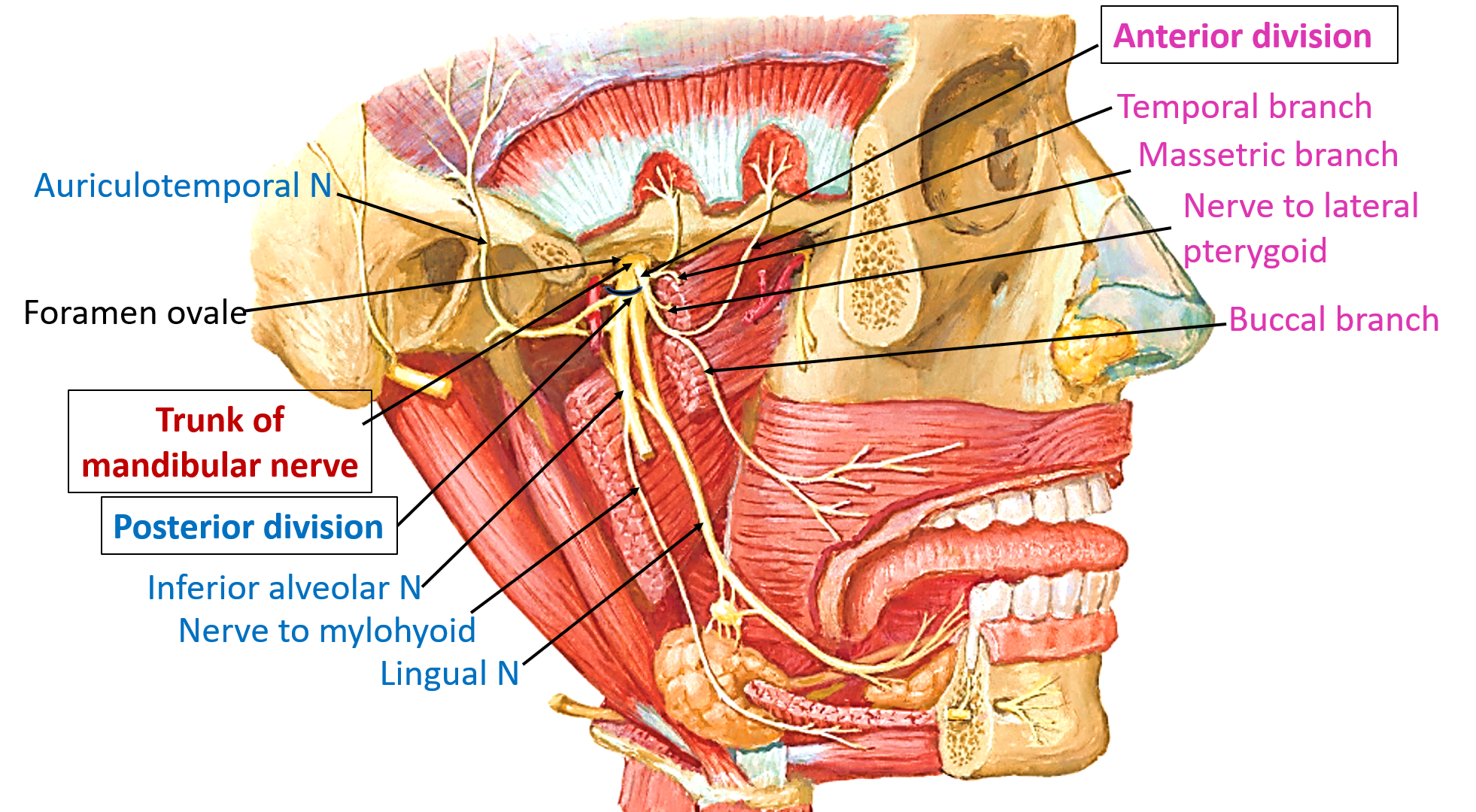
What are the main muscle groups of the head and neck?
