respiration module 5
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
what are the 3 Co-enzymes in respiration
coA
FAD
NAD
function of coA
Accepts acetate ( 2 C) forming acetyl coA during link reaction
Acetyl coA breaks down → 2C ( kreb cycle)
what vitamins synthesis the co-enzymes
NAD → B3
FAD → B2
coA → B5
Function of FAD
helps dehydrogenases in krebs cycle
how many ATP molecules does FAD produce in oxidative phosphorylation ?
1.5 ATP
differences between NAD and NADP
NADP contains additional phosphate group on ribose sugar
definition of a coenzyme
non protein molecule that allows a enzyme to work
what do FAD and NAD act as
hydrogen carriers to other molecules
mitochondrion structure ( Image)
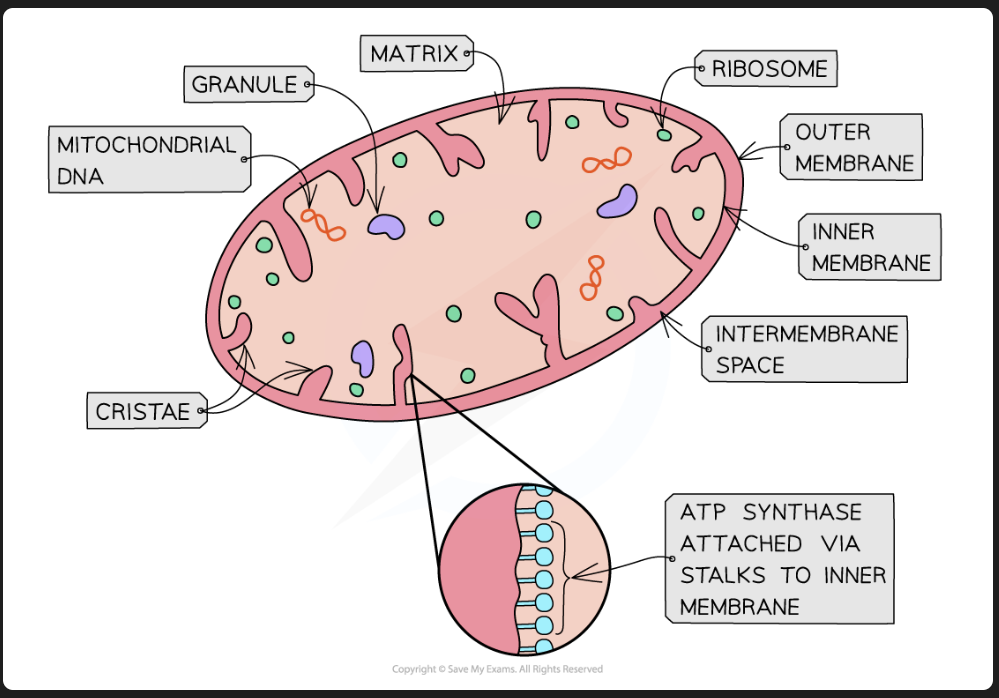
adaptation of Mitochondrion
folded cristae increases SA : Vol ratio to maximise respiration
what are the 4 stages of Aerobic respiration
1) Glycolysis
2) the Link reaction
3) Krebs cycle
4) Oxidative phosphorylation
acronym to remember stages of Respiration
Girls Lick Kids Often
where does Glycolysis occur
Cytoplasm
where does the Link reaction and krebs cycle
matrix of Mitochondrion
role of respiration
makes ATP to releases energy from respiratory substrates
examples of respiratory substrates
glucose
fatty acids
amino acids
Why does glycolysis occur in cytoplasm
glucose cant cross outer mitochondrion membrane
pyruvate can
why does glycolysis happen in both anaerobic and aerobic respiration
anaerobic process → doesn’t require Oxygen
function of glycolysis
makes pyruvate from glucose
how many carbons does pyruvate contain
3 C
