M6: Microbiology, Parasitology, and Public Health - Bacteriology - Part 2 - Gram Positive Cocci
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
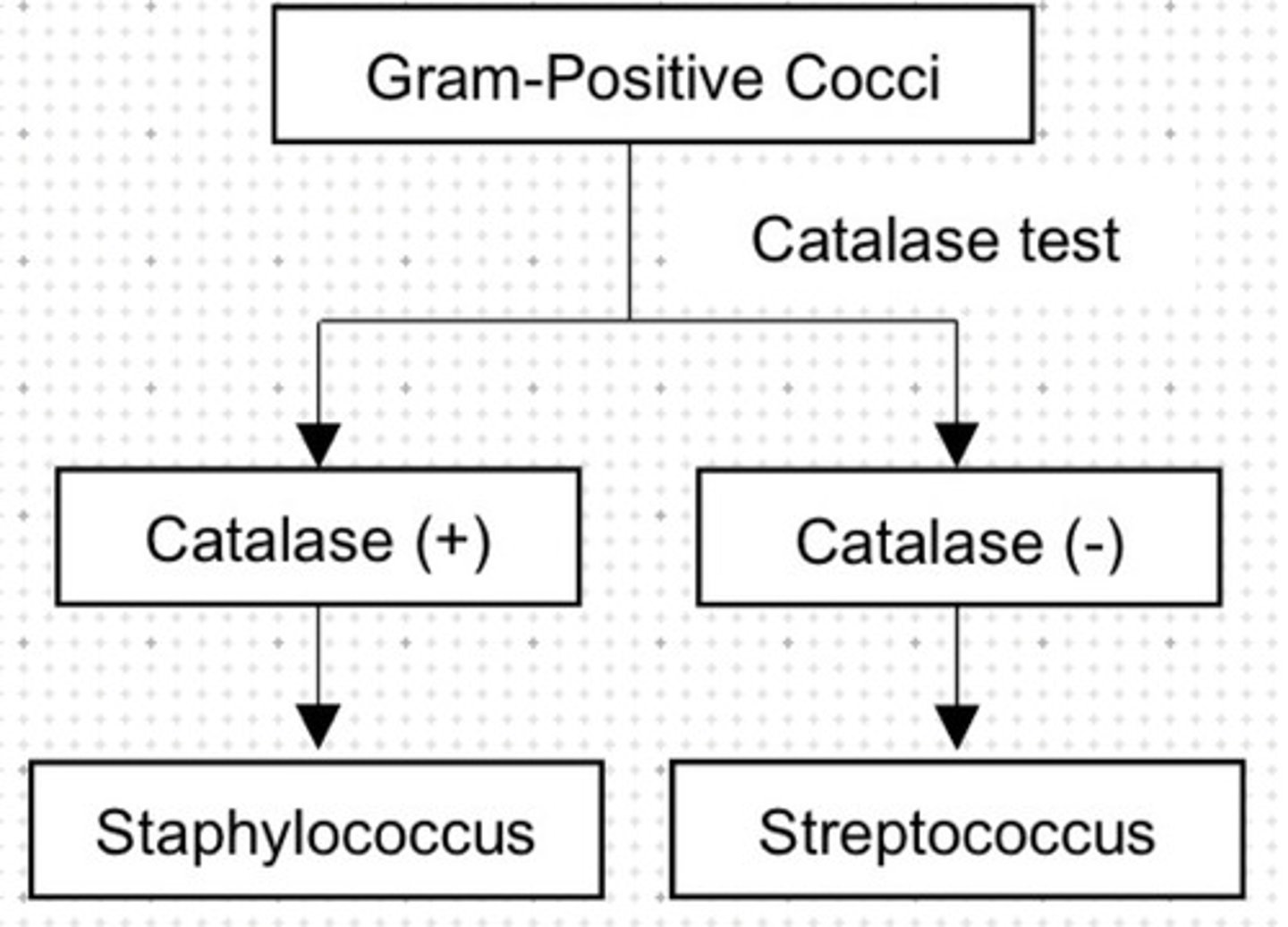
Catalase positive gram positive cocci.