Soft palate muscles
Hyoid muscles
Masticatory muscles
Cervical muscles
Facial expression muscles
muscles of the tongue
Pharyngeal muscles
Mention the insertion and origin of each masticatory muscle
Masseter
Origin: zygomatic arch and zygomatic bone
Insertion: lateral surface of the ramus and angle of the mandible
Temporalis
Origin: temporal fossa and temporal fascia
Insertion: coronoid process and anterior border of the ramus of the mandible
Medial pterygoid
Origin:
• deep head: medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate (sphenoid)
• superficial head: maxillary tuberosity and pyramidal process of the palatine bone
Insertion: medial surface of the ramus and angle of the mandible (pterygoid tuberosity)
Lateral pterygoid
Origin:
• superior head: greater wing of the sphenoid
• inferior head: lateral surface of the lateral pterygoid plate
Insertion: neck of the mandibular condyle, articular disc, and capsule of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
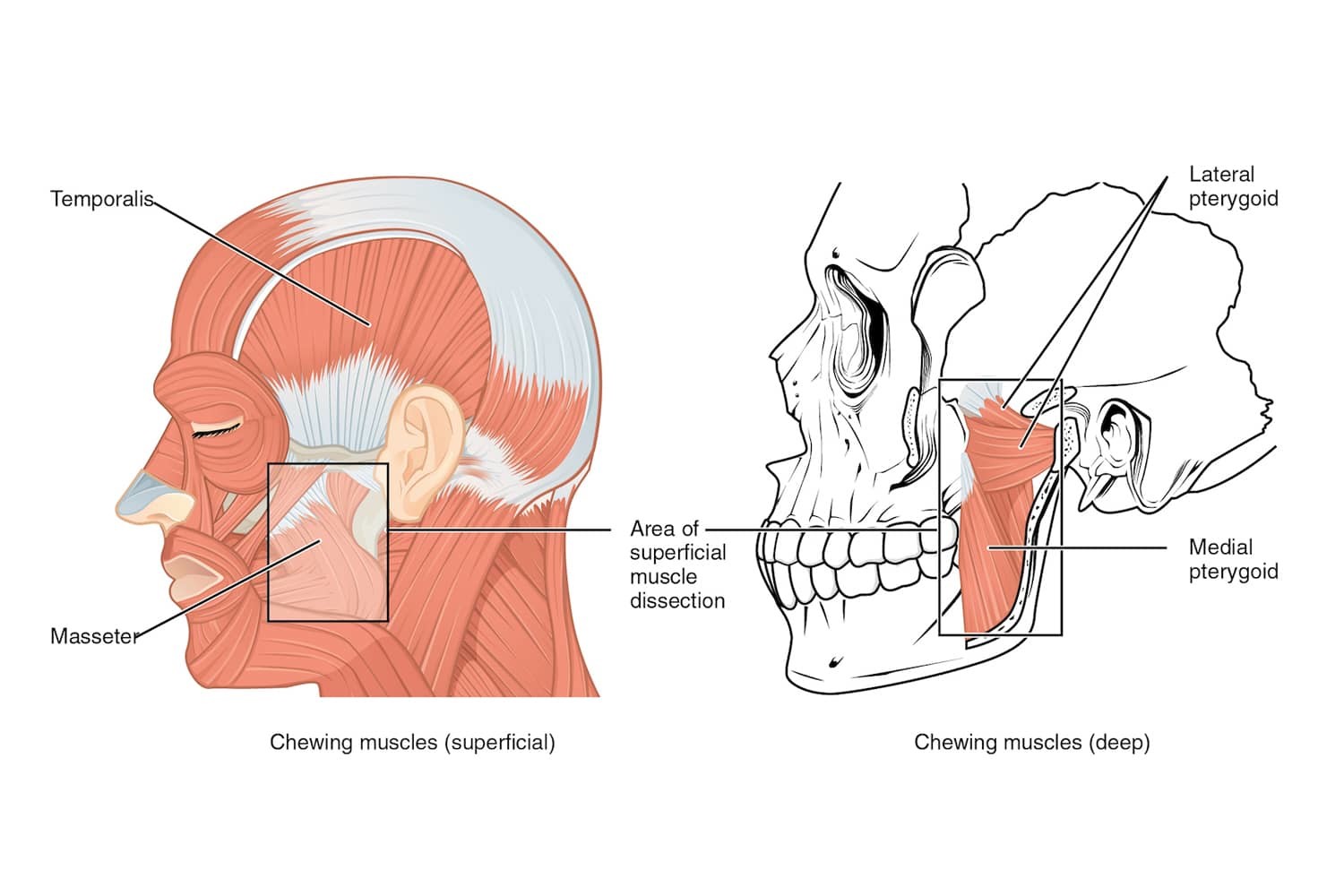
What are the main masticatory muscles?