what type of process is Phosphorylation
active process requires ATP
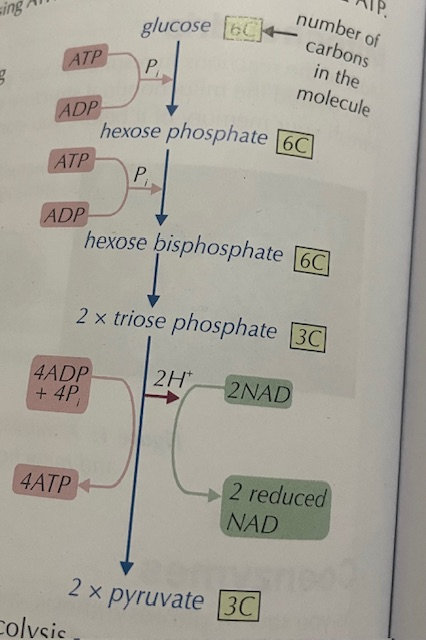
glycolysis process
Glucose → Hexose phosphate → Hexose bisphosphate → 2x TP → 2x Pyruvate
How to remember glycolysis intermediates
Gross → glucose
people → Phosphate ( Hexose)
beat → Bisphosphate ( Hexose)
To → TP
Porn → Pyruvate
Which stages of Glycolysis does phosphorylation happen
Glucose → hexose Phosphate → Hexose Biphosphate
what happens to TP in Glycolysis
TP gets oxidised → loses 2 H⁺ to form Pyruvate
2 H⁺ reduce 2 NADs to 2 NADH
what are the products of Glycolysis
2 ATP
2 NADH
2 pyruvate
Glycolysis how many ATPs are made and why
2 ATP
phosphorylation of Glucose to Hexose Bisphosphate → use 2 ATP
Oxidation of TP to pyruvate makes 4 ATP
2 stages of glycolysis
active phosphorylation of Glucose to Hexose Bisphosphate
Oxidation of TP to 2 pyruvates
what do the products of Glycolysis go
2 NADH → Oxidative phosphorylation
2 pyruvate → actively transported to Link reaction
2 ATP → used for energy
where does Oxidative phosphorylation occur
Inner mitochondrial membrane
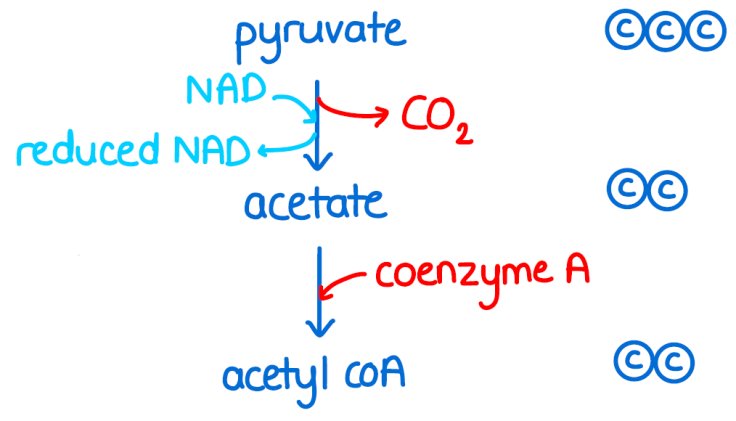
function of the Link reaction
Converts Pyruvate → Acetyl coA
how many carbons does acetate contain?
2C
what happens in the Link reaction
Pyruvate is decarboxylated and Oxidised
loses Carbon → forms CO₂
loses H⁺ → forms NADH
forms acetate which combines to CoA
forming Acetyl CoA
how many times does the Link reaction and krebb cycle for 1 molecules of glucose
Twice
products of Link reaction
2x Acetyl CoA → goes to krebs cycle
2 NADH
2 CO₂
what happens to all NADH and FADH formed