a. Staphylococcus
b. Streptococcus
a. Staphylococcus
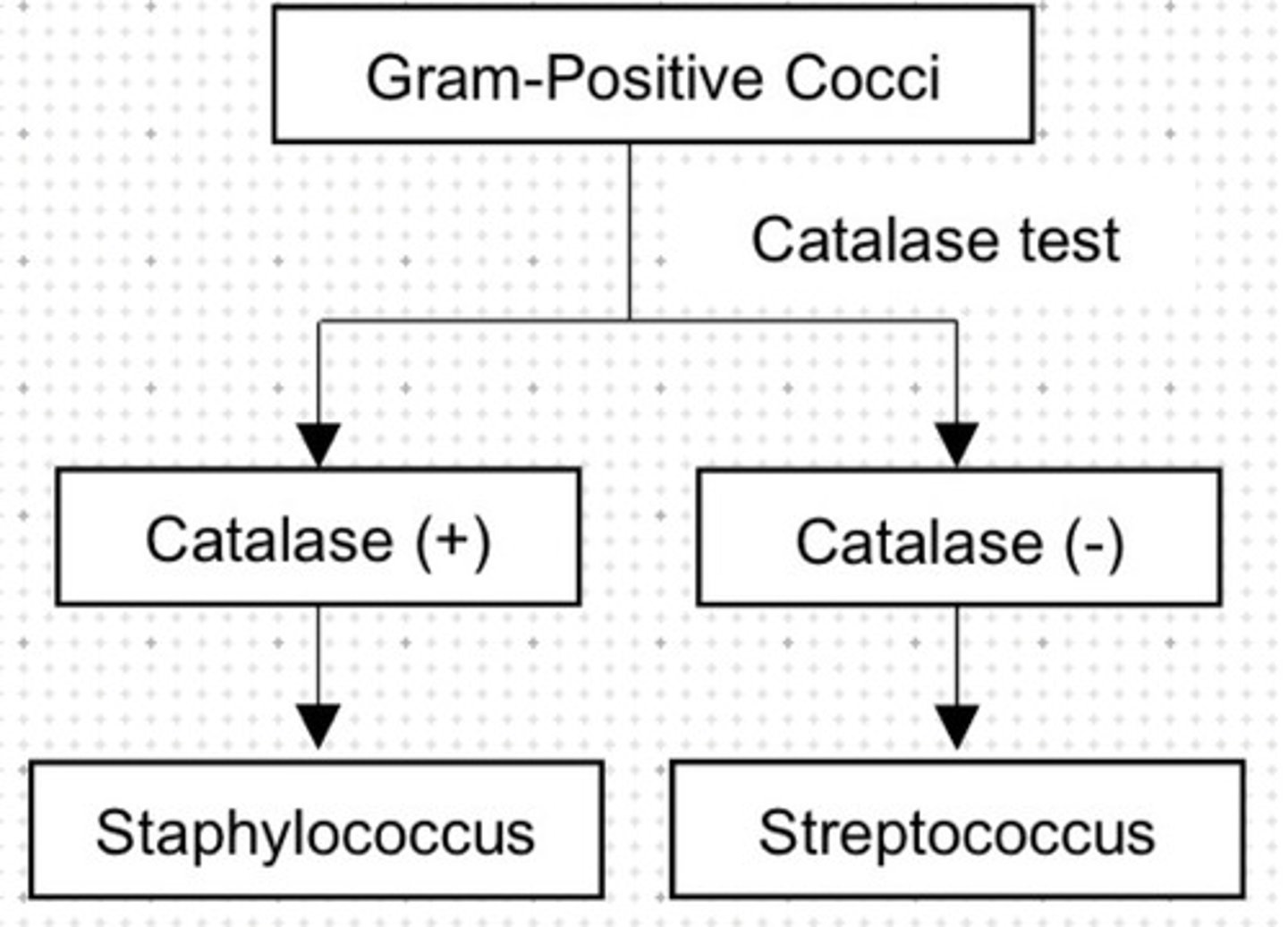
Catalase negative gram positive cocci.
