brainstem as an integrative center; brainstem nuclei in the medulla, pons and midbrain
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
dorsal funiculus
contains large diameter processes of dorsal root ganglion neurons; carry sensory information to medulla
contains 2 fasiculi - fasiculus gracilus and fasiculus cuneatus
fasiculus gracilius
carry touch information from lower limbs (below T6)
fasiculus cuneatus
carry touch information from upper limbs (above T6)
fasiculus gracilus
fasiculus cuneatus
cervical spinal cord cross-section structures
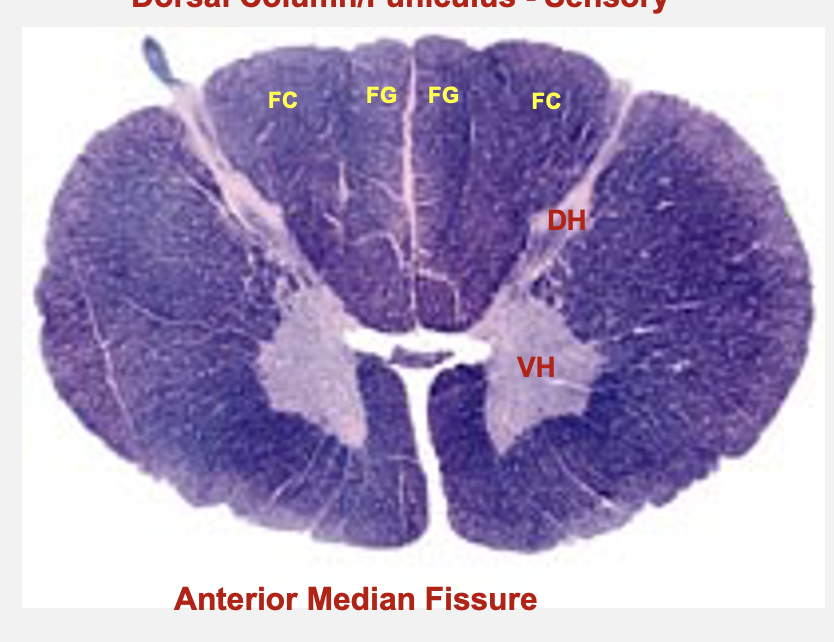
fasiculus gracilus
nucleus gracilus
fasiculus cuneatus
nucleus cuneatus
spinal nucleus of V