masseter
temporalis
medial pterygoid
lateral pterygoid
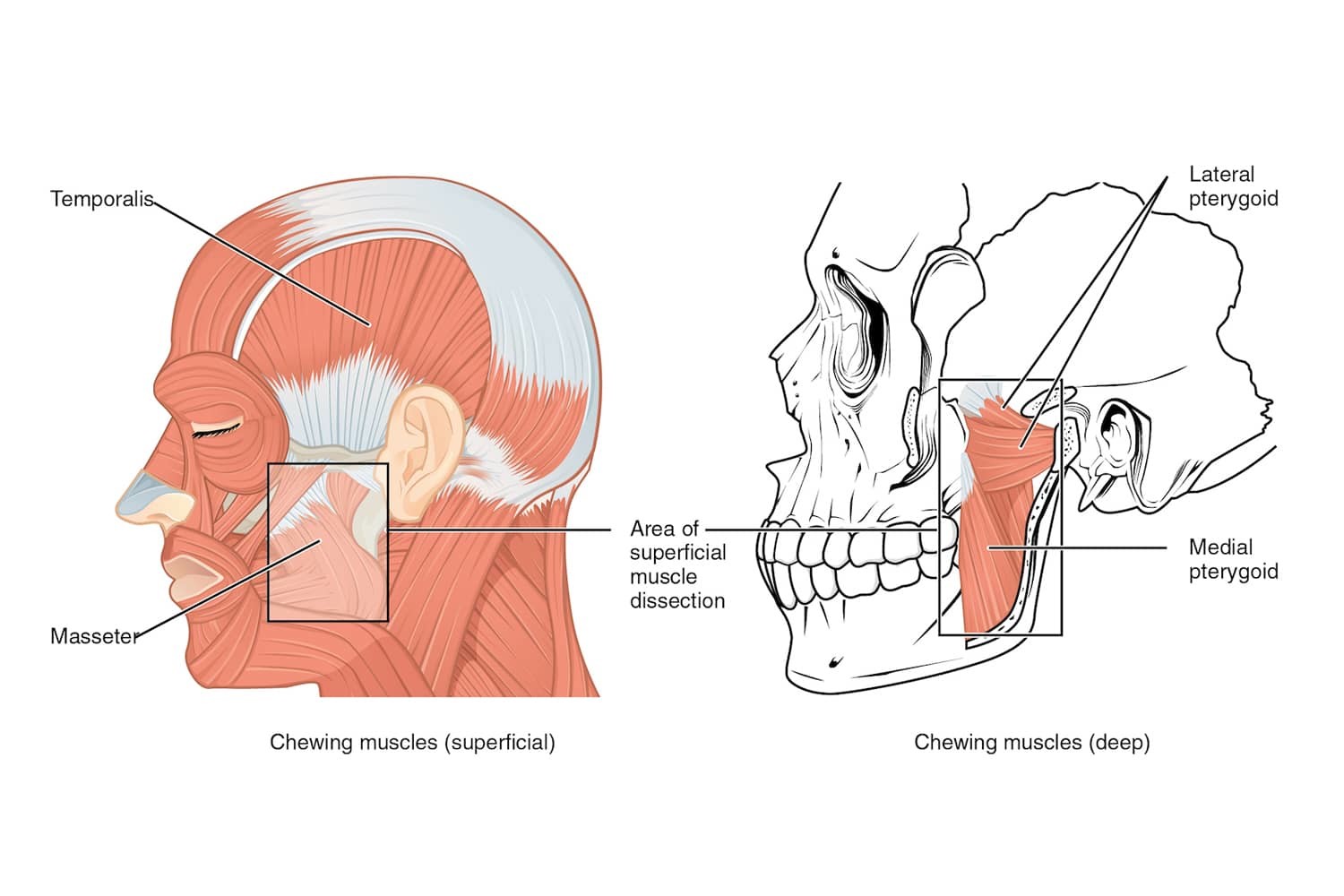
Define process
General terms for any prominences on bony surfaces
What are the most common facial expression muscles?
Orbicularis oris m
Buccinator m
Risorius m
Zygomaticus m
Levator anguli oris m
Depressor anguli oris m
Platysma m
Orbicularis Oculi m
Frontalis m
Mention insert,origin and movement of Orbicularis oris m?
Mention insert,origin and movement of Buccinator?
Mention insert,origin and movement of Risorius
Mention insert,origin and movement of Levator anguli oris
Mention insert,origin and movement of depressor anguli oris
T or F The innervation of all facial expression muscles is by the fifth cranial nerve?
False.
Innervation of all facial expression muscles is by the cranial nerve VII
Which bone does not articulate with any other bones?
Hyoid bone
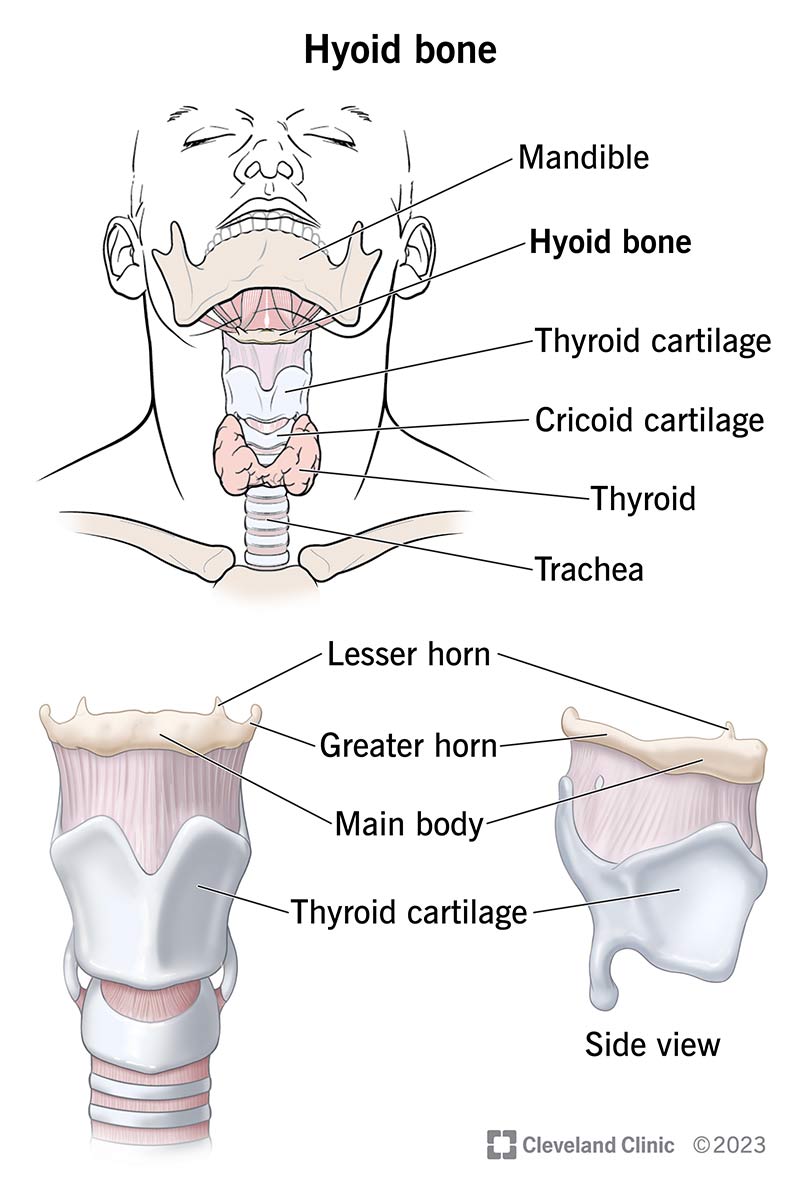
Which muscle makes up the floor of the mouth?