a. Staphylococcus
b. Streptococcus
b. Streptococcus
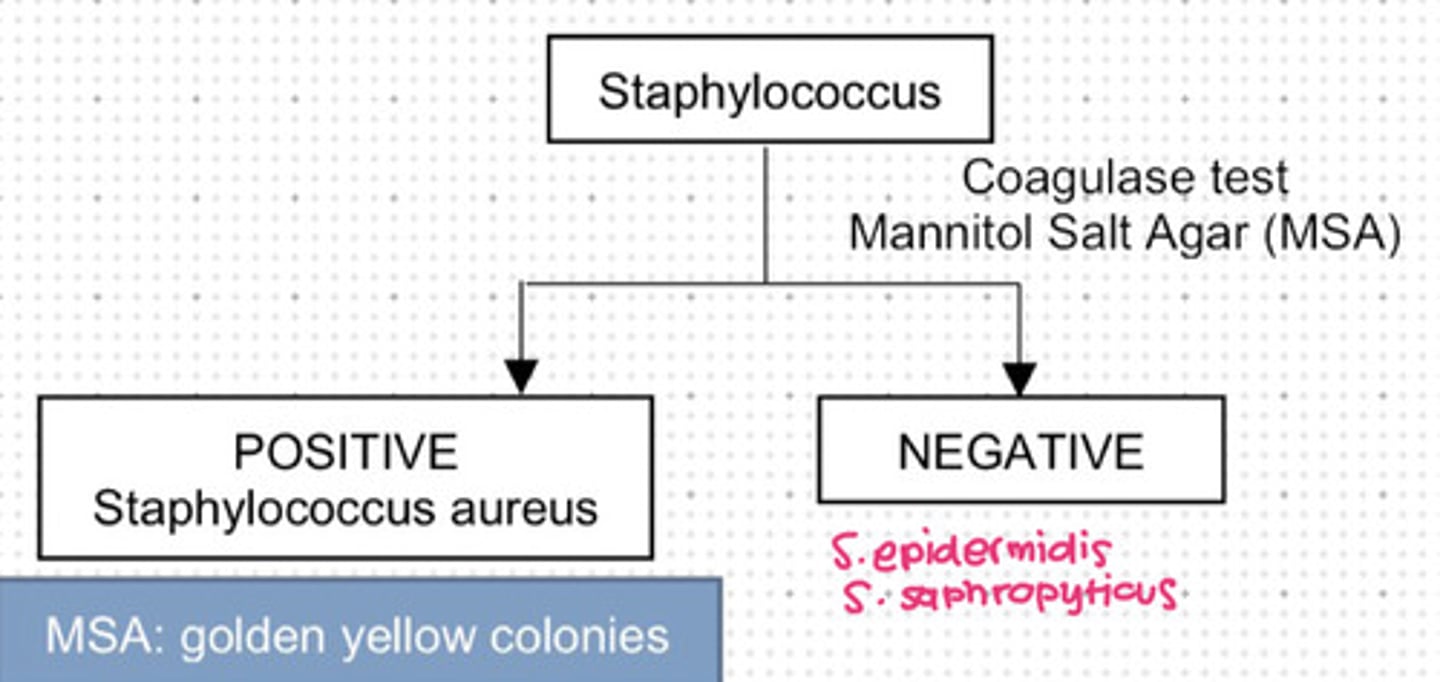
Used for coagulase test of Staphylococcus.
a. Mannitol Salt Agar
b. Novobiocin Sensitivity
c. Optochin Sensitivity
d. Bacitracin Sensitivity
a. Mannitol Salt Agar
Staphylococcus that is coagulase positive.
a. Staphylococcus aureus
b. Staphylococcus epidermis
c. Staphylococcus saphropyticus
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
a. Staphylococcus aureus
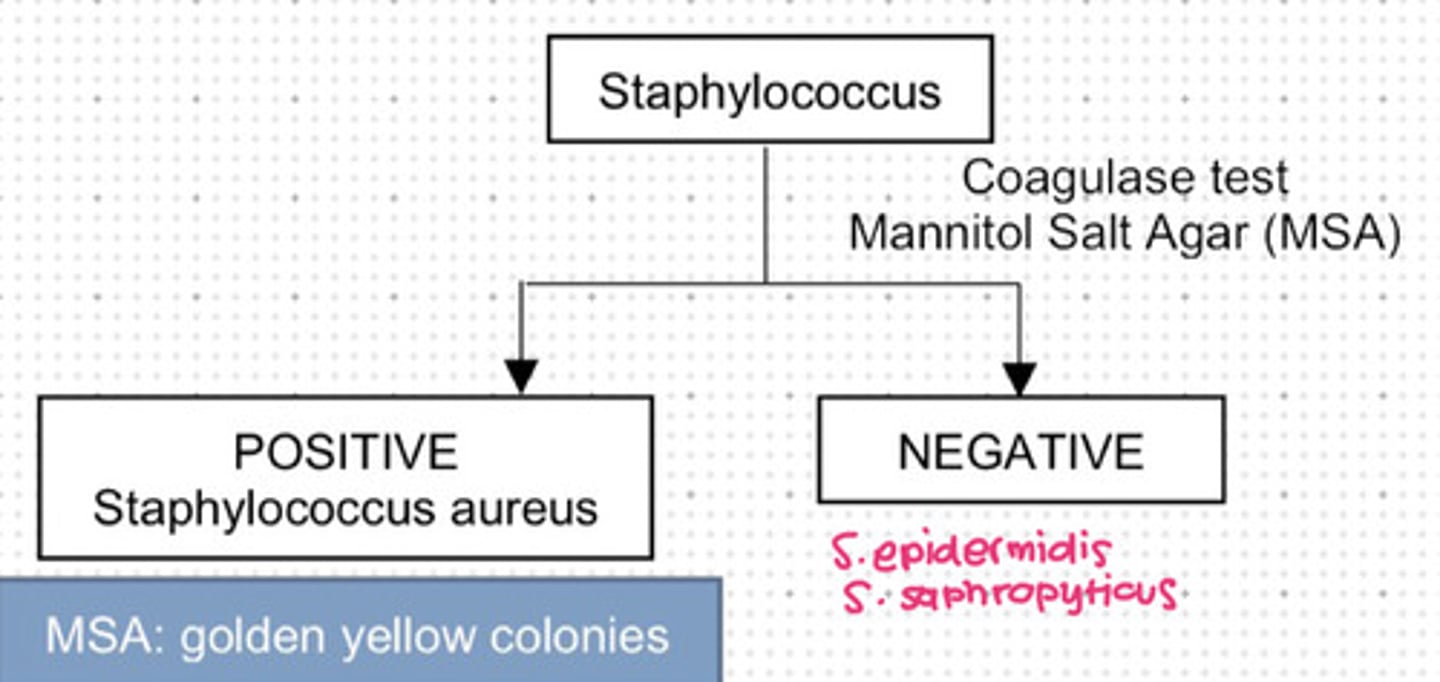
Staphylococcus that is coagulase negative.