spinal tract of V
spino-medullary junction cross section structures
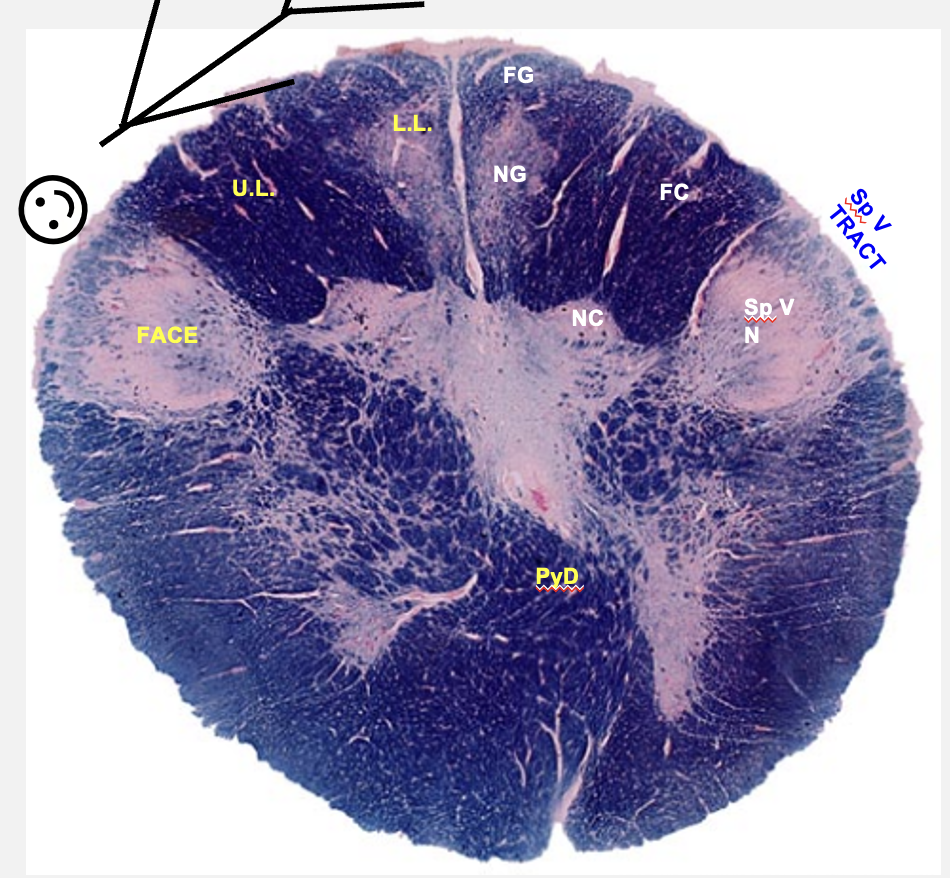
nucleus garcilus
gracile tubercle
fasiculus gracilus axons synpase in BLANK BLANK to form the BLANK BLANK
nucleus cuneatus
cuneate tubercle
fasiculus cuneatus axons synapse in BLANK BLANK to form the BLANK BLANK
spinal nucleus of V
trigeminal tubercle
spinal tract of V axons synpase in BLANK BLANK BLANK BLANK to form the BLANK BLANK
nucleus gracilus and cuneatus
carry fine touch, discrimination, propioception, and vibration from upper/lower limbs
spinal nucelus of V
carry pain and temperature information from face
trigeminal ganglion
contains cell bodies of origin of the trigeminal nuclear complex
