PCEU 507 Exam 4 Review
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are the three types of tablet coatings that we discussed?
a. Sugar
b. Film
c. Enterica
d. All of the above
d. All of the above
Which of the following tablet excipients is an enteric coating (select all that apply)?
a. Methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate copolymer
b. Sodium lauryl sulfate (SDS)
c. Cellulose acetate phthalate
d. Titanium dioxide
e. Talc
f. Eudragit
g. Sodium chloride
h. Polyetylene glycol
i. Starch
a. Methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate copolymer
c. Cellulose acetate phthalate
f. Eudragit
What is the approximate residence time of a tablet in the stomach and small inestines (SmI)?
a. Stomach: 12 hrs; SmI: 16 hrs
b. Stomach: 1 hr; SmI: 4 hrs
c. Stomach: 0.25 hrs; SmI: 12 hrs
d. Stomach: 6 hrs; SmI: 6 hrs
b. Stomach: 1 hr; SmI: 4 hrs
What is the purpose(s) of an enteric coating?
a. It allows water molecules to enter the tablet rapidly
b. It allows the tablet to glide smoothly through the stomach and reach the small intestines with little resistance
c. It protects the API from acid degradation while dissolving in the higher pH small intestines
c. It protects the API from acid degradation while dissolving in the higher pH small intestines
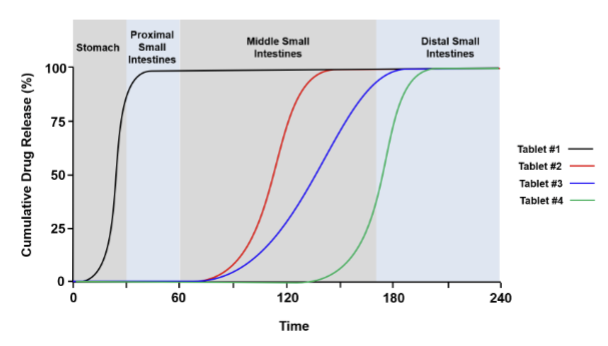
The following cumulative drug release (%) vs time plots for 4 different tablet formulations is provided
below. Identify the tablet formulations that contain an enteric coating? Tablet 1, 2, 3, and 4.
Tablets 2, 3, and 4
How does increasing hydroxypropyl methycellulose (HPMC) concentration affect atenol release
rates?
a. It increases the release rate because it improves solubility
b. It decreases the release rate because of the formation of a thicker gel layer thus increasing viscosity and lowering drug diffusion
c. HPMC increases Atenolol release due to the reduced viscosity of the gel layer and increased porosity, facilitating faster drug diffusion.
d. The release rate of Atenolol decreases as the HPMC concentration increases. This is due to HPMC’s hydrophobic nature, which limits water penetration and slows the dissolution process, making the release more sustained
b. It decreases the release rate because of the formation of a thicker gel layer thus increasing viscosity and lowering drug diffusion
How does ethylcellulose (EC) matrices affect drug release rates?
a. HPMC increases Atenolol release due to the reduced viscosity of the gel layer and increased porosity, facilitating faster drug diffusion.
b. The release rate of Atenolol decreases as the EC concentration increases. This is due to EC’s hydrophobic nature, which limits water penetration and slows the dissolution process, making the release more sustained
c. The release rate of Atenolol decreases as the EC concentration increases. This is due to EC’s hydrophobic nature, which limits water penetration and slows the dissolution process, making the release more sustained
d. It increases the release rate because it improves solubility
c. The release rate of Atenolol decreases as the EC concentration increases. This is due to EC’s hydrophobic nature, which limits water penetration and slows the dissolution process, making the release more sustained
How does adding lactose into a HPMC matrix increase Atenolol release?
a. Lactose increases Atenolol release due to the reduced viscosity of the gel layer and increased porosity, facilitating faster drug diffusion.
b. The release rate of Atenolol decreases as the Lactose concentration increases. This is due to Lactose’s hydrophobic nature, which limits water penetration and slows the dissolution process, making the release more sustained
c. Lactose decreases the release rate because of the formation of a thicker gel layer thus increasing viscosity and lowering drug diffusion
d. It increases Atenolol release due to an enhanced erosion effect
a. Lactose increases Atenolol release due to the reduced viscosity of the gel layer and increased porosity, facilitating faster drug diffusion.