a. Staphylococcus aureus
b. Staphylococcus epidermis
c. Staphylococcus saphropyticus
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
e. b and c
Staphylococcus epidermis
Staphylococcus saphropyticus
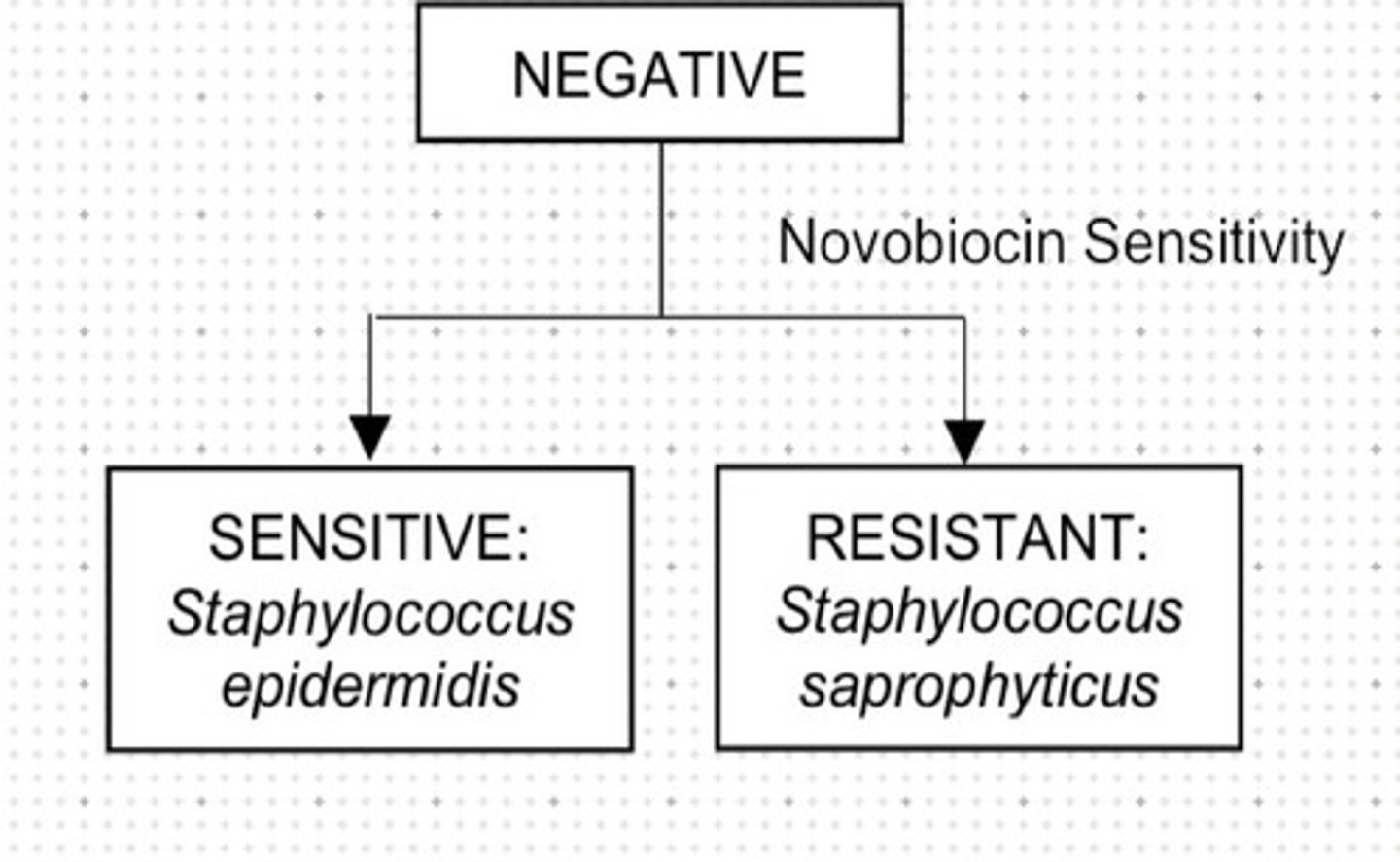
Used for differentiating S. epidermis from S. saphrophyticus.