nucleus gracilus
nucleus cuneatus
spinal tract of V
spinal nucleus of V
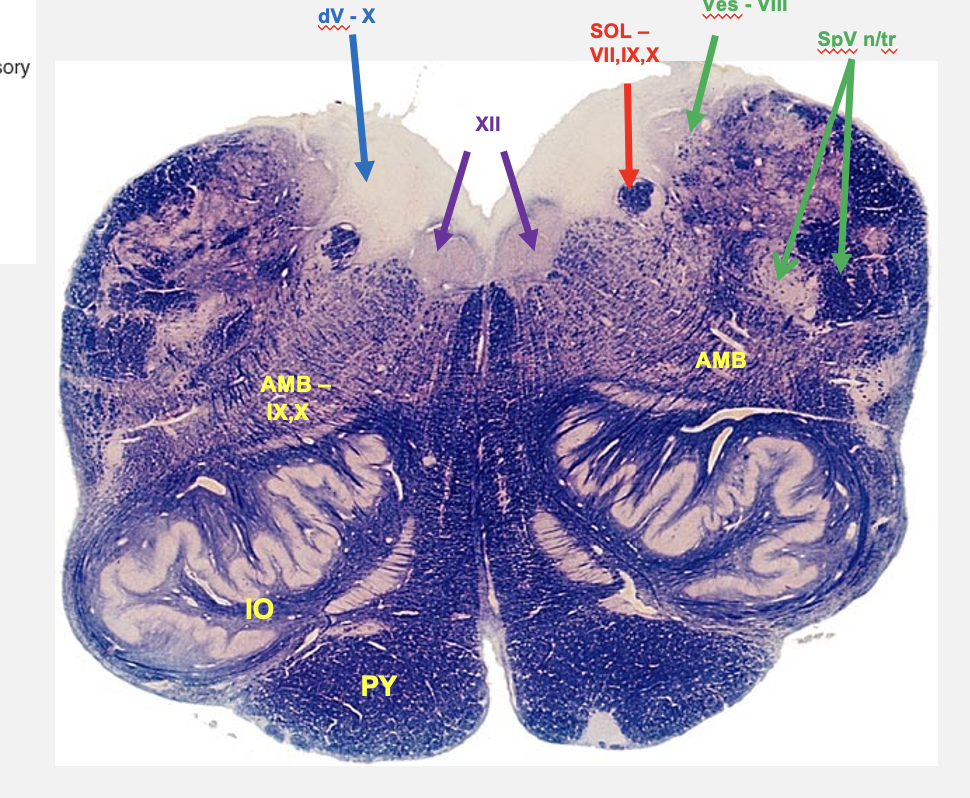
caudal medulla cross section structures
hypoglossal nucleus
dorsal visceral motor vagal nucleus
nucleus ambiguus
nucleus solitarius
vestibular nucleus
spinal nucleus of V
spinal tract of V
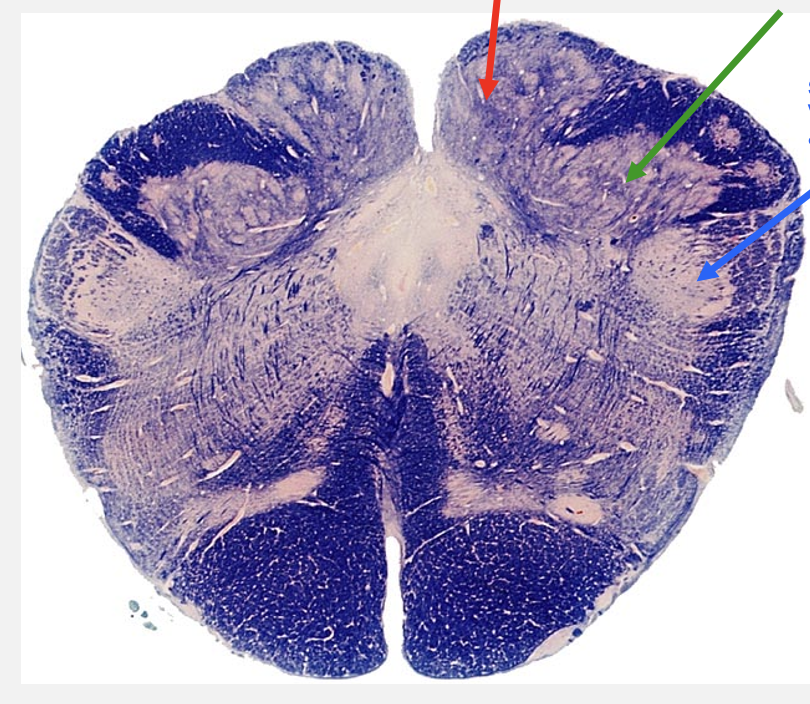
rostral medulla cross section structures
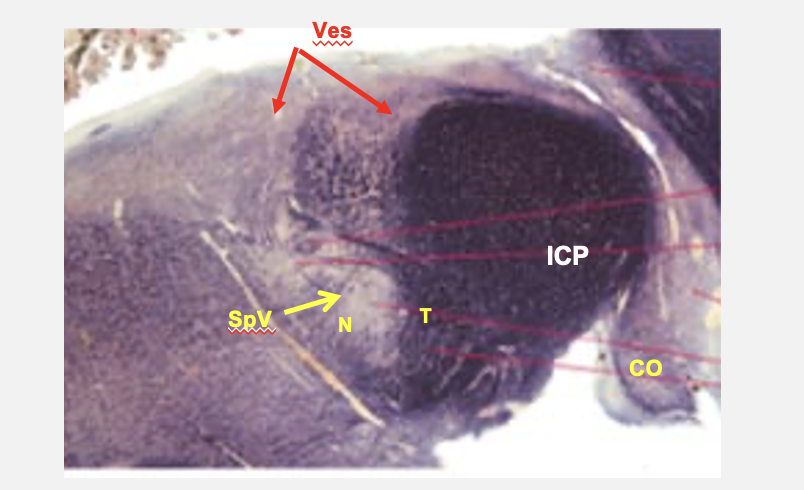
cochlear nucleus
ICP
vestibular nucleus
spinal tract of V
spinal nucleus of V
ponto-medullar junction cross section structures
vertebral arteries
PICA
anterior spinal arteries
blood supply of medulla
vertebral artery