go to oxidative phosphorylation
what happens to CO₂ formed in Link reaction
excreted as a waste product
which stages of Respiration produce CO₂
Link reaction
Krebs cycle
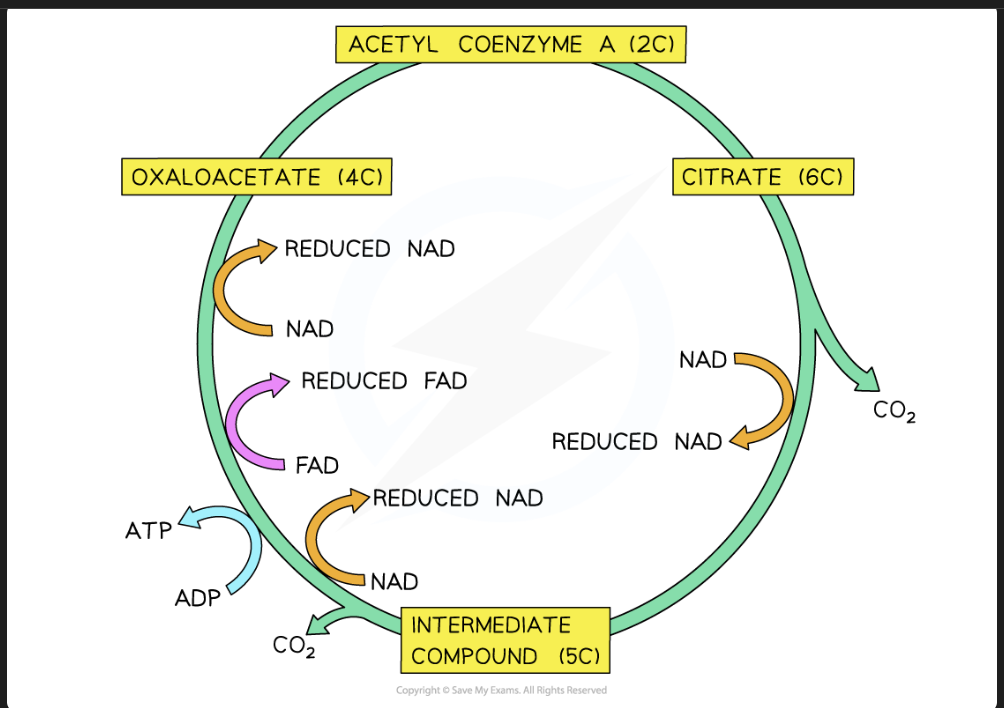
stages of Krebb cycle
Formation of Citrate
Formation of 5 carbon compound
Regeneration of oxaloacetate
Krebb cycle formation of citrate
acetate (2C) combines with oxaloacetate (4C)→ citrate ( 6C)
CoA leaves back to link reaction
Krebb cycle Formation of 5 carbon compound
citrate ( 6C) is decarboxylated and dehydrogenated → 5 carbon compound
produces CO₂
H⁺ forms NADH
Krebb cycle Regeneration of Oxaloacetate
5 carbon compound converted to Oxaloacetate
decarboxylation → loses CO₂
dehydrogenation → 2 NADH and 1 FADH
ATP is formed ( substrate level phosphorylation)
when does substrate level phosphorylation happen in respiration
Krebs cycle
how many times does the krebs cycle turn for 1 glucose molecule
twice
products of 1 turn of krebs cycle
1 coA
Oxaloacetate
2 CO₂
1 ATP
3 NADH
FADH
Oxidative phosphorylation process
NADH and FADH are oxidised → H₂ → 2H⁺ + 2e⁻
e⁻ move along electron transport chain → releases energy for electron carriers to pump protons from matrix to intermembrane space
creates a proton electrochemical gradient
protons move back into mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase causes
ATP synthase to convert ADP + Pi → ATP
( process is chemiosmosis)
at end of chain protons electrons and O₂ combine to form water ( 2 H₂O)
Role of O₂ in respiration
what is the final electron acceptor in Oxidative phosphorylation
Krebbs cycle image
Link reaction image