a. Mannitol Salt Agar
b. Novobiocin Sensitivity
c. Optochin Sensitivity
d. Bacitracin Sensitivity
b. Novobiocin Sensitivity
Sensitive on novobiocin.
a. Staphylococcus epidermis
b. Staphylococcus saphropyticus
a. Staphylococcus epidermis
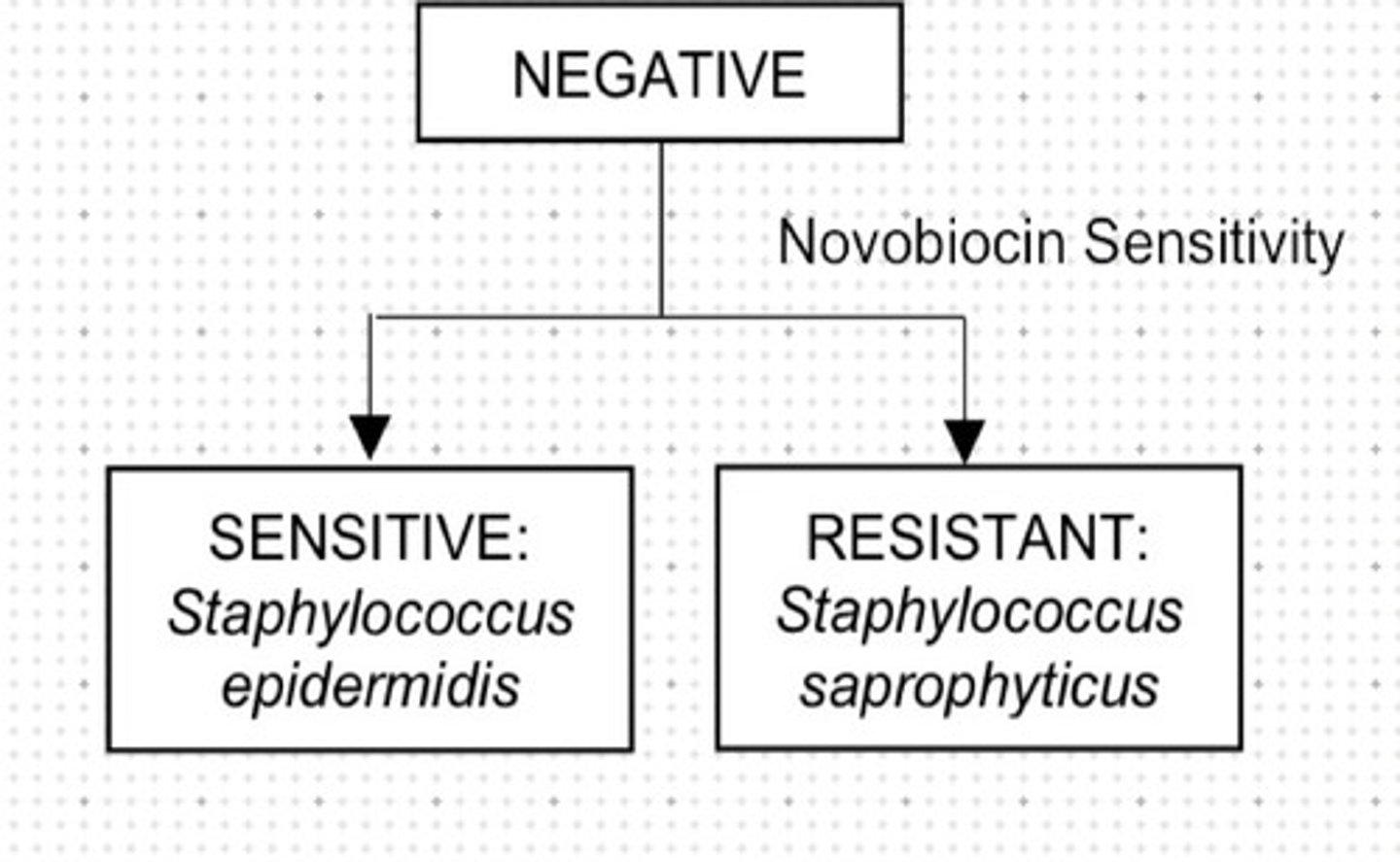
Resistant on novobiocin.