supplies blood to ventral and lateral medulla
anterior spinal arteries
supplied blood to midline structures in medulla and medial tegmentum
PICA
supplies blood to dorsal and lateral medulla including cranial nerve nuclei and cerebellum
pontine nuclei
neurons in basilar pons form this; they give rise to axons that cross the midline and project to cerebellym as pontocerebellar projections
pontocerebellar projections
axons that form the middle cerebellar peduncles
basilar pons cross section
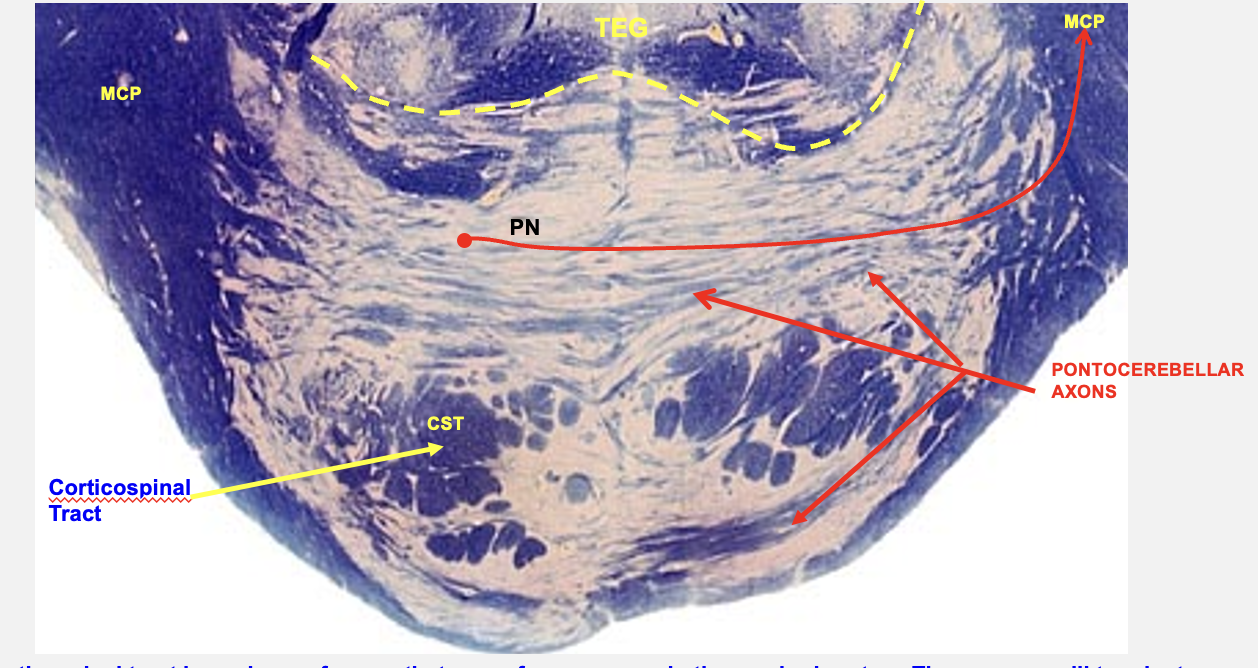
corticospinal tract
made up of axons that arose from neurons in the cerebral cortex; these axons will terminate on motor neurons in the spinal cord
mediate voluntary control of movement