Glycoly sis Reaction Image
how many ATP molecules are made for each 1 molecule of glucose
28 ATP
why does substrate level phosphorylation happen in Krebb cycle
Phosphate group combines with ADP from intermediate
Oxidative phosphorylation image
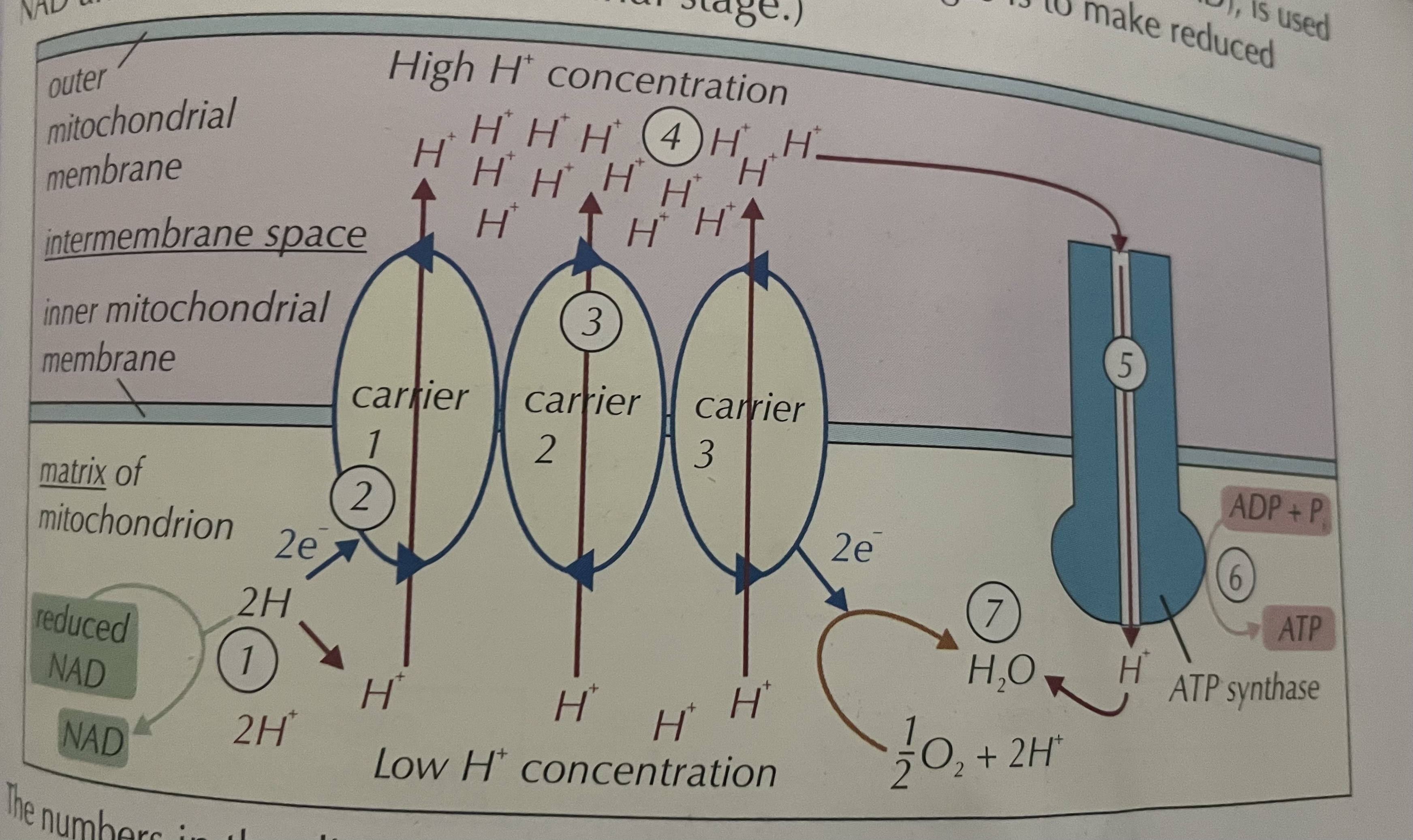
2 quantitative changes in intermembrane space as a result of oxidative phosphorylation
PH decreases → more acidic
increase in Positive charge → higher H⁺ conc
why does aerobic respiration yield fewer molecules than theoretical maximum
ATP is used in the shuttle mechanism transport NADH into membrane
proton leakage from matrix to intermembrane
Structural features of mitochondria that show its evolved from bacteria
Double membrane
Mitochondria has DNA and ribosomes
what stage of respiration happens in anaerobic and aerobic respiration
Glycolysis
what are the two types of Anaerobic respiration
Alcoholic fermentation
Lactate fermentation
similarities between Alcoholic and lactate fermentation
Both occur in cytoplasm
both produce 2 ATP
glycolysis occurs in both
differences between Alcoholic and lactate fermentation
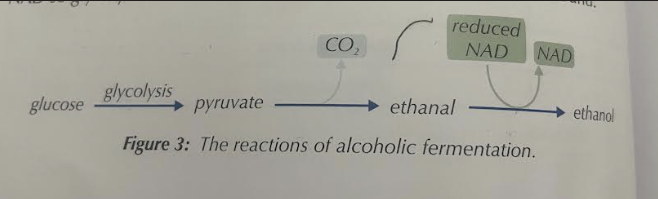
Alcoholic → occurs in yeast cells, produces ethanol, produces CO₂
Lactate → Occurs in mammals, produces lactate and produces ethanal intermediate
what happens to excess lactate in body
Converted into glucose by gluconeogenesis in liver
Why can glycolysis occur without O₂
Glycolysis requires NAD
Production of lactate regenerates NAD
How is lactate formed in Lactate fermentation
NADH ( from glycolysis) reduces pyruvate → forms lactate and NAD.