a. Staphylococcus epidermis
b. Staphylococcus saphropyticus
b. Staphylococcus saphropyticus
Used for determination of alpha hemolysis resistance or sensitivity of streptococcus.
a. Mannitol Salt Agar
b. Novobiocin Sensitivity
c. Optochin Sensitivity
d. Bacitracin Sensitivity
c. Optochin Sensitivity
Quellung reaction.
a. Mannitol Salt Agar
b. Novobiocin Sensitivity
c. Optochin Sensitivity
d. Bacitracin Sensitivity
c. Optochin Sensitivity
Streptoccous that is alpha hemolytic and sensitive optochin.
a. Streptococcus pneumoniae
b. Viridans streptococcus
a. Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptoccous that is not alpha hemolytic, resistant to optochin.
a. Streptococcus pneumoniae
b. Viridans streptococcus
b. Viridans streptococcus
Beta hemolysis resistance is determined through:
a. Mannitol Salt Agar
b. Novobiocin Sensitivity
c. Optochin Sensitivity
d. Bacitracin Sensitivity
e. 0.5% NaCl
d. Bacitracin Sensitivity
Streptococcus that is beta hemolytic
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
a. Streptococcus pyogenes - The Group A Beta Hemolytic Streptococcus (GABHS)
Streptococcus that is resistant to beta hemolysis.
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
b. Streptococcus agalactiae - Group B Streptococcus (GBS)
Used to determine gamma hemolysis of streptococcus.
a. Mannitol Salt Agar
b. Novobiocin Sensitivity
c. Optochin Sensitivity
d. Bacitracin Sensitivity
e. 0.5% NaCl
e. 0.5% NaCl
Gamma hemolytic.
a. Enterococcus species
b. Streptococcus bovis
a. Enterococcus species
Gamma hemolysis resistant.
a. Enterococcus species
b. Streptococcus bovis
b. Streptococcus bovis
Staphylococcus aureus virulence factor that causes boils, furuncle, carbuncle.
a. Lipase
b. Exfoliatin
c. Enterotoxin B
d. B-lactamase
e. Protein A
a. Lipase
Staphylococcus aureus virulence factor that causes Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS).
a. Lipase
b. Exfoliatin
c. Enterotoxin B
d. B-lactamase
e. Protein A
b. Exfoliatin
Staphylococcus aureus virulence factor that causes foods poisoning and toxic shock syndrome (SSSS + hypotension).
a. Lipase
b. Exfoliatin
c. Enterotoxin B
d. B-lactamase
e. Protein A
c. Enterotoxin B
Staphylococcus aureus virulence factor that causes antibiotic resistance.
a. Lipase
b. Exfoliatin
c. Enterotoxin B
d. B-lactamase
e. Protein A
d. B-lactamase
Staphylococcus aureus virulence factors except:
a. Protein A
b. Techoic acid
c. Capsule
d. Hyaluronidase
e. None
e. None
Staphylococcus aureus is a humam normal flora found in the:
a. Mouth
b. Nares
c. Lungs
d. Trachea
e. Genital
b. Nares
S. aureus route of transmission:
a. Droplet
b. Direct
c. Food borne
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
S. aureus can cause the following diseases except:
a. Acute endocarditis
b. Food poisoning
c. Pneumonia
d. Septic arthritis and osteomyelitis
e. Scalded skin syndrome
f. None
f. None
S. aureus can cause the following diseases except:
a. Skin and soft tissue infections
b. Toxic shock syndrome
c. Pneumonia
d. Septic arthritis and osteomyelitis
e. Scalded skin syndrome
f. None
f. None
S. aureus disease that is common among IV drug and affect the tricuspid valve.
a. Acute endocarditis
b. Food poisoning
c. Pneumonia
d. Septic arthritis and osteomyelitis
e. Scalded skin syndrome
a. Acute endocarditis
S. aureus releases heat stable toxin causing:
a. Acute endocarditis
b. Food poisoning
c. Pneumonia
d. Septic arthritis and osteomyelitis
e. Scalded skin syndrome
b. Food poisoning - usually in salad and mayonnaise
Causes toxic shock syndrome associated with use of tampon causing rashes and hypotension but produce negative blood culture.
a. S. aures
b. S. epidermis
c. S. saprophyticus
a. S. aures.