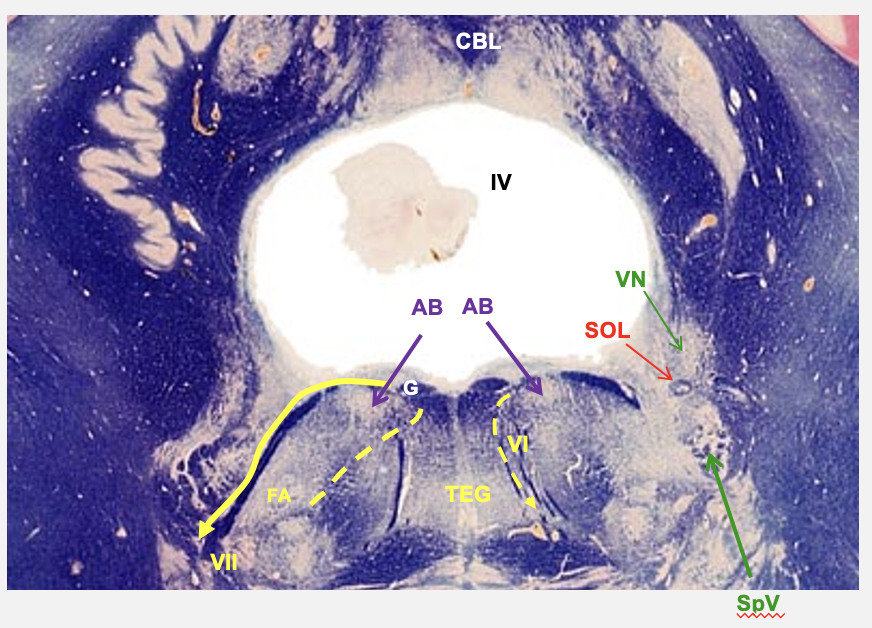
abducens nucleus
facial nucleus
nucleus solitarius
vestibular nucleus
spinal nucleus of V
caudal pons cross section stuctures
trigeminal nuclear complex
consist of 3 nuclei
main sensory nucleus
spinal nucleus
mesencephalic nucleus
mescephalic nucleus
receive propioception informationf rom muscles of mastication
sensory neurons here failed to migrate to periphery
motor V
nucleus that contains neurons that have axons that innervate muscles of mastication
pontine arteries
superior cerebellar arties
vascular supply of pons
pontine arteries
supplies blood to basilar pons
superior cerebellar arteries