Mylohyoid muscle
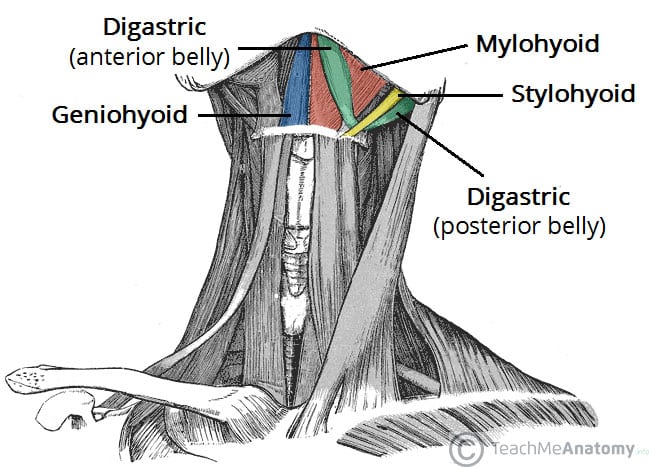
True or False: ALL hyoid muscles insert into the same named bone
True
Mention all suprahyoid group muscles
Genio+hyoid
Mylo+hyoid (Mylove)
Stylo+myoid
Digastric
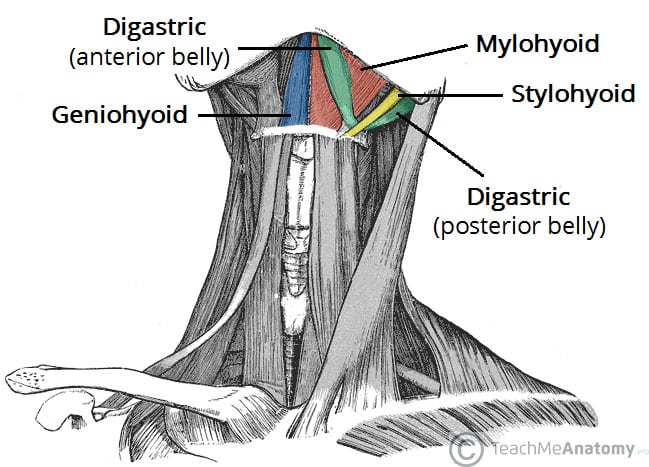
The main functions of the hyoid muscles are ______ and _______
Swallowing and mastication
The hyoid muscles are divided into: ______ and _______
Suprahyoid muscles and Infrahyoid muscles
The muscles of the infrahyoid muscle group are:
un homosexual externo tiró (omo,sterno, thyro)+hyoid
Sternothyroid muscle
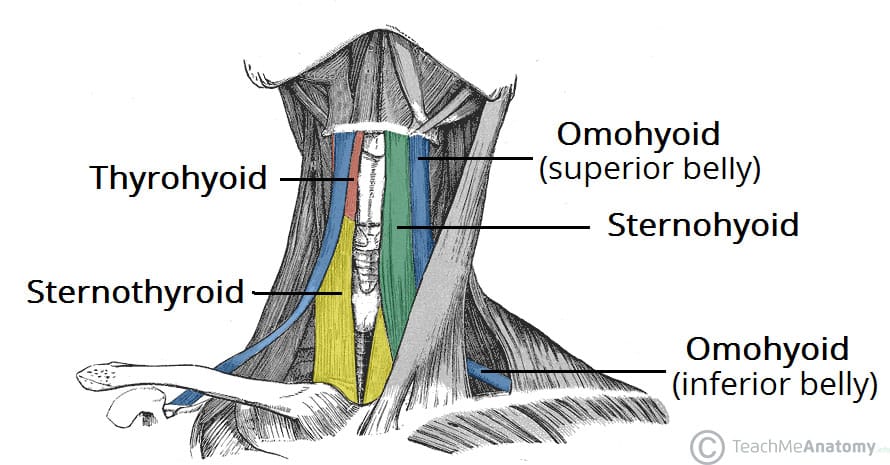
The muscle of the infrahyoid group muscle are innervated by C#_ to C#_
C1 to C3
Mention the action and function of both hyoid muscle groups
Suprahyoid group and infrahyoid group both function in swallowing or deglutition.