Anti-staphylococcal penicillin
a. Methicillin
b. Oxacillin
c. Nafcillin
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Anti-staphylococcal penicillin that is nephrotoxic.
a. Methicillin
b. Oxacillin
c. Nafcillin
d. a and b
e. All
a. Methicillin
Anti-staphylococcal penicillin that is causes rashes.
a. Methicillin
b. Oxacillin
c. Nafcillin
d. a and b
e. All
c. Nafcillin
DOC for MRSA.
a. Vancomycin
b. Linezolid
c. Streptogramins
d. a and b
e. All
a. Vancomycin
DOC for VRSA.
a. Vancomycin
b. Linezolid
c. Streptogramins
d. a and b
e. All
b. Linezolid
Alternative for VRSA.
a. Vancomycin
b. Linezolid
c. Streptogramins
d. a and b
e. All
c. Streptogramins
Has porcelain white colonies and is normal flora of the skin.
a. Staphylococcus aureus
b. Staphylococcus epidermis
c. Staphylococcus saprophyticus
b. Staphylococcus epidermis
Prefers foreign bodies forming biofilms and causes bacterial endocarditis in patients with prosthetic heart valves observed post operatively.
a. Staphylococcus aureus
b. Staphylococcus epidermis
c. Staphylococcus saprophyticus
b. Staphylococcus epidermis
Has colorless colonies and is normal flora of the vagina.
a. Staphylococcus aureus
b. Staphylococcus epidermis
c. Staphylococcus saprophyticus
c. Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Number 2 cause of UTI in sexually active females.
a. Staphylococcus aureus
b. Staphylococcus epidermis
c. Staphylococcus saprophyticus
c. Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Treatment for S. saprophyticus.
a. Vancomycin
b. Linezolid
c. Streptogramins
d. Fluoroquinolones
d. Fluoroquinolones
Group A beta hemolytic streptococcus.
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
d. Viridans streptococcus
e. Nonenterococcus
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes virulence factor except:
a. Protein M, Exotoxin A
b. Streptokinase
c. Streptolysin O and S
d. Streptodornase
e. Hyaluronidase
f. None
f. None
Fibrinolytic
a. Protein M, Exotoxin A
b. Streptokinase
c. Streptolysin O and S
d. Streptodornase
e. Hyaluronidase
b. Streptokinase
Spreading factor
a. Protein M, Exotoxin A
b. Streptokinase
c. Streptolysin O and S
d. Streptodornase
e. Hyaluronidase
e. Hyaluronidase
Antigenic.
a. Streptolysin O
b. Streptolysin S
a. Streptolysin O
Non antigenic
a. Streptolysin O
b. Streptolysin S
b. Streptolysin S
S. pyogenes suppurative infections except:
a. Pharyngitis
b. Cellulitis
c. Impetigo
d. Erysipelas
e. None
e. None
Flat ill defined redness that when severe, become necrotizing fascitis.
a. Pharyngitis
b. Cellulitis
c. Impetigo
d. Erysipelas
b. Cellulitis
Honey crusted lesions.
a. Pharyngitis
b. Cellulitis
c. Impetigo
d. Erysipelas
c. Impetigo
Painful red rash with orange peel.
a. Pharyngitis
b. Cellulitis
c. Impetigo
d. Erysipelas
d. Erysipelas
S. pyogenes non suppurative infections except:
a. Scarlet fever
b. Toxic shock syndrome
c. Rheumatic heart fever
d. Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
e. None
e. None
S. pyogenes exotoxin A causes:
I. Scarlet fever
II. Toxic shock syndrome
III. Rheumatic heart fever
IV. Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
a. I, II
b. I, III
c. II, III
d. III, IV
a. I, II
Scarlet fever
Toxic shock syndrome
S. pyogenes M protein causes:
I. Scarlet fever
II. Toxic shock syndrome
III. Rheumatic heart fever (RHF)
IV. Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
a. I, II
b. I, III
c. II, III
d. III, IV
d. III, IV
Rheumatic heart fever (RHF)
Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
Also known as the 2nd disease which is manifested as sandpaper rash, strawberry tongue, and sore throat.
a. Scarlet fever
b. Toxic shock syndrome
c. Rheumatic heart fever (RHF)
d. Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
a. Scarlet fever
Less severe than that caused by S. aureus. Its difference is it produce positive blood culture and negative rash.
a. Scarlet fever
b. Toxic shock syndrome
c. Rheumatic heart fever (RHF)
d. Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
b. Toxic shock syndrome
M protein of S. pyogenes causes what type of hypersensitivity?
a. I
b. II
c. III
d. IV
c. III
Preceded by strep throat infection and has the mechanism of action of molecular mimicry.
a. Scarlet fever
b. Toxic shock syndrome
c. Rheumatic heart fever (RHF)
d. Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
c. Rheumatic heart fever (RHF)
Diagnosis for rheumatic heart fever except:
a. Joint arthritis
b. Carditis
c. Nodules
d. Erythema marginatum
e. Sydenham chorea
f. None
f. None - These are the JONES criteria
Management for rheumatic heart fever caused by S. pyogenes.
