bio-DNA quiz
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1
New cards
Genetics
the science that studies how characteristics (or traits) get passed from one parent to offspring (called inheritance)
2
New cards
what year(s) did scientists determine that DNA was the molecule that stored genetic information
the 1920's
3
New cards
DNA stands for
Deoxyribonucleic acid
4
New cards
DNA is composed of...
a string of nucleotides
5
New cards
DNA strings are made of 3 parts…
5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose, A phosphate group, A nitrogen base (4 choices; Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thymine)
6
New cards
Edwin Chargaff
determined that A=T & G=C, base pairing system
7
New cards
Rosalind Franklin
used an X-ray to show that 2 DNA strands were twisted
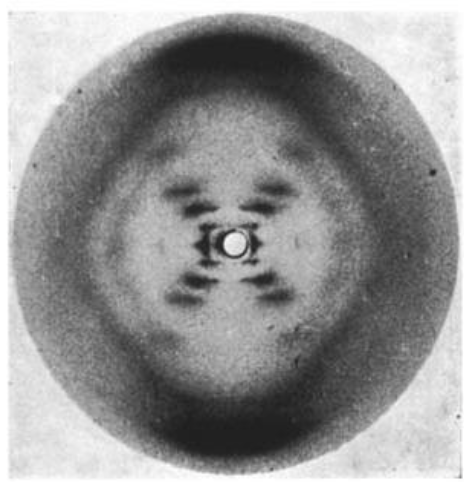
8
New cards
Francis Crick & James Watson
Used Franklin’s picture to create the first model of DNA
9
New cards
Adenine pairs with…
thymine
10
New cards
Guanine pairs with…
cytosine
11
New cards
The shape of DNA
double helix
12
New cards
double helix
\-composed of alternating deoxyribose sugar and phosphate groups
\-commonly called the “sugar-phosphate backbone”
\-looks like a twisted ladder
\-The rungs of the ladder are made of nitrogen bases
\-WEAK SO THAT THEY CAN BREAK AND COME BACK TOGETHER
\-commonly called the “sugar-phosphate backbone”
\-looks like a twisted ladder
\-The rungs of the ladder are made of nitrogen bases
\-WEAK SO THAT THEY CAN BREAK AND COME BACK TOGETHER
13
New cards
gene
a segment of DNA that codes for the protein, thereby causing a genetic characteristic of a trait, ike Hair color, eye color, or height
14
New cards
cells are constantly...
growing and dividing, which must be accomplished without breaking the DNA strands
15
New cards
In order to protect the DNA….
it is tightly coiled around proteins called **histones** and condensed into **chromosomes**
16
New cards
DNA can....
tell many things about a person and genetic differences between people are very important so diseases are not as deadly
17
New cards
DNA replication
when a cell divides, DNA must be copied, requires the strands to be unwound first
18
New cards
replication fork
\-After the DNA is unwound from the histones, an enzyme called helicase “unzips” the two strands of DNA
\-This location is known as the replication fork.
\-This location is known as the replication fork.
19
New cards
DNA polymerase
brings nucleotides to match one of the DNA strands (known as the parent strand)
20
New cards
Stem cell(s)
a cell that has not been assigned a part yet
21
New cards
DNA replication is a semi-conservative process because....?
only half of each parent strand remains in the new DNA molecule
22
New cards
SUMMARY OF DNA REPLICATION:
To make it easy to move DNA without damage, it is wrapped around __**histones**__ and condensed into __**chromosomes**__. To copy the DNA (called DNA __**replication**__), enzymes separate the two strands and use one side as the blueprint to make a __**complementary**__ strand.
23
New cards
SUMMARY OF DNA:
DNA is the molecule that stores genetic information for cells. It is shaped like a double helix with bases on the inside. These match in pairs with A bonding with T and C bonding with G
24
New cards
histone
a group of basic proteins that help protect DNA
25
New cards
chromosome
\-a structure of nucleic acids and protein
\-found in the __nucleus__ of most living cells
\-carries genetic information in the form of genes
\-found in the __nucleus__ of most living cells
\-carries genetic information in the form of genes
26
New cards
complementary DNA strands
two strands of DNA with corresponding bases/chains (google definition: (either of the two chains that make up a double helix of DNA, with corresponding positions on the two chains being composed of a pair of complementary bases)