Advantages of Glycolysis being anaerobic
small amounts of ATP can be produced keeping biological processes (Muscle contractions ) going
Lactate fermentation ( Image)
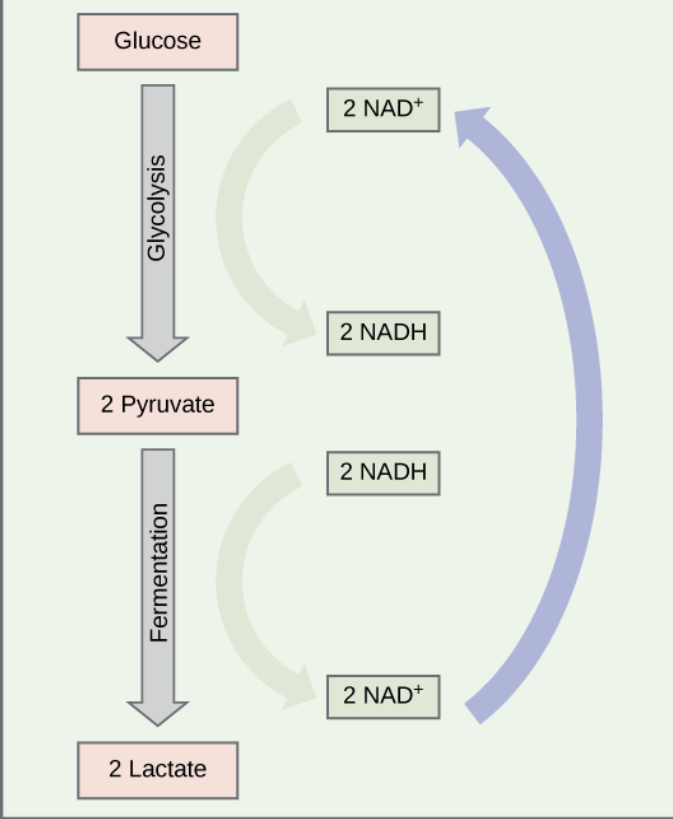
Advantages of Anaerobic respiration
provides a Survival Advantage in low O₂ environments
Produces ATP quickly
allows for muscle contractions ( No O₂)
Regenerates NAD so glycolysis can continue
How is ethanol formed in Alcoholic fermentation
Pyruvate loses CO₂ → forms ethanal → NADH reduces ethanal → Ethanol + NAD ( reused in glycolysis)
Alcoholic fermentation ( Image)
Why does Anaerobic respiration have a lower ATP yield then Aerobic
Anaerobic respiration → only glycolysis occurs ( produces 2 atp)
No krebs cycle and Oxidative phosphorylation → require O₂
Why does NADH produce more ATP then FADH
NADH → Electrons flow through more electron carriers then FADH
why is lactate ( lactate acid) toxic?
Denature enzymes and proteins → muscle fatigue
decrease cell pH
Why is lactate fermentation unsustainable ?
ATP is used to convert Lactate into Glucose
net loss of ATP
What are respiratory substrates
Biological molecules that can be broken down in respiration to release energy
How can triglycerides ( Lipids) be used as Respiratory substrates
Broken down into glycerol + 3 fatty acids
glycerol → pyruvate enters krebb cycle
fatty acids undergo beta oxidation → acetyl CoA → generates many ATP
Disadvantages of using proteins as respiratory substrate
less proteins for enzymes → less enzymes
deamination uses ATP - decreases net ATP production
what are the respiratory substrates
Carbohydrates
proteins
Lipids
where do proteins and lipids enter respiration
In krebs cycle
what is the RQ of the respiratory substrates
Carbohydrates → 1
Lipids → 0.7
Proteins → 0.8 - 0.9
How can proteins be used as Respiratory substrates
broken down into amino acids ( deamination) → Pyruvate
(Respiratory substrate ) Hydrogen atom amount and ATP production relationship
Higher the Hydrogen atoms per unit mass = More NADH and FADH → more ATP generated
Respiratory quotient equation
(Molecules of CO₂ released / Molecules of O₂ consumed)
Uses of a respiratory quotient
Tell us type of respiratory substrate used
type of respiration ( anaerobic or aerobic)
what does a RQ of 1 or below show
Aerobic respiration
What does a RQ of 1 or above show
Respiring anaerobically and aerobically
why do plants have Low RQ
CO₂ released in respiration is being used in photosynthesis
Similarities between Yeast and mammal respiration
Both use glucose
NADH gets oxidised
Why do lipids have the highest energy value released
Most hydrogen atoms per unit mass of respiratory substrate ( named)
what does Beta Oxidation produce
FADH
NADH
What does Q10 mean / show
every 10°C increase the rate x2
what does a negative distance on respirometer mean
liquid/ meniscus moves backwards/downwards
RQ value and C-H bond ratio
Lower the C-H bonds = the higher the RQ value
( less energy required to break bonds)