In addition, the infrahyoid muscle group acts in the speech.
Suprahyoid muscles=depression of the mandible
Infrahyoid muscles= stabilizes the hyoid bone
Mention innervation for geniohyoid muscle
C1 (via cranial nerve XII)
Mention the innervation for digastric muscle
V3 and VII
Mention the innervation for the mylohyoid muscle
V3
Mention the innervation for the stylohyoid muscle
VII

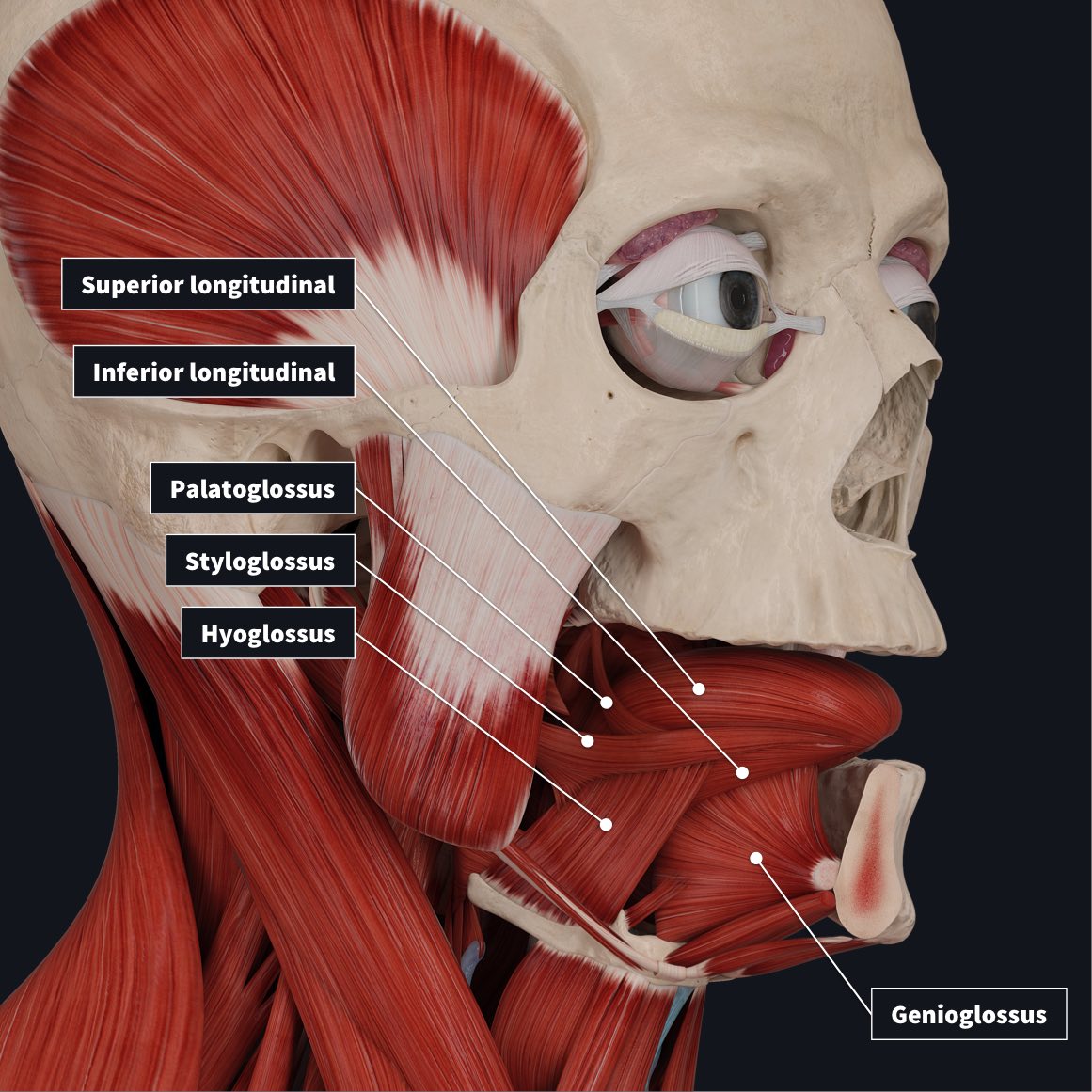
What are the intrinsic muscles of the tongue and their function?
Superior longitudinal
Inferior longitudinal
Transverse muscles
Vertical muscles
They give shape and size to the tongue, guide our speech, eating and swallowing.
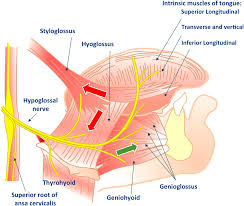
Which nerve innervates the intrinsic muscles of the tongue? Do they have motor or sensory innervation or both?