a. Pen G
b. Vancomycin
c. Fluoroquinolones
d. Chloramphenicol
e. Supportive management
a. Pen G
Disease caused by S. pyogenes which is preceded by a skin infection and pathology is through immune complex formation.
a. Scarlet fever
b. Toxic shock syndrome
c. Rheumatic heart fever (RHF)
d. Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
d. Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN)
Management for post streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN).
a. Pen G
b. Vancomycin
c. Fluoroquinolones
d. Chloramphenicol
e. Supportive management
e. Supportive management
Normal flora of vagina which route of transmission is through an infected birth canal.
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
d. Viridans streptococcus
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
Causes neonatal sepsis and meningitis.
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
d. Viridans streptococcus
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
Treatment for neonatal sepsis and meningitis causes by S. agalactiae.
a. Pen G
b. Ampicillin + Gentamicin
c. Amoxicillin + Gentamicin
d. Chloramphenicol
e. Supportive management
b. Ampicillin + Gentamicin
A pneumococcus specifically a lancet-shaped diplococci.
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
d. Viridans streptococcus
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
Capsule is positive to Quelling reaction.
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
d. Viridans streptococcus
e. Enterococcus
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
Diseases caused by S. pneumoniae.
a. Community acquired pneumonia
b. Meningitis in elderly
c. Otitis media
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
f. All
Treatment for community acquired pneumonia (CAP).
a. 2nd/3rd gen cephalosporin + extended macrolide
b. 3rd gen cephalosporin
c. High dose penicillin
d. Ampicillin + Gentamicin
a. 2nd/3rd gen cephalosporin + extended macrolide
Treatment for meningitis in elderly.
a. 2nd/3rd gen cephalosporin + extended macrolide
b. 3rd gen cephalosporin
c. High dose penicillin
d. Ampicillin + Gentamicin
b. 3rd gen cephalosporin
The only 2nd generation cephalosporin that can pass the blood brain barrier.
a. Cefotetan
b. Cefoxetin
c. Cefuroxime
d. Cefaclor
c. Cefuroxime
Treatment for otitis media caused by S. pneumoniae.
a. 2nd/3rd gen cephalosporin + extended macrolide
b. 3rd gen cephalosporin
c. High dose penicillin
d. Ampicillin + Gentamicin
c. High dose penicillin
Vaccine for S. pneumoniae
a. PCV13
b. PPV23
c. Both
d. None of these
c. Both
Prevnar.
a. PCV13
b. PPV23
c. Both
d. None of these
a. PCV13
Pneumo23.
a. PCV13
b. PPV23
c. Both
d. None of these
b. PPV23
Streptococcus mutans which is normal flora of the mouth.
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
d. Viridans streptococcus
e. Enterococcus
f. Nonenterococcus
d. Viridans streptococcus
Overgrowth may cause dental caries.
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
d. Viridans streptococcus
e. Enterococcus
f. Nonenterococcus
d. Viridans streptococcus
May present with subacute bacterial endocarditis in patients with prosthetic heart valves.
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
d. Viridans streptococcus
e. Enterococcus
f. Nonenterococcus
d. Viridans streptococcus
Normal flora of the GIT which may lead nosocomial infections.
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
d. Viridans streptococcus
e. Enterococcus
f. Nonenterococcus
e. Enterococcus
Enterococcus specie:
a. E. faecalis
b. E. faecium
c. Both
d. None of these
c. Both
Primary treatment for enterococcus infection.
a. Vancomycin
b. Linezolid
c. Streptogramin
d. a and b
e. b and c.
f. All
a. Vancomycin
Treatment for VRE infection.
a. Vancomycin
b. Linezolid
c. Streptogramin
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
e. b and c
Linezolid
Streptogramin
Pathogen that are highly associated with antimicrobial resistance.
I. Enterococcus faecium
II. Staphylococcus aureus
III. Klebsiella pneumoniae
IV. Actinobacter baumanii
V. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
VI. Enterobacter species: E. coli
a. I, II, III, IV, V, VI
b. I, II, III, IV, V
c. II, III, IV, V
d. II, III, IV, V, VI
e. I, II, III
a. I, II, III, IV, V, VI
Streptococcus bovis.
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
d. Viridans streptococcus
e. Enterococcus
f. Nonenterococcus
f. Nonenterococcus
Can cause marantic endocarditis in patient with abdominal cancer.
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Streptococcus agalactiae
c. Streptococcus pneumoniae
d. Streptococcus mutans
e. Enterococcus faecium
f. Streptococcus bovis
f. Streptococcus bovis