MARKETS, EFFICIENCY, AND PUBLIC POLICY
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Conditions for markets to work well:
-Private property - the rights to the thing bought/sold
-Institutions e.g. government - enforcing property rights
-Social norms – respecting property rights
-Ability to write complete and enforceable contracts that can be evaluated in a court of law
When do Markets fail?
When property rights are missing, incomplete, or are difficult to enforce with a contract.
Causes of market failure under perfect competition
-External effects
-Asymmetric information
-Incomplete contracts
Possible solutions of market failure
Private bargaining and government policies
What is an externality?
An effect of an economic decision that is not specified as a benefit or liability in the contract
Negative external effect formula
MSC > MPC
What is pareto efficient level
Price = Marginal Social Cost
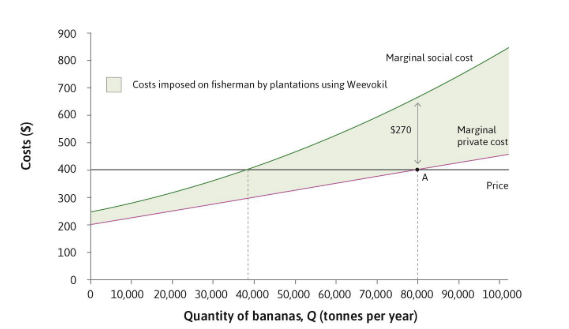
What are the solutions to an externality
Bargaining and compensation
How does solution: Bargaining work
-Legally assign property rights to the externality (e.g. the right to pollute, the right to clean air)
-Private bargaining between parties involved will result in a Pareto-efficient allocation regardless of which party has the property rights, in the absence of transaction costs.
-May be more effective than government intervention because private parties have more of the necessary information.
-However, transaction costs (costs of acquiring information, enforcing the contract, or collective action) can be a major obstacle in reality.
Will private bargaining between parties lead to Pareto-efficient allocation?
Yes