They are innervated by hypoglossal nerve or cranial nerve XII. They have motor innervation ONLY
Which muscles of the tongue provide shape and size to the tongue in addition to guiding our speech, eating and swallowing?
Intrinsic nerve
Mention the three pairs of extrinsic muscles
Genio and Stylo +glossus (2)
Hyoglossus (from hyoid bone to tongue)
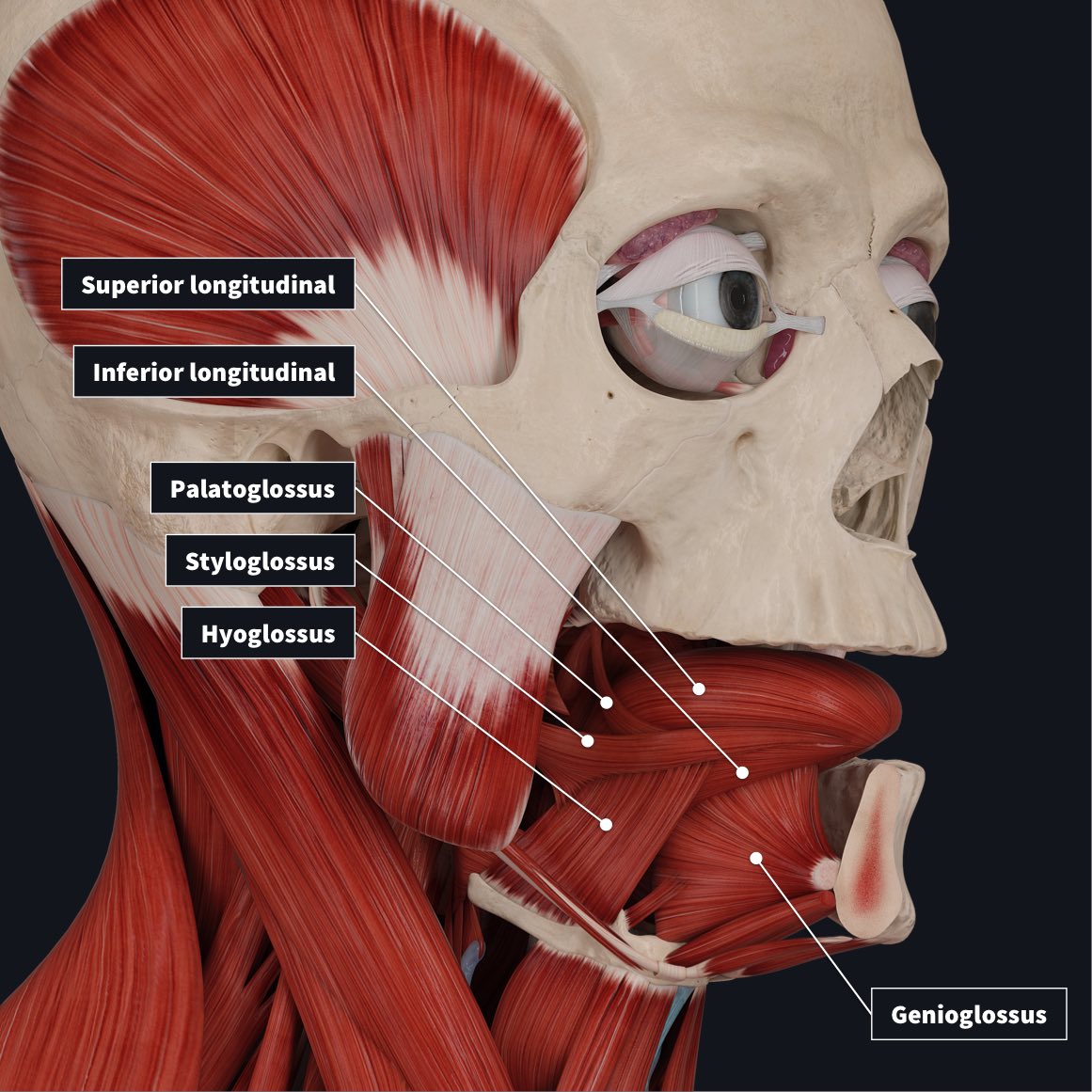
Mention each function of the extrinsic muscles of the tongue
Geniohyoid-G=gear=forward or protrusion of the tongue
Stylohyoid-S=retraction of the tongue
Hyoid-Depression of the tongue
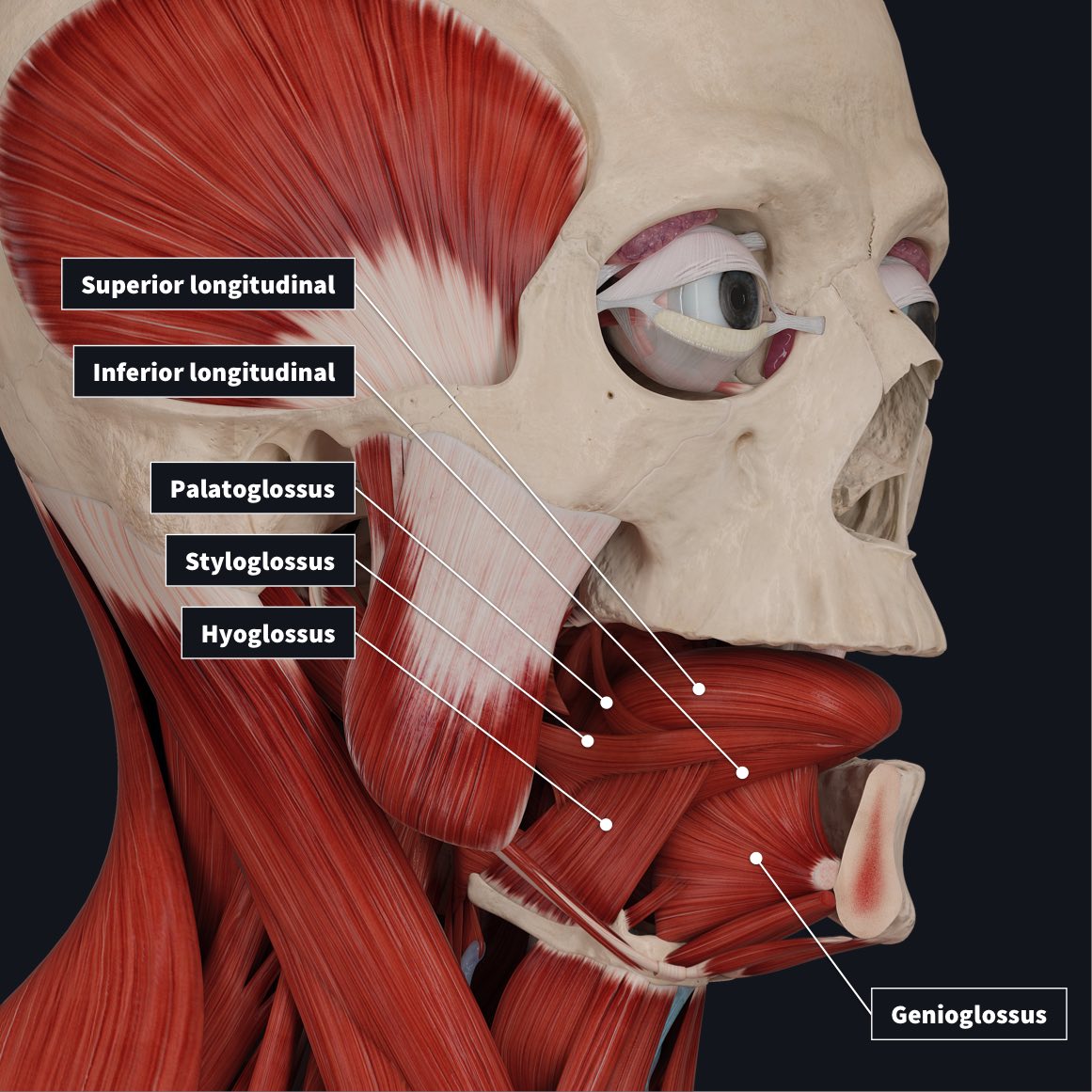
Which nerve/s innervate the extrinsic muscles of the tongue?
motor innervation: cranial nerve XII
sensory innervation= anterior 2/3’s V3 and cuerda timpánica (chorda tympanic) posterior 1/3 by cranial nerve IX (glossopharyngeal)