supplied blood to lateral tegmentum area of rostral pons
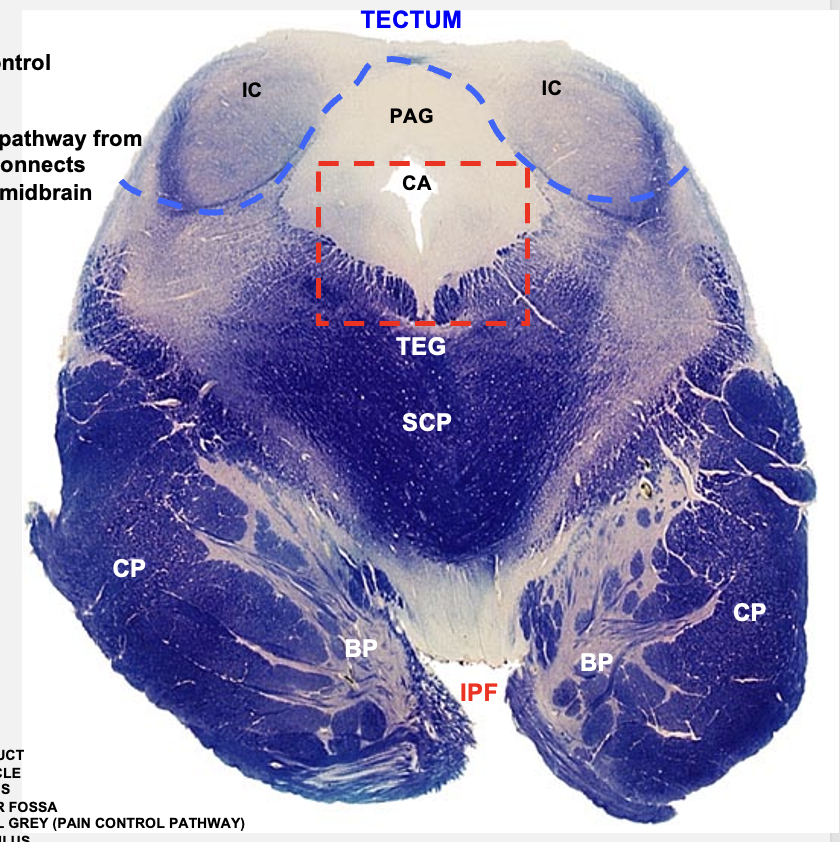
inferior colliculus
relay auditory information
superior colliculus
receives input from retina; reflex reactions
cerebral peduncle
interpeduncular fossa
basilar pons
superior cerebellar peduncle
tegmentum
cerebral aquduct
periaqueductal gray
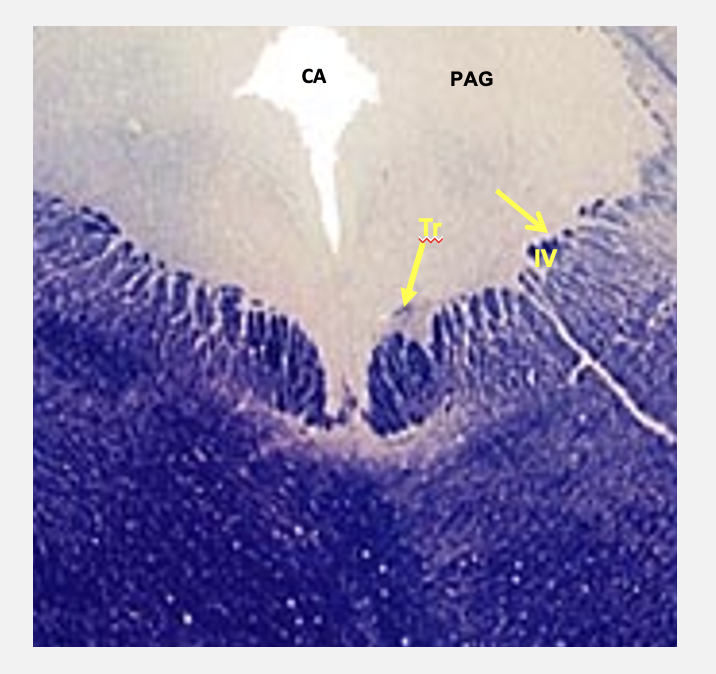
troclear nucleus
inferior colliculus
caudal midbrain cross section structures
troclear nucleus
located in caudal midbrain; troclear nerve is the only cranial nerve that exits from dorsal aspect of brain; also only cranial nerve that crosses to innervate contralateral muscle
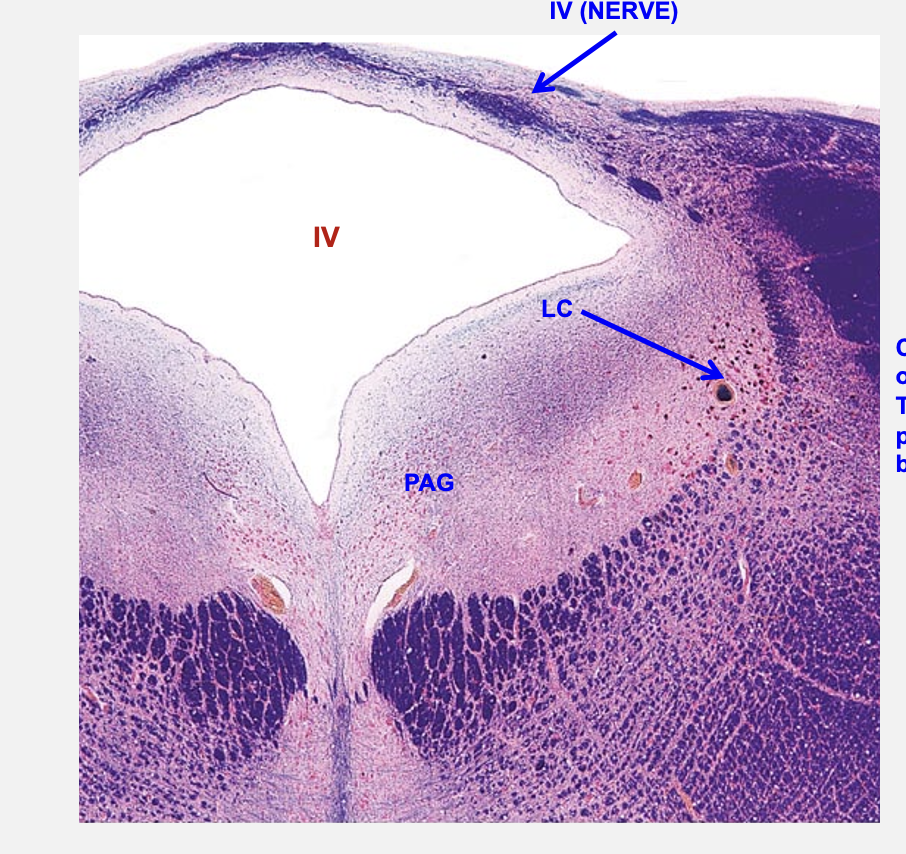
locus ceruleus