Which of the following is not a principal mechanism of aerosol particle deposition in the airway?
a. Interial impaction
b. Gravitational sedimentation
c. Brownian motion
d. Subliminal desication
d. Subliminal desication
What is the critical parameter dictating the fate of inhaled particles in the lung?
a. Particle size
b. Particle size
c. Particle size
d. All of the above (Particle size! :D)
d. All of the above (Particle size! :D)
What are the three main categories of pulmonary drug delivery devices?
a. Pressurized metered dose inhalers (MDIs)
b. Dry powder inhalers (DPIs)
c. Nebulizers
d. Vape pen
a. Pressurized metered dose inhalers (MDIs)
b. Dry powder inhalers (DPIs)
c. Nebulizers
Which of the following is considered an advantage of a DPI?
a. Portability
b. Low cost
c. Propellant free
d. Breath activated
a. Portability
c. Propellant free
d. Breath activated
Which of the following is considered an disadvantage of a DPI?
a. Inefficient drug delivery
b. Must coordinate with inhalation and button pushing
c. Dependent on patient’s ability to inhale
d. Affected by humidity
c. Dependent on patient’s ability to inhale
d. Affected by humidity
Which of the following is considered an advantage of a MDI?
a. Portability
b. Low cost
c. Propellant free
d. Breath activated
a. Portability
b. Low cost
Which of the following is considered a disadvantage of a MDI?
a. Inefficient drug delivery
b. Must coordinate with inhalation and button pushing
c. Dependent on patient’s ability to inhale
d. Affected by humidity
a. Inefficient drug delivery
b. Must coordinate with inhalation and button pushing
What is the typical percent of drug deposited delivered to the lung using a pMDI and DPI?
a. 1%
b. 5%
c. 20%
d. 50%
e. 100%
c. 20%
What are the three potential pathways for absorption of drugs across the skin?
a. Transcellular
b. Transcendental
c. Paracellular
d. Transappendageal
a. Transcellular
c. Paracellular
d. Transappendageal
What are the three primary layers of skin?
a. Epidermis
b. Dermis
c. Transdermis
d. Hypodermis
a. Epidermis
b. Dermis
d. Hypodermis
he key physiochemical properties of APIs that affect dermal absorption are?
a. <600 Da molecular weight
b. Log P between 1 and 3
c. Negatively charged drugs below skin pI
d. All of the above
d. All of the above
What are the four USP ointment groups?
a. Oleaginous
b. Absorption base
c. Water removal base
d. Water soluble base
e. All of the above
e. All of the above
What best described insulin:
a. A RNA-based drug of approximately 5800 Da molecular weight
b. A small molecule hormone synthesized in ancient Egypt
c. A protein hormone with two chains connected via disulfide bonds
d. A large 150kDa protein produced by immune cells
c. A protein hormone with two chains connected via disulfide bonds
What is the mechanism of action for how insulin regulates glucose levels?
a. It binds glucose in the blood
b. It transforms glucose into fructose which is readily cleared by the liver
c. It binds the insulin receptor triggering the biosynthesis of glucose transport proteins (e.g., GLUT 4)
c. It binds the insulin receptor triggering the biosynthesis of glucose transport proteins (e.g., GLUT 4)
What is the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes
a. T1D patients can not produce sufficient glucose whereas T2D patients can not produce sufficient insulin
b. T1D patients can not produce sufficient insulin whereas T2D patients develop insulin resistance
c. T1D patients develop diabetes later in life whereas T2D patients are born with diabetes
b. T1D patients can not produce sufficient insulin whereas T2D patients develop insulin resistance
When was recombinant insulin first produced for pharmaceutical use?
a. 1978
b. 1983
c. 1922
d. 1999
a. 1978
How have scientists engineered insulin to affect the release rate?
a. Substitute specific amino acids that favor or disfavor multimer association/crystal
formation.
b. Add zinc to the formulation to favor hexamer formation
c. Add phenolic preservatives to favor more stable hexamer formation
d. All of the above
d. All of the above