Mention the name/location of all papilla found on the tongue
Which papilla are most abundant and which are the fewest?
Which papilla are associated with hairy and geographic tongues?
Which papilla contains no taste buds, where are they located?
Mention main pharyngeal muscles
Soft palate muscles: tensor veli palatine, levator veli palatine, palatoglossous muscle and palatal pharyngeus muscle
Uvula muscles
Pharyngeal constrictor muscle
Stylopharygeus muscle
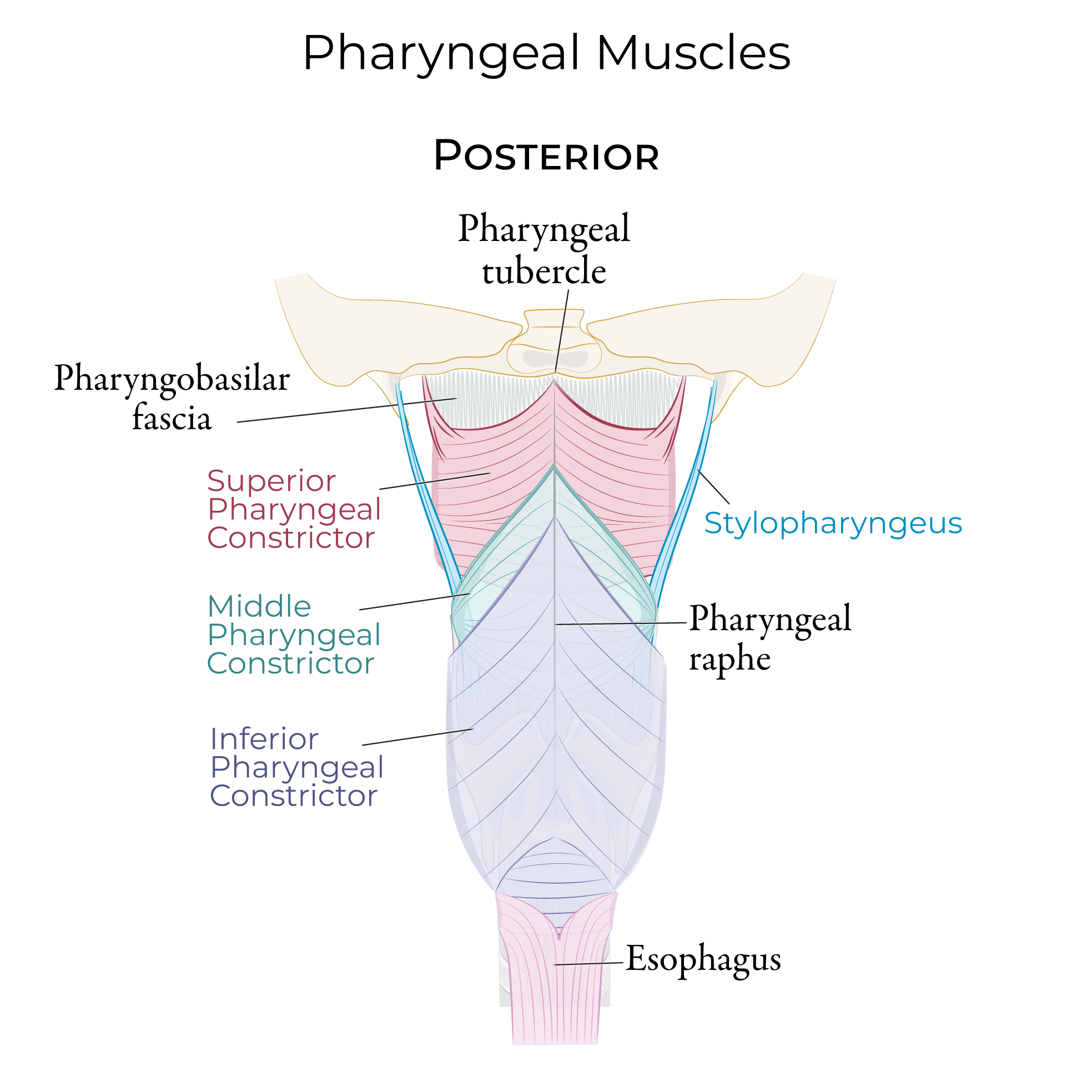
Mention the function and innervation of stylopharygeus muscle
Function: Lifting and widening of the phraynx
Innervation: Cranial nerve IX (Glossopharyngeus)
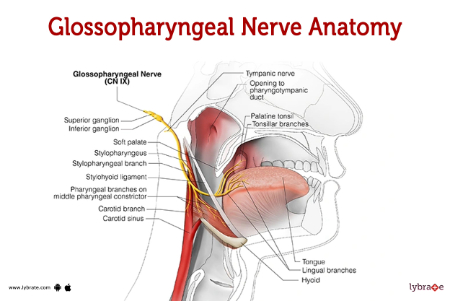
Mention the function and innervation of pharyngeal constrictor muscle