primary source of norepinephrine to the brain; important for alerting responses
cerebral peduncle
interpeduncular fossa
substania nigra
red nucleus
tegmentum
ventral tegmental area
oculomotor nucleus
cerebral aqueduct
periaqueductal gray
superior colliculus
rostral midbrain cross section structures
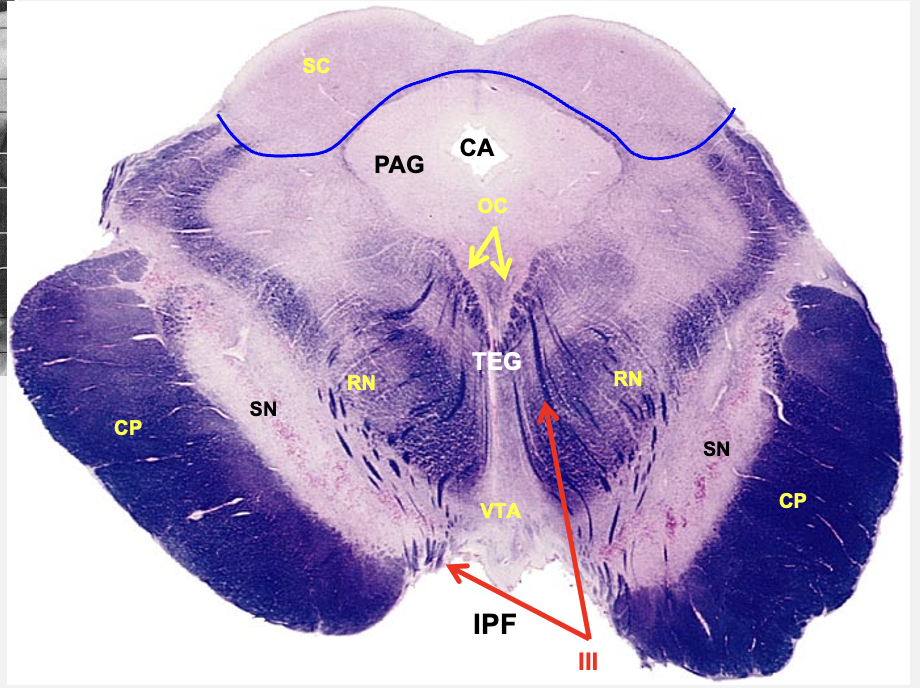
substania nigra
located in rostral midbrain; related to motor control and basal ganglia - source of dopamine for basal ganglia
red nucleus
related to motor control and cerebellum
ventral tegmental area
source of dopamine for forebrain
reticular formation
tegmentum
posterior cerebral artery
posterior communicating arteries
blood supply for midbrain