Pharyngeal plexus like most pharyngeal muscles except for stylopharyngeus muscle
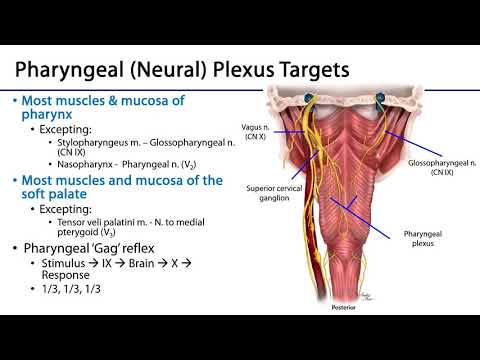
Which nerve innervates most soft palate and uvula muscles?
Pharyngeal plexus
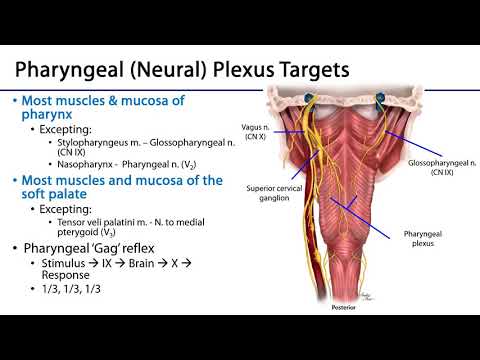
Which nerve innervates tensor veli palatine
V3
Which soft palate muscle initiates swallowing?
Palatoglossus muscle (lifts the base of the tongue, depresses the soft palate)

Mention main soft palate muscles, function and innervation
Palatoglossus muscle- they lift the base of the tongue and depress the soft palate initiating swallowing
Other soft palate muscles include: levator and tensor veli palatine muscles and the palatal pharyngeus muscle
Which oral cavity fold extends from the junction of hard and soft palates to the mandible, and is referred to as a raphe
Pterygomandibular fold or raphe